
The intricate world of motorcycle machinery encompasses a vast array of components, each playing a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and reliability. Understanding how these elements interact within the overall structure is essential for both enthusiasts and professionals alike. This exploration delves into the specific arrangement and functionality of various parts, shedding light on the engineering behind modern motorcycles.
By examining a comprehensive overview of individual components, one can gain insight into the design and engineering choices that shape a motorcycle’s capabilities. This knowledge not only aids in effective maintenance and repair but also enhances the overall riding experience. In this discussion, we will highlight the significance of each section, showcasing how they contribute to the machine’s efficiency and safety.
Moreover, familiarizing oneself with the layout and connectivity of these components allows for more informed decision-making when it comes to modifications and upgrades. This resource serves as a guide for those seeking to deepen their understanding of motorcycle mechanics and to navigate the complexities of assembly and maintenance with confidence.
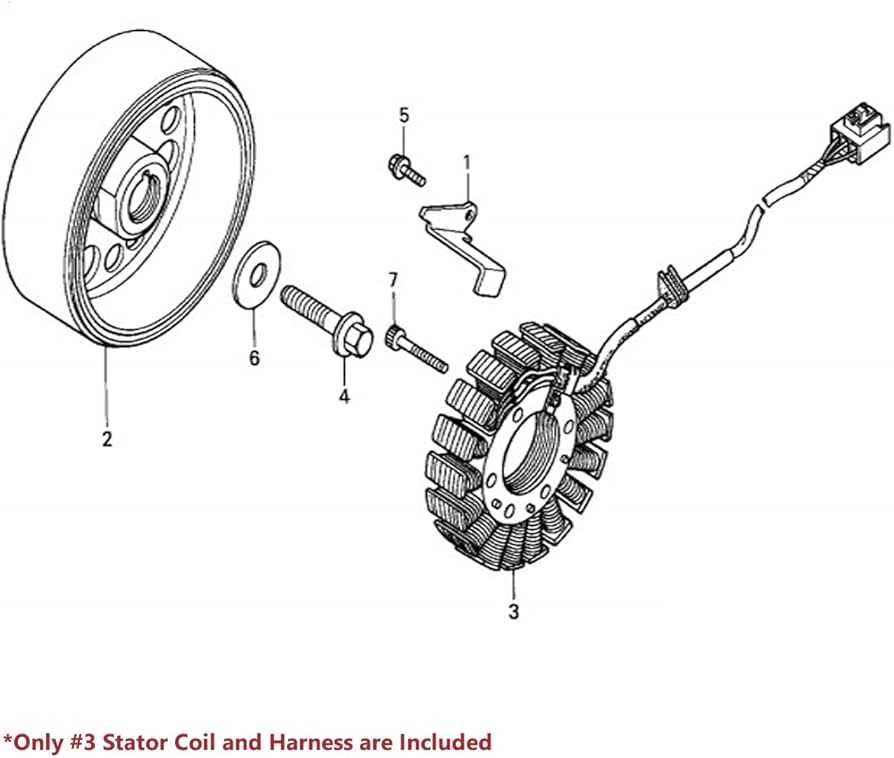 tags: Overview of 2005 CBR600RR Components”>
tags: Overview of 2005 CBR600RR Components”>
This section provides a comprehensive overview of the essential elements and assemblies that constitute a high-performance motorcycle. Understanding the various components is crucial for maintenance, repair, and customization, ensuring optimal functionality and safety.
Engine Assembly
The heart of the motorcycle, the engine assembly, consists of various integral parts that work together to provide power and efficiency.
- Cylinder block
- Piston and rings
- Cylinder head
- Crankshaft
Transmission System
The transmission system is vital for power transfer from the engine to the wheels, allowing smooth acceleration and deceleration.
- Clutch
- Gearbox
- Chain and sprockets
Chassis Framework
The chassis framework supports all components, ensuring structural integrity and stability during operation.
- Frame
- Subframe
- Footpegs
Suspension Components
Suspension components play a critical role in rider comfort and handling by absorbing shocks and providing stability.
- Front forks
- Shock absorber
- Swingarm
Brake System
The brake system is essential for safety, providing the ability to slow down or stop the motorcycle effectively.
- Brake calipers
- Brake pads
- Brake rotors
Electrical System
The electrical system powers all electronic components and includes wiring, switches, and the battery.
- Wiring harness
- Ignition system
- Lighting components
Cooling System
A well-functioning cooling system prevents overheating and ensures the engine operates within safe temperature limits.
Understanding the Parts Diagram
Grasping the layout of a motorcycle’s components is essential for both maintenance and repair. A well-structured visual representation helps enthusiasts and mechanics identify individual elements, their functions, and how they interact within the overall system. This understanding is crucial for effective troubleshooting and ensuring optimal performance.
The illustration serves as a valuable tool, breaking down complex assemblies into understandable sections. Each component is labeled, allowing users to quickly reference specific items when sourcing replacements or conducting repairs. Familiarity with this visual guide can greatly enhance the efficiency of any service task.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Engine | The powerhouse that drives the motorcycle. |
| Transmission | Transfers power from the engine to the wheels. |
| Suspension | Absorbs shocks and maintains stability. |
| Brakes | System used for deceleration and stopping. |
| Fuel Tank | Stores fuel for the engine. |
Main Assembly Parts Explained
The main assembly of a motorcycle comprises various critical components that work together to ensure optimal performance and safety. Understanding these elements is essential for effective maintenance and repair. This section will explore the fundamental components that make up the core structure of the vehicle.
- Frame: The backbone of the motorcycle, providing structural integrity and stability. It supports the engine and other key elements.
- Engine: The heart of the motorcycle, responsible for generating power. It comprises multiple subcomponents, including the cylinder, pistons, and crankshaft.
- Suspension System: This includes front forks and rear shock absorbers that enhance ride comfort and handling. It absorbs shocks from the road and maintains tire contact.
- Wheels: Essential for movement, the wheels are equipped with tires that provide grip and control. They are connected to the frame via axles and bearings.
- Braking System: This system includes discs and calipers, crucial for stopping the vehicle. Proper functioning of this assembly is vital for rider safety.
Each of these elements plays a pivotal role in the motorcycle’s overall functionality, and familiarity with them is beneficial for any rider or mechanic.
Key Engine Components Overview
The engine is the heart of any motorcycle, playing a crucial role in its performance and efficiency. Understanding the fundamental elements that comprise this vital unit is essential for both maintenance and optimization. This section delves into the primary components that contribute to the functionality and reliability of the engine, highlighting their importance and interconnections.
Essential Elements of the Engine
Among the critical components are the cylinder block, which houses the cylinders and facilitates combustion; the crankshaft, responsible for converting linear motion into rotational force; and the camshaft, which regulates the timing of the engine’s intake and exhaust valves. Each part works in harmony to ensure smooth operation and peak performance.
Supporting Systems and Their Roles
Additionally, supporting systems such as the lubrication and cooling mechanisms are vital for maintaining optimal operating temperatures and reducing wear. The oil pump circulates lubricant throughout the engine, while the cooling system prevents overheating. Understanding these components helps in grasping how the engine maintains its longevity and efficiency.
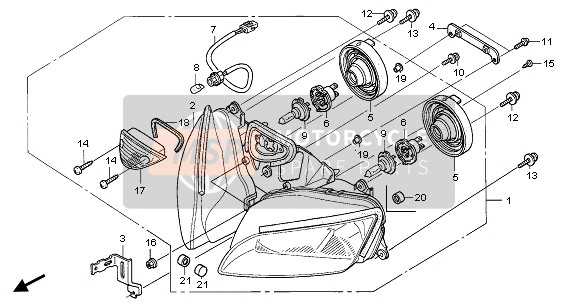
Electrical System Parts Breakdown
The electrical system of a motorcycle is a vital component that ensures the proper functioning of various subsystems. It encompasses a variety of elements that work together to facilitate ignition, lighting, and communication functions. Understanding the components involved can greatly assist in troubleshooting and maintenance efforts.
Main Components
- Battery: The primary power source that supplies energy to start the engine and power electrical accessories.
- Starter Motor: Responsible for turning the engine over during the ignition process.
- Regulator/Rectifier: Converts alternating current (AC) produced by the stator into direct current (DC) for the battery and electrical systems.
- Ignition Coil: Generates the high voltage needed to create a spark at the spark plugs.
- Wiring Harness: A network of wires that connects various electrical components, ensuring effective communication and power distribution.
Additional Elements

- Fuses: Safety devices that protect electrical circuits from overloads.
- Switches: Allow the rider to control different electrical functions, such as lights and ignition.
- Light Assemblies: Include headlights, taillights, and turn signals for visibility and communication with other road users.
- Instrument Cluster: Displays vital information such as speed, fuel level, and warning lights.
Suspension System Components Guide
The suspension system of a motorcycle plays a crucial role in providing a smooth and stable ride. This system comprises various elements that work together to enhance handling, comfort, and safety while navigating different road conditions. Understanding these components is essential for both maintenance and performance optimization.
Key Elements of the Suspension System
The primary components of the suspension system include the forks, rear shock absorbers, swingarm, and various linkages. Each part serves a specific function, contributing to the overall performance of the motorcycle. The forks are responsible for absorbing impacts from the front wheels, allowing for better control during rides. Shock absorbers, on the other hand, help to dampen oscillations and maintain stability, particularly when the motorcycle encounters bumps or uneven surfaces.
Importance of Proper Maintenance
Regular inspection and maintenance of suspension components are vital for ensuring optimal performance. Worn or damaged parts can significantly affect handling and safety. It is important to check for leaks, corrosion, or any signs of wear. Additionally, proper adjustments to preload and damping settings can enhance ride quality and responsiveness, adapting the motorcycle to various riding conditions.
Braking System Parts Description
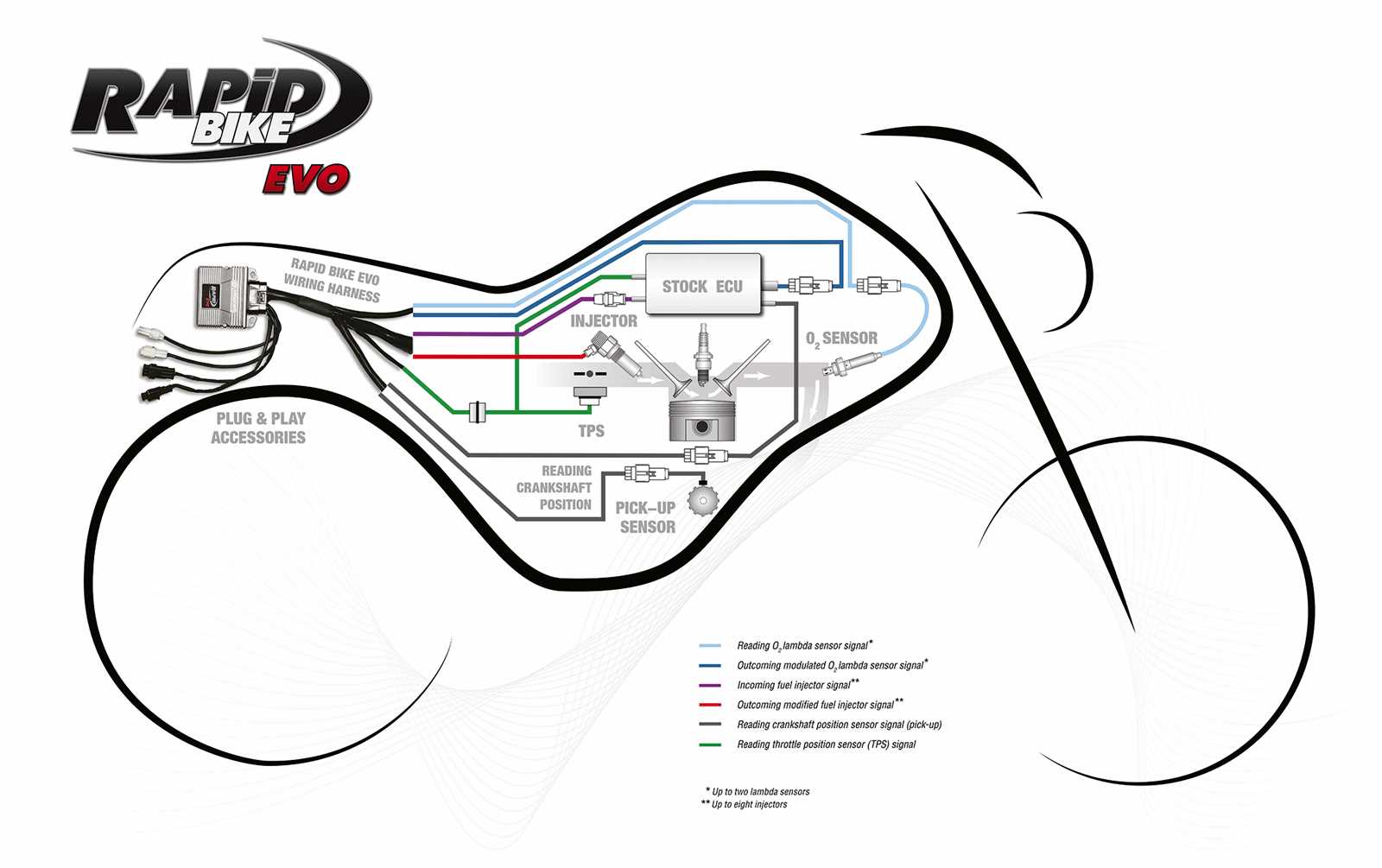
The braking mechanism is essential for ensuring safety and control in any motorcycle. Understanding the components involved in this system can enhance the maintenance and performance of the vehicle. Below is a detailed overview of the primary elements that comprise the braking system.
- Brake Caliper: This component houses the brake pads and applies pressure to them, which creates friction against the brake disc to slow down the motorcycle.
- Brake Pads: Made from materials that provide high friction, these pads press against the rotor to generate stopping power.
- Brake Rotor (Disc): A circular metal piece that rotates with the wheel. When the brake pads clamp down on it, the motorcycle decelerates.
- Master Cylinder: This part converts the mechanical force from the brake lever into hydraulic pressure, which engages the brake calipers.
- Brake Lines: Flexible tubes that transfer hydraulic fluid from the master cylinder to the brake calipers, allowing for effective force transmission.
- Brake Fluid: A hydraulic fluid that transfers force from the master cylinder to the calipers, crucial for the system’s operation.
Regular inspection and maintenance of these components are vital for optimal functionality. Any signs of wear or damage should be addressed promptly to ensure the safety of the rider.
Transmission and Drive Elements
The transmission and drive components play a crucial role in the overall performance of a motorcycle, ensuring the effective transfer of power from the engine to the wheels. These elements are designed to work in harmony, allowing for smooth acceleration and reliable handling.
Key components of the transmission system include gears, clutches, and shafts, which facilitate the shifting of power at varying speeds. The arrangement and design of these elements directly influence the responsiveness and agility of the vehicle, making them essential for both casual riding and competitive performance.
The drive mechanism often encompasses chains, belts, or shafts that connect the transmission to the rear wheel. Each type of drive has its advantages, affecting factors such as maintenance, durability, and efficiency. Understanding the intricacies of these components enables riders to appreciate their bike’s capabilities and make informed choices regarding modifications or repairs.
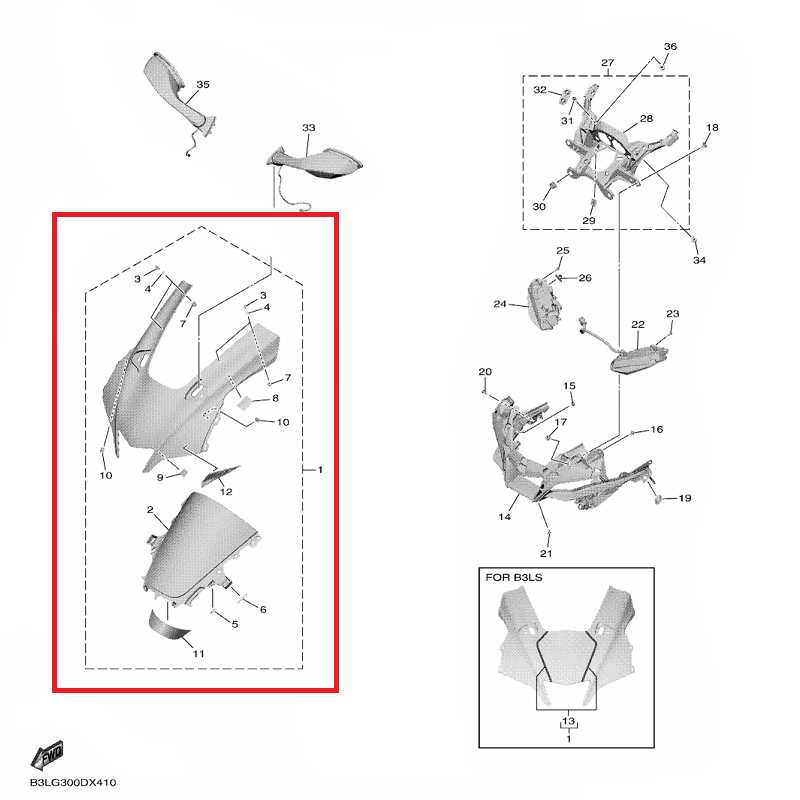
Bodywork and Fairing Parts List
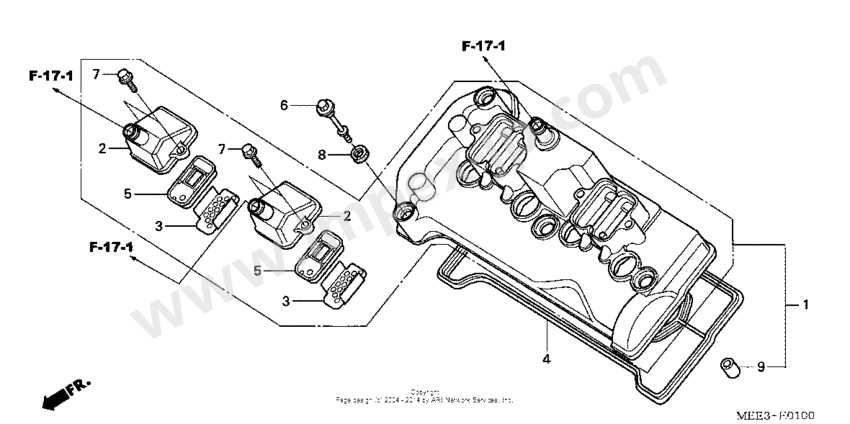
This section outlines the essential components related to the outer shell and protective coverings of the motorcycle. These elements play a crucial role in both aesthetics and functionality, providing a sleek appearance while safeguarding internal mechanisms from external elements.
Key Components Overview
The following items are vital for maintaining the integrity and appearance of the motorcycle. Proper selection and installation ensure optimal performance and a polished look.
| Component Name | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Front Fairing | The primary cover at the front, which houses headlights and instruments. | Enhances aerodynamics and protects internal parts. |
| Side Panels | Components that cover the sides of the frame. | Contributes to overall styling and protects engine parts. |
| Tail Section | The rear cover that completes the bike’s silhouette. | Hides the seat assembly and electrical components. |
| Windshield | A transparent barrier mounted on the front fairing. | Reduces wind resistance and protects the rider’s face. |
Maintenance Considerations
Regular inspection and upkeep of these outer elements are essential for ensuring longevity and performance. Attention to cracks, paint conditions, and secure fittings can prevent further damage and enhance the motorcycle’s visual appeal.
Fuel System Components Overview
The fuel system in a motorcycle plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and efficiency. It is designed to manage the delivery of fuel from the tank to the engine, maintaining the right pressure and flow rate for effective combustion. Understanding the key elements of this system is essential for troubleshooting and maintenance.
Key Components
Several primary components make up the fuel system. These include the fuel tank, fuel pump, fuel filter, and fuel injectors. Each part works in harmony to transport fuel efficiently, ensuring that the engine receives the appropriate amount of fuel at all times.
Functionality of Each Component
The fuel tank serves as the storage unit for the fuel, while the fuel pump is responsible for transporting the fuel from the tank to the engine. The fuel filter plays a vital role in keeping the fuel clean by removing impurities, and the fuel injectors are crucial for delivering the correct amount of fuel directly into the combustion chamber. Regular inspection and maintenance of these components help in sustaining the performance of the vehicle.
Cooling System Parts Explanation
The cooling system in a motorcycle plays a vital role in maintaining optimal engine temperature, preventing overheating, and ensuring efficient performance. Understanding the various components involved is essential for proper maintenance and repair. Each part contributes to the overall function, promoting longevity and reliability of the engine.
Key elements of the cooling system include the radiator, water pump, and thermostat, among others. These components work together to circulate coolant, dissipate heat, and regulate temperature. Below is a detailed overview of these crucial elements.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Radiator | Dissipates heat from the coolant, cooling it before it returns to the engine. |
| Water Pump | Circulates the coolant throughout the system, ensuring efficient heat transfer. |
| Thermostat | Regulates coolant flow based on temperature, allowing for optimal heating and cooling. |
| Hoses | Transport coolant between the engine, radiator, and other components. |
| Coolant | Absorbs and transfers heat, preventing the engine from reaching excessive temperatures. |
Accessories and Optional Components
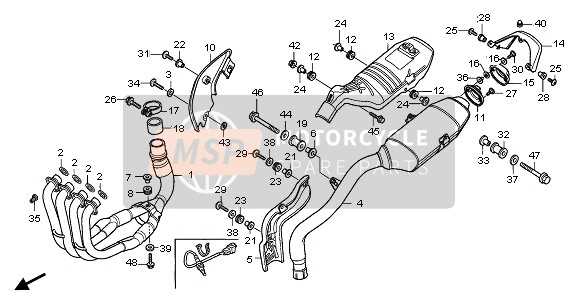
Enhancing the riding experience often involves incorporating various enhancements and additional elements designed to improve performance, comfort, and aesthetics. These accessories can range from functional items that enhance usability to aesthetic modifications that personalize the machine.
One of the most sought-after additions includes upgraded windshields that provide better aerodynamics and protection from the elements. Additionally, custom seat options can significantly enhance comfort during long rides, allowing for a more enjoyable journey.
For those looking to improve handling and stability, aftermarket suspension components can be invaluable, offering adjustments tailored to individual riding styles. Furthermore, additional lighting options not only increase visibility but also contribute to a unique appearance.
Storage solutions, such as saddlebags and tail packs, provide practicality for daily commutes or longer trips, allowing riders to carry essentials securely. Ultimately, the choice of accessories and optional components enables riders to tailor their machines to fit their unique preferences and riding conditions.
Maintenance Tips for Parts Longevity
Ensuring the durability of your vehicle’s components requires regular attention and care. By following specific maintenance practices, you can extend the life of crucial elements, enhancing performance and reliability over time.
Regular Cleaning: Keeping parts clean from dirt and debris is essential. Utilize appropriate cleaning agents and tools to remove contaminants that could cause wear or corrosion.
Frequent Inspections: Conduct routine checks to identify any signs of wear or damage early. Look for cracks, leaks, or unusual noises that may indicate potential issues.
Lubrication: Applying suitable lubricants to moving components helps reduce friction and wear. Ensure to use the correct type of lubricant for each application to maintain optimal performance.
Timely Replacements: Recognize when certain elements have reached the end of their life cycle. Replacing worn parts promptly prevents further damage to surrounding components and ensures smooth operation.
Proper Storage: When not in use, store your vehicle in a dry, climate-controlled environment. This practice prevents moisture accumulation and protects against rust and deterioration.
By implementing these strategies, you can significantly enhance the lifespan of your vehicle’s components, ensuring they perform efficiently for years to come.