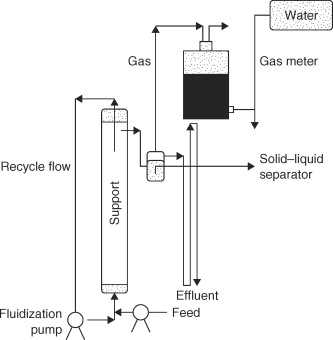
In the realm of utility management, precision in measurement is essential for both efficiency and safety. Analyzing the structure of these measurement devices reveals a complex interplay of various elements, each contributing to the overall functionality. By dissecting these components, one can gain valuable insights into how these instruments operate and maintain accuracy over time.
The inner workings of these devices consist of several key elements that work in tandem. Each segment plays a pivotal role in the overall process, from initiating the measurement to displaying the results. Understanding these individual segments not only enhances comprehension but also aids in troubleshooting and maintenance efforts.
As we delve deeper into this topic, we will explore each component’s function and importance. This examination will provide a clearer perspective on how these intricate systems function and their relevance in everyday applications, ultimately contributing to more informed usage and management practices.
Understanding Gas Meter Components
Comprehending the elements involved in the measurement of gaseous substances is crucial for ensuring accurate consumption tracking and system efficiency. Each component plays a significant role in the overall functionality and reliability of the measurement process. In this section, we will explore these elements and their contributions to effective monitoring.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Flow Sensor | Detects the volume of gas passing through, converting it into measurable data. |
| Pressure Regulator | Maintains a consistent pressure level, ensuring accurate readings and safe operation. |
| Display Unit | Shows the measured consumption in a user-friendly format for easy interpretation. |
| Valves | Control the flow direction and shut off the supply when necessary to ensure safety. |
| Sealing Mechanism | Prevents unauthorized access and tampering, preserving the integrity of the readings. |
Each of these elements contributes to a cohesive system, ensuring that monitoring and reporting are both precise and reliable. Understanding their individual functions helps users appreciate the complexities involved in accurate consumption measurement.
Overview of Gas Meter Functions
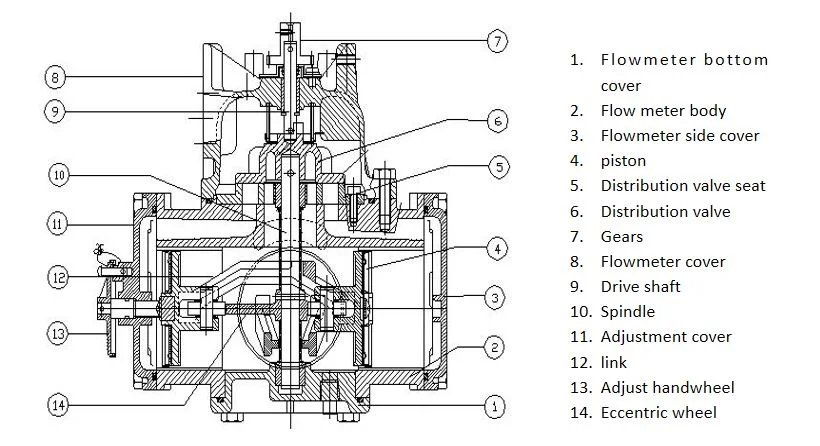
This section explores the essential roles played by devices that measure the flow of natural energy sources. Understanding these functions is crucial for efficient resource management and accurate billing.
- Measurement: These instruments quantify the volume of energy consumed over time.
- Monitoring: They track usage patterns, allowing users to identify trends and optimize consumption.
- Billing: Accurate readings ensure fair charges based on actual consumption.
- Safety: They detect irregularities, helping prevent potential hazards related to leaks or malfunctions.
In summary, these devices serve multiple functions that contribute to effective energy management, safety, and financial accuracy.
Main Parts of a Gas Meter
This section explores the essential components of a measurement device used for tracking the consumption of combustible fuels. Understanding these elements is crucial for both functionality and maintenance.
Key Components
- Measuring Chamber: This section captures the flow of the substance, allowing accurate readings.
- Indicator Dial: Displays the consumption level, providing real-time data.
- Inlet Valve: Regulates the entry of the substance into the device.
- Outlet Valve: Manages the exit flow, ensuring safety and efficiency.
Supporting Elements
- Seals: Ensure no leaks occur, maintaining integrity.
- Calibration Mechanism: Allows for precise adjustments to guarantee accuracy.
- Housing: Protects the internal components from environmental factors.
How Gas Measurement Works
This section explores the principles behind quantifying the flow of a particular substance through a system. Understanding these fundamentals is essential for various applications, including residential and industrial uses. Various components and technologies play crucial roles in ensuring accurate readings and efficient monitoring.
Key Principles of Measurement
- Flow Rate: The volume of the substance moving through a conduit per unit of time.
- Pressure: The force exerted by the substance, impacting the flow characteristics.
- Temperature: Influences density and can affect measurement accuracy.
Measurement Technologies
- Diaphragm Systems: Utilize flexible membranes to gauge flow through displacement.
- Ultrasonic Devices: Employ sound waves to calculate the velocity and subsequently the flow rate.
- Positive Displacement: Measure the volume by capturing discrete quantities of the substance.
Types of Gas Meters Available
Various instruments for measuring gaseous substances are essential for accurate consumption tracking and management. Each type serves distinct functions, catering to different needs in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
- Diaphragm Devices: These are commonly used in homes and small businesses. They operate by utilizing a flexible diaphragm that moves with pressure changes, allowing for precise readings.
- Rotary Units: Typically found in larger facilities, these devices use rotating mechanisms to measure flow, making them suitable for high-capacity applications.
- Ultrasonic Instruments: Known for their accuracy, these employ sound waves to determine flow rates. They are increasingly popular in industrial contexts where precision is paramount.
- Electronic Models: These advanced instruments provide digital readings and often come with smart features for remote monitoring and data analysis.
- Coriolis Flow Sensors: Highly precise, these sensors measure mass flow and are ideal for specialized applications in various industries.
Understanding the differences among these instruments is crucial for selecting the right one for specific requirements, ensuring efficiency and reliability in measurement.
Common Issues with Gas Meters
Understanding typical problems that can arise with measurement devices is essential for maintaining efficiency and safety. These issues can range from mechanical failures to inaccuracies in readings, which may lead to unexpected expenses or even hazards in usage.
Mechanical Failures
One of the most prevalent concerns involves wear and tear of internal components. Over time, moving parts can become damaged or obstructed, resulting in a failure to record consumption accurately. Regular maintenance can help mitigate these risks.
Inaccurate Readings
Another significant issue is the potential for erroneous readings, often caused by external factors like temperature fluctuations or pressure changes. Such inaccuracies can result in billing disputes or incorrect assessments of usage. It’s crucial to address these discrepancies promptly to ensure reliable performance.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Key reasons for consistent maintenance include:
- Enhanced safety by identifying potential risks early.
- Improved efficiency, leading to lower operational costs.
- Extended lifespan of equipment, delaying the need for replacements.
- Consistent performance, ensuring optimal functionality at all times.
To maximize benefits, consider implementing a regular maintenance schedule, which may include:
- Routine inspections and cleanings.
- Timely replacements of worn components.
- Documentation of maintenance activities for future reference.
Ultimately, regular maintenance not only safeguards your investment but also promotes a reliable and safe environment for all users.
Reading Your Gas Meter Accurately
Understanding how to measure your energy consumption effectively is crucial for managing household expenses and ensuring efficient usage. Accurate readings enable users to monitor their intake and detect any anomalies that may indicate a leak or malfunction.
To begin, familiarize yourself with the display features. Most models have a series of dials or digital indicators that showcase usage levels. It’s essential to note the reading correctly, as any oversight can lead to inaccurate billing.
When taking a reading from a dial-based system, start from the leftmost dial and move to the right, recording each number in sequence. If the pointer is between two numbers, always record the lower value to avoid overestimating your consumption. For digital displays, simply read the numbers as shown.
Regular monitoring can help you identify patterns in your usage, allowing for adjustments in behavior to conserve resources. Additionally, keep an eye out for any sudden spikes, which may indicate issues that need addressing.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure your readings are as precise as possible, contributing to better management of your energy resources and ultimately leading to more sustainable practices.
Safety Precautions for Gas Meters
Ensuring safety during the usage and maintenance of essential utility devices is crucial for preventing accidents and promoting efficiency. Adhering to proper protocols can minimize risks associated with leaks and malfunctions.
General Guidelines

- Regularly inspect for any visible signs of wear or damage.
- Ensure proper ventilation in areas where devices are installed.
- Do not block or obstruct any access points.
Emergency Procedures
- In case of a suspected leak, evacuate the area immediately.
- Do not use electrical switches or devices until the issue is resolved.
- Contact emergency services or a qualified technician for assistance.
Gas Meter Installation Guidelines
Proper setup of the measurement device is crucial for accurate monitoring and efficiency. Following systematic steps ensures that the installation process is seamless, safe, and compliant with regulations.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Choose an appropriate location, ensuring easy access and safety from environmental hazards. |
| 2 | Gather necessary tools and materials for a successful installation. |
| 3 | Carefully connect the device to the supply line, following manufacturer specifications. |
| 4 | Test for leaks using soapy water or a dedicated leak detection solution. |
| 5 | Verify functionality by monitoring readings to ensure accuracy and reliability. |
Adhering to these guidelines fosters safety and enhances the longevity of the equipment.
Regulatory Standards for Gas Meters
The implementation of specific guidelines ensures the accuracy and safety of measuring devices used in various industries. These regulations are designed to protect consumers and maintain consistency across different applications, fostering trust in the technology employed.
Importance of Compliance

Adhering to established norms is crucial for manufacturers and service providers. Compliance not only enhances reliability but also minimizes the risk of malfunctions, ensuring that consumers receive fair billing based on precise measurements.
International and Local Regulations
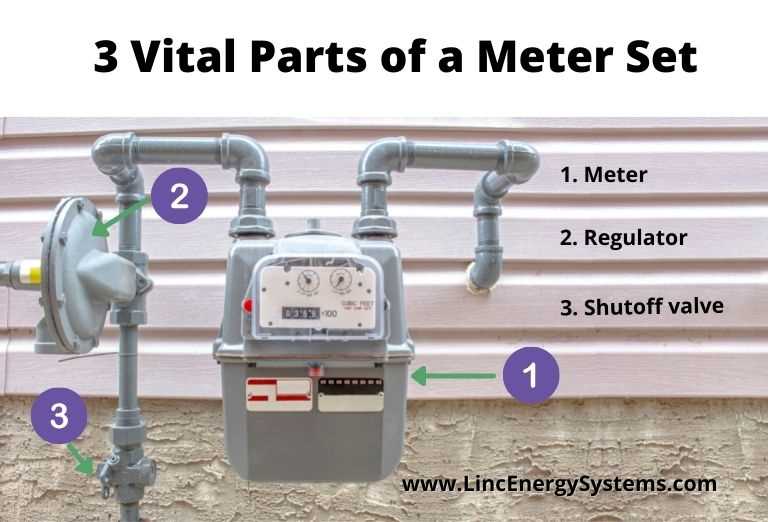
Different regions may enforce varying criteria, but most aim for high standards of performance and safety. Organizations such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and local regulatory bodies outline specific requirements, thereby creating a framework that industry players must follow.
Advancements in Gas Meter Technology
Recent developments in the realm of energy measurement have ushered in innovative solutions that enhance accuracy and efficiency. These advancements focus on integrating digital technologies and smart features, ultimately transforming how consumption is tracked and analyzed.
Smart Technologies Integration
Modern energy measurement devices now incorporate advanced sensors and connectivity features, enabling real-time monitoring. This shift towards smart technologies allows users to access data remotely, enhancing convenience and promoting energy-saving practices.
Improved Accuracy and Efficiency
Innovations in materials and design have led to more precise instruments that reduce error margins. With enhanced calibration methods, these devices ensure reliable readings, contributing to better resource management and reduced waste.
Future Trends in Gas Metering
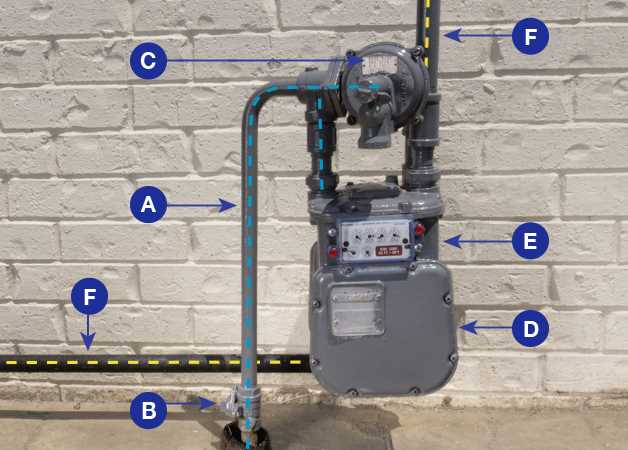

The evolution of measurement technology is set to transform the landscape of utility management. As industries increasingly focus on efficiency and sustainability, innovative solutions are emerging to enhance accuracy and data collection capabilities.
One significant trend is the integration of smart technology. The advent of IoT devices allows for real-time monitoring and automated data transmission, improving responsiveness to consumption patterns. This shift not only facilitates better resource management but also enables consumers to track usage more effectively, fostering awareness and promoting energy-saving practices.
Moreover, advancements in analytics are poised to play a crucial role in predictive maintenance and operational efficiency. Utilizing big data, organizations can anticipate issues before they arise, minimizing downtime and extending the lifespan of equipment. This proactive approach enhances reliability and reduces costs associated with unexpected failures.
Additionally, the move towards renewable energy sources is influencing measurement solutions. As diverse energy options become more prevalent, adaptive systems capable of handling various fuels will be essential. This flexibility will ensure that monitoring technologies remain relevant in an ever-changing energy landscape.
Lastly, regulatory frameworks are evolving to support innovative practices. With increasing emphasis on transparency and sustainability, new standards are likely to emerge, pushing companies to adopt more advanced monitoring techniques to comply with environmental goals.