Outboard motors are complex systems that rely on the seamless integration of multiple elements. These machines are essential for providing propulsion and performance for various watercraft, making it crucial to understand the various elements involved in their operation. For anyone seeking to maintain or repair these engines, having a clear view of how the different sections interconnect is invaluable.
This guide delves into the various components that make up a common marine propulsion system. By examining the individual segments and how they function together, you can gain a deeper understanding of the mechanical layout. This knowledge ensures a more efficient approach when handling repairs or upgrades.
Whether you’re looking to troubleshoot, replace specific elements, or simply learn more about how each section operates, this overview provides the essential insights needed to keep your equipment in optimal condition. Understanding the overall arrangement of these systems is the first step toward ensuring long-term reliability and performance.
Overview of Key Components

This section provides a detailed look at the essential elements that make up the mechanical and electrical systems of the motorized equipment. Understanding how these different parts interact and work together is crucial for proper maintenance and repair.
Mechanical Elements
- Power Source Unit – The core component that generates the necessary energy to drive the system.
- Cooling Mechanism – Ensures that the engine remains within safe temperature limits during operation.
- Propulsion System – Transfers the power generated into motion, allowing efficient operation.
Electrical Systems
- Ignition Circuit – Responsible for initiating the engine’s operation, ensuring smooth starts.
- Control Wiring – A network of connections that regulate the performance and response of various components.
- Charging Assembly – Keeps the electrical systems powered during extended use.
Engine Structure and Assembly
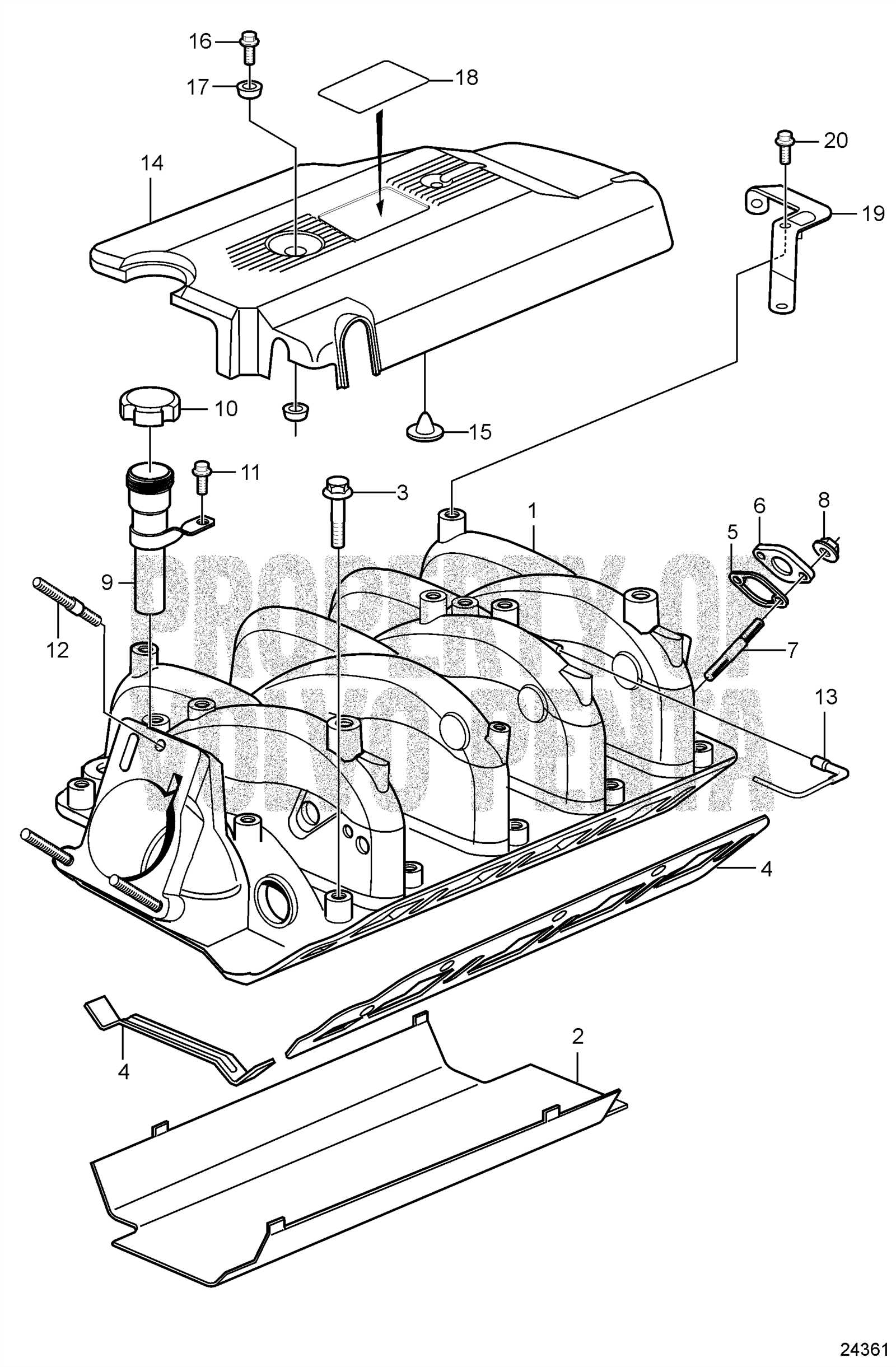
The overall design of a motor system is complex, involving various interconnected components that must function seamlessly together. Understanding the architecture and how these elements fit together is crucial for efficient performance and maintenance.
Core Components Overview
The central framework of the engine is built around several key segments. These include the cylinder arrangement, the drive mechanism, and the cooling system. Each section is meticulously engineered to deliver power, reduce friction, and maintain temperature stability during operation.
Assembly Configuration

The assembly process involves careful placement of each component within the structure. Precision is essential during the alignment of internal parts to ensure maximum efficiency. Below is a simplified breakdown of the engine’s main assemblies and their roles:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Cylinder Block | Houses the cylinders and provides a solid structure for the moving parts. |
| Crankshaft | Converts the vertical movement of pistons into rotational force. |
| Pistons | Move up and down within the cylinders, driven by combustion. |
| Cooling System | Regulates temperature to prevent overheating and ensure smooth operation. |
Fuel System and Delivery Mechanism
The engine’s fuel system is a critical component responsible for ensuring smooth operation by efficiently managing the flow of fuel to the combustion chamber. Understanding how the system works can help in maintaining optimal performance and troubleshooting common issues related to fuel delivery.
Main Components of the Fuel System
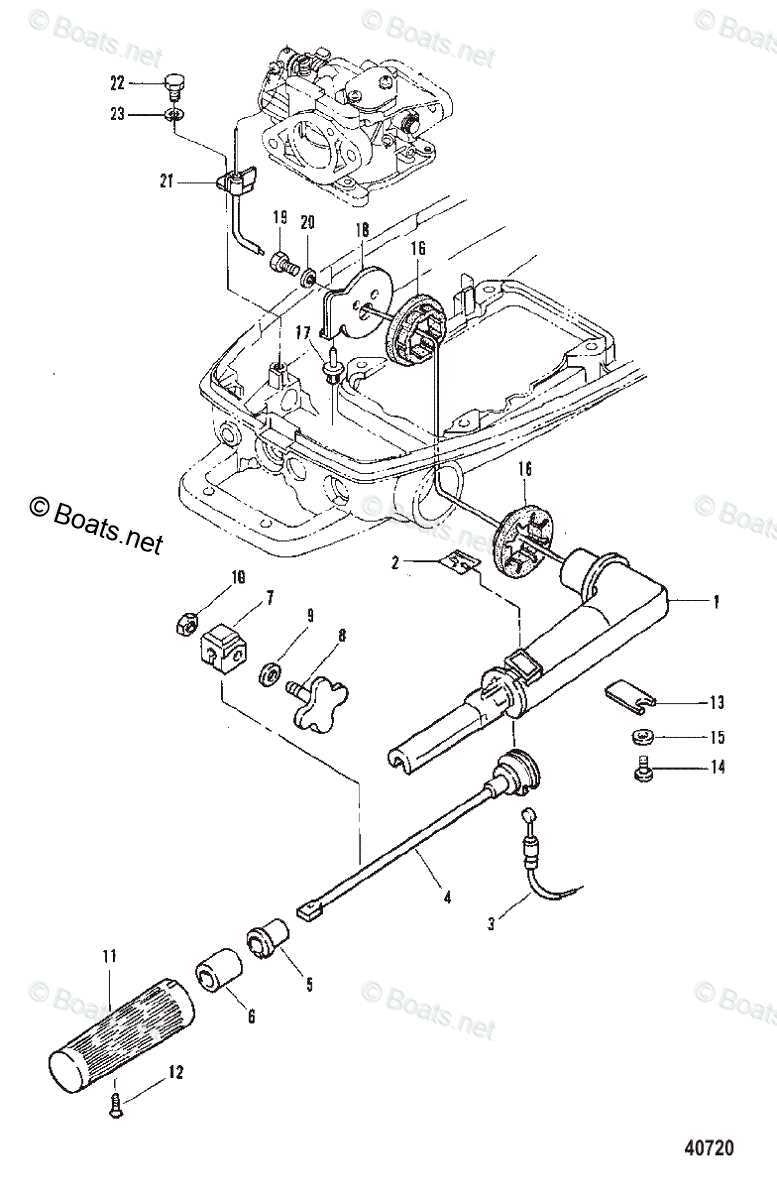
Key elements include the fuel pump, injectors, and filters, which work in unison to deliver a consistent supply of fuel. The pump ensures that the correct pressure is maintained, while the injectors distribute the fuel in precise amounts. Filters play a vital role in keeping the fuel clean and free from impurities.
Common Fuel Delivery Challenges
Issues such as clogged filters or faulty injectors can disrupt the balance of the fuel system, leading to reduced performance or engine malfunctions. Regular maintenance, including checking the pump and cleaning filters, is essential for the efficient operation of the engine’s fuel delivery mechanism.
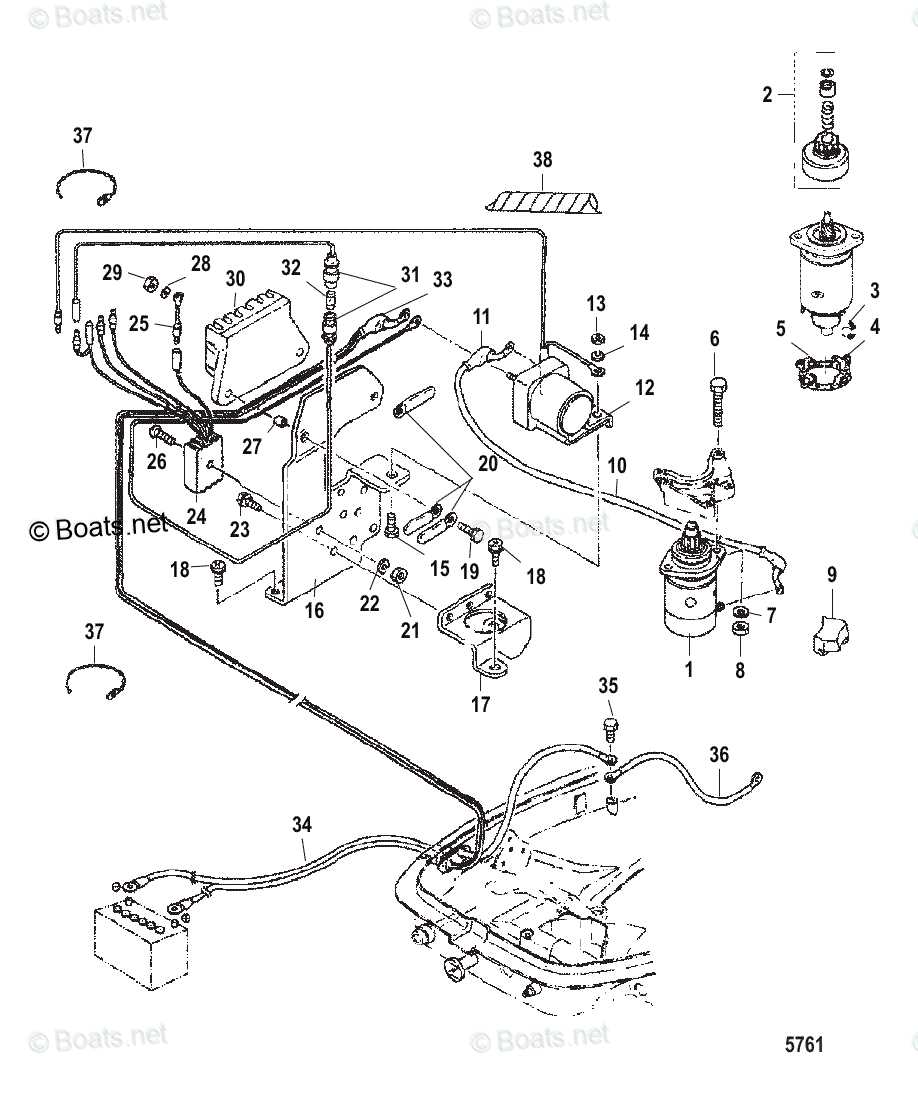
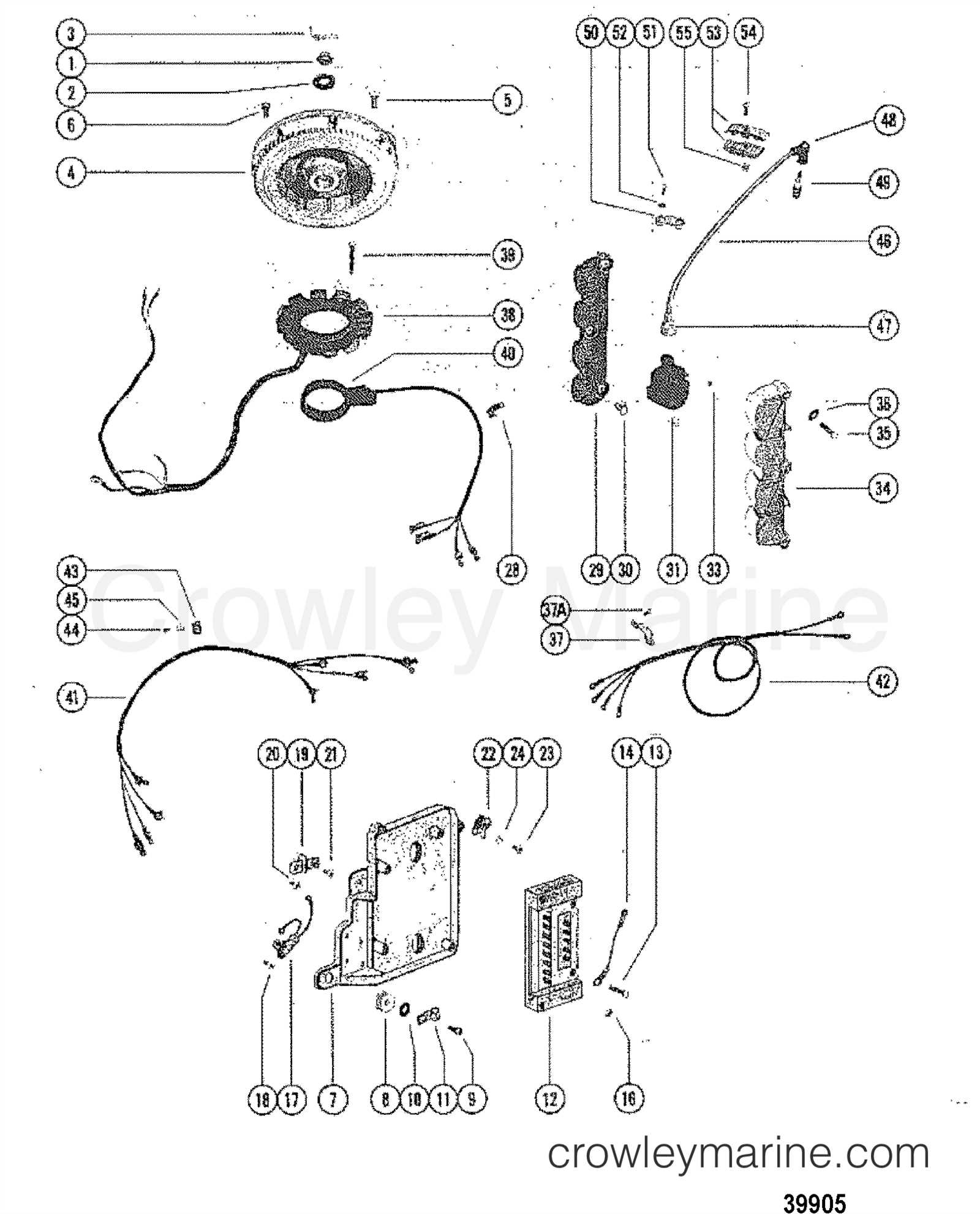
Electrical System and Wiring Layout
The electrical network within an engine is vital for ensuring smooth operation and performance. Understanding how the various connections and circuits interact helps in troubleshooting and maintenance, ensuring all components function optimally. A clear grasp of the arrangement and flow of electrical power aids in identifying potential issues before they escalate.
The layout typically consists of key elements such as power distribution, grounding points, and signal transmission paths. Each of these plays a critical role in delivering the necessary energy to different systems, enabling the motor to operate efficiently. Familiarizing yourself with these pathways is essential for maintaining and improving overall reliability.
When assessing the system, pay attention to the wiring structure, which interconnects all crucial components. Proper installation and periodic inspection are crucial to avoid potential failures or malfunctions. This section covers the foundational aspects of the electrical structure, aiming to provide insight into the organization and functionality of the connections.
Cooling and Lubrication Parts
Efficient temperature control and adequate lubrication are crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of an engine. Understanding the components involved in these systems helps to maintain proper function, prevent damage, and reduce the need for repairs.
Key Elements in Temperature Control
- Thermostat: Regulates the flow of coolant to keep the engine within an ideal temperature range.
- Water pump: Ensures the circulation of coolant throughout the system, allowing heat dissipation.
- Heat exchanger: Transfers excess heat from the engine to the external environment to prevent overheating.
Lubrication System Components
- Oil pump: Circulates lubricant through the system to reduce friction and wear on moving parts.
- Oil filter: Removes contaminants from the oil, ensuring clean lubrication for better performance.
- Pressure relief valve: Maintains the correct oil pressure to ensure consistent delivery to critical areas.
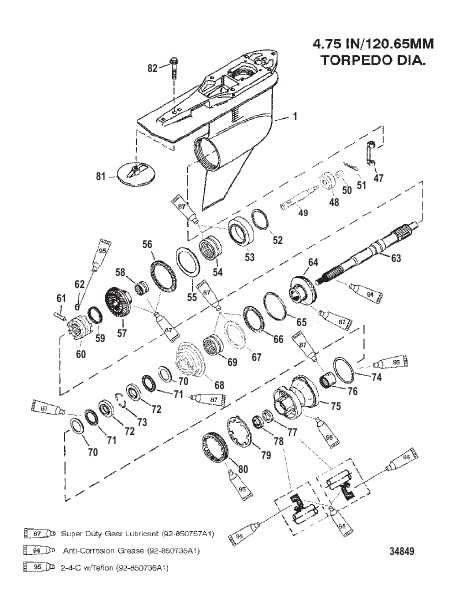
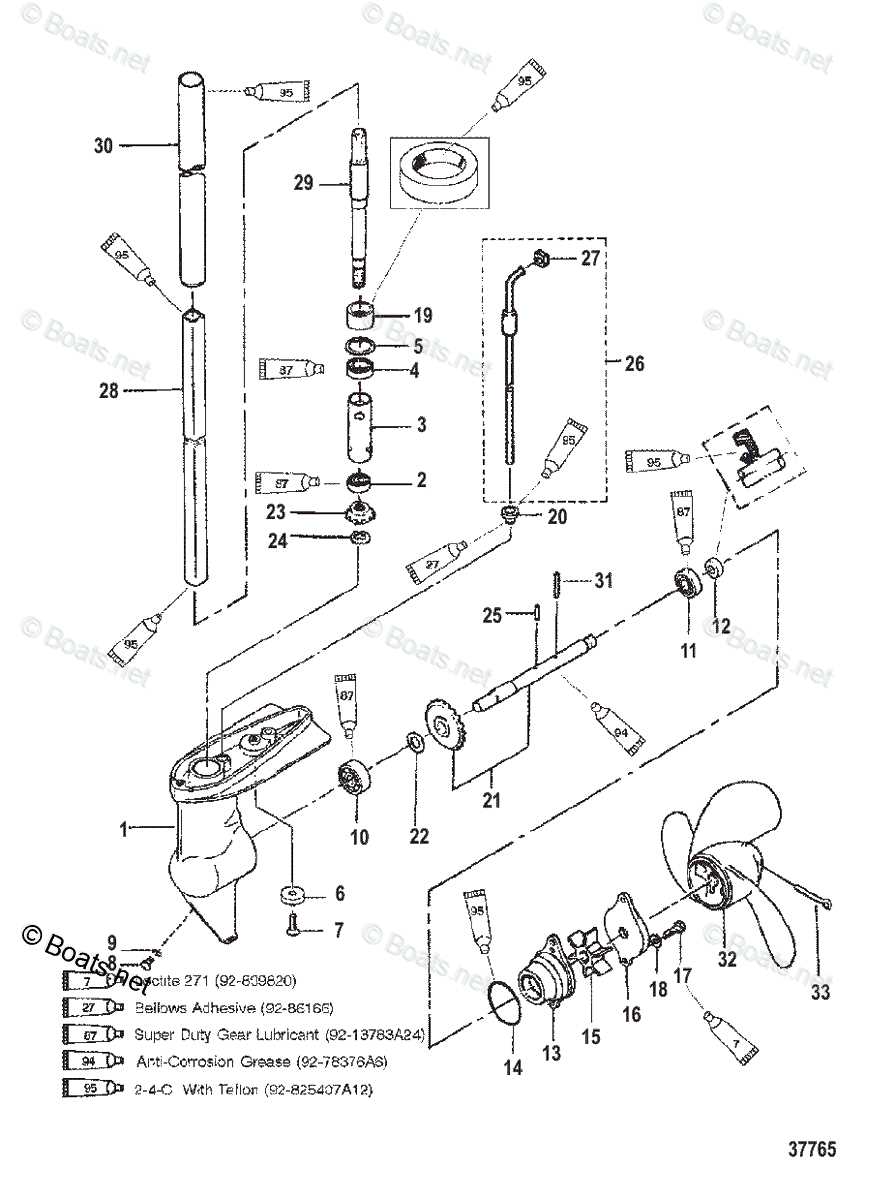
Propeller and Gear Mechanism
The interaction between the rotating blades and the transmission system is vital for the efficient movement of watercraft. This assembly transforms the engine’s power into thrust, enabling navigation through various aquatic environments. Understanding this mechanism helps in maintaining performance and optimizing functionality.
Components of the System

- Propeller Blades: These are designed to convert rotational energy into forward motion.
- Hub: The central part that connects the blades to the shaft, providing stability and support.
- Shaft: A critical element that transmits power from the engine to the propeller.
- Gear Assembly: This includes gears that adjust the rotational speed and torque delivered to the propeller.
Functionality Overview
- The engine generates rotational energy.
- This energy travels through the shaft, reaching the gear assembly.
- The gears modify the speed and torque, enhancing efficiency.
- The adjusted energy is transferred to the propeller blades, creating thrust.
- Thrust propels the vessel forward, allowing for smooth navigation.
Control and Steering Components
In any marine vessel, the elements responsible for navigation and maneuvering play a vital role in ensuring optimal performance and safety. These components facilitate the smooth operation of steering mechanisms, enabling precise direction changes and responsiveness to various sea conditions.
Steering Systems are designed to provide effective control over the vessel’s trajectory. This includes the helm, which is the primary interface for the operator, as well as the associated linkages that transmit movement to the rudder or outboard motor. A well-functioning steering assembly is crucial for maintaining stability and maneuverability during operation.
Control Mechanisms encompass various switches and levers that allow the operator to adjust speed and direction seamlessly. These controls must be intuitive and reliable, ensuring that the operator can make quick decisions in changing environments. Regular maintenance and inspection of these components are essential to prevent malfunction and ensure safe navigation.
Exhaust and Emission Management
Effective control of exhaust gases and emissions is crucial for maintaining optimal engine performance and meeting environmental regulations. This aspect involves the management of various components that work together to ensure that harmful byproducts are minimized, promoting cleaner operation and sustainability. Understanding the functions and interactions of these elements is essential for troubleshooting and enhancing the overall efficiency of the system.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Catalytic Converter | Converts harmful gases into less harmful emissions through chemical reactions. |
| Exhaust Manifold | Collects exhaust gases from the engine cylinders and directs them to the exhaust system. |
| Oxygen Sensor | Monitors oxygen levels in the exhaust and provides feedback for optimal fuel-air mixture. |
| Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System | Reduces nitrogen oxide emissions by recirculating a portion of the exhaust back into the engine’s intake. |
| Muffler | Reduces noise produced by the exhaust gases while allowing for efficient gas flow. |
Ignition and Power Distribution
The ignition system and power distribution network are crucial components that ensure the efficient operation of marine engines. They work together to manage electrical flow, enabling reliable starting and optimal performance. Understanding how these systems interact can significantly enhance troubleshooting and maintenance efforts.
Ignition refers to the mechanisms that initiate combustion within the engine cylinders. This process is vital for generating the power needed to propel the vessel. A well-functioning ignition setup typically includes components such as the ignition coil, spark plugs, and associated wiring. Each part must be in good condition to ensure a consistent spark, which directly influences engine responsiveness and fuel efficiency.
Power distribution, on the other hand, involves the management of electrical currents throughout the vessel’s electrical system. It encompasses the routing of electricity from the battery to various components, including the ignition system, lights, and other accessories. A reliable power distribution system ensures that all electrical components receive the necessary voltage and current, preventing failures and enhancing overall functionality.
Maintaining both the ignition and power distribution systems is essential for optimal engine performance. Regular inspections and timely replacements of worn-out components can prevent unexpected breakdowns and ensure a smooth boating experience. Familiarity with these systems allows boat owners to address issues promptly, contributing to the longevity and reliability of their marine engines.
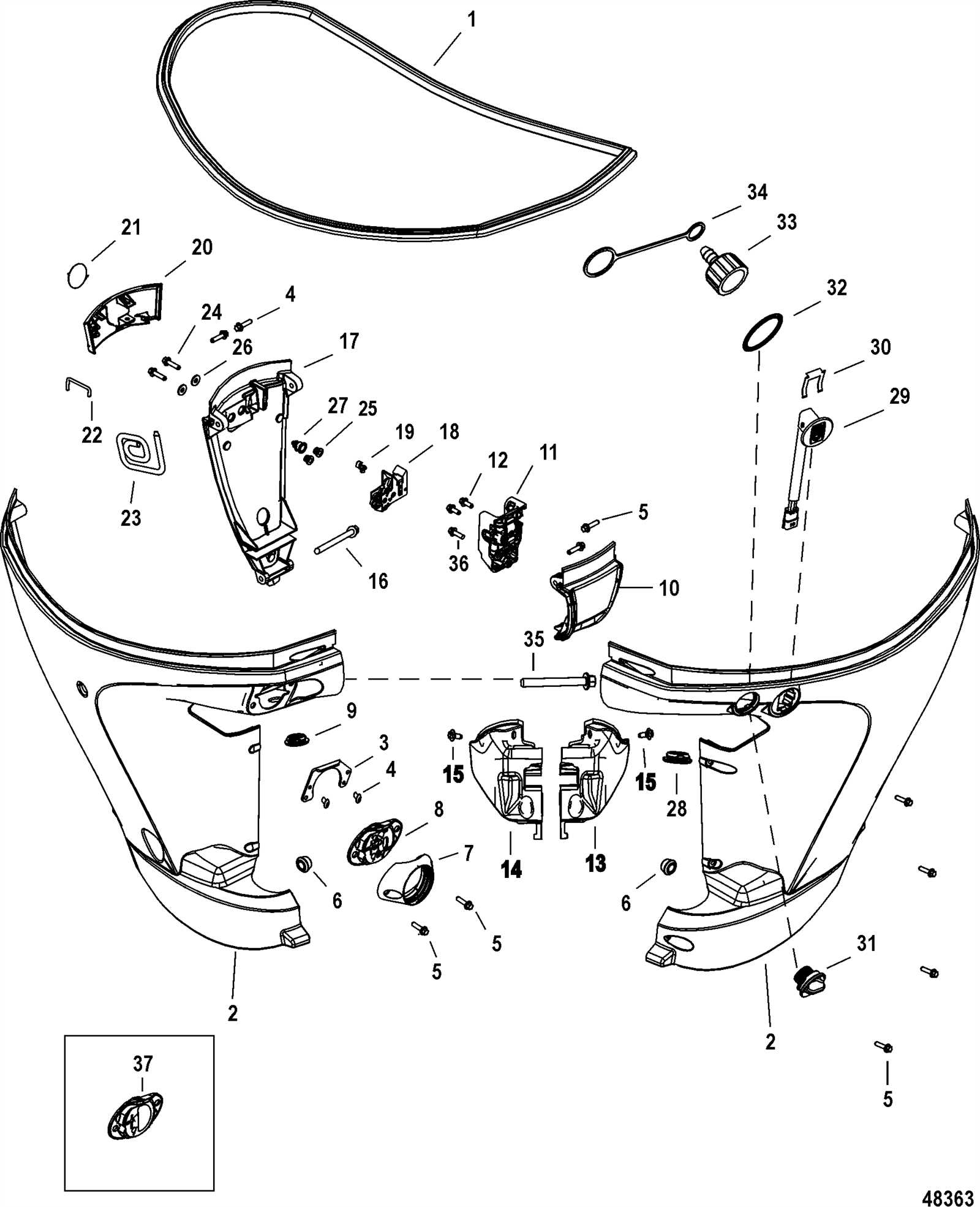
Mounting and Vibration Reduction Elements
Proper installation and effective vibration dampening are crucial for maintaining optimal performance and longevity of marine engines. The arrangement of these components plays a significant role in minimizing noise and movement that could lead to mechanical failure. This section explores various strategies and elements designed to enhance stability and reduce the adverse effects of vibrations.
When securing an engine to its base, it is essential to utilize high-quality mounts that can absorb shocks and vibrations. These mounts often feature specialized materials that provide flexibility while ensuring a solid connection. The design and placement of these supports must be carefully considered to create an optimal balance between rigidity and dampening capability.
In addition to mounts, incorporating vibration isolation pads can significantly improve comfort and reduce noise levels. These pads are strategically placed to enhance the separation between the engine and surrounding structures. By effectively absorbing vibrations, they contribute to a smoother operation and protect adjacent components from wear and damage.
Regular inspection and maintenance of these elements are vital for long-term performance. Over time, mounts and isolation pads may wear out or lose their effectiveness. Prompt replacement ensures continued protection against vibrations and contributes to the overall reliability of the engine system.
Maintenance and Replacement Parts
Regular upkeep and timely substitution of components are vital for the longevity and optimal performance of your vessel’s engine. Identifying the correct elements for servicing and ensuring their proper installation can significantly enhance reliability and efficiency during operation.
It is essential to refer to the manufacturer’s recommendations for the maintenance schedule and specific components that may require periodic replacement. Below is a table outlining some common items to consider when performing maintenance:
| Component | Description | Recommended Replacement Interval |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Filter | Helps keep fuel clean and free from impurities. | Every 100 hours or annually |
| Oil Filter | Removes contaminants from engine oil. | Every 100 hours or annually |
| Spark Plugs | Ignite the air-fuel mixture in the engine cylinders. | Every 200 hours or as needed |
| Belt | Transfers power to various engine components. | Every 3 years or as needed |
| Water Pump Impeller | Circulates water to cool the engine. | Every 2 years |
Staying on top of these essential items not only prevents unexpected breakdowns but also ensures smooth operation and longevity of the machinery. Always consult with a certified technician for any replacements to maintain optimal functionality.