Shift Linkage: Connects the gear selector to
Detailed View of Transmission Parts
The transmission system is a complex mechanism that ensures the smooth transfer of power from the engine to the wheels. Understanding its structure is crucial for maintaining efficient vehicle performance. This section focuses on the internal components that work together to manage speed and torque conversion.
Gears play a vital role in adjusting the rotational force, allowing the vehicle to adapt to different driving conditions. These gears are precisely engineered to handle various loads and speeds.
Another essential component is the clutch assembly, which enables the driver to shift between different modes of power delivery. This process is crucial for ensuring a seamless transition between gears without damaging the system.
The transmission also features intricate systems like the valve body, which directs fluid to control the movement of gears. The cooperation of these elements is what ensures the vehicle’s adaptability and long-term reliability.
Brake System Diagram for 2006 F250
The braking mechanism in a vehicle plays a crucial role in ensuring safety and proper control. A clear understanding of how each component functions together is essential for maintenance and repair. The setup involves several interconnected parts that work to stop the vehicle efficiently under different conditions.
Main Components Overview
The essential elements include the brake pedal, master cylinder, and brake lines, which are responsible for transmitting force from the driver’s foot to the wheels. Each component has a specific role in converting mechanical force into the pressure needed to apply the brakes.
Hydraulic and Mechanical Elements
Modern systems primarily rely on hydraulics, but they also incorporate mechanical aspects for added reliability. The brake fluid, under pressure, moves through the lines, activating the calipers and pads. This coordinated action ensures the vehicle comes to a halt smoothly and efficiently, whether it’s an emergency stop or gradual deceleration.
Key Elements of the Brake Setup
The braking system is a critical component of any vehicle, ensuring safety and control while driving. Understanding the essential parts involved can help in maintenance and troubleshooting. This section delves into the primary elements that constitute an effective braking mechanism.
Major Components
- Brake Pads: These friction elements press against the rotors to slow down or stop the vehicle.
- Brake Rotors: Discs that rotate with the wheels and provide a surface for the brake pads to clamp onto.
- Calipers: Hydraulic components that house the brake pads and create pressure to facilitate braking.
- Brake Lines: Hoses that transport hydraulic fluid from the master cylinder to the calipers.
Fluid Dynamics
The hydraulic fluid plays a vital role in the braking process. It transmits force from the brake pedal to the calipers, ensuring efficient operation. Regular checks and maintenance of the fluid levels can enhance braking performance and longevity.
By familiarizing oneself with these key elements, vehicle owners can better appreciate the functionality and importance of a well-maintained braking system.
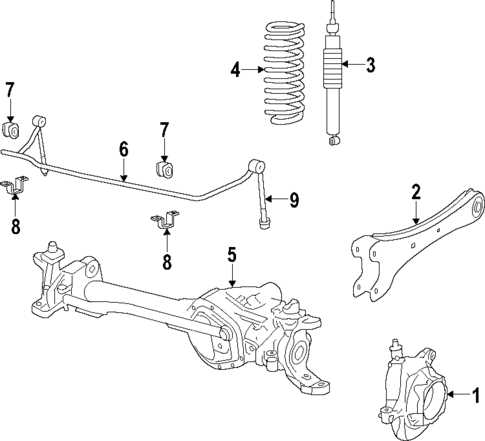
Suspension System Parts Breakdown
The suspension system plays a crucial role in ensuring a smooth ride and handling characteristics of a vehicle. Understanding its components is essential for maintaining optimal performance and safety. This section will provide a comprehensive overview of the different elements that comprise this vital system.
Main Components
At the heart of the suspension setup are various components that work together to absorb shocks and provide stability. Key elements include:
- Shock Absorbers: These devices control the oscillations of the springs, enhancing ride quality.
- Coil Springs: They support the weight of the vehicle and absorb road imperfections.
- Control Arms: These link the suspension to the vehicle’s frame, allowing for controlled movement.
Additional Elements
In addition to the main components, there are other parts that contribute to the overall functionality of the system:
- Sway Bar: This component helps reduce body roll during turns, improving stability.
- Bushings: These rubber components provide cushioning and reduce vibration between moving parts.
- Mounting Hardware: Essential for securing components in place, ensuring a reliable setup.
Each of these elements plays a significant role in the overall performance of the suspension system, highlighting the importance of regular inspections and maintenance for vehicle longevity.
How Suspension Works in the F250
The suspension system in heavy-duty vehicles plays a crucial role in ensuring a smooth and stable ride. It is designed to absorb shocks from the road and maintain optimal contact between the tires and the surface, enhancing both handling and comfort.
This system typically comprises several key components, including springs, shock absorbers, and control arms. Springs bear the weight of the vehicle, allowing it to handle varying loads while providing the necessary flexibility. Shock absorbers dampen the energy from bumps and dips, preventing excessive bouncing and maintaining vehicle stability.
Furthermore, the alignment and configuration of these components contribute to the overall performance. A well-tuned suspension allows for precise steering and improved traction, essential for navigating challenging terrains. Regular maintenance of the suspension system is vital to ensure its longevity and effectiveness, providing drivers with a dependable and comfortable experience.
Electrical System Overview for 2006 F250
The electrical framework of a heavy-duty vehicle plays a critical role in ensuring its optimal functionality and reliability. This section delves into the various components that make up the electrical setup, highlighting their interconnections and significance in the overall operation.
Main Components
The core elements of the electrical system include the battery, alternator, and various wiring harnesses. The battery provides the necessary power to start the engine and run electrical accessories, while the alternator recharges the battery and powers the vehicle’s electrical systems when the engine is running.
Wiring and Connections
A well-organized network of wires connects all electrical components, facilitating efficient power distribution. Regular maintenance of these connections is essential to prevent electrical failures and ensure the longevity of the system.
Important Wiring and Circuitry Details
Understanding the intricacies of electrical connections and circuitry is crucial for optimal vehicle performance. Properly functioning wiring ensures that all electrical components operate seamlessly, enhancing the overall reliability and efficiency of the machine.
Electrical systems are often complex, consisting of various circuits that manage power distribution and communication between components. Paying close attention to wiring layouts can help identify potential issues that may arise due to wear, corrosion, or improper connections. Regular inspections and maintenance are essential to ensure that each circuit performs as intended.
Documentation of wiring schematics serves as a valuable resource for troubleshooting and repairs. Familiarity with these details allows for informed decision-making when addressing electrical concerns. Utilizing the correct tools and following best practices during any electrical work will contribute to lasting improvements and prevent future complications.
Cooling System Components of the F250
The cooling system of a heavy-duty vehicle plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal engine performance and longevity. It consists of several essential elements that work together to regulate temperature and prevent overheating during operation.
- Radiator: This component dissipates heat from the coolant as it circulates through the system, ensuring the engine remains at an efficient temperature.
- Water Pump: Responsible for circulating coolant throughout the engine and radiator, the water pump is vital for maintaining proper flow and temperature control.
- Thermostat: This device regulates the coolant flow based on the engine’s temperature, opening and closing to maintain a steady operating temperature.
- Coolant Reservoir: This tank holds extra coolant, allowing the system to expand and contract as temperatures fluctuate, ensuring optimal levels are maintained.
- Hoses: Flexible tubes connect various components, facilitating the flow of coolant between the engine, radiator, and other parts of the cooling system.
Understanding these components helps in troubleshooting and maintaining the cooling system, ultimately ensuring the vehicle operates smoothly and efficiently.
Main Parts of the Cooling Mechanism
The cooling system of a vehicle plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal operating temperatures. It consists of several key components that work together to dissipate heat generated by the engine, ensuring efficient performance and preventing overheating.
Key Components
- Radiator: The main device responsible for cooling the coolant that circulates through the engine.
- Water Pump: This component facilitates the movement of coolant throughout the system, ensuring effective heat transfer.
- Thermostat: A valve that regulates coolant flow based on temperature, allowing the engine to reach its ideal operating temperature quickly.
- Cooling Fans: These fans assist in drawing air through the radiator, enhancing heat dissipation when the vehicle is stationary or moving slowly.
Supporting Elements
- Coolant Reservoir: A container that holds extra coolant, allowing for expansion and ensuring a continuous supply.
- Hoses: Flexible tubes that connect various components, enabling the flow of coolant between them.
- Heater Core: A smaller radiator that provides heat to the vehicle’s interior, utilizing coolant from the engine.
Fuel System Parts and Connections
The fuel system plays a crucial role in ensuring that the engine receives the proper amount of fuel for efficient operation. Understanding the various components and their interconnections is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting.
This system typically includes the fuel tank, fuel pump, fuel lines, injectors, and filters. Each element works in harmony to deliver fuel from the tank to the engine. The fuel pump is responsible for transferring fuel, while the injectors atomize it for optimal combustion.
Connections between these components are vital for preventing leaks and ensuring a steady flow of fuel. Regular inspection of hoses and fittings can help identify potential issues before they escalate, contributing to the longevity of the engine’s performance.