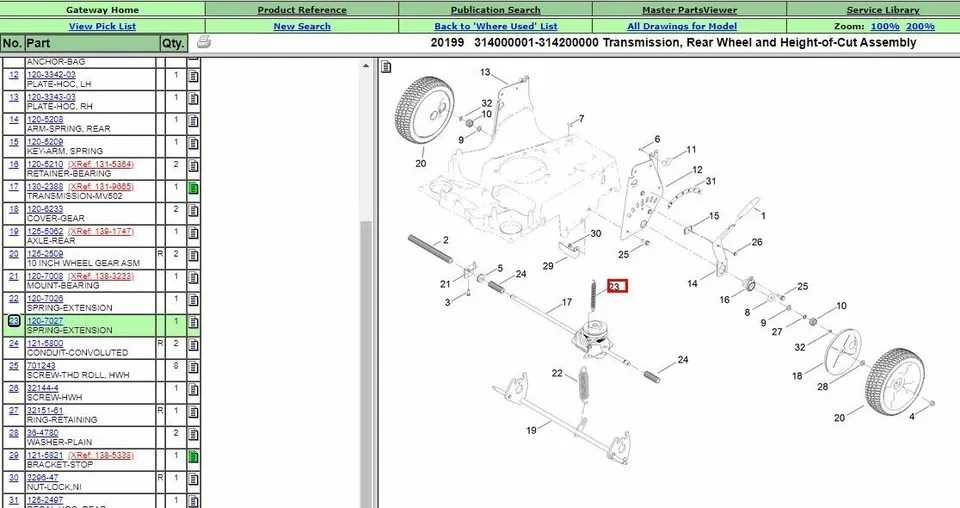
Understanding the structure and arrangement of various elements within a mechanical system can significantly improve both efficiency and accuracy in maintenance and assembly. This section provides a detailed exploration of how each element interacts and contributes to the overall functionality of the system.
Efficient organization of these elements allows for better identification and replacement processes, ensuring smooth operation. Whether you’re dealing with maintenance or upgrades, knowing how these components are placed within the system is essential for streamlined work.
In this guide, we’ll explore the placement and interaction of critical elements, helping you navigate the complexities of the assembly. With this information, your understanding of the system’s layout will become clearer, making repairs and modifications easier and faster.
Overview of Key Components

In this section, we will explore the essential elements that make up the structure and functionality of the system. Each element plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth operation and optimal performance.
Core Unit: The central mechanism responsible for driving the overall functionality, ensuring that all operations are executed efficiently and consistently.
Support Structures: These elements provide stability and alignment, guaranteeing that the main components are securely positioned and function harmoniously.
Connector Elements: Critical for linking various segments, these ensure seamless communication and integration between different sections of the system.
Understanding these essential elements is key to grasping how the system functions as a whole and contributes to its performance.
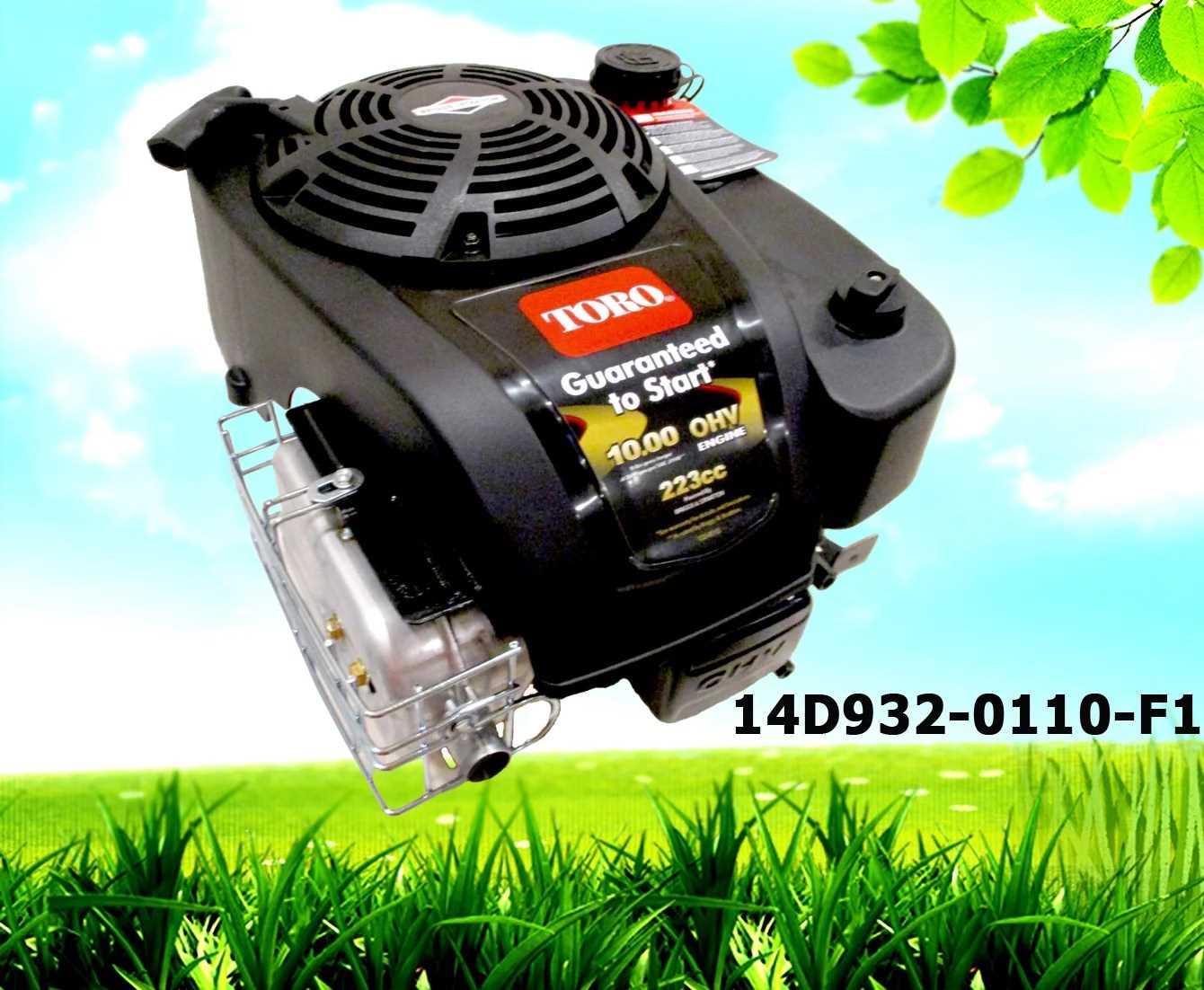
Engine Section Breakdown
The engine is a critical component, consisting of multiple interconnected elements that work together to ensure optimal performance. This section focuses on explaining the structure and key functions of the various components found within the system. Understanding how each element interacts can provide valuable insights for maintenance and troubleshooting.
Main Components
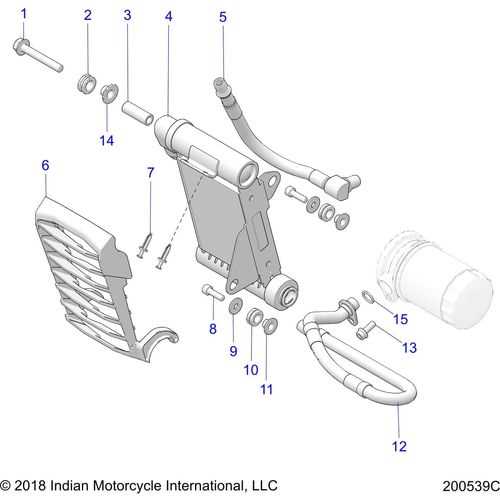

The core structure of the engine includes the cylinder, pistons, crankshaft, and connecting rods. These parts play vital roles in generating power through a controlled combustion process. Each component is precisely designed to withstand high temperatures and pressure, ensuring efficiency and durability.
Sub-systems Overview
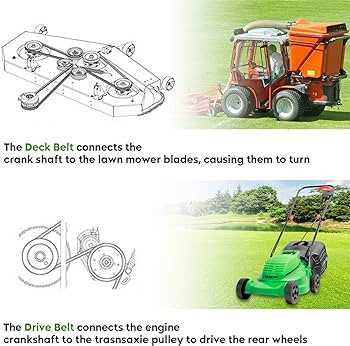
Several auxiliary mechanisms support the engine’s operation, such as the lubrication system, cooling system,
Transmission Assembly Layout
The layout of the transmission system includes multiple components that work together to ensure the smooth operation of the vehicle’s drivetrain. Understanding the arrangement of these elements is crucial for both maintenance and repair tasks.
- Gearbox Components: The gearbox consists of various gears and shafts that are responsible for transmitting power from the engine to the wheels.
- Clutch System: This section allows for the disengagement and engagement of the engine, making it possible to shift gears efficiently.
- Drive Shafts: These connect the transmission to the wheels, transferring the rotational force necessary for movement.
- Synchronization Mechanism: Ensures smooth transitions between different gears by aligning them at the correct speeds.
This structured approach to the transmission system highlights the importance of each component in delivering power from the engine to the wheels, ensuring optimal vehicle performance.
Suspension and Steering Mechanism
The suspension and steering system are crucial components that ensure a vehicle’s stability and handling. These systems work in harmony to provide comfort during movement and allow the operator to maintain control even on challenging road surfaces. Their design affects not only the smoothness of the ride but also the safety and precision of the vehicle’s response to steering inputs.
Key Features of the Suspension System

- Absorbs shocks from uneven terrain to provide a smooth ride.
- Maintains the vehicle’s balance and ensures consistent wheel contact with the ground.
- Enhances safety by reducing the impact of road irregularities on the chassis and passengers.
Functionality of the Steering Mechanism
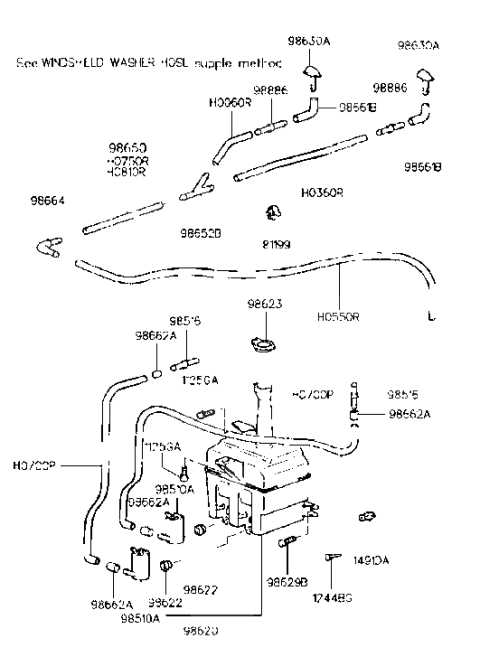
- Converts the driver’s input into precise movement of the wheels.
- Allows for accurate maneuvering, improving vehicle responsiveness.
- Works alongside the suspension to ensure stability during cornering and sudden turns.
Electrical System and Wiring
The electrical system in any equipment is a crucial component that ensures proper functionality. It is responsible for distributing energy to various elements, maintaining connectivity, and supporting the device’s operational efficiency.
Main Components
- Wiring harnesses: These are designed to connect different sections of the system, allowing for efficient power distribution.
- Connectors: Secure electrical connections between different parts of the system, ensuring stable power flow.
- Fuses: Provide safety by preventing electrical overloads, protecting sensitive components from damage.
Wiring Layout
The layout of the wiring must be well-organized and insulated to prevent any risk of short circuits or interruptions in the power supply. Proper installation is key to maintaining system stability and ensuring that each element receives adequate energy.
Fuel System Configuration
The configuration of the fuel system is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and efficiency in any engine. A well-structured fuel delivery setup is essential for proper combustion and overall functionality.
This section will outline the key components and their roles within the fuel system:
- Fuel Tank: The storage unit where fuel is held before being pumped to the engine.
- Fuel Pump: Responsible for transporting fuel from the tank to the engine at the required pressure.
- Fuel Filter: Cleans the fuel by removing impurities and particles that could harm the engine.
- Fuel Injectors: Atomize the fuel and deliver it into the combustion chamber for efficient burning.
- Fuel Pressure Regulator: Maintains consistent fuel pressure to ensure optimal engine operation.
Understanding the interplay between these components is vital for troubleshooting issues and enhancing performance. Regular maintenance of the fuel system can lead to significant improvements in fuel efficiency and engine responsiveness.
Brake Components and Layout

The braking system is a critical element of any vehicle, responsible for ensuring safety and control during operation. Understanding the various elements that make up this system is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting. This section delves into the different components involved, their arrangement, and their functions within the overall assembly.
Key Elements of the Braking System

Each component of the braking assembly plays a unique role in delivering optimal performance. Here are some of the primary elements commonly found:
Component Description Brake Pads Friction materials that press against the rotor to slow down or stop the vehicle. Brake Rotor The disc that the brake pads clamp onto, allowing for effective deceleration. Caliper The device that houses the brake pads and applies pressure to them when the brake is engaged. Master Cylinder Generates hydraulic pressure to activate the calipers and engage the brakes. Understanding the Layout
The arrangement of the braking components is designed for maximum efficiency. The strategic positioning of each part ensures that force is applied evenly, providing reliable stopping power. Regular inspection of these elements is vital to maintaining the overall effectiveness of the braking system.
Cooling System Parts

The efficiency of any machinery significantly depends on its thermal management components. These elements work in harmony to regulate temperature, ensuring optimal performance and preventing overheating. Understanding the role of each component is essential for maintaining a reliable cooling mechanism.
Radiators serve as the primary unit for dissipating heat, allowing coolant to release excess temperature into the atmosphere. Meanwhile, water pumps circulate the coolant throughout the system, facilitating continuous flow and maintaining a balanced temperature. Additionally, thermostats play a crucial role by regulating the flow of coolant based on the engine’s temperature, ensuring it operates within the desired range.
Moreover, hoses connect various components, providing pathways for coolant to travel efficiently. The integrity of these hoses is vital, as any leaks can compromise the entire system. Lastly, cooling fans assist in enhancing airflow through the radiator, especially during low-speed operations or when the vehicle is stationary, further supporting the cooling process.
Body Structure and Frame

The design and construction of a vehicle’s body play a crucial role in its overall performance and safety. A robust framework not only supports the external components but also ensures stability and rigidity. Understanding the intricacies of the structure is essential for maintenance and repair.
The frame serves as the foundation, providing support for various elements and ensuring proper alignment. It is typically made from durable materials that can withstand various stresses during operation. The integration of the body with the frame is a vital aspect, as it impacts the vehicle’s aerodynamics and aesthetics.
Component Description Material Chassis The main support structure of the vehicle Steel or aluminum Cross members Support beams that add strength and stability Steel Body panels Exterior sections that define the vehicle’s shape Composite materials or sheet metal A thorough understanding of the body composition and framework can significantly aid in diagnosing issues and enhancing performance. Regular inspections and maintenance of these components ensure the longevity and reliability of the vehicle.
Exhaust System Diagram
The exhaust assembly plays a crucial role in the efficient operation of an engine by directing harmful gases away from the vehicle. Understanding its layout can help in diagnosing issues and performing maintenance effectively.
This section outlines the key components and their functions within the exhaust configuration:
- Exhaust Manifold: Collects gases from the engine cylinders.
- Catalytic Converter: Reduces harmful emissions through chemical reactions.
- Resonator: Modifies sound frequencies produced by the exhaust system.
- Muffler: Silences the noise from the engine and exhaust gases.
- Tailpipe: Discharges the treated gases into the atmosphere.
Each element contributes to the overall functionality and efficiency of the exhaust mechanism. Regular inspections can prevent potential issues, ensuring optimal performance and compliance with environmental standards.