Understanding the layout and structure of various elements within a vehicle is crucial for maintenance and repair. Each system, whether it involves electrical connections, mechanical assemblies, or fluid networks, plays a pivotal role in the overall functionality of the vehicle. A clear and accurate representation of these elements provides a valuable resource for diagnosing issues and ensuring proper installation of replacement components.
In this section, we will explore how different sections of the vehicle’s internal and external systems are interconnected. Detailed illustrations of various assemblies can simplify the process of identifying the precise location of specific elements. Whether dealing with the engine, suspension, or other critical systems, having access to this information ensures efficiency and precision during repairs.
Overview of Key Components in the Vehicle
The structure of any vehicle is a complex system that relies on various essential elements working together to ensure functionality, safety, and performance. Understanding the major units and how they interact can help maintain and troubleshoot the overall system.
- Engine: The heart of the machine, converting fuel into the power needed to move. Its efficiency and health are vital for smooth operation.
- Transmission: Responsible for transferring the energy from the engine to the wheels, allowing the vehicle to change speed and direction smoothly.
- Suspension System: A key feature that ensures comfort and handling, absorbing shocks from the road and maintaining tire contact with the surface.
- Braking Mechanism: This ensures safety by allowing the vehicle to slow down or stop when necessary, often involving both mechanical and hydraulic components.
- Electrical Network: Powers everything from the lights to the onboard computer systems, managing energy distribution throughout the vehicle.
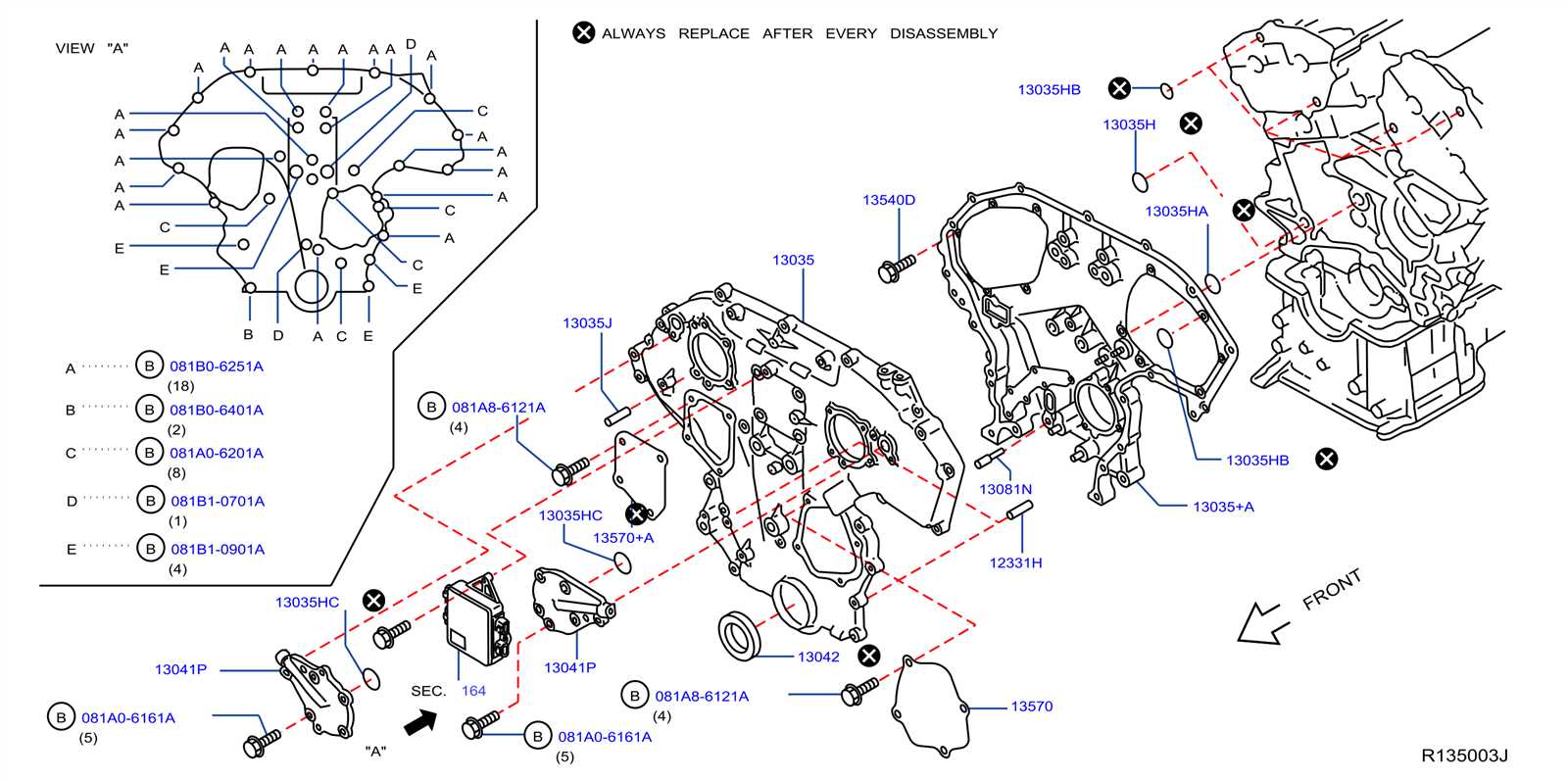
- Engine Layout and Major Parts
The core design of the power unit is a complex yet efficient system, where each component is strategically placed to ensure optimal performance. Understanding the structure and organization of these elements helps in both routine maintenance and troubleshooting, providing a clear insight into how the entire mechanism functions together.
Key Components: The central structure, often referred to as the block, serves as the foundation, housing essential elements such as the cylinders, pistons, and crankshaft. Together, these parts drive the conversion of fuel into mechanical energy. Surrounding the core, you’ll find systems like the fuel delivery mechanism, the air intake, and the exhaust manifold, which are critical in managing the engine’s breathing and fuel efficiency.
Additionally, the cooling system, featuring the radiator and other elements, ensures temperature regulation, while the electrical system, including the alternator and starter, manages
Transmission System and Its Components
The transmission system is crucial for ensuring that power generated by the engine is efficiently transferred to the wheels. It allows the vehicle to operate smoothly across various speeds and terrains by adjusting the ratio of engine output to wheel rotation. This mechanism not only impacts performance but also affects fuel efficiency and overall driving experience.
Key components work together within the system to ensure seamless operation. Below are the main parts that contribute to the proper functioning of this essential setup:
- Gearbox: The core unit that controls the selection of gears, ensuring smooth transitions and power distribution.
- Clutch: A crucial mechanism responsible for engaging and disengaging the connection between the engine and the transmission.
- Driveshaft: This component transfers power from the transmission to the differential, allowing the wheels to turn.
- Torque Converter: Vital for automatics, this device adjusts the flow of power between the engine and transmission.
- Differential: Manages the distribution of power to the wheels, allowing them to rotate at different speeds during turns.
The harmony of these components
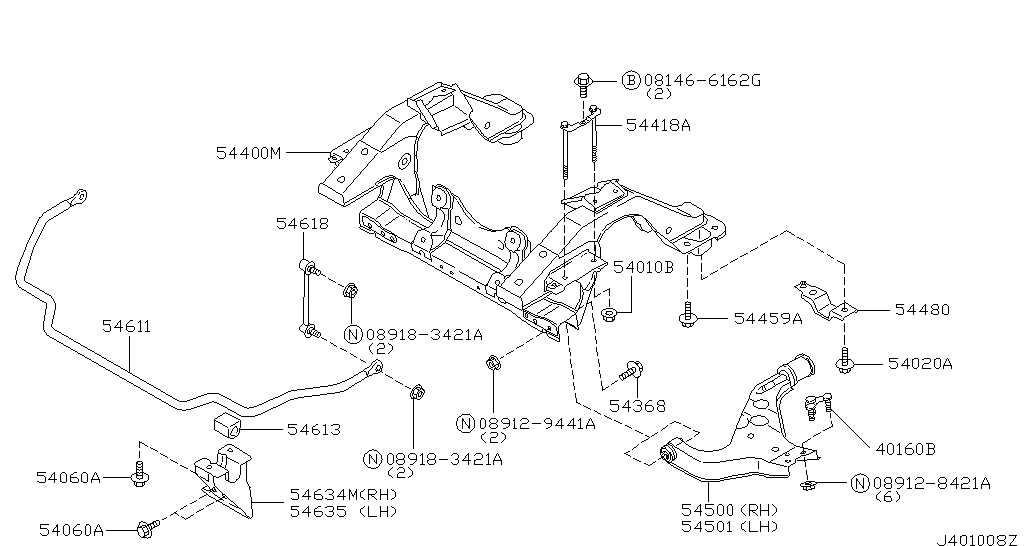
Suspension Structure and Functions
The framework responsible for ensuring a smooth and controlled ride is a complex system of components designed to absorb shocks and maintain vehicle stability. This system is crucial for handling uneven terrain and providing a balanced driving experience, regardless of the road conditions. Its overall function is to connect the wheels to the body in such a way that movements are controlled, and unwanted vibrations are minimized.
The system is divided into several key areas, each contributing to different aspects of performance, safety, and comfort. Let’s examine how these elements work together:
Component Function Shock Absorbers These elements are designed to dampen the impact from the road, allowing the vehicle to remain steady even on bumpy surfaces. Springs Responsible for absorbing the initial impact and providing the vehicle with the ability to return to its original position after compression. Control Arms These structures manage the vertical motion of the wheels, ensuring alignment and limiting excessive movement that could Exhaust System Design
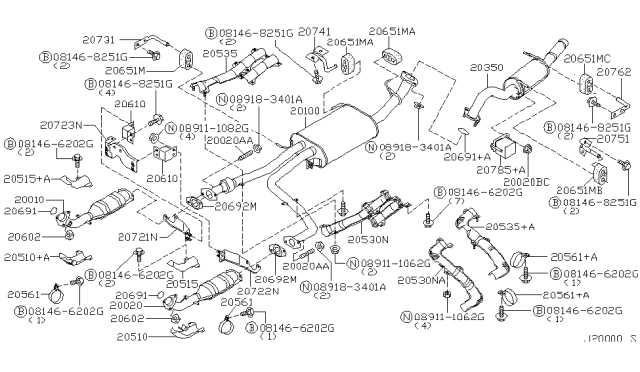
The layout of the exhaust system plays a critical role in ensuring efficient removal of gases produced during combustion. This system impacts not only engine performance but also the overall efficiency of the vehicle, contributing to reduced emissions and enhanced fuel economy. Its configuration typically involves several components that work in unison to manage and guide the gas flow from the engine to the exterior environment.
Component Function Muffler Reduces the noise produced by the exiting gases, ensuring a quieter ride. Catalytic Converter Transforms harmful pollutants into less harmful emissions before they leave the system. Exhaust Manifold Collects gases from multiple cylinders and directs them into a single pipe. Oxygen Sensor Monitors the oxygen levels in the exhaust, helping to regulate the air Braking Mechanism Layout
The braking system is a critical component in ensuring vehicle safety and performance. It comprises various elements that work together to decelerate or halt motion effectively. Understanding the configuration of these components is essential for both maintenance and enhancement of the overall braking performance.
Key components of the braking mechanism include:
- Brake Pedal: The initial point of action where force is applied by the driver.
- Master Cylinder: Converts the mechanical force from the pedal into hydraulic pressure.
- Brake Lines: Transmit hydraulic fluid from the master cylinder to the brake calipers.
- Brake Calipers: House the brake pads and are responsible for applying pressure to the rotors.
- Brake Rotors: The discs that rotate with the wheels and provide the surface for the brake pads to create friction.
- Brake Pads: Friction materials that press against the rotors to slow down the vehicle.
Additional elements may include:
- Brake Booster: Assists in amplifying the force applied to the brake pedal.
- Anti-lock Braking System (ABS): Prevents wheel lock-up during braking, enhancing control.
- Drums and Shoes: Used in some systems as an alternative to discs for providing braking force.
Each component plays a vital role in the system’s functionality. Regular inspection and maintenance are crucial to ensure optimal performance and safety during operation.
Cooling System Parts Overview
The cooling system plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal operating temperatures within the engine. It is designed to dissipate heat generated during combustion, ensuring that the engine runs smoothly and efficiently. This section will explore the various components involved in this essential system, highlighting their functions and interconnections.
Radiator Functionality
The radiator is a key element, responsible for transferring heat away from the engine coolant. As the coolant circulates through the engine, it absorbs heat and then passes through the radiator, where it is cooled by air flowing through its fins. This process helps to regulate the engine temperature and prevents overheating.
Water Pump and Thermostat
The water pump is vital for circulating coolant throughout the engine and the radiator, ensuring efficient heat exchange. The thermostat acts as a temperature regulator, opening and closing to control the flow of coolant based on the engine’s temperature, thus maintaining a stable operating environment.
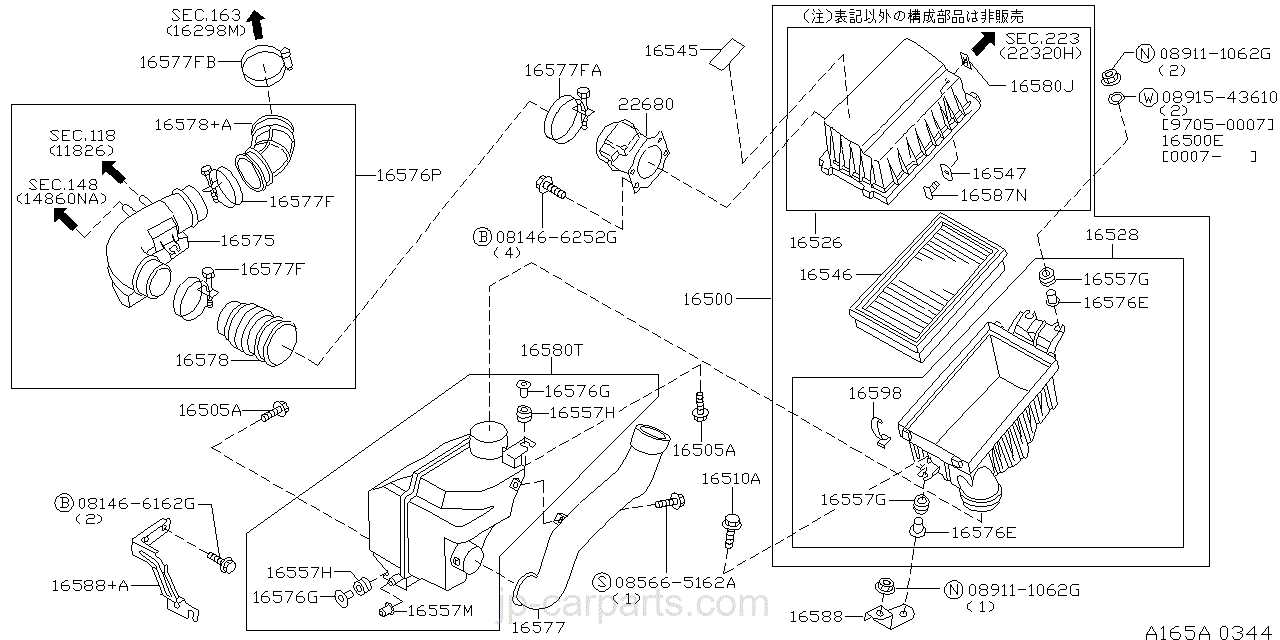
Fuel System Components Breakdown
The fuel system plays a crucial role in the efficient operation of an engine, ensuring that the right amount of fuel is delivered for optimal performance. Understanding the various elements of this system helps in diagnosing issues and maintaining overall functionality.
Key Elements of the Fuel System
At the core of the fuel delivery mechanism is the fuel tank, which stores the gasoline until it is needed. Fuel is then drawn from the tank by a fuel pump, which is responsible for moving it through the lines to the engine. Proper functioning of the pump is essential for maintaining adequate pressure and flow rates.
Fuel Delivery and Management
Once the fuel reaches the engine, it passes through a series of fuel injectors or a carburetor, depending on the design. These components regulate the flow and ensure that the right mixture of fuel and air enters the combustion chamber. Additionally, the system includes various sensors that monitor parameters such as pressure and temperature, allowing for adjustments to optimize performance.
Electrical Wiring and Connections

The integrity of electrical circuitry is vital for the optimal functioning of any vehicle. A well-organized layout ensures that various components communicate effectively, allowing for reliable operation of systems such as lighting, ignition, and infotainment. Understanding the arrangement and connections within the electrical network can help in troubleshooting issues and performing maintenance tasks efficiently.
Overview of Electrical Components
This section explores the various electrical elements found within the system. Key components include fuses, relays, and connectors, each serving a specific purpose in maintaining the flow of electricity. Fuses protect circuits from overloads, relays facilitate the operation of high-current devices through low-power switches, and connectors ensure secure links between wiring harnesses.
Wiring Harness Layout
The wiring harness is the backbone of the electrical system, consisting of bundled wires that transmit power and signals throughout the vehicle. Proper routing and securing of the harness are crucial to prevent wear and interference from other mechanical parts. Understanding the layout helps in identifying potential problem areas and ensures ease of access during repairs.
Interior Features and Equipment
The cabin of this vehicle is designed to provide both comfort and functionality, catering to the needs of its occupants. A thoughtful arrangement of components enhances the overall driving experience, making every journey enjoyable.
- Seating: Spacious and comfortable seating options, available in various materials, offer support for both short trips and long journeys.
- Dashboard Layout: A user-friendly dashboard integrates essential controls and displays, ensuring drivers can access vital information with ease.
- Climate Control: An advanced climate control system maintains a pleasant atmosphere within the cabin, allowing for customized temperature settings.
- Infotainment System: A state-of-the-art multimedia system provides entertainment and connectivity options, including radio, CD player, and Bluetooth capabilities.
- Storage Solutions: Ample storage compartments and cup holders are strategically placed throughout the interior, enhancing convenience for all passengers.
Additionally, various safety features, such as airbags and stability control systems, contribute to a secure environment for all occupants. The combination of these elements ensures that the vehicle meets the diverse needs of families and adventurers alike.
Exterior Body Parts and Panels
The exterior components of a vehicle play a crucial role in both aesthetics and functionality. These elements not only define the overall appearance but also contribute to the protection and aerodynamics of the automobile. Understanding the various sections can aid in maintenance, repairs, or upgrades, ensuring optimal performance and visual appeal.
Key Components
- Fenders
- Bumpers
- Hoods
- Doors
- Tailgates
- Quarter panels
- Grilles
Functionality of Body Elements
Each of these exterior elements serves specific purposes:
- Fenders: Protect the wheels and prevent debris from being thrown onto other vehicles.
- Bumpers: Absorb impact during low-speed collisions and provide safety to both pedestrians and occupants.
- Hoods: Cover the engine compartment, allowing for access during maintenance while contributing to the vehicle’s aerodynamics.
- Doors: Provide entry and exit for passengers while enhancing security.
- Tailgates: Facilitate access to the rear storage area, often doubling as a load-bearing surface.
- Quarter panels: Form the sides of the vehicle, contributing to structural integrity.
- Grilles: Allow airflow to the engine, aiding in cooling and engine performance.
Each of these components can be customized or replaced, allowing for personalization and improved vehicle performance.
Lighting and Indicator System
The illumination and signaling mechanisms play a crucial role in ensuring safety and visibility while navigating various environments. This system encompasses a range of components that provide essential information to both the driver and other road users, thereby enhancing overall driving experience.
Components Overview
At the heart of the illumination system are the headlights, which illuminate the road ahead during low-light conditions. Additionally, the tail lights and brake lights serve to indicate the vehicle’s presence and actions to those behind. Turn signals provide vital communication about intended directional changes, while fog lights improve visibility in adverse weather conditions.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular inspection of the lighting and signaling components is essential to ensure optimal functionality. Burnt-out bulbs should be replaced promptly to maintain visibility, while corroded connections may require cleaning to restore proper operation. Ensuring that all lights are in working order is vital for both safety and compliance with traffic regulations.
Steering Mechanism and Linkage
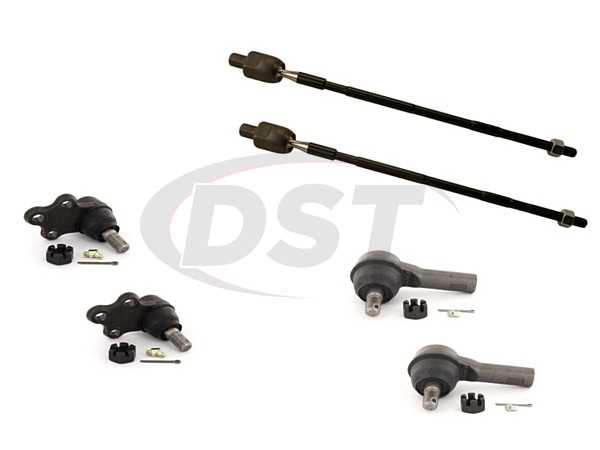

The steering system plays a vital role in vehicle control and maneuverability. It encompasses various components that work in harmony to enable the driver to navigate with precision. Understanding the configuration and function of these elements is essential for maintenance and repairs.
This section outlines the essential parts involved in the steering mechanism, including their arrangement and interaction within the assembly. A detailed look at each component provides insight into their individual roles and the overall performance of the steering system.
Component Description Steering Wheel The primary interface for the driver, allowing control of the vehicle’s direction. Steering Column A shaft connecting the steering wheel to the steering gear, transmitting motion. Steering Gear A mechanism that converts the rotational motion of the steering wheel into linear motion. Linkage Assemblies of rods and joints that connect the steering gear to the wheels, facilitating movement. Pitman Arm A lever that transfers motion from the steering gear to the linkage. Idler Arm Supports the linkage on the opposite side of the steering gear, maintaining alignment. Drag Link A connecting rod that links the pitman arm to the steering knuckles, influencing wheel movement. Steering Knuckles Pivot points that allow the wheels to turn in response to the steering input. Maintaining the steering mechanism’s integrity is crucial for safe driving. Regular inspections and timely replacements of worn-out components ensure that the system remains responsive and effective.