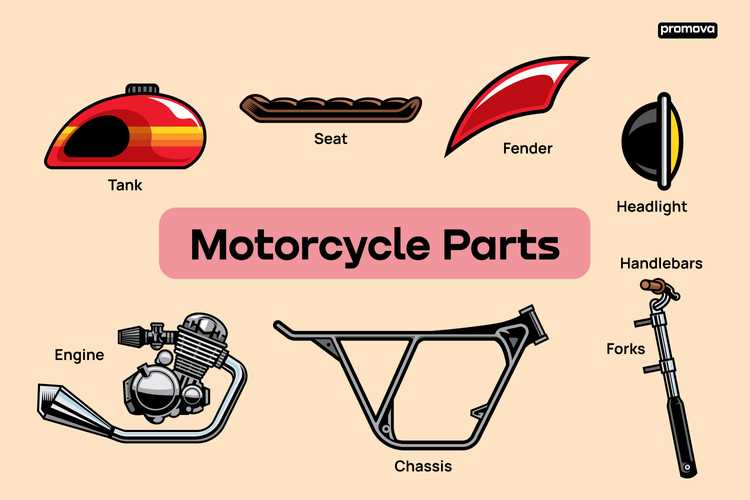
Understanding the essential elements that make up a two-wheeled vehicle is key to appreciating its engineering. From the core frame to the intricate mechanisms that drive the machine forward, each element plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth operation and safety.
In this section, we’ll explore various structural and mechanical features that come together to create a functioning and efficient vehicle. By breaking down these components, we’ll gain insight into how they work together to deliver performance and stability on the road.
Whether you are a beginner or a seasoned enthusiast, learning about these crucial features will enhance your knowledge of how these vehicles operate and what makes them reliable for everyday use or high-speed adventures.
Diagram of Motorcycle Parts

The structure of a two-wheeled vehicle consists of various essential elements, each serving a specific function to ensure proper operation. These components work together harmoniously, providing balance, power, and control for the rider. Understanding how these elements are connected helps in maintaining and enhancing the vehicle’s performance.
Key Structural Elements

- The main frame is the backbone, supporting all other elements and providing strength and stability.
- The propulsion unit generates energy that drives the machine forward.
- The suspension system ensures smooth movement over uneven surfaces, improving comfort and control.
Functional Systems
- The steering mechanism allows the rider to navigate the vehicle in
Main Components of a Motorcycle
Every two-wheeled vehicle consists of essential elements that allow it to function smoothly. These parts work together to ensure stability, power, and control while riding. Understanding the key elements is important for maintaining and improving performance.
- Frame: The backbone of the vehicle, providing structure and supporting all other components.
- Engine: The power source that drives the wheels and propels the vehicle forward.
- Suspension: Ensures a smooth ride by absorbing shocks from uneven surfaces.
- Wheels: Provide contact with the ground, allowing for movement and balance.
Engine Structure and Functions
The core of any mechanical system that powers a two-wheeled vehicle lies in its engine. Understanding how the engine is built and operates is essential for grasping the overall mechanics of the vehicle’s movement. The structure is designed to convert fuel into energy, which is then harnessed to generate motion. Below, we explore the primary components and their roles in this process.
Main Components of the Engine
Key elements such as the cylinders, pistons, and valves work in unison to create controlled combustion. The cylinders house the pistons, which move in a coordinated pattern, compressing the fuel-air mixture for ignition. Valves regulate the flow of gases, ensuring smooth intake and exhaust.
Functions of the Engine

The engine’s function revolves around generating power
Understanding the Motorcycle Transmission
The transmission plays a crucial role in transferring power from the engine to the wheels, allowing for control over speed and torque. It is responsible for ensuring that power is delivered efficiently under varying conditions, such as during acceleration or when riding uphill.
Main Components of the System
Several elements work together within the system to manage the transfer of power. These include gears, shafts, and a clutch, all of which must function in harmony to provide a smooth riding experience.
Component Function Clutch Disconnects power flow for gear shifts Gearbox Alters the speed and torque through different gear ratios Shafts Types of Motorcycle Braking Systems
Braking mechanisms in two-wheeled vehicles play a crucial role in ensuring safety and control during rides. There are various systems that offer different levels of efficiency and performance, each suited for particular driving conditions. Understanding the main options helps in choosing the most suitable one for specific needs.
Mechanical Drum Brakes
Drum brakes are one of the oldest and simplest systems. They consist of a drum and shoes that press against the inside of the drum to slow down the vehicle. This system is typically found on older or smaller models.
- Simple design and easy to maintain
- Less effective under heavy braking
- Common in rear wheel applications
Hydraulic Disc Brakes
Disc brakes are a more modern and powerful solution, providing better heat dissipation and more reliable stopping power. These are usually found on more advanced models, offering superior performance in a variety of conditions.
- Better
Suspension Mechanism Overview
The suspension mechanism plays a crucial role in ensuring a smooth and controlled ride. It acts as a system that absorbs shocks and vibrations, providing stability and comfort. Understanding its components and functionality is essential for maintaining performance and safety during operation.
Key Functions
- Shock Absorption: Reduces the impact of bumps and irregularities in the surface.
- Stability: Enhances balance, ensuring that the structure remains steady during various maneuvers.
- Tire Contact: Maintains optimal contact between the wheels and the ground, improving traction and control.
Components of the System
- Springs: Store and release energy, aiding in shock absorption.
- Dampers: Control the speed of spring movement, preventing excessive bouncing.
- Linkages: Connect various elements, allowing for coordinated movement and adjustment.
Frame and Chassis Design
The structure and assembly of a two-wheeled vehicle play a crucial role in determining its performance, safety, and overall functionality. The design of these elements is essential for ensuring stability, durability, and aesthetic appeal. A well-engineered framework supports various components and enhances the rider’s experience through improved handling and comfort.
Key Considerations in Design
Several factors influence the creation of the frame and chassis, including materials used, geometry, and intended use. Choosing the right materials is vital, as they affect weight, strength, and cost. The geometric layout impacts how the vehicle handles under different conditions, while the purpose dictates specific design requirements to optimize performance.
Materials and Construction Techniques
Modern vehicles utilize a variety of materials, each offering distinct advantages. Steel, aluminum, and composite materials are commonly employed due to their unique properties. Construction methods have also evolved, leading to innovations such as welding, tube bending, and casting, which enhance the structural integrity and efficiency of the design.
Material Advantages Common Uses Steel Durable, cost-effective Entry-level models Aluminum Lightweight, corrosion-resistant Sport and high-performance models Composite High strength-to-weight ratio Luxury and specialized vehicles Electrical System and Wiring Diagram
The electrical framework is crucial for the proper functioning of any two-wheeled vehicle. It encompasses various components that facilitate the operation of essential systems, ensuring that everything works in harmony. Understanding this framework is vital for troubleshooting and maintenance, allowing enthusiasts and mechanics alike to ensure reliability and efficiency.
Key Components
This section outlines the primary elements that make up the electrical system. Each component plays a significant role in the overall performance and safety of the vehicle.
Component Function Battery Stores electrical energy for starting the engine and powering accessories. Ignition System Provides the spark necessary to ignite the fuel-air mixture in the engine. Lighting Includes headlamps, taillights, and turn signals for visibility and safety. Wiring Harness Connects all electrical components, allowing for efficient power distribution. Understanding the Wiring Layout
Familiarity with the layout of the wiring can help identify issues and facilitate repairs. Knowing how components are interconnected allows for easier troubleshooting and enhances the ability to make modifications or upgrades.
Fuel System and Carburetor Layout

The fuel system is a crucial component of any internal combustion engine, responsible for delivering the appropriate amount of fuel for optimal performance. Understanding its structure and functionality is essential for anyone interested in enhancing engine efficiency or troubleshooting issues related to fuel delivery.
Components of the Fuel System
The fuel system typically includes several key elements: the fuel tank, fuel pump, fuel lines, and the carburetor. Each of these components works together to ensure that fuel is transported from the tank to the engine. The fuel tank stores the fuel, while the pump moves it through the lines and into the carburetor for mixing with air before combustion.
Carburetor Functionality
The carburetor plays a vital role in the fuel system by mixing the correct proportions of air and fuel to create a combustible mixture. This process involves a series of jets and passages that regulate the flow of fuel and air, ensuring optimal engine performance across various speeds and loads. Proper adjustment and maintenance of the carburetor can significantly influence the efficiency and responsiveness of the engine.
Exhaust System and Its Components
The exhaust system plays a crucial role in optimizing performance and enhancing the overall experience of a vehicle. It is designed to guide waste gases away from the engine while minimizing noise and harmful emissions. Understanding the various elements within this system is essential for maintenance and performance tuning.
Components of the Exhaust System include several key elements, each serving a specific function:
- Exhaust Manifold: This component collects gases from the engine cylinders and directs them into the exhaust system.
- Catalytic Converter: A critical element that reduces harmful emissions by converting toxic gases into less harmful substances.
- Resonator: This part helps to refine the sound of the exhaust and can also improve the overall efficiency of the system.
- Muffler: Designed to reduce noise, it plays a significant role in managing sound levels produced by the engine.
- Exhaust Pipes: These tubes transport exhaust gases from the engine to the outside atmosphere, ensuring efficient flow and reduced back pressure.
Regular inspection and maintenance of the exhaust system are vital for optimal operation, fuel efficiency, and compliance with environmental standards.
Wheel and Tire Assembly Explanation
The wheel and tire assembly is a crucial component that influences the overall performance and handling of a two-wheeled vehicle. This assembly not only supports the weight but also ensures stability and traction on various surfaces. Understanding its elements and functions can enhance the riding experience and contribute to better maintenance practices.
Components of the Assembly
The wheel and tire assembly consists of several key elements, each serving a specific purpose. The main components include the rim, tire, inner tube, and valve stem. Together, these elements work to provide support and grip while allowing for necessary adjustments in pressure and alignment.
Component Description Rim The outer edge of the wheel that holds the tire in place. Tire The rubber covering that provides traction and absorbs shock. Inner Tube A sealed air chamber that maintains the tire’s pressure. Valve Stem Allows for inflation and deflation of the inner tube. Importance of Maintenance
Regular inspection and maintenance of the wheel and tire assembly are essential for optimal performance. Ensuring proper inflation, checking for wear and tear, and maintaining alignment can significantly improve safety and efficiency. By taking proactive measures, riders can enhance the longevity and functionality of this vital component.