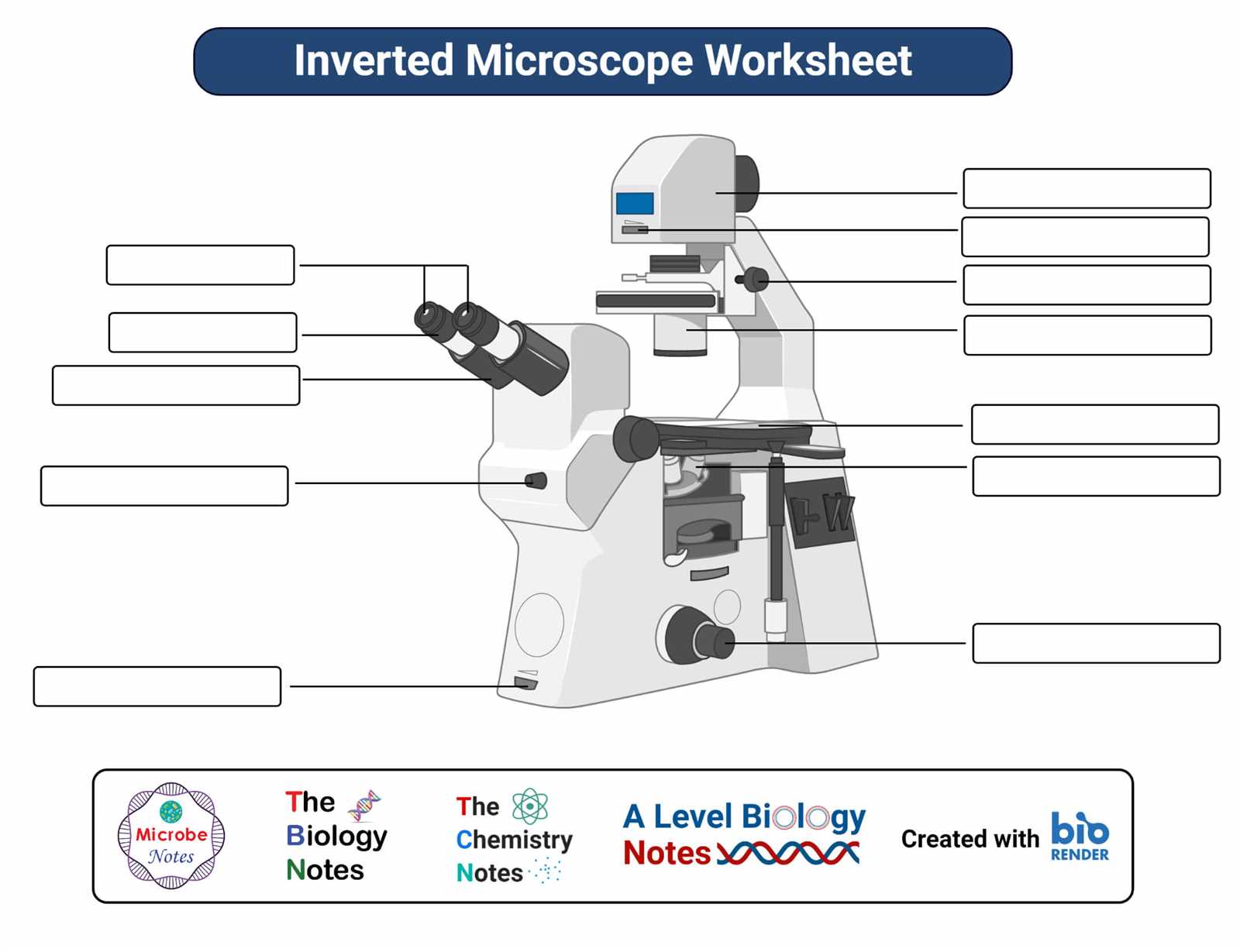
When exploring the world of scientific observation, a key tool that magnifies small objects comes into play. This device is designed with a complex set of components that work together to provide detailed views of materials that are not visible to the naked eye. Each element of the device plays a crucial role in enhancing clarity and precision, offering users the ability to examine fine details.
The layout of this instrument includes various sections responsible for gathering light, focusing it, and presenting a clear image to the viewer. These sections are carefully arranged to ensure optimal performance, allowing for seamless transitions between different magnification levels. By understanding the structure and purpose of each part, one can make the most of this tool in scientific and educational settings.
In this article, we will break down the key elements that contribute to the efficiency and accuracy of this magnifying device. With a deeper understanding of how these parts function together,
Understanding the Structure of a Compound Microscope
Exploring the design of this optical device reveals its intricate assembly. It contains several key elements, each contributing to the magnification process, making it possible to observe minuscule objects. The construction integrates a combination of lenses and mechanical adjustments, allowing precise focus and image clarity.
Main Optical Elements
The key to achieving clarity lies in the coordinated use of multiple lenses. The primary set is responsible for gathering and magnifying the light, while the secondary set refines and focuses the image. These elements work together to offer a detailed view of objects not visible to the naked eye.
Mechanical Components
The mechanical structure ensures the stability and flexibility of the device. It supports various adjustments, enabling users
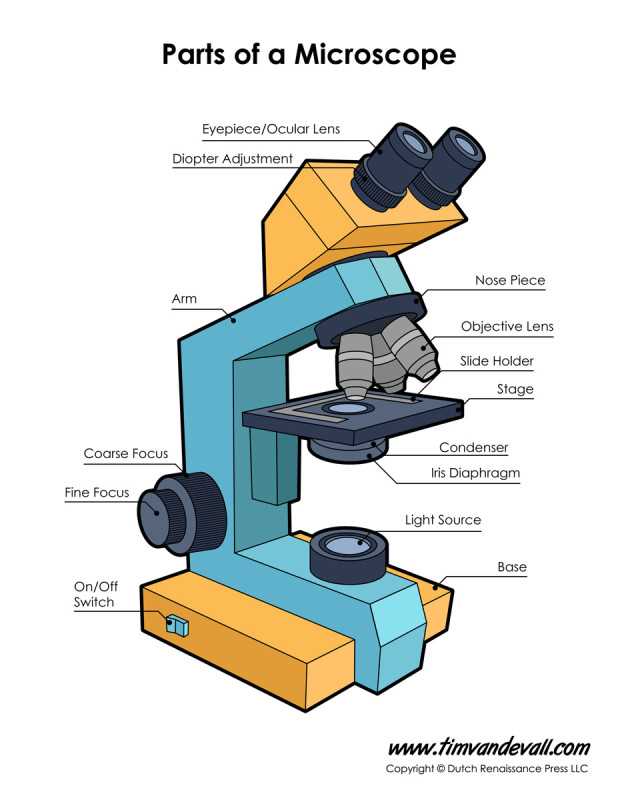
Main Components of a Compound Microscope
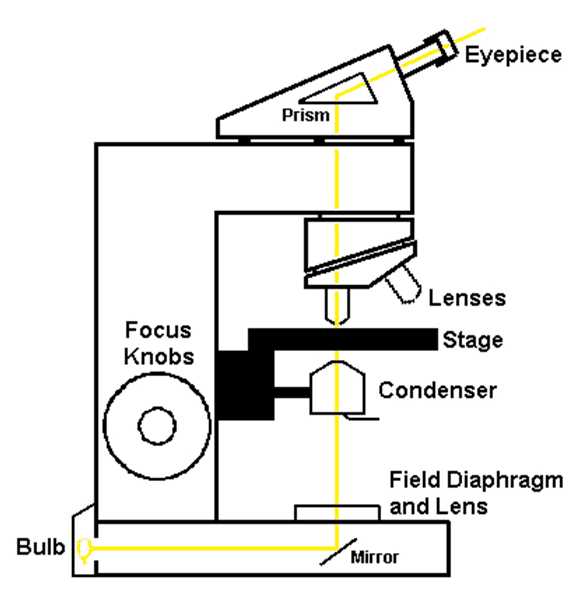
The device consists of several essential elements that work together to allow detailed observation of tiny objects. Each element plays a vital role in adjusting and focusing the view, enhancing the clarity and precision of what is being observed.
- Eyepiece: The topmost lens through which the observer looks. It magnifies the image produced by other optical elements.
- Objective Lenses: Positioned closer to the specimen, these lenses provide various levels of magnification, allowing the user to zoom in for more detail.
- Stage: A flat platform where samples are placed. It often includes clips to hold the object in place during observation.
- Microscope Body and Framework Explained
The physical structure of this optical instrument is crucial for providing stability and ease of use. It includes various components designed to support the device’s functionality, ensuring accurate observation and a comfortable experience for the user.
Base and Support Mechanism
The foundation of the instrument, often referred to as the base, provides a sturdy platform. This ensures that the device remains stable during operation. The support mechanism connects the base to the upper section, maintaining balance while allowing for controlled movements during adjustments.
Adjustment Controls and Arm Structure
The arm connects the lower section to the viewing area. This structural element plays a vital role in handling and maneuverability. Alongside it, adjustment controls, such as fine and coarse focus, allow precise modifications
Focusing Mechanism: Coarse and Fine Adjustment
The focusing system is crucial for achieving clarity in viewing objects. It allows the observer to bring the image into focus by adjusting the distance between the lens and the sample. This process involves two levels of control that work together to provide a sharp and detailed image.
Coarse adjustment is the first step, enabling larger movements to quickly bring the view closer to focus. It is typically used when switching between samples or making initial adjustments. This stage is essential for setting the general position.
After the initial alignment, the fine adjustment mechanism takes over. This control allows for more precise tuning, refining the focus in small increments to enhance the clarity and detail of the viewed object. The combination of both adjustments ensures a smooth transition from a rough to a highly accurate focus.
Importance of Eyepiece and Objective Lenses
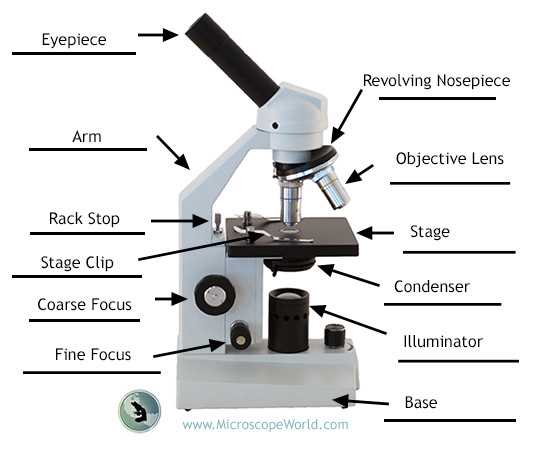
The eyepiece and objective lenses play crucial roles in the overall function of optical instruments. Each component contributes to enhancing the clarity and detail of the viewed object. Together, they work to provide a magnified and sharp image, making it easier to observe even the smallest details.
While the eyepiece allows for comfortable viewing, the objective lens is responsible for gathering light and focusing on the subject. These lenses come in different magnifications, offering flexibility depending on the level of detail required. The combination of both lenses ensures that observations are accurate and precise, which is essential for various applications.
Component Function The Function of the Stage and Stage Clips
The stage serves as a crucial platform in optical instruments, providing a stable base for specimens during examination. It allows for precise positioning and manipulation, ensuring that the area of interest is optimally aligned with the light source and the lens system.
Stage clips play an essential role in securing the slides, preventing any unwanted movement that could disrupt observations. These clips are designed to hold the specimen in place firmly, enabling clear and focused viewing. Additionally, they facilitate quick adjustments when needed, enhancing the overall efficiency of the observation process.
By offering a stable and secure environment, the stage and its clips contribute significantly to the accuracy and quality of visual analysis, making them indispensable components of any optical examination tool.
Light Source and Its Role in Microscopy
The illumination element is a vital component in optical observation systems, as it significantly impacts the clarity and quality of visualized specimens. Its primary function is to provide sufficient brightness and contrast, enabling detailed examination of minute structures.
Effective lighting enhances the visibility of features that may otherwise remain hidden in shadow or darkness. By adjusting the intensity and direction of illumination, observers can achieve optimal clarity and focus on various aspects of the subject. Different types of illumination, such as transmitted or reflected light, offer unique advantages depending on the nature of the specimen and the desired outcome of the examination.
In summary, the illumination source plays an indispensable role in enhancing the functionality of optical systems, allowing for precise observation and analysis of intricate details within samples. Properly managing this component is essential for achieving the best possible results in visual investigations.
How the Diaphragm Controls Light Intensity
The diaphragm serves a crucial role in regulating the amount of illumination that reaches the specimen being examined. By adjusting the aperture, it allows for precise control over the light’s brightness, which is essential for achieving clear and detailed observations.
Mechanism of Light Regulation
The diaphragm’s functionality is based on the following mechanisms:
- Adjustable Aperture: The diaphragm features an opening that can be widened or narrowed to either increase or decrease light flow.
- Contrast Enhancement: By manipulating the light intensity, the diaphragm helps enhance the contrast between the specimen and its background, facilitating better visibility of details.
- Reduction of Glare: Proper adjustment minimizes excessive brightness that could lead to glare, making it easier to analyze the sample.
Importance in Observation
Effective use of the diaphragm contributes significantly to the quality of the viewing experience:
- It enables the user to adapt to varying conditions of the sample being observed.
- It supports the examination of transparent or translucent specimens by allowing optimal light levels.
- Proper lighting leads to more accurate interpretations and analyses of the subject matter.
Exploring the Condenser and Its Uses
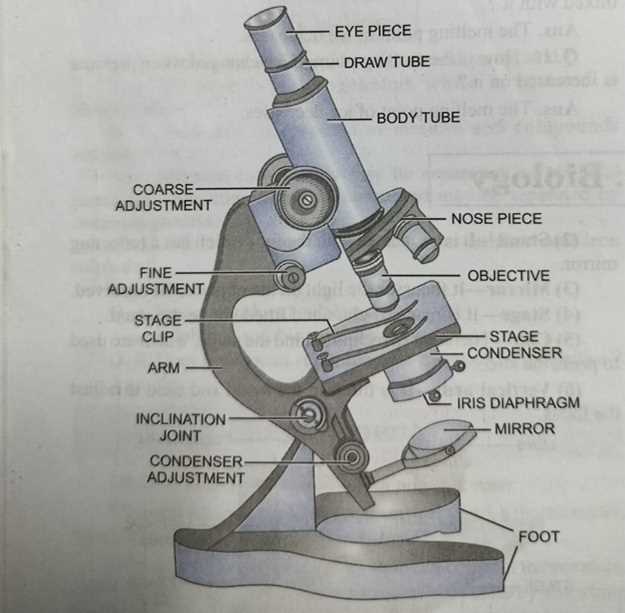
The condenser plays a vital role in enhancing the quality of observations in optical instruments. By focusing and directing light onto the specimen, it significantly improves clarity and detail. Understanding its structure and functions can greatly enhance the user experience and effectiveness of these devices.
Structure and Functionality
This optical component is typically situated beneath the stage, allowing for optimal light control. Its main elements include:
- Lens System: Comprising multiple lenses to converge light rays.
- Adjustment Mechanism: Enabling users to manipulate the light intensity and focus.
Applications of the Condenser
The uses of this component extend across various fields, offering significant benefits:
- Enhancing Image Contrast: It improves the contrast of the image, making fine details more visible.
- Facilitating Different Illumination Techniques: Different types of lighting, such as darkfield or phase contrast, can be achieved by adjusting the condenser.
- Optimizing Light Distribution: A well-positioned condenser ensures even light distribution, crucial for accurate observations.
The Role of the Revolving Nosepiece
The revolving nosepiece is a crucial component in optical instruments, enhancing the user experience by allowing seamless transitions between different lenses. Its design facilitates quick adjustments, making it easier for users to select the appropriate magnification for their observations.
This element serves several essential functions:
- Lens Switching: It enables the rapid exchange of various lenses, thus accommodating different levels of detail.
- Stability: The structure provides a secure and stable mount for each lens, ensuring consistent performance during observations.
- User Convenience: By allowing easy rotation, it minimizes the time spent changing lenses, enhancing efficiency in both education and research.
Overall, the revolving nosepiece significantly contributes to the versatility and functionality of the optical instrument, making it indispensable for effective examination and analysis.
Understanding the Function of the Arm and Base
The structure that connects various elements of a visual instrument plays a crucial role in its overall stability and functionality. This essential framework not only supports the optical components but also provides a foundation for user interaction, enhancing the overall experience of observation.
The arm serves as a vital link between the upper optical assembly and the lower support system. It allows for adjustments in positioning, enabling the user to view specimens from different angles. Its design often incorporates ergonomic features to facilitate ease of use during prolonged examination sessions.
The base, on the other hand, provides the necessary stability required for effective operation. A well-constructed foundation minimizes vibrations and ensures that the instrument remains steady during observation. Additionally, it often houses important components such as illumination systems, contributing to the clarity and quality of the visual experience.