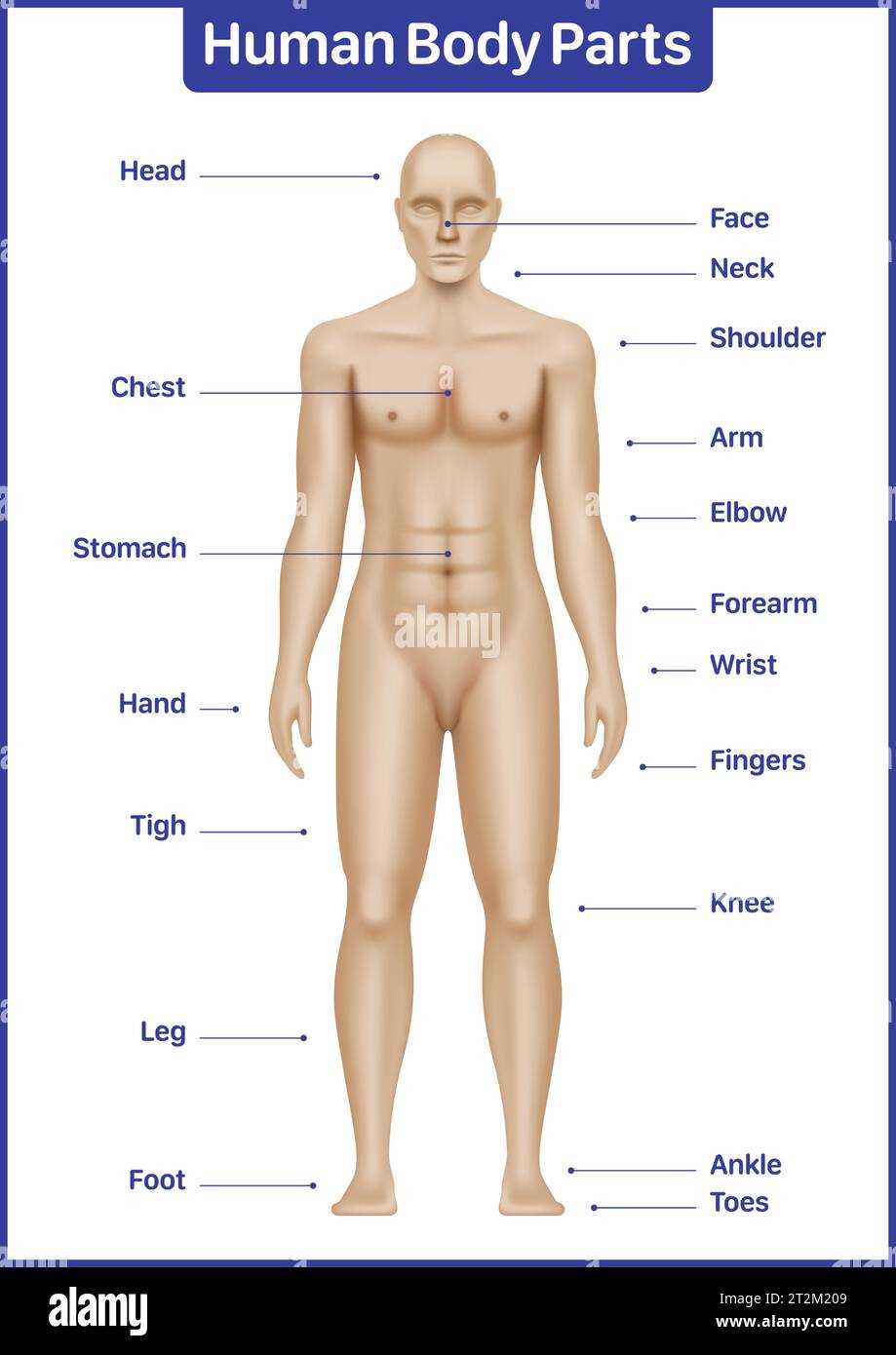
Understanding human anatomy is essential for various fields, including medicine, biology, and health education. Visual representations serve as effective tools for grasping complex systems. By examining a visual reference, individuals can enhance their knowledge of various physiological components, their functions, and interrelationships.
Utilizing a clear visual aid fosters deeper comprehension of how different elements interact within an organism. Engaging with such resources encourages curiosity and supports learning in both academic and practical environments. The process of familiarizing oneself with essential systems promotes a more holistic view of health and wellness.
By exploring these illustrations, learners can better appreciate the intricacies involved in anatomy. This foundational understanding is invaluable for aspiring professionals and those interested in improving their overall health literacy.
Understanding the Human Anatomy
Exploring intricate systems that compose living organisms reveals remarkable complexity and organization. Each structure plays a significant role in overall functionality and interconnects with others to maintain balance. A deeper understanding of these components enhances appreciation for how they work harmoniously to support life.
Key Systems in Human Composition
Various systems operate collectively to ensure survival and health. For instance, the circulatory system facilitates transportation of essential nutrients and oxygen, while the respiratory system manages gas exchange. Additionally, the muscular and skeletal frameworks provide support and enable movement, allowing individuals to interact with their environment.
Importance of Studying Structures
Grasping these foundational elements fosters a greater understanding of health, wellness, and medical advancements. Knowledge about how different systems interact aids in diagnosing ailments and implementing effective treatments. Engaging with this subject matter encourages a holistic view of wellness, promoting proactive measures for maintaining optimal health.
Major Organ Systems Overview
Human anatomy comprises various intricate systems, each playing a crucial role in maintaining overall function and health. These interconnected networks work harmoniously to support vital processes necessary for life. Understanding these systems allows for a deeper appreciation of how physiological functions are carried out effectively.
Cardiovascular System circulates blood throughout the organism, delivering essential nutrients and oxygen while removing waste products. This intricate network includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood, working tirelessly to sustain life.
Respiratory System facilitates gas exchange, enabling oxygen intake and carbon dioxide expulsion. Through a series of organs, including the lungs and airways, this system ensures that cells receive the oxygen needed for energy production.
Digestive System transforms ingested food into energy and essential nutrients. Comprising organs such as the stomach, intestines, and liver, it breaks down complex substances into simpler forms that can be absorbed and utilized by the organism.
Nervous System coordinates responses to internal and external stimuli. This complex network includes the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves, facilitating communication between various parts and enabling quick reactions to changes in the environment.
Musculoskeletal System provides structure, support, and movement. Composed of bones, muscles, and connective tissues, it enables locomotion and protects vital organs, allowing for a dynamic interaction with surroundings.
Each of these systems operates in unison, showcasing the complexity and efficiency of human anatomy. A comprehensive understanding fosters awareness of how different functions contribute to overall well-being and health.
Key Functions of Each System
This section explores essential roles performed by various physiological systems, highlighting their significance in maintaining overall health and functionality. Each system is intricately connected, contributing uniquely to the complex machinery that sustains life.
Circulatory System
- Transports oxygen and nutrients to cells.
- Removes carbon dioxide and waste products.
- Regulates body temperature and pH levels.
Nervous System
- Coordinates responses to internal and external stimuli.
- Facilitates communication between different regions.
- Processes sensory information to enable perception.
Respiratory System
- Facilitates gas exchange, providing oxygen for cellular respiration.
- Removes carbon dioxide from the bloodstream.
- Regulates pH levels through the control of carbon dioxide concentration.
Digestive System
- Breaks down food into essential nutrients.
- Absorbs nutrients into the bloodstream.
- Eliminates indigestible waste from the organism.
Identifying Muscle Groups
The human structure consists of various muscle clusters that play crucial roles in movement, stability, and overall functionality. Understanding these clusters can aid in recognizing how they contribute to daily activities, athletic performance, and rehabilitation processes.
Upper Region: This area includes sets responsible for arm movements, lifting, and providing shoulder stability. Key muscles here contribute to tasks like reaching, pushing, and pulling.
Core Area: Central muscles help maintain balance and support posture. They play an essential role in stabilizing the spine and assisting with rotational movements. A strong midsection enhances efficiency in numerous physical activities.
Lower Region: Muscles in this section are vital for walking, running, and jumping. They support weight-bearing activities and contribute significantly to leg power and mobility. This region also provides the necessary strength for movements like squatting and climbing.
Recognizing these distinct groups is vital for tailoring exercise routines, improving flexibility, and preventing strain or injury. Each cluster works in coordination, allowing fluid and efficient movement.
Exploring the Skeletal Structure
The intricate framework within us provides support and shape, serving as a foundation for our entire form. It is composed of interconnected elements that ensure stability, facilitate movement, and offer protection to various vital components. This structure adapts to different stages of growth, helping maintain balance and posture throughout life.
Each segment of this framework is designed with a specific purpose, contributing to overall mobility and endurance. It functions not only as a rigid scaffold but also as a dynamic system capable of repair and adaptation. By understanding this architecture, we can appreciate how every section contributes to the harmonious operation of the whole.
Importance of the Nervous System
The network that coordinates activities and sensations throughout the human structure plays a crucial role in maintaining balance and well-being. It acts as a communication hub, transmitting messages that enable movement, perception, and responses to various stimuli. Its functions extend beyond basic reflexes, influencing thoughts, emotions, and memory processes.
Coordination and Control
This intricate system ensures that actions are synchronized, allowing muscles and organs to work together effectively. It helps in regulating internal processes, maintaining vital functions like heartbeat, digestion, and breathing. Through a series of complex pathways, it interprets external signals, making adjustments that ensure stability.
- Regulates and integrates activities across different regions.
- Enables conscious and subconscious responses to changes.
- Supports voluntary actions and involuntary reflexes.
Role in Sensory Perception
The sensory components gather information from the environment, translating it into signals that are processed and interpreted. This allows an individual to experience touch, taste, smell, vision, and hearing, creating an awareness of surroundings. The ability to adapt to new conditions depends greatly on this system’s efficiency.
- Processes external cues and environment
Circulatory System Components Explained
The circulatory network functions to transport essential elements throughout the organism, ensuring proper functioning and overall health. It involves a series of interconnected structures that work together to maintain a continuous flow of vital substances.
- Central Pump: This muscular organ ensures a steady flow by contracting and relaxing rhythmically, propelling the necessary fluids through various channels.
- Transport Channels: These are the pathways that carry fluids to and from different regions. They are categorized based on their function–some deliver nutrients, while others return by-products for processing.
- Exchange Sites: Small, thin-walled vessels serve as points where vital exchanges occur between the fluid and surrounding tissues, allowing for efficient nutrient delivery and waste removal.
- Supportive Structures: These components assist in maintaining pressure within the system and help prevent backflow, ensuring the one-way movement of circulating elements.
Together, these elements form a comprehensive network that adapts to the needs of the organism, supporting life by maintaining a consistent flow and facilitating critical exchanges.
Digestive Tract Pathway Explained
The intricate journey of nourishment absorption involves a complex sequence, where each segment contributes uniquely to the transformation of food into energy. It is a well-coordinated system that ensures nutrients are broken down efficiently, facilitating their absorption and utilization. Understanding this process provides insight into how the internal system maintains energy balance and supports overall well-being.
Mouth and Saliva: This journey starts where the initial breakdown begins. Chewing mixes the intake with enzymes, starting the conversion into simpler forms.
Passage Through the Throat: From here, the softened mixture moves down a muscular tube, guided smoothly towards the next phase of digestion.
Stomach’s Role: In this chamber, powerful acids and enzymes further break down the mixture into a semi-liquid form, preparing it for nutrient extraction.
Small Channel for Absorption: The long, winding tube that follows is where the majority of nutrient extraction takes place. Tiny structures line this passage, maximizing the intake of vitamins, minerals, and other essential components.
Respiratory System Anatomy Insights
This section explores a complex network crucial for delivering essential gases to living organisms. It highlights the vital components involved in this exchange and how they work together to support life. Each element has a specific role, ensuring efficient airflow and maintaining proper functions in different settings.
Key Structures and Functions
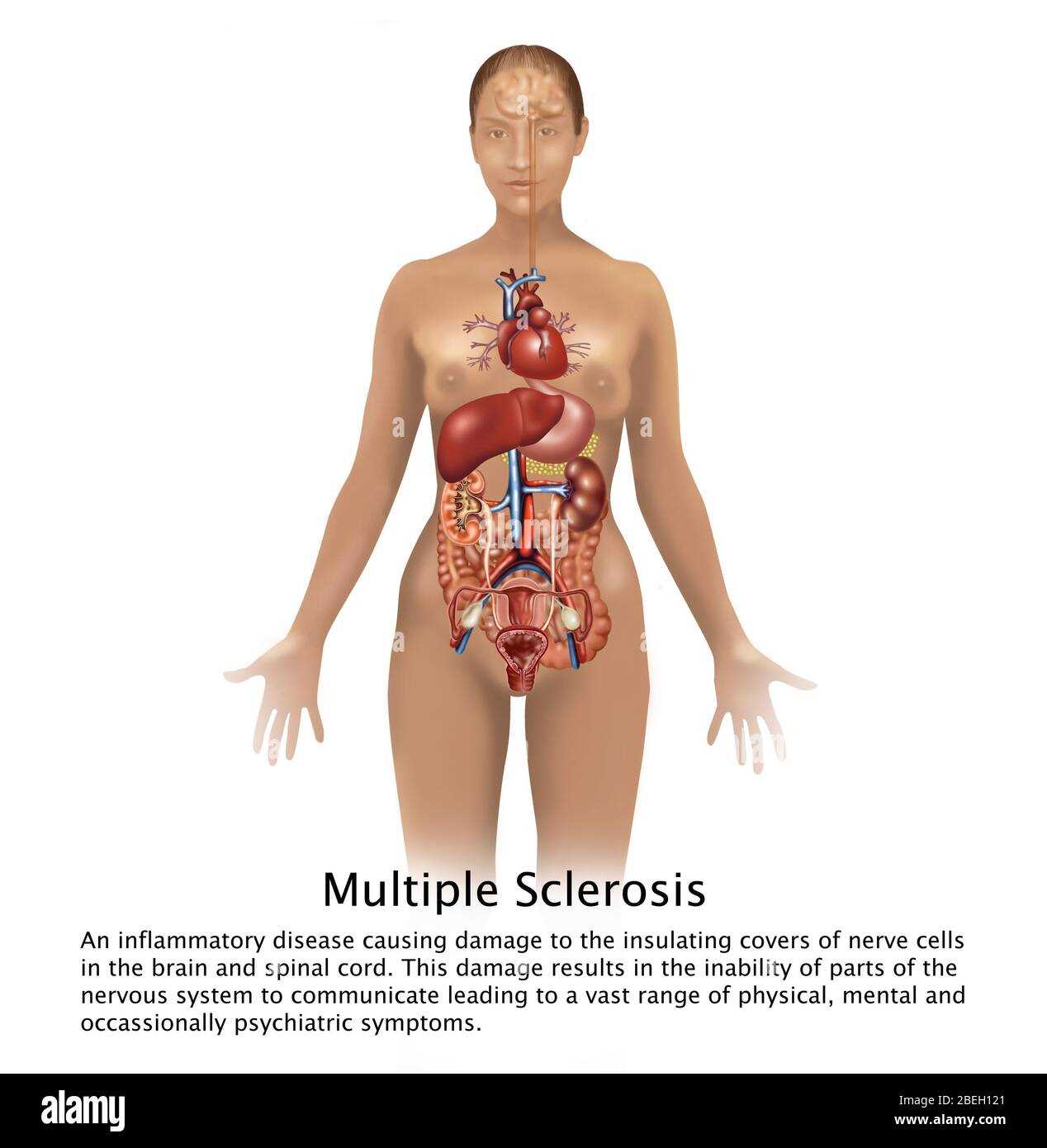
The system includes various passageways and organs that filter and direct airflow. Starting from entry points, air travels through a series of channels where it is warmed and moistened. Specific areas are responsible for gas exchange, facilitating the process that sustains cellular energy production. A deeper look into each structure reveals its contribution to maintaining a balanced environment.
Main Elements Overview
Component Description Nasal Cavity Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air before it proceeds deeper. Trachea A sturdy tube that channels air toward lower sections, protected by cartilage rings. Bronchi Divides airflow Endocrine Glands and Their Roles
Various specialized organs release chemical messengers into the circulatory system, influencing numerous processes. Each of these structures has a unique function, contributing to the regulation of growth, metabolism, and overall stability within the system.
- Pituitary Organ: Known as a central controller, it directs other glands to release their signals, impacting growth and reproductive processes.
- Thyroid Structure: This component is crucial for controlling energy conversion rates, affecting how efficiently nutrients are processed and used.
- Adrenal Units: Positioned above the kidneys, these components respond to stress by releasing substances that adjust blood flow and pressure.
- Pineal Component: Regulates daily cycles and sleep patterns by releasing substances in response to light levels, helping maintain internal balance.
- Pancreas: Essential in managing glucose levels, it produces substances that either lower or elevate sugar concentrations in the bloodstream.
These intricate systems work together, ensuring coordination and balance, making each element indispensable for maintaining stability and proper function.
Immune System Defense Mechanisms
The human defense network acts as a complex shield, safeguarding internal functions against harmful invaders. This sophisticated system recognizes and neutralizes various foreign substances, ensuring stability within. It operates through a series of layered responses, each designed to address different challenges and maintain well-being.
- Barrier Defenses: These serve as the first line of protection, preventing unwanted substances from entering deeper regions. They include physical and chemical components that work together to block entry points.
- Innate Reactions: A rapid response team that activates upon initial contact with intruders. It utilizes specialized cells and molecules to quickly confront potential threats.
- Adaptive Reactions: This mechanism learns and remembers encounters with specific agents. It provides a targeted response, adapting over time to recognize and efficiently eliminate repeated challenges.
- Cellular Support: Specialized units contribute to the identification and elimination of harmful agents. They play a crucial role in coordinating responses, communicating signals, and eliminating compromised elements.
- Humoral Support: This aspect involves proteins circulating in fluids that bind to intruders, aiding in their removal. It helps to neutralize toxins and mark them for destruction by other cells.
Together, these
Mapping the Sensory Organs
Understanding how our senses are distributed helps to appreciate the intricate ways we perceive our surroundings. Each of these components has a unique role, connecting directly to the brain to interpret various stimuli. This overview explores the primary systems that allow us to experience everything from light and sound to taste and touch.
Visual Perception
Our ability to see relies on a complex structure, which captures light and converts it into signals for the brain to process. This system includes a delicate mechanism that adjusts to varying levels of brightness, helping to focus on objects near and far. The interpretation of colors and shapes begins here, allowing us to make sense of our visual environment.
Auditory Reception
The mechanism for hearing is designed to detect and analyze sound waves, transforming them into signals that the brain can interpret. This capability allows us to recognize different pitches and volumes, helping in everything from communication to enjoying music. By translating vibrations into comprehensible information, this system connects us to the world of sound.