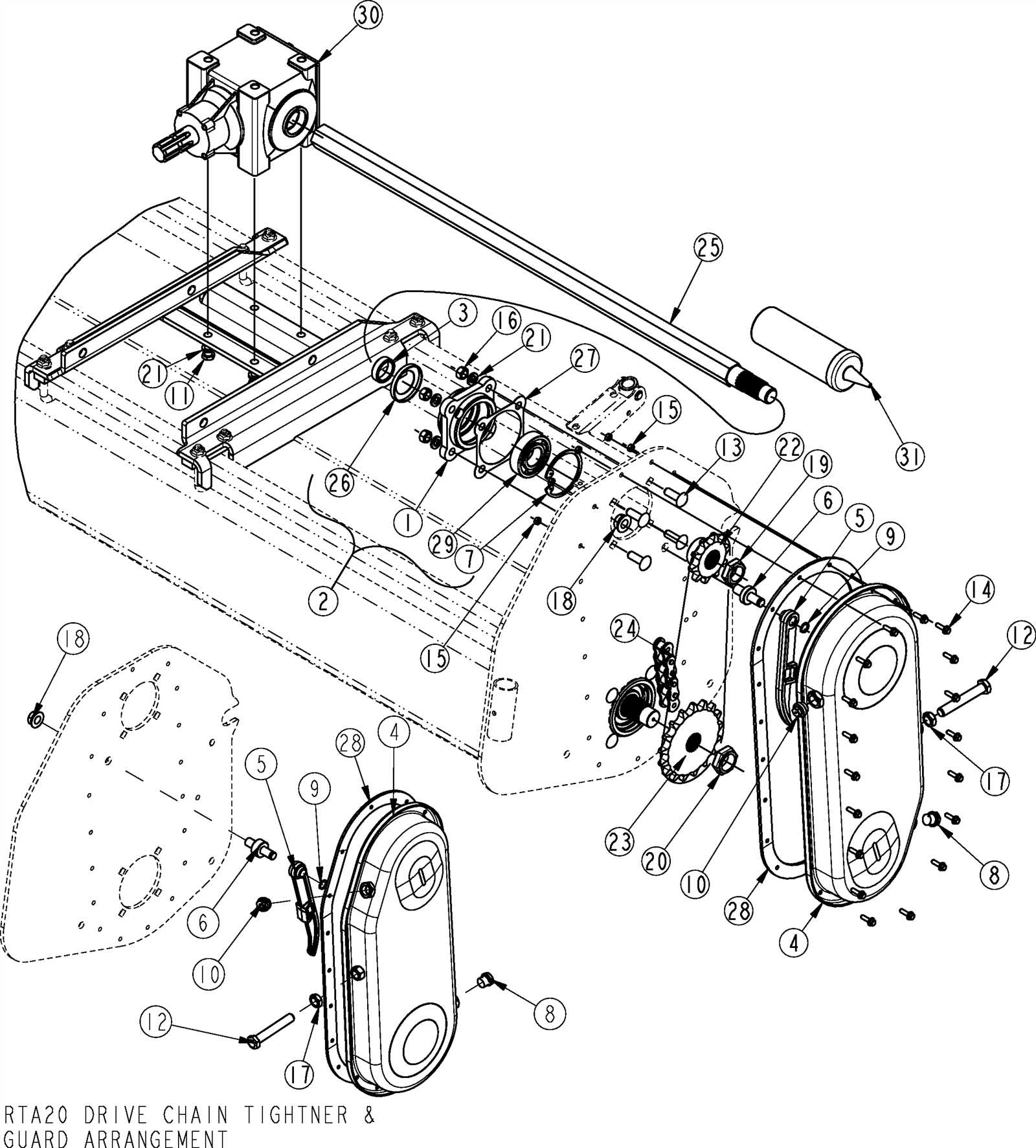
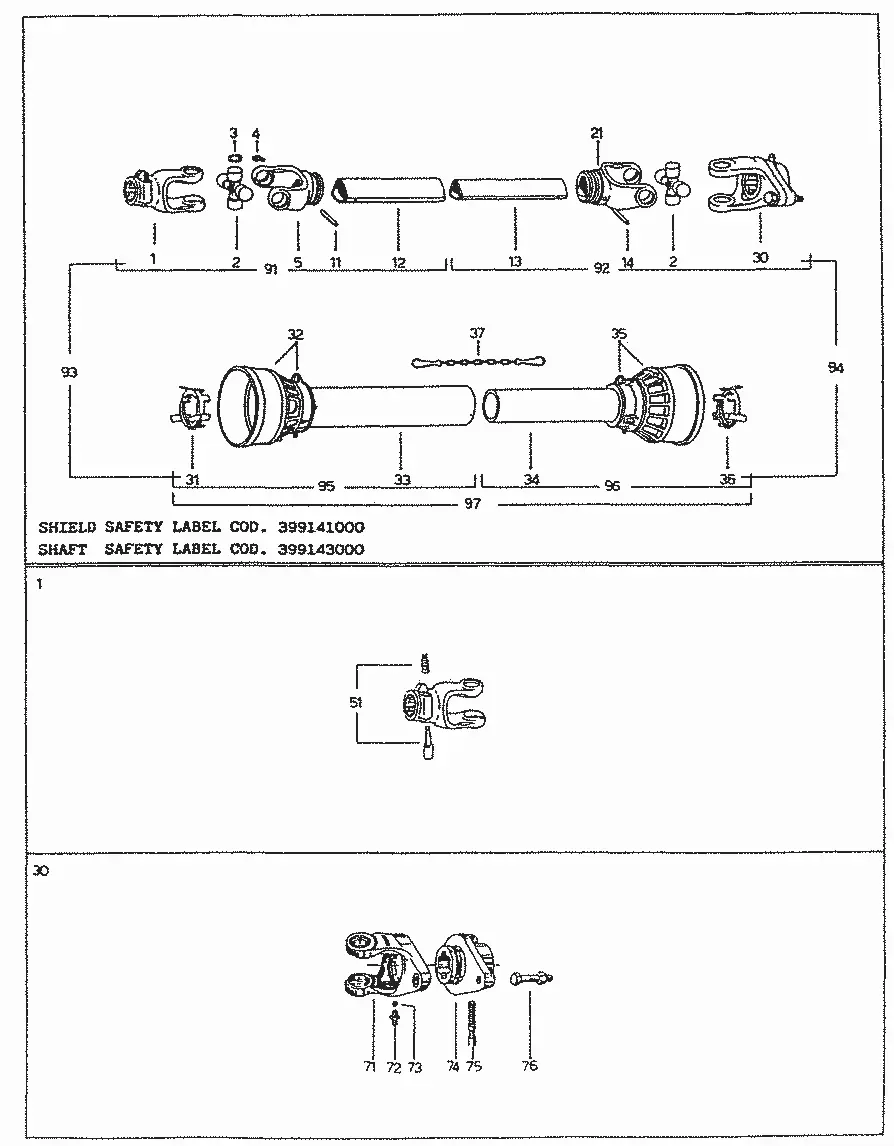
Understanding how the various elements of agricultural machinery interact is crucial for maintaining and repairing your equipment. Each section of the machine is composed of several interconnected parts, each with a specific role in ensuring the tool operates smoothly. Familiarizing yourself with the layout and the function of these components can greatly improve your ability to diagnose and resolve any issues that may arise.
In this guide, we will explore the detailed structure and key elements of one such machine, breaking down its core components. By gaining insight into the arrangement of these parts, you will be better prepared to perform routine checks, repairs, and replacements when necessary. This knowledge is invaluable for ensuring long-term reliability and optimal performance of your equipment.
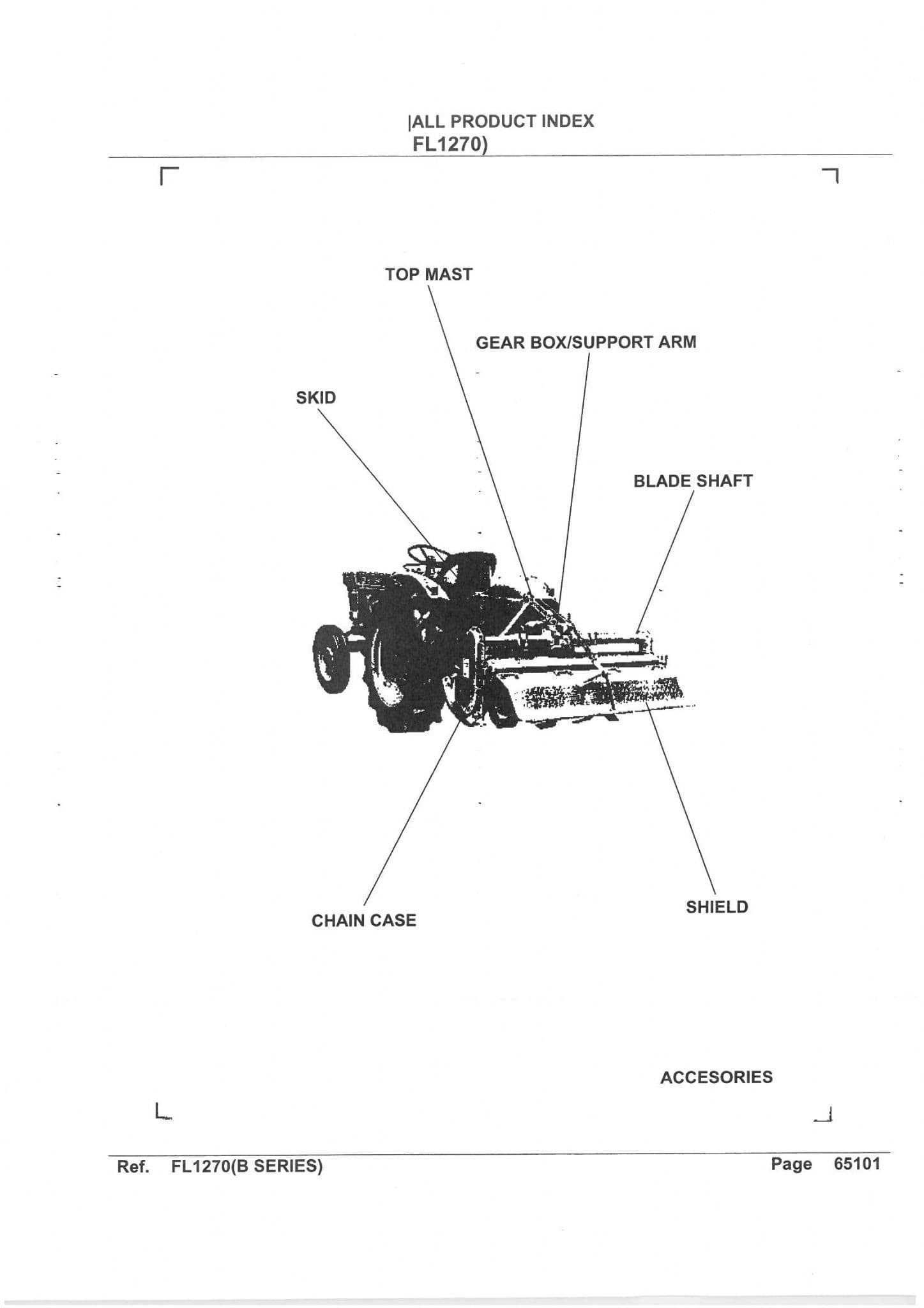
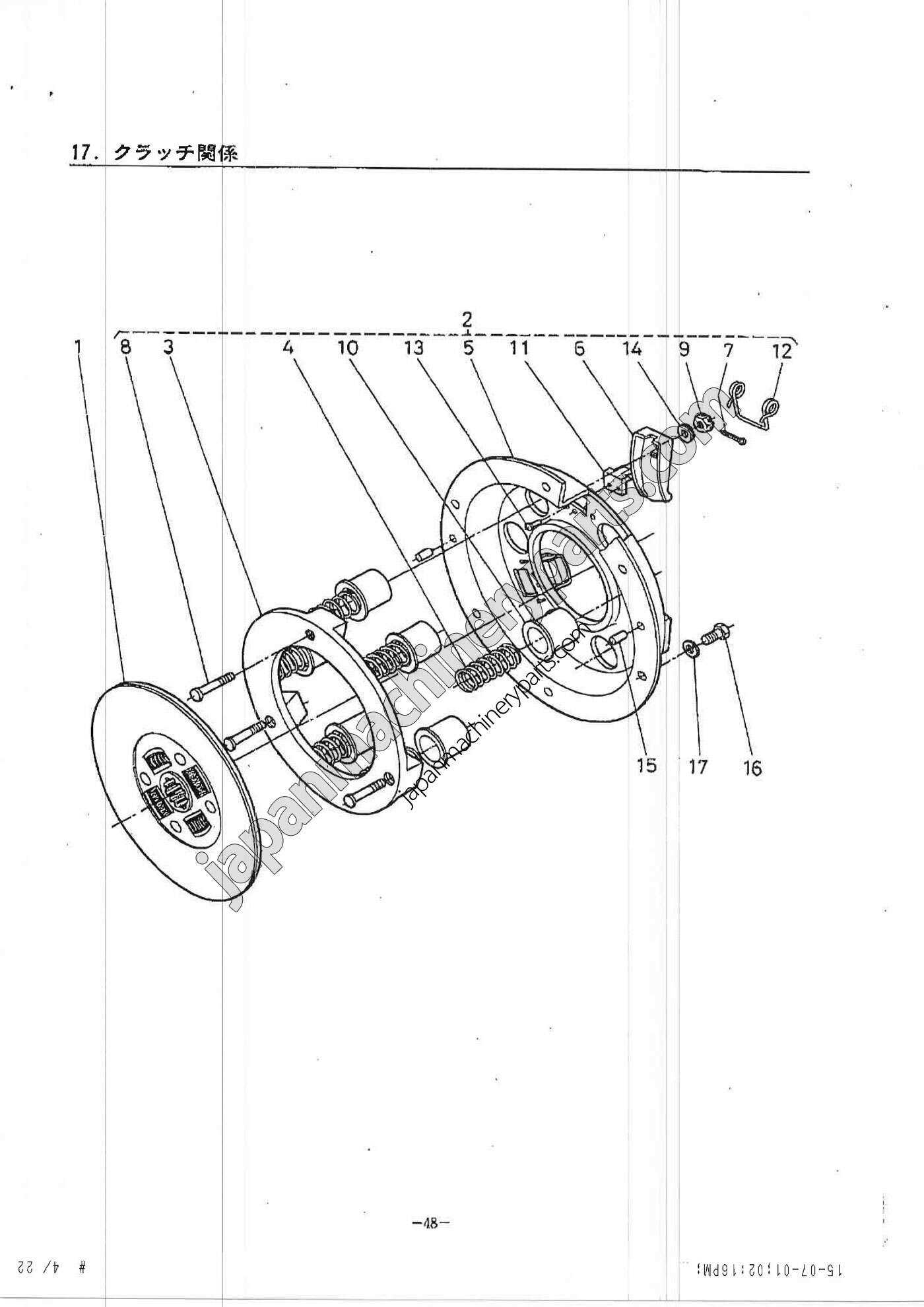
Understanding Components of a Kubota Tiller
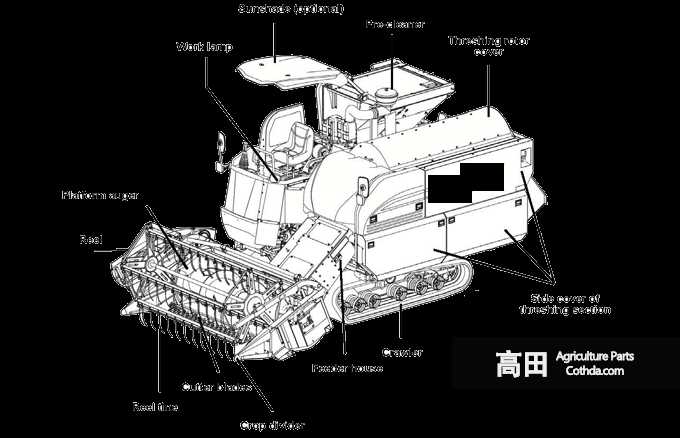
The effectiveness of any agricultural machine depends on the precise coordination of its various sections and mechanisms. Each element plays a vital role in ensuring smooth operation, from managing the soil to facilitating proper power transfer. By recognizing these elements, users can better maintain their equipment and ensure longevity in performance.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Rotary Blades | Responsible for breaking and turning the soil, providing the foundation for efficient soil cultivation. |
| Gearbox | Connects the power source to the rotating blades, adjusting the speed and torque for optimal ground engagement. |
| Transmission System | Distributes power from the engine to the working parts, ensuring consistent and balanced operation. |
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Fuel Tank | Stores the fuel required for operation. |
| Fuel Pump | Moves fuel from the tank to the engine. |
| Fuel Filter | Removes impurities from the fuel before it enters the engine. |
| Fuel Injector | Atomizes the fuel for efficient combustion within the engine. |
| Fuel Lines | Transport fuel between the tank, pump, and engine components. |
Each element of the fuel system is interconnected, creating a pathway that ensures fuel reaches the engine in a timely and efficient manner. Regular inspections and maintenance of these components can significantly enhance the longevity and performance of the machinery.
Hydraulic System Parts and Usage
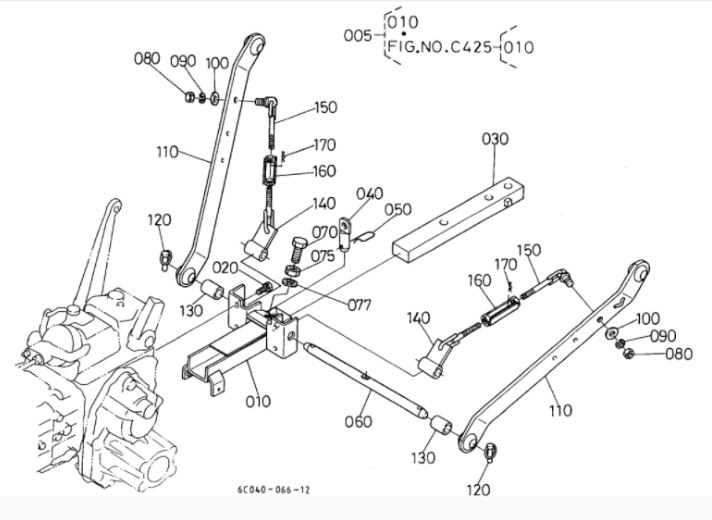
The hydraulic mechanism in agricultural machinery plays a crucial role in enhancing performance and operational efficiency. Understanding its components and functions is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. This system primarily utilizes fluid power to facilitate various tasks, ensuring that the equipment operates smoothly under different conditions.
Key components of the hydraulic mechanism include:
- Hydraulic Pump: This component generates flow and pressure, transforming mechanical energy into hydraulic energy.
- Hydraulic Cylinder: Responsible for converting hydraulic energy back into mechanical energy, enabling movement of attached implements.
- Control Valves: These regulate the flow and direction of the hydraulic fluid, allowing operators to control the speed and force applied by the machinery.
- Reservoir: Stores hydraulic fluid, ensuring that the system has an adequate supply for operation.
- Filters: Essential for maintaining fluid cleanliness, filters prevent contaminants from entering the system and causing damage.
- Hoses and Fittings: These components transport hydraulic fluid between different parts of the system, facilitating effective communication and functionality.
Proper usage and maintenance of these components are vital for optimal performance. Regular checks and timely replacements can significantly extend the lifespan of the hydraulic system and enhance overall productivity. Understanding the role of each component allows for more informed decisions during operation and repair.
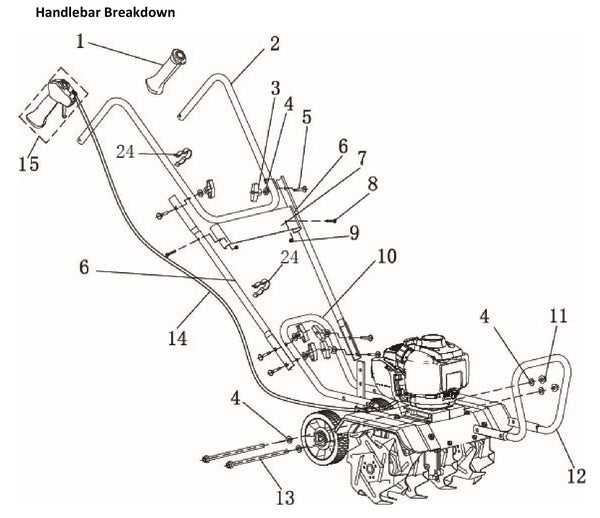
Maintenance Tips for Moving Components

Ensuring the longevity and efficiency of any machinery requires regular attention to its mobile elements. These components are vital for optimal performance, and neglecting them can lead to malfunctions or decreased functionality. By implementing proper care techniques, users can maintain smooth operation and extend the lifespan of their equipment.
Regular Lubrication
Lubrication is crucial for reducing friction and wear between moving parts. Using the appropriate type of grease or oil as recommended by the manufacturer will help keep components operating smoothly. Be sure to check the lubrication levels regularly and apply new lubricant when necessary to prevent rust and corrosion.
Inspection and Cleaning
Frequent inspections of moving components are essential for identifying potential issues early. Look for signs of wear, damage, or unusual noise during operation. Additionally, keeping parts clean from dirt and debris can prevent buildup that may hinder performance. Regular cleaning can also enhance visibility for inspections and maintenance tasks.
Electrical Systems and Safety Features
The functionality and reliability of any agricultural machinery greatly depend on its electrical systems and integrated safety mechanisms. These components work together to ensure efficient operation while minimizing risks during use. Understanding these systems is essential for maintaining optimal performance and ensuring user safety.
Key Electrical Components
- Power Supply: The source of energy that powers the entire unit, usually provided by a battery or alternator.
- Wiring Harness: A network of wires that connects different electrical components, facilitating communication and power distribution.
- Control Switches: Devices that allow the operator to manage various functions, enhancing usability and control.
- Fuses and Relays: Safety devices that protect electrical circuits from overloads, preventing potential damage.
Safety Features
- Emergency Stop Mechanism: A crucial feature that allows the operator to immediately halt operation in case of an emergency.
- Overload Protection: Systems designed to automatically shut down the machinery when excessive load is detected, preventing mechanical failures.
- Grounding Systems: Essential for preventing electrical shocks by providing a safe path for electricity to ground.
- Warning Lights and Alarms: Indicators that alert the operator to potential issues, ensuring timely responses to problems.