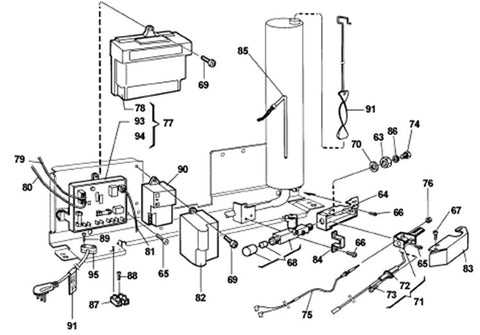
The internal structure of many cooling appliances is built with a variety of key elements, each serving a specific function to ensure efficient operation. When you dive into the intricate design of these systems, you’ll find that each segment has been carefully placed to optimize cooling performance and reliability. Proper knowledge of the layout and how each component interacts is crucial for maintaining and troubleshooting these devices.
Whether you’re looking to repair or replace specific modules, understanding their location and function is essential. From the cooling unit to the electrical connections, every piece plays an important role in ensuring the smooth operation of your appliance. Having a clear visual reference can make it much easier to identify where issues may arise and how to address them effectively.
By familiarizing yourself with the arrangement of the various segments, you can significantly improve your ability to maintain and repair these systems. This not only prolong
Understanding the Layout of Dometic RM2652
The structure of this refrigeration unit is thoughtfully designed to optimize functionality and user experience. By recognizing the key components and their arrangement, it becomes easier to understand the overall operation and troubleshoot potential issues. This section will walk through the major elements of the unit, offering insights into how everything is connected and works together to maintain optimal performance.
Main Components and Their Functions
- Cooling System: At the core of the appliance is its cooling mechanism, which is responsible for regulating temperature inside the unit.
- Control Panel: This interface allows users to adjust settings, monitor status, and choose operational modes.
- Venting System:
Main Components Overview
This section highlights the essential elements that contribute to the functionality and operation of the system. Each component plays a critical role in ensuring smooth performance, from cooling mechanisms to power management.
- Cooling Unit: The core of the system, responsible for maintaining a stable temperature through a combination of heat absorption and dissipation processes.
- Thermostat: This control unit monitors and regulates temperature settings, ensuring the system remains within desired operational ranges.
- Control Board: Acts as the central hub, coordinating various functions such as temperature regulation, energy input, and safety measures.
- Heat Source: Provides the necessary thermal energy to initiate the cooling cycle. Typically, multiple heat sources are available for different energy inputs.
- Sealed System: Contains a refrigerant medium that circulates
Exploring the Cooling System Parts
The cooling mechanism in this type of equipment consists of various essential components that work together to maintain an efficient temperature regulation process. These elements ensure optimal performance by utilizing heat absorption and dissipation techniques, which are crucial for maintaining the desired environment within the unit. Each piece plays a specific role in ensuring smooth operation and longevity of the overall cooling function.
One of the primary elements is the condenser, responsible for releasing accumulated heat outside the unit. This is complemented by the evaporator, which absorbs the heat from inside the system. Additionally, the heat exchanger contributes by transferring thermal energy between fluids, further supporting the cooling process. Together, these components form the backbone of the temperature control system, ensuring its reliable and continuous function.
Electrical Circuit Breakdown
The electrical system within a refrigeration unit plays a crucial role in maintaining its functionality. By analyzing its wiring structure, we can better understand how different components interact to ensure proper operation. This breakdown focuses on the flow of electricity and how it powers essential functions, highlighting key elements involved in the energy distribution process.
Power Supply and Control
At the core of the system is the power source, which provides the necessary energy for the appliance to function. The power is directed through control mechanisms, such as switches and relays, which regulate when and how electricity flows to various parts of the system. These controls ensure that the cooling cycle operates efficiently and prevents overloads.
Key Connections and Circuits
Several circuits are responsible for handling different tasks, including temperature regulation, automatic defrosting, and fan operation. Each circuit is designed to perform a specific function, and the seamless connection between them ensures optimal performance. Understanding these connections is vital for
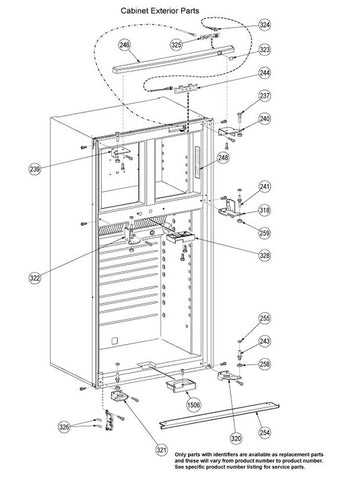
Door Assembly and Seal Components
The door assembly plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the refrigeration system. Its design ensures effective insulation and prevents air leakage, which is vital for optimal cooling performance. The seal components surrounding the door are key to preventing warm air from entering and cold air from escaping.
Main Elements of the Door Assembly
- Outer Frame: Provides structural support and stability for the door. It’s crafted to fit securely onto the main body.
- Inner Panel: Serves as the internal surface, designed to withstand temperature fluctuations and provide easy access to the storage space.
- Hinges: Allow smooth opening and closing, ensuring the door remains tightly sealed when shut.
- Latch
Burner and Ignition Parts
The burner and ignition components are critical for ensuring the smooth operation of your system. These elements work together to provide reliable heat generation, and they are designed for efficient energy transfer. Proper functionality of these parts is essential for maintaining the overall performance of the appliance.
Burner: The burner serves as the primary source of heat, converting fuel into energy. It requires regular maintenance to prevent clogs or reduced efficiency, ensuring that heat output remains consistent.
Ignition System: The ignition mechanism activates the burner. This component includes the spark assembly, which creates the necessary spark to ignite the fuel. Regular checks on the spark electrode and wiring are crucial to prevent any issues with the ignition process.
Absorption Unit Functions
The absorption unit serves a crucial role in refrigeration systems, operating through a unique process that leverages heat to facilitate cooling. This mechanism is particularly efficient in applications where traditional compressor-based cooling methods may be less effective or practical.
At its core, the absorption unit employs a refrigerant and an absorbent to create a continuous cycle of evaporation and condensation. As the refrigerant evaporates, it absorbs heat from the surrounding environment, leading to a drop in temperature. The absorbent then collects the refrigerant vapor, allowing the system to maintain an ongoing cooling effect.
One of the significant advantages of this technology is its ability to operate using alternative heat sources, such as propane or electricity. This versatility makes it suitable for various applications, including recreational vehicles and off-grid settings. Furthermore, the absorption unit is known for its quiet operation, providing a comfortable environment without the noise associated with traditional cooling systems.
Overall, understanding the functions of the absorption unit is essential for optimizing its performance and ensuring efficient cooling in various settings. This knowledge can assist users in troubleshooting issues and maintaining the longevity of the refrigeration system.
Control Board and Wiring Details
The control unit plays a crucial role in managing the operation of refrigeration systems, ensuring efficient functionality and reliability. Understanding the layout and connections of this component is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. This section provides insights into the configuration of the control board and its associated wiring, facilitating better comprehension for users and technicians alike.
Overview of the Control Unit
The control board is the central hub for electrical signals, regulating various functions of the cooling apparatus. It features several connectors, each corresponding to specific components, such as the compressor, fan, and temperature sensors. Familiarity with these connections allows for accurate diagnostics and repairs, ensuring optimal performance of the cooling system.
Wiring Configuration
The wiring setup is vital for the safe and efficient operation of the refrigeration unit. Each wire is color-coded and designated for particular functions, which helps in identifying the correct connections during installation or repairs. Adhering to the specified wiring layout is imperative to prevent malfunctions and potential hazards. Regular inspections of the wiring integrity can help in identifying wear or damage, promoting longevity and reliable operation of the system.
Gas Valve and Related Mechanisms
The gas control unit plays a crucial role in the operation of appliances that utilize gas for heating or refrigeration. This component regulates the flow of gas, ensuring safe and efficient functioning of the system. Understanding the mechanisms associated with the gas valve is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Components of the Gas Control System
- Gas Valve: The primary element that controls the gas flow to the burner or heating element.
- Thermocouple: A safety device that detects whether the pilot light is lit, preventing gas flow if the flame goes out.
- Regulator: Maintains the pressure of the gas supplied to the system, ensuring consistent performance.
- Burner Assembly: Where the gas is ignited, producing the necessary heat for the appliance.
Functionality and Safety Features
Each component within the gas control system must work seamlessly together to provide reliable operation. The gas valve opens and closes in response to signals from the thermocouple, which monitors the flame presence. If the flame extinguishes, the thermocouple signals the valve to shut off, thereby preventing gas leaks. Regular inspections and maintenance of these components are vital for ensuring optimal performance and safety.
Airflow and Ventilation Setup
Ensuring optimal airflow and ventilation is crucial for maintaining the efficiency and longevity of cooling appliances. Proper air circulation not only enhances performance but also prevents overheating and potential damage. In this section, we will explore key considerations and best practices for setting up an effective airflow system.
Understanding Airflow Dynamics is essential for creating an efficient environment. Air needs to flow freely around the unit to remove excess heat generated during operation. Blocking air intakes or exhausts can lead to reduced efficiency and increased wear on components. To achieve the best results, ensure that there is adequate space around the appliance for air to circulate freely.
Placement and Orientation play a significant role in ventilation effectiveness. When positioning the unit, consider factors such as proximity to walls, obstructions, and sunlight exposure. Ideally, it should be installed in a shaded area with sufficient clearance from surrounding structures. This positioning helps in minimizing heat buildup and maximizing cooling performance.
Moreover, installing vents can further enhance airflow. Strategically placed vents allow fresh air to enter while expelling warm air efficiently. Utilizing fans or exhaust systems can also assist in promoting circulation, especially in confined spaces. Regular maintenance, including cleaning vents and checking for blockages, is vital to ensure uninterrupted airflow.
In conclusion, a well-planned airflow and ventilation setup significantly contributes to the overall efficiency and durability of cooling systems. By understanding airflow dynamics, carefully considering placement, and implementing proper ventilation strategies, users can achieve optimal performance and longevity from their appliances.
Thermostat and Temperature Control
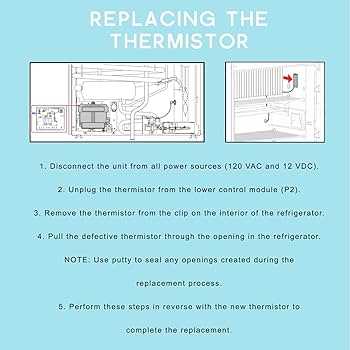
The thermostat plays a crucial role in regulating temperature within cooling and refrigeration units. Its primary function is to maintain a consistent environment by monitoring and adjusting the internal temperature based on the desired settings. Understanding how this component operates can greatly enhance efficiency and performance.
Temperature control is essential for preserving the quality of stored items. An effective thermostat ensures that the internal climate remains stable, preventing fluctuations that could compromise food safety or damage sensitive materials. Proper adjustment and maintenance of this device are key to achieving optimal functionality.
Component Description Thermostat Sensor Detects the internal temperature and sends signals to the control unit. Control Knob Allows users to set the desired temperature manually. Temperature Display Provides a visual readout of the current temperature inside the unit. Control Circuit Processes information from the sensor and regulates the cooling system. Fan Control Manages the operation of the cooling fan to maintain airflow. Regular inspection and timely replacement of these components are vital to ensure effective temperature regulation. By maintaining these elements in good working order, users can enjoy reliable performance and enhanced longevity of their refrigeration systems.
Maintenance Tips for Key Parts
Proper upkeep of essential components in refrigeration units is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Regular maintenance not only helps in preventing potential issues but also enhances efficiency, reducing energy consumption. This section offers valuable insights into maintaining the primary elements of these systems.
1. Clean the Condenser Coils: Dust and debris can accumulate on the condenser coils, obstructing airflow. Regularly cleaning these coils with a soft brush or vacuum helps maintain proper heat exchange, allowing the appliance to operate effectively.
2. Check Door Seals: Inspecting door gaskets for wear or damage is essential. A tight seal prevents cool air from escaping, ensuring energy efficiency. If the seals are brittle or cracked, consider replacing them promptly.
3. Monitor the Drainage System: A clogged drainage system can lead to water accumulation, resulting in leaks or mold growth. Ensure that the drain is clear of debris and that water flows freely. Periodic cleaning with warm, soapy water can help maintain this component.
4. Test the Thermostat: The thermostat regulates the temperature inside the unit. Regular testing for accuracy ensures that the system maintains the desired environment. If the readings are inconsistent, recalibration or replacement may be necessary.
5. Inspect Electrical Connections: Periodically check all electrical connections for signs of wear or corrosion. Secure connections are vital for safe and reliable operation. If any frayed wires or loose connections are found, repair them immediately.
Following these maintenance tips will significantly contribute to the reliability and efficiency of your refrigeration unit, helping you avoid costly repairs and prolong its lifespan.
Common Issues with RM2652 Components
Understanding the typical challenges associated with these cooling units is essential for maintaining their performance and longevity. Various components can experience malfunctions, leading to operational inefficiencies and the need for timely interventions. This section explores some prevalent problems encountered with these appliances and offers insights into potential solutions.
1. Ineffective Cooling: One of the most frequent issues is inadequate cooling, which can stem from various factors. Blocked vents, faulty fans, or low refrigerant levels may contribute to insufficient temperature control. Regular checks and maintenance can help mitigate these problems.
2. Electrical Failures: Electrical issues can manifest as power outages or erratic performance. Loose connections, blown fuses, or malfunctioning thermostats can disrupt the functioning of the unit. Identifying and rectifying these faults promptly is crucial to ensure consistent operation.
3. Water Leaks: Leaking water is another common concern, often resulting from damaged seals or improper drainage. Inspecting seals and ensuring the drainage system is clear can prevent water accumulation and subsequent damage to surrounding areas.
4. Noise Issues: Unusual noises during operation can indicate mechanical problems, such as worn bearings or loose components. Addressing these noises early can prevent more significant damage and ensure smoother functionality.
5. Odor Emissions: Foul odors can emanate from the unit due to mold or bacteria growth within the appliance. Regular cleaning and maintenance are essential to avoid such issues and ensure a pleasant environment.
By recognizing these common challenges and implementing proactive measures, users can enhance the efficiency and lifespan of their cooling appliances.