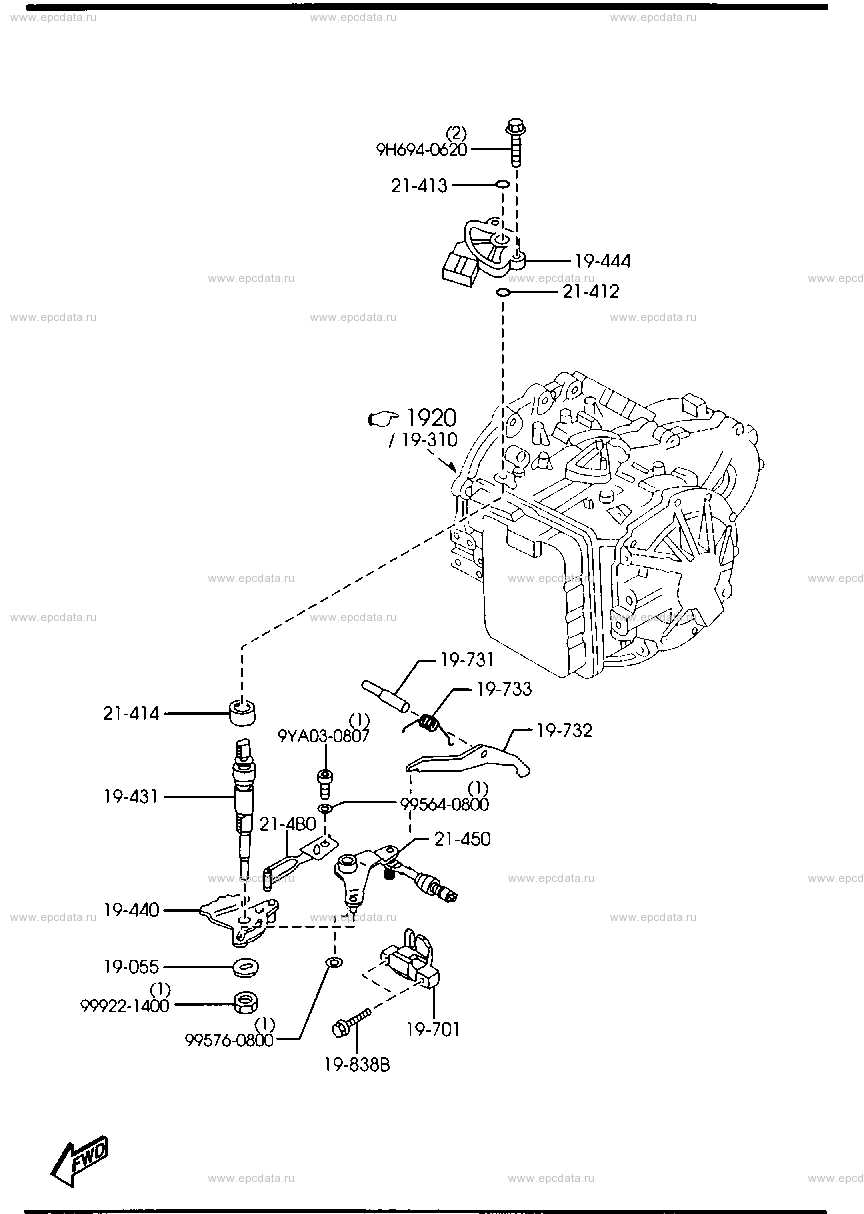
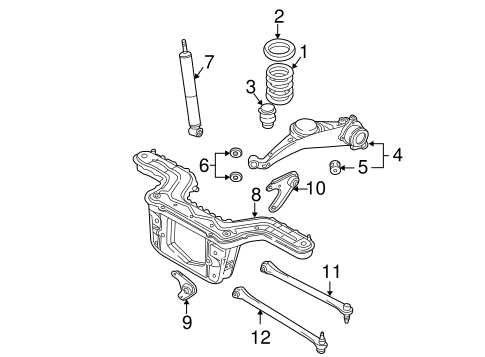
Understanding the intricate layout of mechanical systems is crucial for maintaining and repairing vehicles effectively. Each element has a specific role in ensuring smooth operation, and recognizing how these elements connect can aid in diagnosing and resolving potential issues.
In this section, we will explore the fundamental organization of key mechanisms. Highlighting the various elements involved, we’ll provide insight into how they function together, offering clarity on the essential structures that support the overall system.
By delving into the technical aspects, this guide serves as a helpful resource for anyone looking to gain a deeper understanding of how different components interact within the broader framework of
Vehicle Component Overview
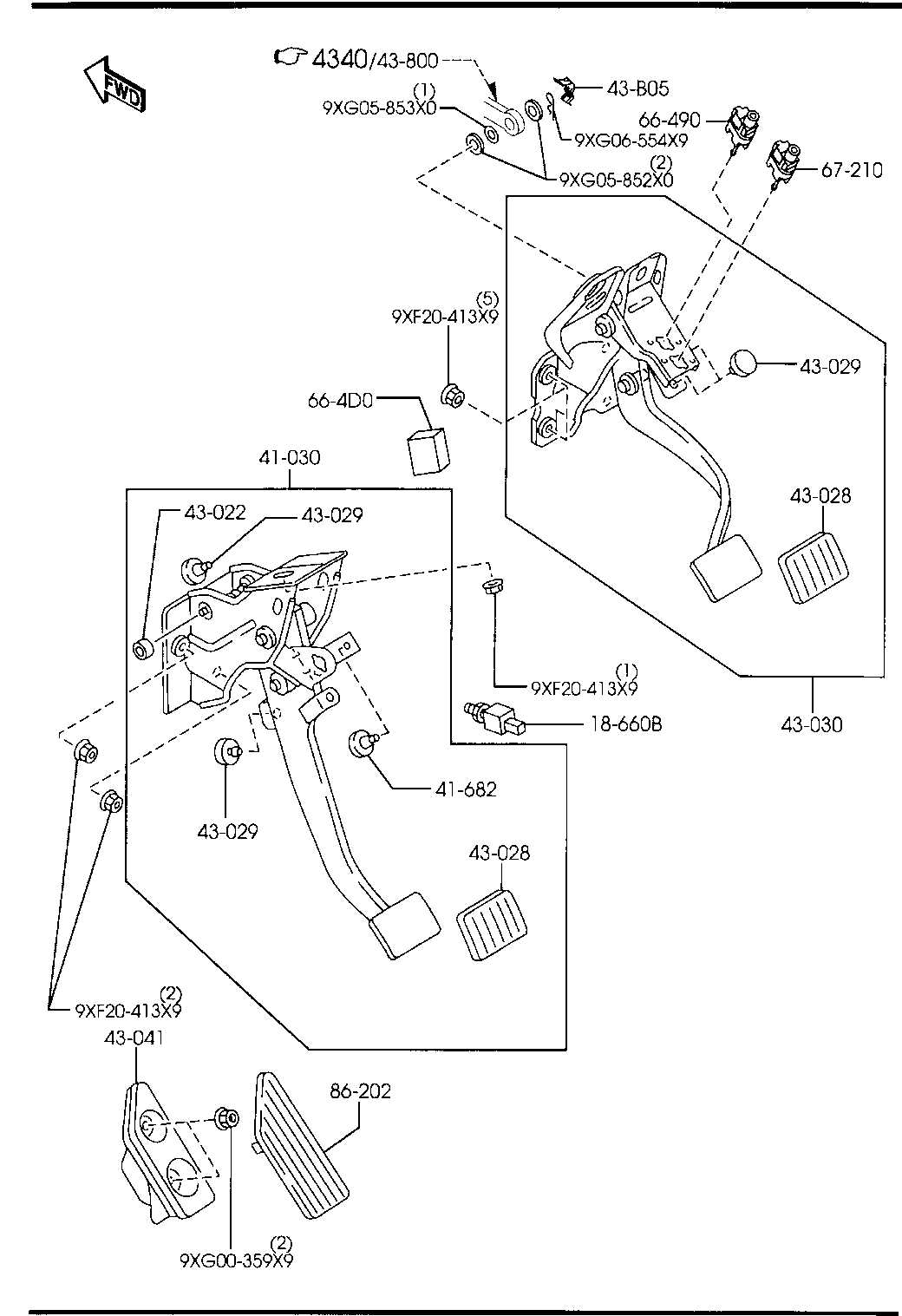
The focus of this section is to provide a detailed understanding of the various essential elements that make up the structure and functionality of the vehicle. These components are crucial for ensuring smooth operation, safety, and efficiency. A clear breakdown of the core systems allows for easier identification and maintenance, improving overall performance and longevity.
Core Mechanical Systems
Key systems within the vehicle’s architecture include those responsible for motion, power transmission, and control. This includes the engine assembly, transmission mechanisms, and various systems related to fuel and exhaust. Together, these components work harmoniously to ensure the vehicle runs efficiently under varying conditions.
Supporting Structures and Functional Elements
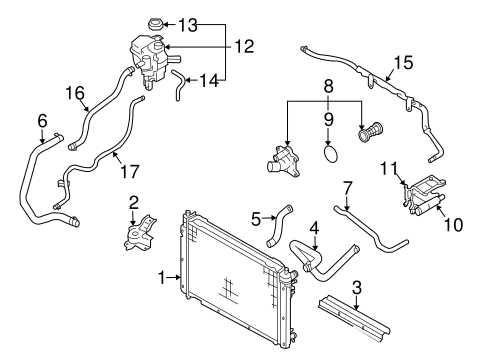
Other essential parts contribute to
Engine Components Breakdown
Understanding the key elements that make up the engine is crucial for proper maintenance and repair. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring the overall performance and efficiency of the system. This section provides a clear look at the main elements within the motor, focusing on their functionality and how they interact with each other.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Cylinder Block | The foundation of the engine, housing the cylinders and other vital parts. |
| Pistons | Move within the cylinders, converting fuel into mechanical energy. |
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Battery | Stores electrical energy for starting the engine and powering accessories. |
| Fuses | Protect circuits from overload by breaking the connection when current exceeds safe levels. |
| Relays | Control the flow of electricity to various systems, allowing for high-current devices to be operated by lower-current switches. |
| Wiring Harness | Connects all electrical components, ensuring proper communication and power distribution. |
Fuel System Components
The fuel system in vehicles is crucial for delivering the necessary energy to the engine. It encompasses various elements that work together to ensure efficient fuel management and optimal engine performance. Understanding these components helps in maintaining the system and addressing any potential issues that may arise.
Key Elements of the Fuel System
Several key components constitute the fuel system, each playing a vital role in the overall functionality. These parts include the fuel pump, fuel injectors, fuel filter, and fuel tank. Together, they ensure that fuel flows smoothly from the tank to the engine, providing the power needed for operation.
Component Functions
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Fuel Pump | Transfers fuel from the tank to the engine. |
| Fuel Injectors | Sprays fuel into the engine cylinders for combustion. |
| Fuel Filter | Removes impurities from the fuel before it reaches the engine. |
| Fuel Tank | Stores fuel until needed by the engine. |
Exhaust System Design
The exhaust system plays a crucial role in vehicle performance and environmental compliance. Its primary function is to channel exhaust gases away from the engine while minimizing noise and emissions. The design of this system is vital for ensuring optimal engine efficiency and meeting regulatory standards.
An effective exhaust system consists of several components that work together harmoniously. These include the manifold, catalytic converter, muffler, and exhaust pipes. Each part is engineered to fulfill specific tasks that contribute to overall performance.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Manifold | Collects exhaust gases from the engine cylinders. |
| Catalytic Converter | Reduces harmful emissions by converting them into less harmful substances. |
| Muffler | Minimizes noise produced by the exhaust gases. |
| Exhaust Pipes | Directs exhaust gases to the rear of the vehicle. |
Design considerations for exhaust systems include material choice, diameter, and routing. High-quality materials enhance durability and performance, while appropriate diameters ensure proper gas flow and pressure management. Proper routing avoids unnecessary bends, which can hinder exhaust efficiency.
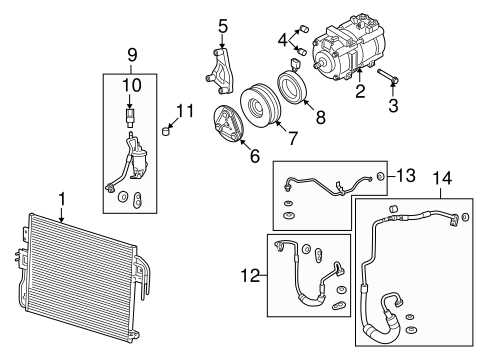
Transmission Assembly Details
This section provides an overview of the components involved in the assembly of a vehicle’s transmission system. Understanding these elements is crucial for maintenance, repair, and enhancement of performance.
Key Components
- Gearbox Housing: The outer casing that encases the internal components.
- Input Shaft: Connects to the engine and transfers power to the transmission.
- Output Shaft: Sends power to the drive wheels.
- Synchronizers: Help match the speed of gears during shifting.
- Clutch Assembly: Engages and disengages the engine from the transmission.
Assembly Process
- Begin by securing the gearbox housing on a clean work surface.
- Insert the input shaft into the housing, ensuring proper alignment.
- Install the synchronizers onto the input shaft as per specifications.
- Attach the output shaft to the housing, ensuring it is properly sealed.
- Finally, install the clutch assembly and secure all components tightly.
Regular inspection of these components is essential for ensuring the longevity and efficiency of the transmission system.
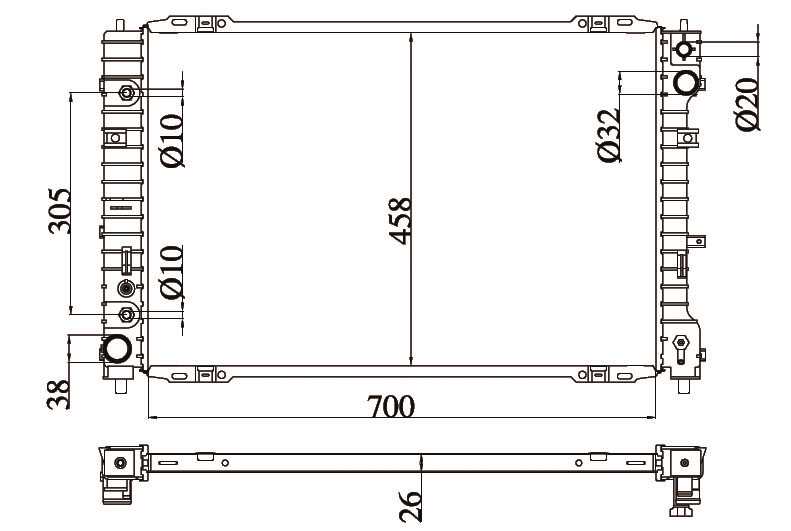
Cooling System Parts Guide
The cooling system is a vital component of any vehicle, ensuring optimal engine temperature and preventing overheating. Understanding the various components involved in this system is essential for maintaining efficiency and performance. This guide will provide an overview of key elements that contribute to the effective operation of the cooling mechanism.
Main Components
- Radiator
- Water Pump
- Thermostat
- Coolant Reservoir
- Hoses and Clamps
Functionality and Maintenance
Each component plays a significant role in regulating the temperature within the engine. Regular checks and timely replacements are crucial for ensuring the system operates efficiently. Below are important maintenance tips:
- Inspect coolant levels regularly.
- Check for leaks in hoses and connections.
- Flush the coolant system periodically.
- Ensure the radiator is clean and free from debris.
Steering Mechanism Breakdown
The steering system is a crucial component of any vehicle, responsible for controlling its direction and ensuring smooth handling. Understanding the various elements that constitute this mechanism is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting. This section will delve into the key components and their functions within the steering assembly, providing insights into how they work together to facilitate precise maneuverability.
Key Components of the Steering Assembly
The primary elements of the steering mechanism include the steering wheel, column, gear, and linkages. Each of these parts plays a vital role in translating the driver’s input into movement. The steering wheel initiates the process, while the column transmits the rotational force to the gear system. This system converts the circular motion into lateral movement, guiding the vehicle as desired.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Proper upkeep of the steering system is imperative for optimal performance and safety. Regular inspections can help identify wear and tear on components such as tie rods and bushings. Additionally, ensuring that the fluid levels are adequate in the steering pump contributes to smoother operation. Neglecting these aspects may lead to diminished handling capabilities and increased risk of accidents.
Body Panel Layout
The configuration of body panels is essential for the structural integrity and aesthetic appeal of any vehicle. Understanding the arrangement and function of these components is crucial for both maintenance and repairs. This section outlines the key elements and organization of the body structure, highlighting their roles and interconnections.
Main Components
- Fenders: Protect the wheels and enhance the vehicle’s profile.
- Hood: Provides access to the engine while contributing to aerodynamics.
- Doors: Allow entry and exit while ensuring safety features.
- Roof: Offers protection from the elements and supports the overall framework.
- Quarter Panels: Define the rear profile and contribute to stability.
Panel Connections
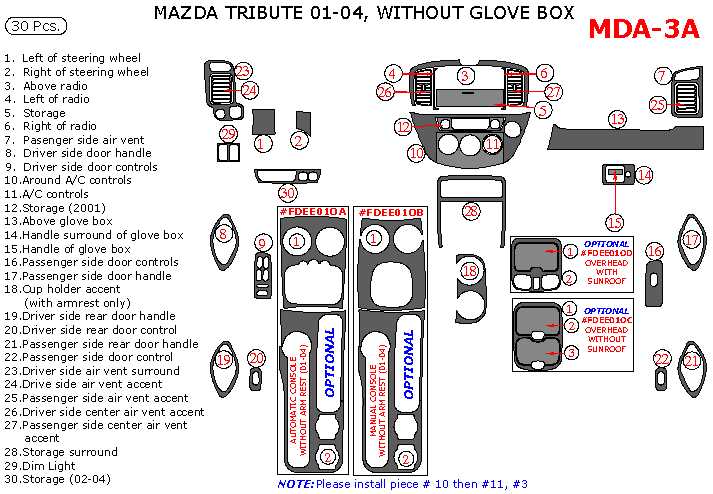
Each body panel is connected through various methods, including welding, bolting, or adhesive bonding. Proper alignment and securing are critical for maintaining the vehicle’s overall strength and safety.
- Ensure panels fit snugly to prevent water ingress.
- Inspect connections regularly for wear and corrosion.
- Replace damaged panels promptly to maintain integrity.
Lighting and Signal Parts Diagram
This section provides a comprehensive overview of the components associated with illumination and signaling systems in vehicles. Understanding the layout and functions of these elements is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key Components
The lighting and signaling systems include various elements that enhance visibility and communication on the road. Each part plays a specific role in ensuring safety and functionality.
Component Overview
| Component Name | Function |
|---|---|
| Headlight Assembly | Illuminates the road ahead for visibility during low-light conditions. |
| Taillight Unit | Signals the presence of a vehicle to those behind, particularly at night. |
| Turn Signal Indicator | Alerts other drivers of intended directional changes. |
| Fog Light | Improves visibility in adverse weather conditions, such as fog or heavy rain. |
| Brake Light | Informs following vehicles when the brakes are applied. |