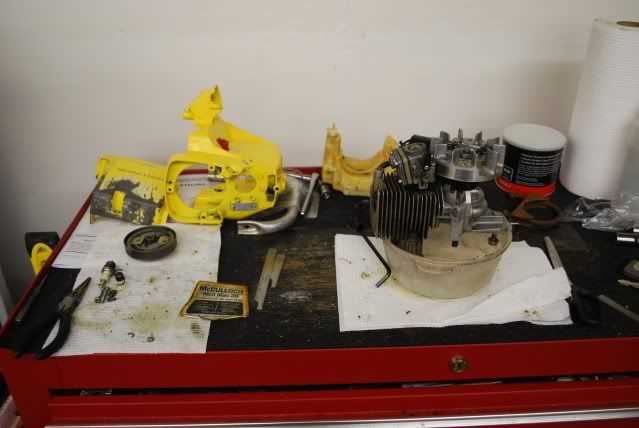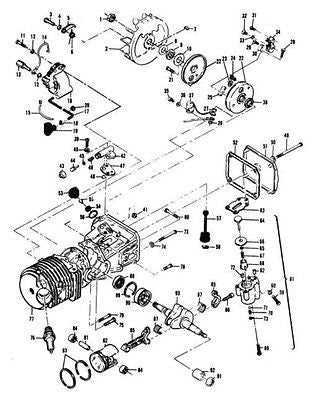
When it comes to ensuring the longevity and smooth operation of your chainsaw, understanding the key elements that make up its structure is crucial. Each component plays a vital role in maintaining the tool’s performance, contributing to both its efficiency and durability. Without a clear view of these internal elements, maintaining and troubleshooting any issues can become a challenge.
In this section, we delve into the various elements that make up a reliable cutting tool. You will discover a detailed overview of its mechanical structure, exploring the key components and their functions. Whether you are performing routine maintenance or replacing certain elements, this guide will provide clarity on how to best care for your tool.
By gaining a deeper understanding of these mechanical aspects, you can ensure your equipment stays in optimal condition, enhancing its lifespan and reducing the need for frequent repairs. The following guide will help you navigate the intricate framework of your equipment’s construction.
Essential Components of the Mcculloch Mini Mac 30
The key elements of this compact chainsaw are designed to work together efficiently, providing optimal performance for various cutting tasks. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring the tool’s reliability and functionality. Understanding these parts is crucial for maintaining and repairing the equipment, ensuring it runs smoothly over time.
Engine Unit: The motor is the powerhouse, responsible for generating the necessary force to drive the cutting chain. It requires regular maintenance to operate effectively, such as fuel management and proper lubrication.
Cutting Chain: The chain is designed to handle tough materials, delivering precision and strength. Ensuring its sharpness and correct tension is critical for safe and effective operation.
Bar: The guide bar provides the path for the chain, determining the cutting reach. Regular inspection of its condition is necessary to avoid wear and tear, which could impact overall performance.
Fuel and Oil Systems: These systems work in harmony to keep the engine running smoothly and the chain lubricated. Regular checks on fluid levels and
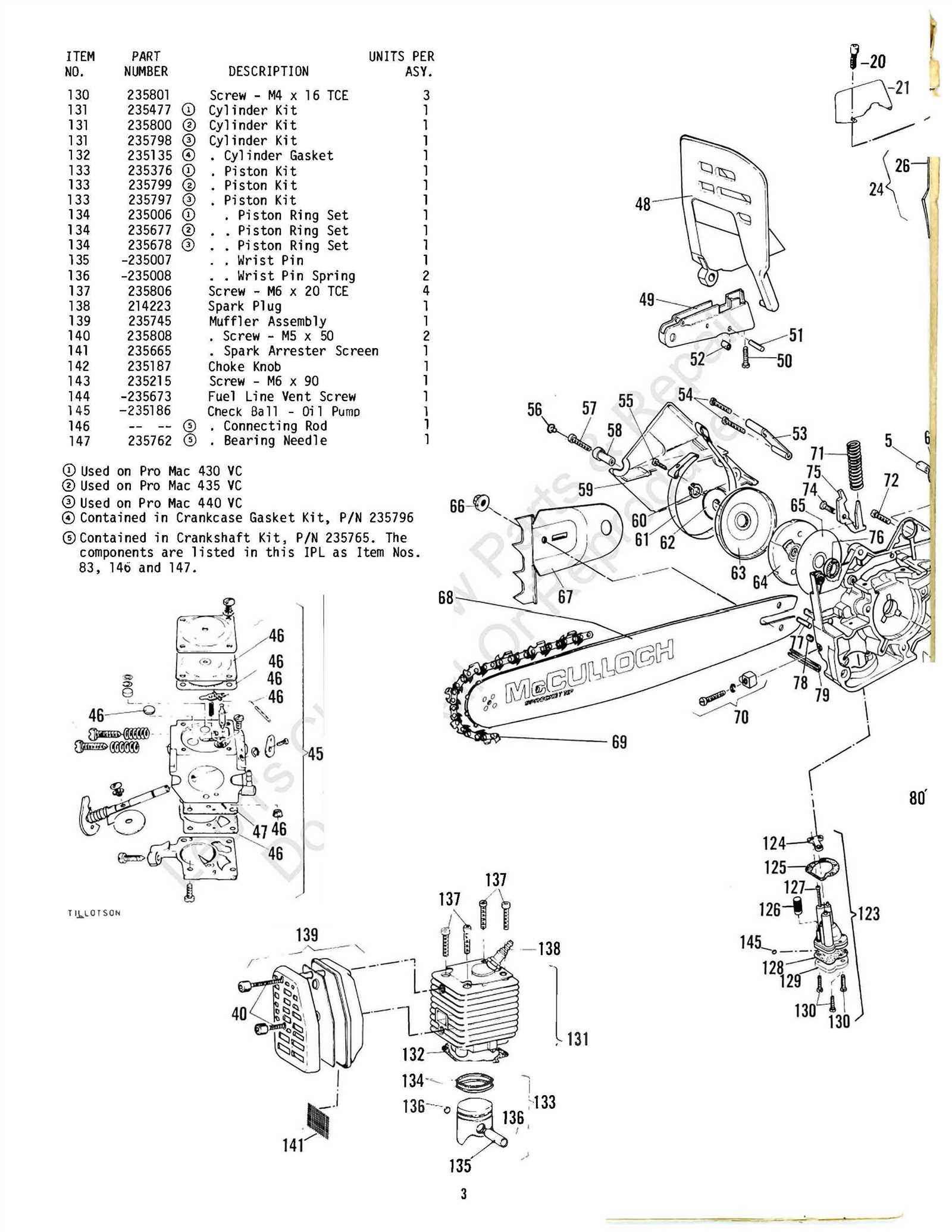
Exploring the Engine Assembly in Detail
The internal structure of the engine plays a pivotal role in the overall performance and functionality of your equipment. Understanding the core components and how they interact within the system is crucial for ensuring optimal operation and longevity. In this section, we will break down the key parts of the engine assembly, focusing on how each element contributes to the smooth running of the machine.
Key Engine Components
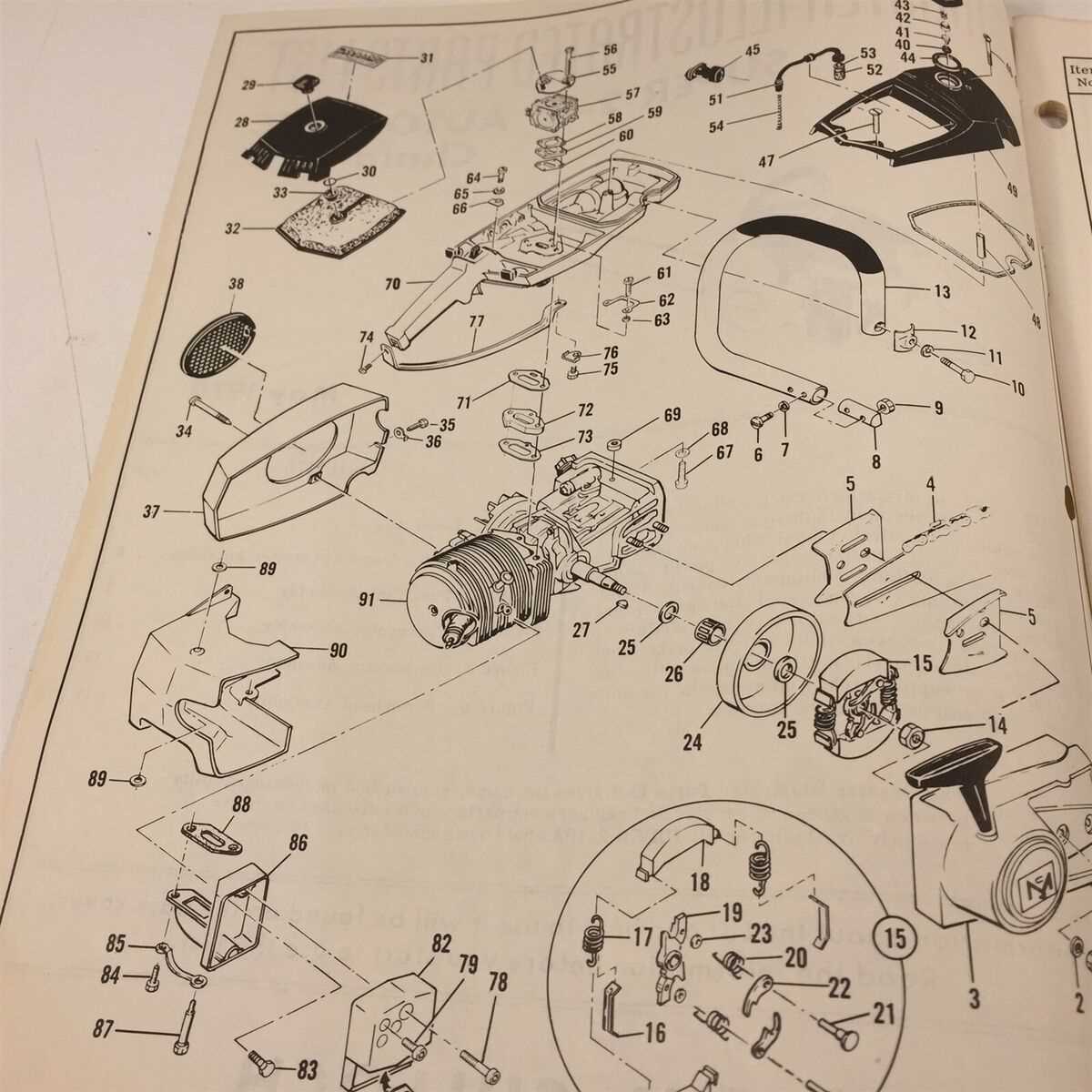
- Cylinder: The core of the engine where fuel combustion occurs, providing the power needed for operation.
- Piston: Moves within the cylinder, transferring the force generated by combustion to the crankshaft.
- Crankshaft: Converts the linear motion of the piston into rotational movement, which drives the rest of the system.
- Carburetor: Regulates the mixture of air and fuel, ensuring efficient combustion within the engine.
Assembly Process and Maintenance

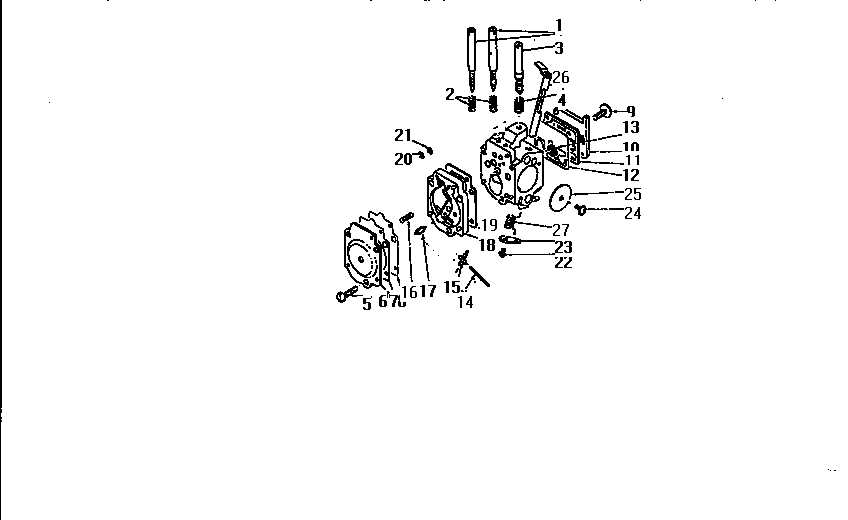
Understanding the Carburetor Structure and Function
The carburetor is a vital component of many small engines, playing a crucial role in the fuel-air mixture that powers the engine. Its design allows for the efficient blending of fuel and air, ensuring optimal combustion for reliable performance.
The primary functions of a carburetor include:
- Mixing air and fuel in the correct ratio.
- Regulating the flow of the fuel-air mixture to the engine.
- Adjusting the mixture based on engine demands, such as during acceleration or idling.
Understanding the structure of the carburetor is essential for troubleshooting and maintenance. Key components include:
- Float Chamber: Maintains a consistent level of fuel for mixing.
- Venturi: A narrowed section that increases airspeed, creating a vacuum that draws fuel into the airstream.
- Jet System: Controls the amount of fuel delivered to the engine.
- Throttle Valve: Regulates airflow into the engine, influencing power output.
By comprehending these components and their roles, users can enhance the performance and longevity of their engines through proper maintenance and adjustments.
Guide to Ignition System Components

The ignition system plays a vital role in ensuring the effective functioning of small engine machinery. It is responsible for generating the spark necessary for combustion, thereby powering the engine. Understanding the various elements of this system is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting, enabling users to achieve optimal performance.
Key Elements of the Ignition System

At the heart of the ignition system lies the spark plug, which ignites the air-fuel mixture within the combustion chamber. This component relies on a high-voltage current, produced by the ignition coil, to create a spark. The coil transforms the battery’s low voltage into a much higher voltage, ensuring a robust spark that can ignite the mixture efficiently.
Additional Components and Their Functions
Other critical elements include the ignition module and the flywheel. The ignition module controls the timing and duration of the spark, optimizing engine performance. Meanwhile, the flywheel is responsible for maintaining momentum, which assists in generating power during the engine’s operation. Together, these components work in harmony to provide reliable ignition and overall engine efficiency.
Overview of Fuel System Parts
The fuel system is essential for the efficient operation of small engines, ensuring that the correct mixture of air and fuel reaches the combustion chamber. This section provides a concise look at the various components that make up this critical system, highlighting their functions and interconnections.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Fuel Tank | A reservoir that holds the fuel before it is delivered to the engine. |
| Fuel Line | A conduit that transports the fuel from the tank to the carburetor. |
| Carburetor | A device that mixes the air and fuel in the correct proportions for combustion. |
| Fuel Filter | A filter that removes impurities from the fuel to prevent clogging and damage to the engine. |
| Purge Bulb | A manual pump that helps prime the fuel system before starting the engine. |
Understanding these components is vital for troubleshooting and maintenance, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of the engine.
Chain and Bar Setup Breakdown
The proper alignment and maintenance of the cutting components is crucial for ensuring the best performance and longevity of your equipment. Understanding how the main elements work together will help achieve optimal functionality and prevent premature wear.
The cutting chain is designed to fit securely around the bar, with its sharp edges facing in the correct direction for efficient cutting. It is important to regularly check for the correct tension in the chain, as too much slack or overtightening can lead to operational issues.
Similarly, the bar plays a key role in guiding the chain during use. Keeping the bar clean and well-lubricated allows for smooth operation and reduces friction, which can otherwise cause excessive wear on both the chain and the bar.
Maintaining the chain and bar also includes inspecting them for signs of damage or wear. Regular checks ensure that these components are in top condition, reducing the likelihood of breakdowns during operation.
Oil Pump and Lubrication System Diagram
The oil pump plays a critical role in maintaining the longevity and smooth operation of the engine. By circulating lubricant throughout key components, this mechanism ensures that friction is minimized, helping to prevent wear and overheating. The layout of the lubrication system provides a clear path for the oil, directing it to the areas where it’s needed the most.
Components of the Lubrication System
This system typically consists of a pump, oil reservoir, and various channels that distribute the lubricant. The pump draws oil from the reservoir and forces it through these channels, delivering it to the engine parts requiring lubrication. Proper maintenance of these elements is essential for efficient performance.
Lubrication Flow and Maintenance

Understanding the flow of oil within the system is key to ensuring optimal engine health. Regular inspection of the pump and channels, along with timely refilling of the oil reservoir, helps prevent issues such as clogging or insufficient lubrication. This process enhances the overall durability of the machine.
Examining the Starter Assembly Mechanism

The starter assembly is an essential part of any small engine, designed to ensure the smooth initiation of the machine’s operation. It functions as the main component responsible for generating the necessary motion to ignite the engine, allowing it to begin its cycle. Understanding the elements of this mechanism is crucial for maintenance and repair.
Below is an overview of the components involved in this process:
| Component | Function | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recoil Spring | Provides tension to retract the starter cord after it has been pulled. | |||||||||||
| Starter Pulley | Holds the starter rope and helps in rewinding it after use. | |||||||||||
| Flywheel | Transfers the rotational force from the pull cord to the engine. | |||||||||||
| Starter Rope | Used to manually
Handle and Safety Features LayoutThe design of the handle and safety elements is carefully structured to ensure user comfort and protection. These components work together to provide a firm grip and safeguard against potential risks during operation. This section outlines the arrangement and functionality of these essential features, highlighting their importance in maintaining both control and safety. Ergonomic Handle PlacementThe handle is positioned for optimal comfort and ease of use, allowing for prolonged operation without strain. The non-slip surface ensures a secure hold, even in wet conditions. This placement also facilitates better maneuverability, enabling users to handle the tool efficiently. Safety Mechanisms
Integrated safety features are strategically located near the handle for quick access. These mechanisms are designed to immediately halt the operation in case of an emergency, significantly reducing the risk of accidents. Below is a breakdown of the key safety components and their functions.
|