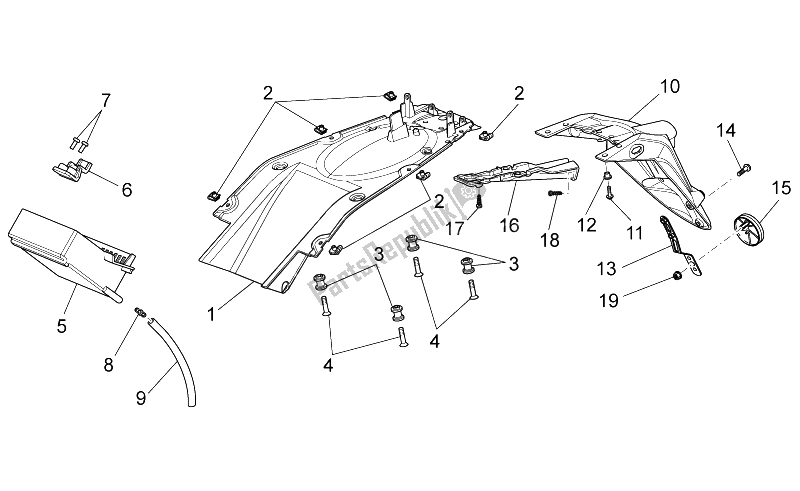
When it comes to maintaining or enhancing a classic two-wheeler, having a clear visualization of the connections and elements is crucial. This section will guide you through the intricate web of mechanical pieces, providing a structured approach to identifying key segments.
Each element plays a vital role in ensuring the seamless operation of the machine, and knowing where everything fits can be the difference between a smooth ride and unforeseen issues. Our focus here is to simplify the exploration of these elements, ensuring that even the most complex structures become easy to comprehend.
By breaking down the different assemblies, you will gain a better understanding of how each piece interacts within the overall framework. This knowledge is invaluable for both novice enthusiasts and seasoned professionals looking to maintain or modify their machine with confidence.
Moto Guzzi Component Breakdown Overview
The mechanical structure of this iconic machine is built upon a network of interconnected systems. Each element plays a vital role in ensuring the overall performance and reliability of the vehicle. Understanding the layout of these components helps in maintenance, troubleshooting, and customization efforts.
Engine Configuration: The power unit is the heart of the vehicle, driving all essential functions. It is comprised of several moving parts, including the crankshaft, pistons, and valves, all working in harmony to generate power. Regular inspection of these areas ensures longevity and efficiency.
Electrical Network: This system is responsible for powering essential electronics and igniting the motor. The wiring harness connects sensors, switches, and control units, coordinating the functionality of lights, ignition, and safety mechanisms.
Chassis and Suspension: The frame serves as the foundation, supporting the engine and providing stability. The suspension system absorbs shocks from uneven roads, ensuring a smooth ride, while also protecting key components from excessive wear.
Understanding Key Mechanical Assemblies
To fully comprehend the workings of a complex machine, it is essential to focus on the individual systems that contribute to its overall functionality. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring smooth operation, and recognizing how these elements interact is key to maintaining and optimizing performance.
Engine Structure and Function: The engine is the powerhouse, driving the entire system through its precise combination of moving parts. Understanding how energy is generated, transferred, and converted into motion is critical for both performance and longevity.
Transmission Mechanisms: These elements are responsible for transferring power from the engine to the wheels, ensuring the machine operates efficiently across varying speeds and terrains. Recognizing the importance of gearing and clutch systems can aid in smoother handling and fewer mechanical issues.
Suspension and Steering: These assemblies are crucial for controlling movement, absorbing shocks, and providing stability. Familiarizing oneself with their operation ensures a more comfortable and controlled experience, while also prolonging the lifespan of critical components.
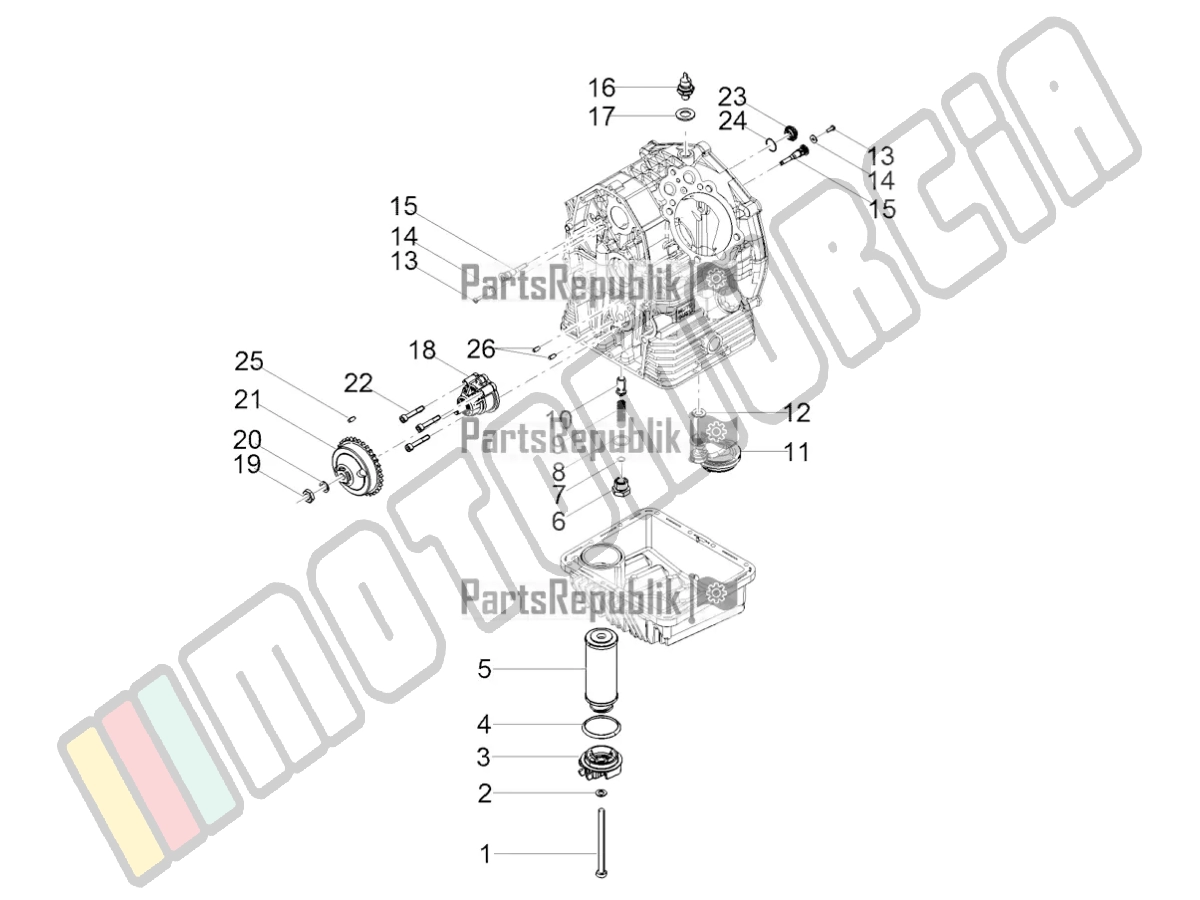
Detailed View of Engine Parts
The internal components of a mechanical engine are crucial to its operation. A clear understanding of these components helps in maintaining and servicing the system effectively. This section provides a closer look at the essential elements, highlighting their purpose and function in the overall mechanism.
- Cylinder Block: The central structure that houses key components such as the pistons and connecting rods. It serves as the foundation of the engine’s operation.
- Pistons: Move within the cylinder to create the necessary compression for fuel combustion. Their motion is vital for converting energy into mechanical work.
- Crankshaft: Transforms the linear movement of the pistons into rotational force, which is transferred to other components of the vehicle.
- Valves: Regulate the flow of air and fuel mixture into the combustion chamber and allow exhaust gases to escape after combustion.
- Camshaft: Controls the timing of valve movements, ensuring precise operation and synchronization within the engine.
Understanding the role of these components is essential for identifying potential issues and performing timely repairs or replacements. Regular inspection ensures the system operates smoothly and efficiently.
Exploring Electrical System Components
The electrical setup in vehicles consists of various interconnected elements that ensure proper functioning and control of different functionalities. Each component plays a crucial role in distributing power and managing the overall system’s efficiency. Understanding how these components are interconnected is essential for effective troubleshooting and maintenance.
Key Power Distribution Units
Power distribution units manage the flow of electricity to different areas of the vehicle. These units ensure that the necessary voltage reaches each system, preventing overloads and maintaining consistent operation. It is important to regularly inspect these units to avoid potential faults in the electrical network.
Wiring and Connectivity
The wiring network forms the backbone of the electrical system, linking various components. High-quality connections are critical for ensuring stable performance and preventing short circuits. Periodically checking the integrity of the wiring can help identify and prevent electrical failures.
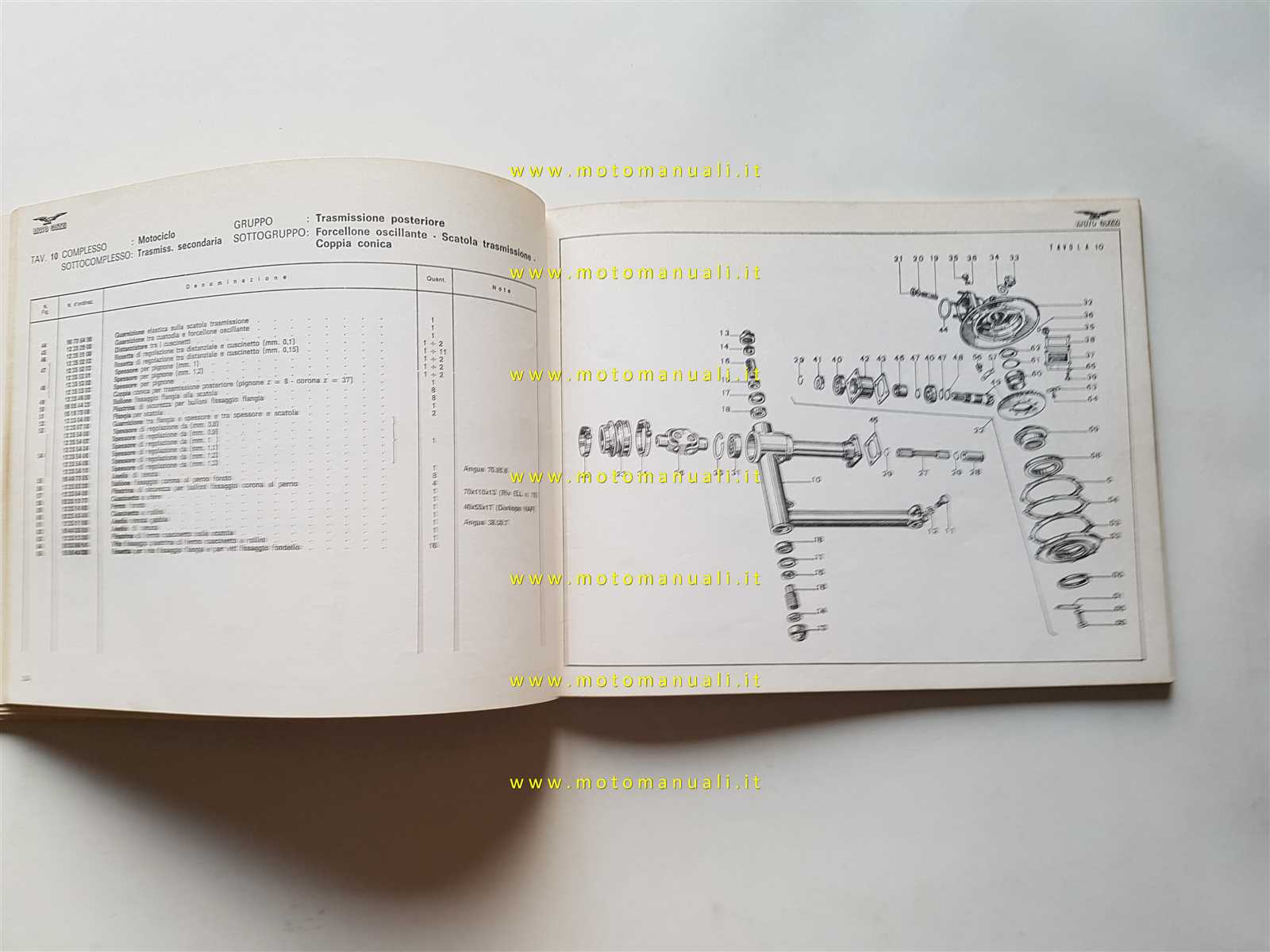
Transmission and Gearbox Parts Layout
The layout of the components involved in power transfer and gear management is critical for understanding how the overall system functions. By exploring the arrangement of key elements, one can gain insights into the smooth operation and efficiency of the entire setup. Proper alignment and organization of these components play a major role in ensuring long-term reliability and performance.
Key Components
- Input shaft – transfers engine power to the transmission system.
- Output shaft – delivers power from the gearbox to the drive system.
- Gear sets – provide the various speed and torque configurations.
- Clutch mechanism – controls the engagement and disengagement of power transfer.
Component Interaction
The interaction between these components determines how effectively the system shifts between different speeds and handles varying load conditions. Understanding the synchronization of these elements helps in diagnosing issues and ensuring smoother transitions between gears.
- Power enters the system through the input shaft.
- The gear sets adjust the speed based on the selected ratio.
- Power is transmitted to the output shaft for further distribution.
Fuel System Structure and Connections

The fuel system plays a crucial role in delivering the necessary energy for optimal engine performance. It comprises various components that work together to ensure a steady supply of fuel, proper pressure, and effective atomization. Understanding the layout and connections of this system is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting.
Components Overview
This system generally includes the fuel tank, pump, filter, injectors, and various hoses. Each element serves a specific function, contributing to the overall efficiency of fuel delivery. The tank stores the fuel, while the pump facilitates its movement toward the engine. A filter is employed to remove impurities, ensuring clean fuel reaches the injectors, which then atomize the fuel for combustion.
Connection Points
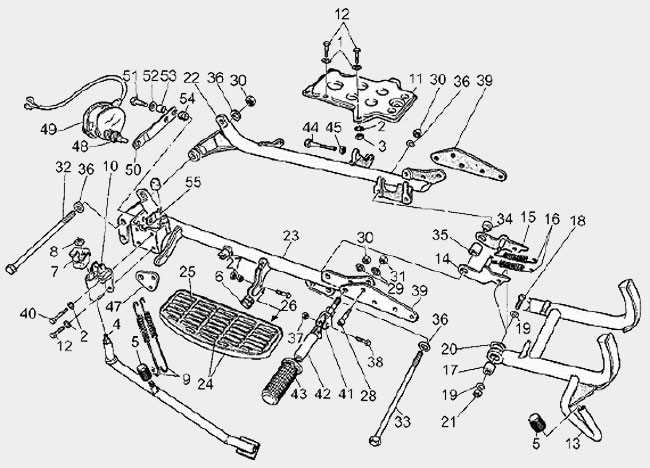
Connections between components must be secure and leak-free to maintain system integrity. Flexible hoses are typically used to link the fuel tank to the pump and filter, allowing for vibrations and movements. Proper routing of these hoses is vital to avoid wear and damage over time. Regular inspections can help identify potential issues before they escalate.
Exhaust System Components Overview
The exhaust system plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and efficiency in any vehicle. It serves to direct exhaust gases away from the engine while minimizing noise and emissions. Understanding the various components that make up this system can greatly enhance maintenance efforts and performance upgrades.
Below are the key elements commonly found within the exhaust system:
- Exhaust Manifold: This component collects gases from the engine cylinders and directs them into the exhaust system.
- Catalytic Converter: A vital part that reduces harmful emissions by converting them into less harmful substances before they exit the vehicle.
- Resonator: Designed to fine-tune the sound of the exhaust gases, helping to eliminate unwanted frequencies and enhance the overall audio experience.
- Muffler: This component significantly reduces noise produced by the engine’s exhaust gases, providing a quieter operation.
- Exhaust Pipes: These pipes transport the gases from the manifold to the muffler and out into the atmosphere, ensuring proper flow and pressure.
- Exhaust Tips: Often a stylistic choice, these are the visible ends of the exhaust system that can enhance the vehicle’s appearance and exhaust flow.
Regular inspections and maintenance of these components can lead to improved performance and longevity of the vehicle. Understanding their functions is essential for any enthusiast looking to optimize their machine.
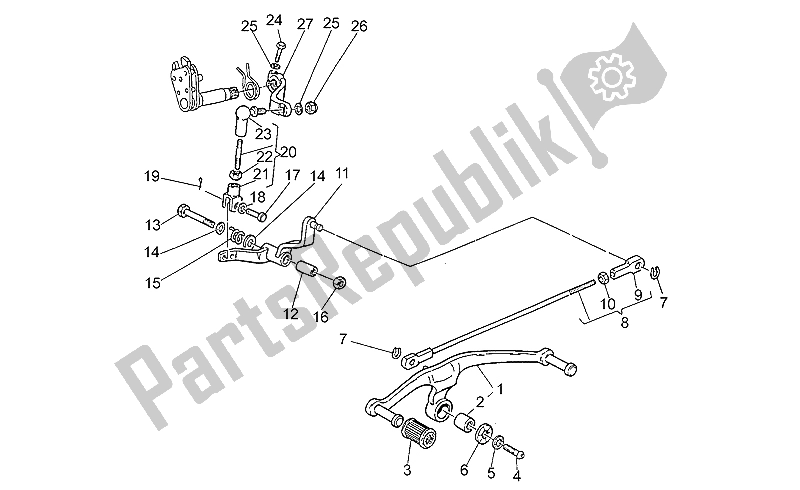
Suspension and Frame Component Details
This section delves into the essential elements that contribute to the stability and comfort of a two-wheeled vehicle. Understanding these components is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and handling characteristics, making it easier to identify any issues that may arise during operation.
Key Elements of Suspension
- Forks: These are pivotal in maintaining front wheel stability and absorbing shocks from uneven surfaces.
- Shock Absorbers: Located at the rear, these devices minimize the impact from bumps, enhancing ride quality.
- Springs: They work in conjunction with shock absorbers, providing support and flexibility.
Frame Components Overview
- Chassis: The main structure that supports the engine and other components, crucial for overall strength.
- Subframe: An auxiliary framework that can hold parts like the seat and rear suspension, providing additional support.
- Mounting Points: These are critical for attaching various components securely, ensuring everything is aligned correctly.
Brake System Part Configuration
The brake assembly is a crucial component of any vehicle, ensuring safety and control during operation. Understanding its configuration is essential for effective maintenance and optimal performance. This section delves into the various elements that make up the braking mechanism, focusing on their arrangement and functionality.
The primary components of the braking mechanism include calipers, rotors, pads, and the hydraulic system. Each part plays a significant role in creating the necessary friction to slow down or stop the vehicle. The calipers house the brake pads and utilize hydraulic pressure to engage them against the rotors. This interaction generates the friction needed for deceleration.
Additionally, the arrangement of these components is designed to maximize efficiency. For instance, the positioning of the rotors affects heat dissipation, which is vital for maintaining performance during extended use. Furthermore, the hydraulic lines must be meticulously routed to prevent leaks and ensure responsive braking action.
Regular inspection and maintenance of the brake assembly are essential for safety. Ensuring that all components are in good condition and correctly configured can significantly enhance the longevity and effectiveness of the entire braking system.
Cooling System Parts and Functionality

The effective management of heat within a vehicle is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. This section explores the essential components involved in maintaining appropriate temperature levels, ensuring that the engine operates smoothly without overheating. Each element plays a vital role in the overall cooling process, contributing to the reliability and efficiency of the machine.
One of the primary components is the radiator, which dissipates heat from the engine coolant. This unit functions by allowing airflow to cool the liquid as it passes through, preventing excessive temperatures. Another critical element is the water pump, which circulates coolant throughout the system, ensuring that it reaches all necessary areas to absorb heat. Additionally, hoses and connectors facilitate the movement of coolant, maintaining a continuous flow between the engine and radiator.
The thermostat acts as a regulator, controlling the coolant flow based on the engine’s temperature. When the engine reaches a certain heat threshold, the thermostat opens, allowing coolant to flow into the radiator. Conversely, it closes when the engine is cool, helping to maintain optimal operating temperatures. Finally, cooling fans provide additional airflow to the radiator when needed, especially during idling or low-speed conditions, further enhancing the cooling system’s efficiency.
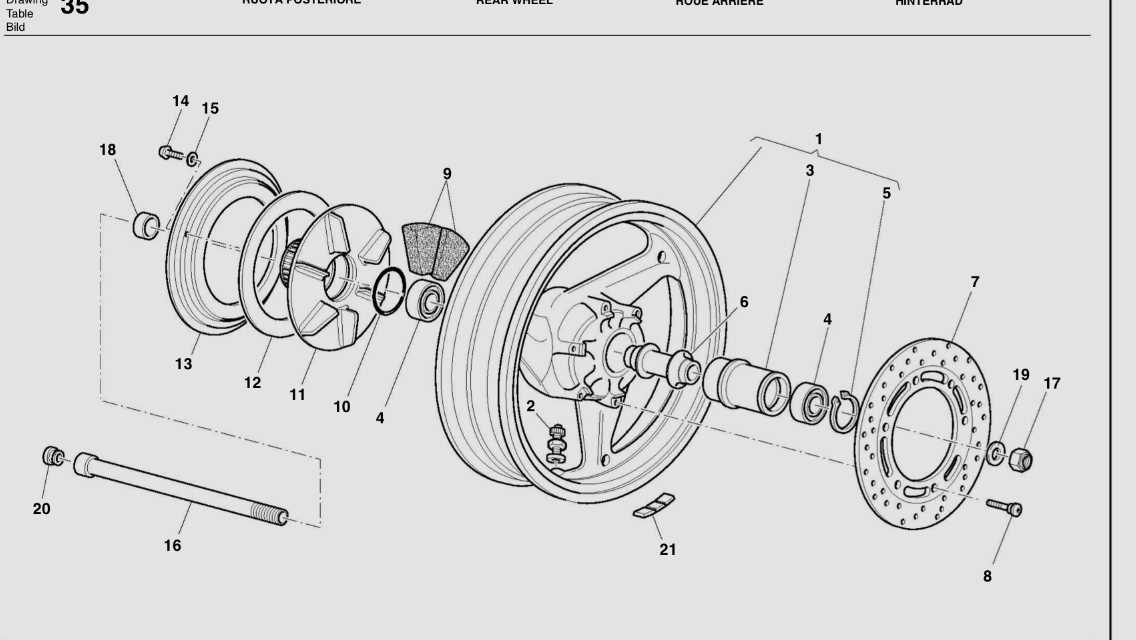
Wheel and Tire Assembly Breakdown
The assembly of wheels and tires plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and safety for any two-wheeled vehicle. Understanding the various components involved in this assembly can greatly enhance maintenance practices and facilitate smoother rides. This section delves into the key elements that constitute the wheel and tire setup, highlighting their functions and interrelations.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Rim | The circular structure that supports the tire and provides the connection to the axle. |
| Tire | A rubber covering that provides traction, absorbs shock, and protects the rim from damage. |
| Inner Tube | A flexible container that holds air within the tire, essential for maintaining pressure. |
| Valve Stem | The component that allows for inflating and deflating the inner tube, typically featuring a valve. |
| Spokes | Thin rods that connect the rim to the hub, providing structural integrity and weight distribution. |
| Hub | The central part of the wheel that attaches to the axle and houses the bearings. |
Lighting and Indicator System Components
The lighting and signaling system is vital for ensuring visibility and safety on the road. This collection of elements works together to illuminate the path ahead and communicate intentions to other road users. Understanding the components involved can enhance both the functionality and aesthetic appeal of the vehicle.
- Headlights: Essential for nighttime visibility, they provide a bright beam to illuminate the road and improve safety during low-light conditions.
- Taillights: These lights signal the presence of the vehicle from behind, ensuring that drivers approaching from the rear are aware of its location.
- Turn Signals: Used to indicate directional changes, these components help communicate maneuvers to other drivers, thereby reducing the risk of accidents.
- Brake Lights: Activating when the brake lever is engaged, these lights signal to those behind that the vehicle is slowing down or stopping.
- Indicator Lights: Often located on the dashboard, these lights provide crucial information regarding the operational status of various systems, such as turn signals and high beams.
- Reflectors: These passive components enhance visibility by reflecting light from other vehicles, making the vehicle more noticeable in low-light conditions.
Maintaining and understanding these components not only ensures compliance with safety regulations but also contributes to a more enjoyable riding experience. Regular checks and timely replacements are essential for optimal performance.