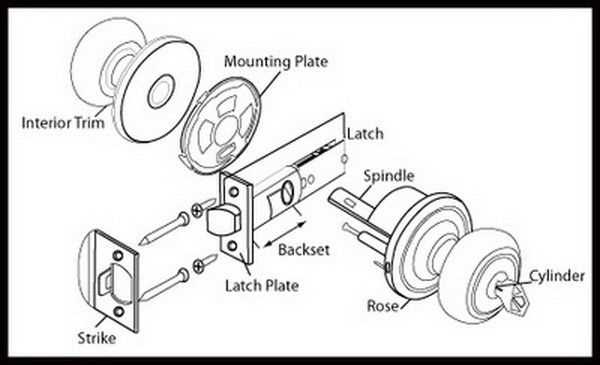
In many everyday items, intricate systems ensure the safety and privacy of personal belongings or restricted spaces. These systems are comprised of multiple interconnected elements that work together to provide reliable security. By exploring these components, it becomes easier to understand how they function seamlessly to create a protective barrier.
Each element within the secure fastening system has a specific role in maintaining the overall functionality. Whether it involves rotating, sliding, or holding parts in place, every section contributes to the successful operation of the device. Recognizing how these elements interact can shed light on the efficiency and durability of the entire mechanism.
This overview provides insight into the core principles of such systems, offering a foundation for a more detailed examination of the individual pieces that make up the whole structure. By understan
Overview of Cylinder Lock Components
Understanding the key elements of this security mechanism is essential for both installation and maintenance. Each part has a distinct function that contributes to the overall operation and reliability of the system. By exploring the internal and external structures, one can gain a clearer understanding of how the entire unit works together to provide security.
Main Structural Elements
The main body consists of several crucial components that interact seamlessly to control access. The internal mechanism includes moving parts that respond to the correct key input, allowing rotation and operation. External components act as barriers, ensuring that only authorized users can engage the mechanism.
Operational Components
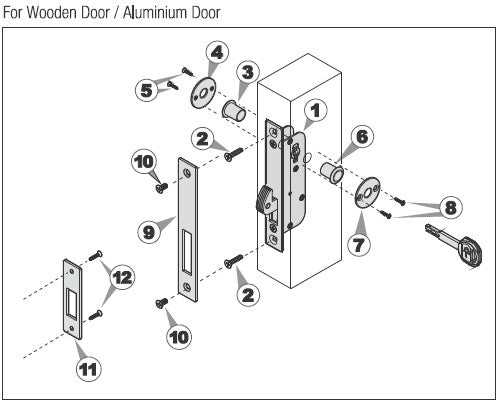
Internal Mechanisms of Cylinder Locks
The intricate workings of modern entry devices rely on a combination of precise components that work together to ensure security and functionality. These elements are housed within a compact structure, and each plays a crucial role in the overall operation, providing both protection and ease of use.
Core Components and Their Function
At the heart of the system is a rotating element, activated by a specially shaped tool, which engages a sequence of internal components. As this tool is inserted, it interacts with small, spring-loaded pins or other elements, creating
Key Pin Functionality in Lock Systems
The mechanism involving key pins plays a crucial role in maintaining the security of various systems. These small components directly influence how effectively the device interacts with its corresponding tool. By ensuring precise alignment, they are fundamental to the smooth operation of the entire process.
Role of Key Pins in the Mechanism
Key pins are arranged in a specific order, and their interaction with the tool determines whether access is granted. Each pin is tailored to fit a particular height or depth, matching the grooves and ridges of the tool used for access.
- Each pin corresponds to a unique cut on the tool.
- Misalignment of even a single pin prevents the system from functioning.
- Key pins differ in size to accommodate different c
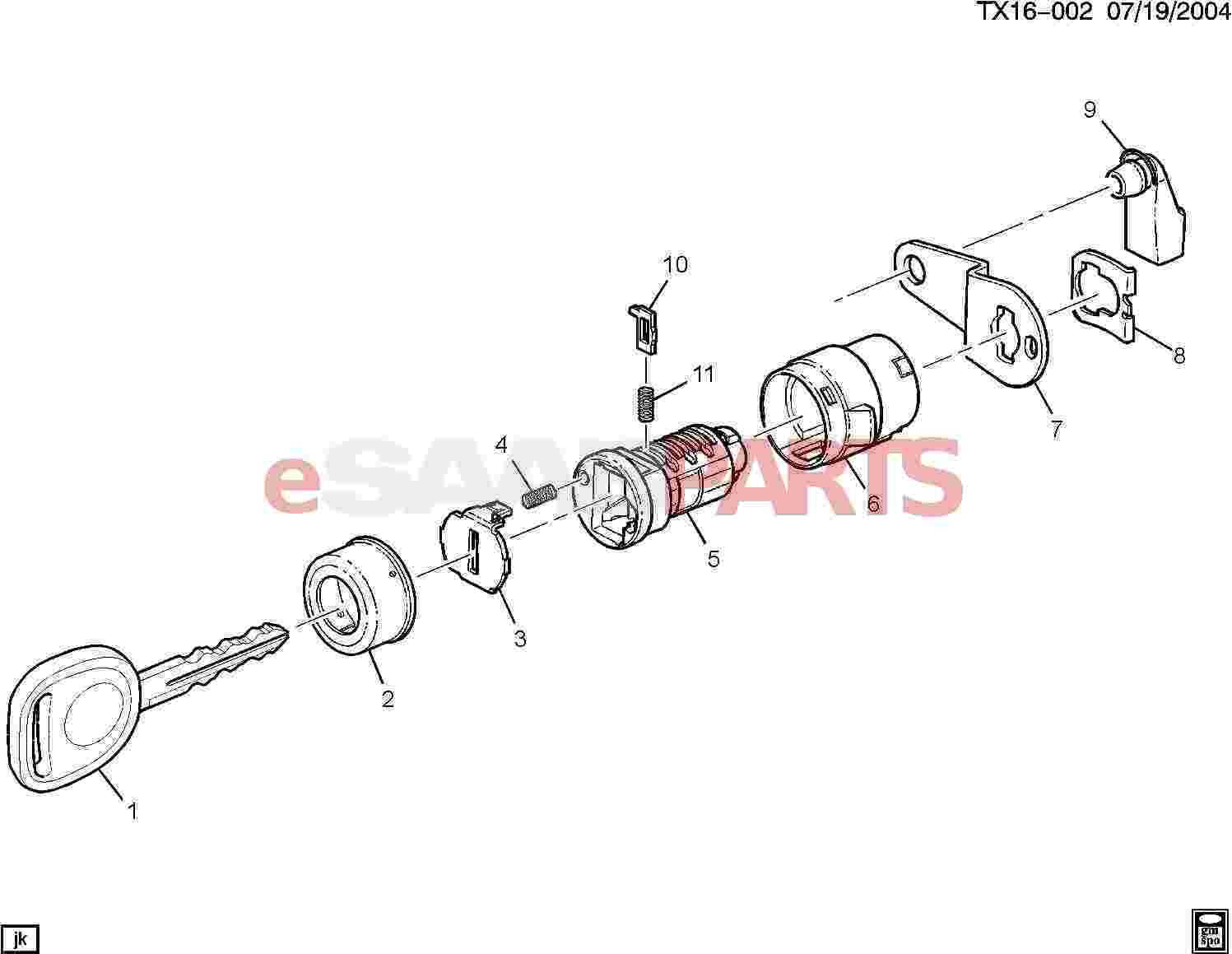
Role of the Plug in Cylinder Locks
The plug serves a crucial function in various locking mechanisms, ensuring effective security and ease of operation. It acts as the core component where the key is inserted, enabling the opening and closing actions. The design and efficiency of the plug directly influence the overall reliability of the locking system.
Functionality and Mechanism
The functionality of the plug revolves around its interaction with different elements within the locking assembly. Here are key aspects:
- Key Insertion: The primary purpose is to accept the key, allowing for seamless engagement with the internal mechanisms.
- Rotation: Upon turning the key, the plug rotates, aligning the internal pins or tumblers, which releases the securing mechanism.
- Rekeying: Certain designs allow for easy rekeying, enhancing versatility and adaptability to changing security needs.
Importance in Security Systems
In the context of security, the plug’s integrity is paramount. A well-constructed plug can prevent unauthorized access and provide peace of mind. Key considerations include:
- Durability: A robust plug resists wear and tampering, ensuring longevity.
- Compatibility: The design should align with various key types, accommodating user preferences and requirements.
- Advanced Features: Some plugs incorporate sophisticated technology, enhancing protection against unauthorized entry.
Understanding the Cylinder Housing Structure
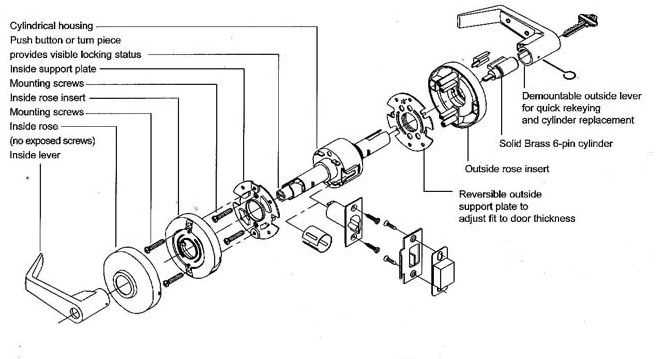
The structure of the housing that encapsulates the core mechanism is essential for ensuring security and functionality. This component serves as the protective shell that holds the internal mechanisms together, providing stability and durability. A deeper comprehension of this structure can enhance one’s ability to troubleshoot and maintain the device effectively.
Key Features of the Housing
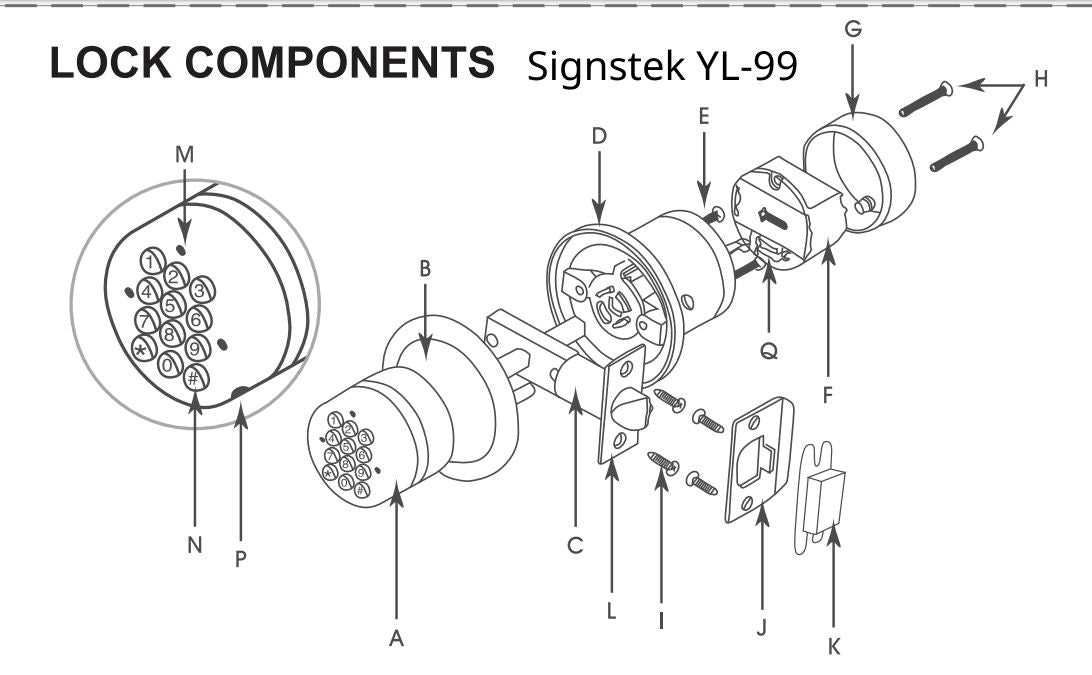
One of the primary features of this casing is its robust material composition, which is designed to resist tampering and wear over time. The durability of the housing is critical for prolonging the lifespan of the internal mechanisms, allowing for consistent performance under various conditions. Additionally, the design often includes features that facilitate installation and removal, making it user-friendly for maintenance purposes.
Functionality and Maintenance
Regular maintenance of the housing is vital for optimal performance. Periodic checks can prevent accumulation of debris and ensure that the protective elements remain intact. Understanding how this outer structure interacts with the inner mechanisms can lead to better care and longevity, ultimately enhancing the overall effectiveness of the entire system.
How Springs Affect Lock Operation
Springs play a crucial role in the functionality of securing mechanisms, ensuring smooth engagement and disengagement. Their design and placement directly influence the overall performance, providing the necessary tension and responsiveness during use.
When a securing device is engaged, springs apply pressure to specific components, allowing them to move precisely into their designated positions. This action is vital for maintaining the integrity of the mechanism, as it ensures that elements align correctly, facilitating seamless operation. The quality and resilience of the springs determine how effectively the device responds to user input.
Additionally, variations in spring tension can lead to differences in operation speed and resistance. A stiffer spring may provide a more secure hold but could also make the mechanism more difficult to manipulate. Conversely, a softer spring allows for easier access but may compromise security. Understanding these dynamics is essential for optimizing the design and functionality of securing mechanisms.
Shear Line and Its Importance
The shear line is a critical concept in the functioning of various securing mechanisms. It represents the specific point where two components interact to enable or restrict movement. Understanding this principle is essential for anyone involved in security solutions, as it directly affects the effectiveness and reliability of the mechanism in question.
Functionality and Mechanics
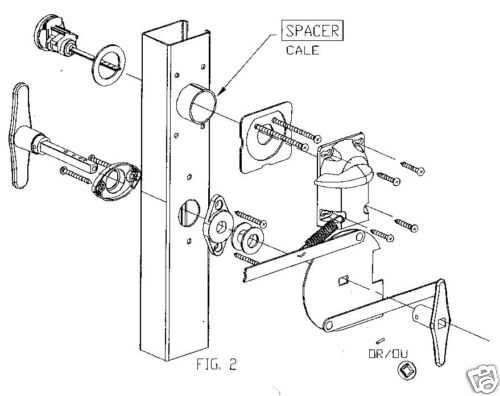
At the shear line, the alignment of internal elements plays a pivotal role in determining whether the device can be operated smoothly. When the internal components are positioned correctly, they allow for seamless engagement and disengagement. This alignment is vital for ensuring that the device operates as intended, providing the necessary security while remaining user-friendly.
Significance in Security
The shear line is not just a mechanical consideration; it also has profound implications for security. A compromised shear line can lead to vulnerabilities, making it easier for unauthorized individuals to gain access. Thus, understanding and maintaining the integrity of this critical point is paramount in the design and evaluation of security mechanisms.
Interaction Between Key and Pins
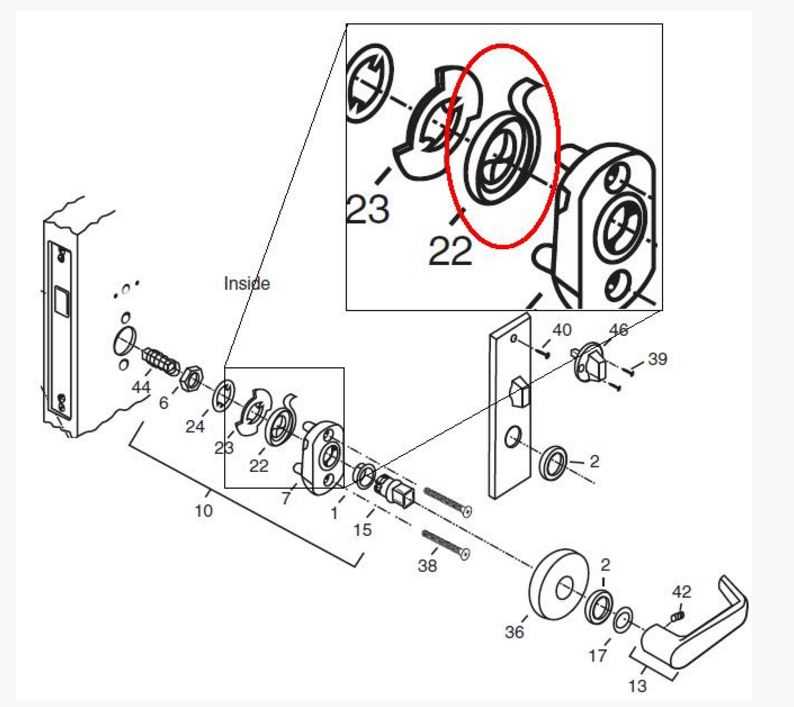
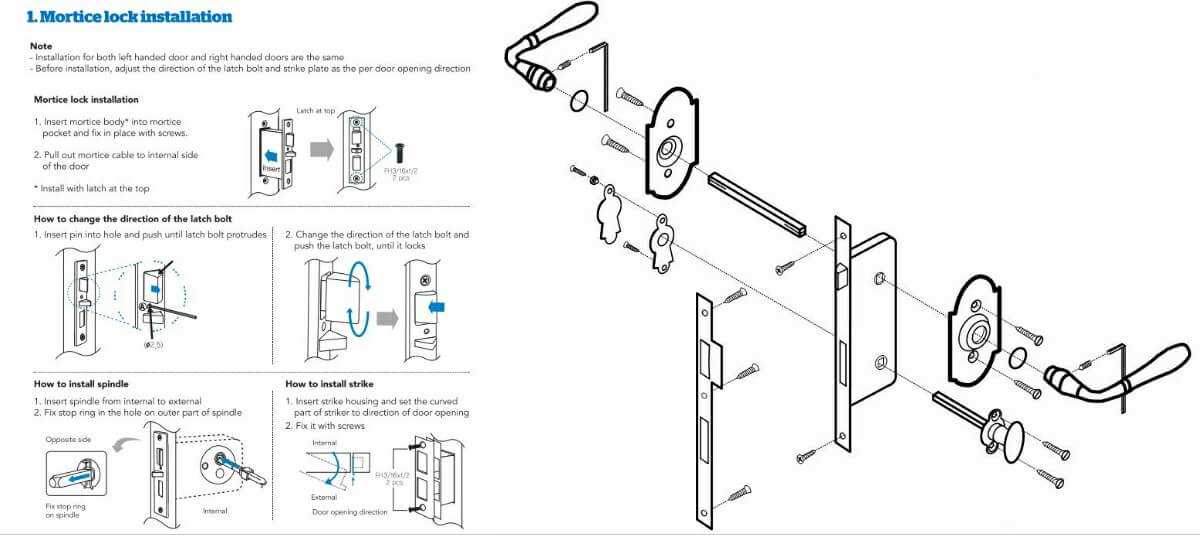
The relationship between the key and the pins is fundamental to the operation of a security mechanism. This interaction determines whether the mechanism will operate smoothly or be rendered ineffective. Understanding this dynamic helps to appreciate how security is achieved through mechanical systems.
When a key is inserted, several crucial actions take place:
- The key’s grooves align with the pins.
- The pins move up and down according to the key’s shape.
- When properly aligned, the pins create a pathway for the mechanism to engage.
Each pin typically consists of two parts: a driver pin and a spring. The mechanics work as follows:
- As the key is turned, it pushes the driver pins upward.
- The springs hold the bottom pins in place, preventing them from moving too high.
- The correct height allows the driver pins to align with a shear line, enabling the turning action.
This interplay ensures that only the correct key can operate the mechanism effectively, providing an essential layer of security.
Lock Security Features and Design
In today’s world, safeguarding personal belongings and ensuring safety is paramount. Various mechanisms are crafted to provide enhanced protection, focusing on their structural integrity and advanced functionalities. The choice of materials, manufacturing techniques, and design intricacies play crucial roles in the overall efficacy of these protective devices.
Durability is one of the primary characteristics of a reliable mechanism. Devices constructed from high-grade metals and composite materials offer resistance to tampering and wear, ensuring long-term performance. Furthermore, the inclusion of anti-drill and anti-pick features significantly raises the barrier against unauthorized access.
Another vital aspect is the mechanical complexity. A sophisticated arrangement of internal components can complicate attempts at forced entry. This complexity can deter intruders, as it often requires specialized knowledge and tools to navigate.
Additionally, the integration of smart technology enhances security measures. Devices equipped with digital interfaces can offer features such as remote monitoring, access logs, and temporary access codes. This technological advancement allows for real-time updates and control, making it easier to manage entry points.
Ultimately, the combination of strong materials, intricate designs, and modern technology culminates in devices that not only protect but also provide peace of mind. Investing in high-quality mechanisms can be a decisive step in achieving a secure environment.
Exploring Different Cylinder Lock Types
Understanding the various mechanisms available in security systems is essential for enhancing protection and ensuring ease of use. Each variant offers unique features that cater to different needs and preferences, making it crucial to explore these options to find the most suitable solution.
Common Variants
Several widely-used variations each serve specific functions and purposes. Below are some notable examples:
Type Description Use Cases Single-Sided Designed for use with a key on one side only, offering a straightforward approach. Interior doors or storage units. Double-Sided Features keyholes on both sides, allowing access from either end. Exterior entrances or secure areas needing dual access. Keyless Utilizes electronic methods, eliminating the need for a traditional key. Smart homes or offices for enhanced convenience. Choosing the Right Option
Selecting the appropriate model requires consideration of security requirements, ease of installation, and user preferences. Each type presents distinct benefits that can significantly impact overall safety and functionality.
Materials Used in Cylinder Lock Construction
In the creation of secure mechanisms, the selection of materials plays a crucial role in ensuring durability, resistance to tampering, and overall functionality. Various substances are employed in crafting these mechanisms, each chosen for its unique properties and benefits.
Common Materials
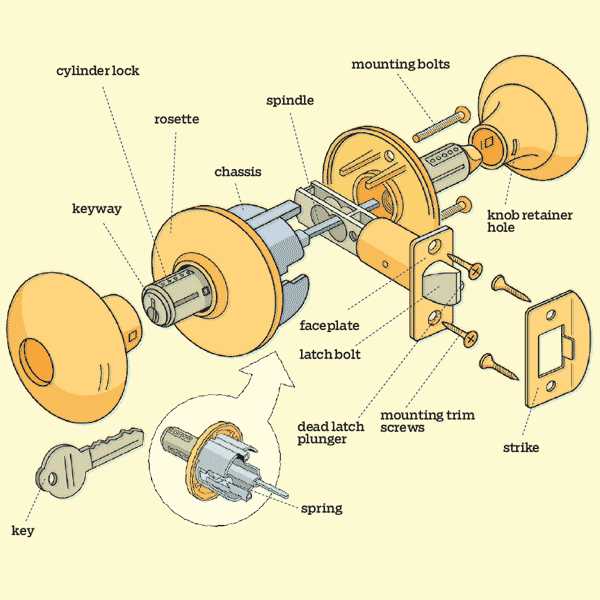
- Brass: Known for its corrosion resistance and strength, brass is frequently utilized in the exterior components of locking mechanisms.
- Steel: This metal offers exceptional strength and durability, making it ideal for internal components that require added security.
- Zinc Alloy: Lightweight and versatile, zinc alloys are often used for creating intricate shapes and designs.
- Plastic: Typically used for internal parts, certain plastics provide a balance of lightweight and cost-effectiveness while maintaining functionality.
Coatings and Finishes
To enhance the performance and appearance of locking mechanisms, various coatings and finishes are applied:
- Nickel Plating: Offers a shiny finish while providing corrosion resistance.
- Powder Coating: A durable finish that protects against scratches and environmental damage.
- Anodizing: Commonly used for aluminum components to increase corrosion resistance and improve surface hardness.