
When it comes to mountain biking, having a clear understanding of your bicycle’s structure is essential for maintenance and performance. This section aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the essential elements that contribute to a well-functioning off-road bicycle. By familiarizing yourself with these components, you can ensure a smoother ride and extend the life of your equipment.
Every cyclist knows that the interplay between various elements significantly affects handling, stability, and overall enjoyment. From the frame that supports your weight to the wheels that carry you over rugged terrain, each part plays a vital role. Recognizing how these components fit together will empower you to make informed decisions when it comes to upgrades or repairs.
In the following sections, we will delve into the intricate details of these essential features. This knowledge not only enhances your riding experience but also helps you troubleshoot issues that may arise during your adventures. By understanding the functionality of each component, you’ll be better equipped to tackle the challenges of the trail.
Understanding the Giant Trance Design
The framework of a contemporary mountain bike plays a crucial role in determining its performance and overall riding experience. By examining the structural elements and engineering principles behind this specific model, riders can gain insights into its efficiency, stability, and adaptability on various terrains. This exploration will shed light on how the integration of innovative materials and design techniques enhances the biking experience.
Key Structural Elements
The architecture of this bike includes various components that work together to optimize functionality and durability. Each section is meticulously crafted to ensure that the bicycle can withstand rigorous use while providing a comfortable ride. Below are some of the essential features:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Frame | Provides support and stability, allowing for efficient power transfer during pedaling. |
| Suspension System | Absorbs shocks from rough terrain, enhancing comfort and control. |
| Wheels | Facilitates movement and provides traction on various surfaces. |
| Braking System | Ensures reliable stopping power, essential for safety on steep descents. |
Material Selection and Innovation
The choice of materials used in the construction of this model significantly impacts its performance and longevity. Manufacturers often prioritize lightweight yet robust materials to optimize speed and handling. Innovations in manufacturing processes allow for precision in creating components that meet rigorous standards, thereby enhancing the bike’s overall capability in diverse riding conditions.
Key Components of the Giant Trance
This section highlights the essential elements that contribute to the overall performance and functionality of the bike. Each component plays a significant role in ensuring a smooth and enjoyable riding experience, making it crucial to understand their features and benefits.
Frame and Suspension
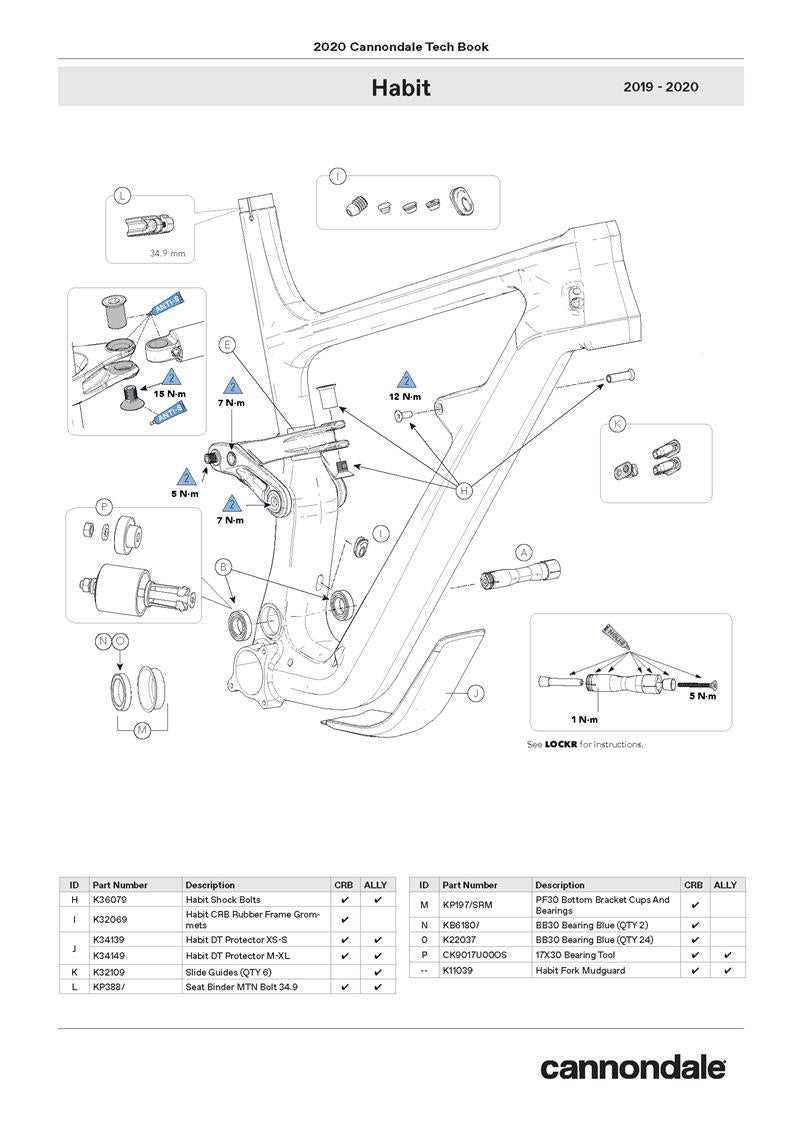
The foundation of any bike is its frame, which provides stability and support. The suspension system is vital for absorbing shocks, enhancing comfort, and improving handling. Key features include:
- Material: Common materials include aluminum and carbon fiber, each offering unique benefits in terms of weight and durability.
- Geometry: The design influences ride characteristics, including agility and stability on various terrains.
- Travel: Refers to the distance the suspension can compress, affecting comfort and performance on rough surfaces.
Drivetrain and Braking System
The drivetrain is responsible for transferring power from the rider to the wheels, while the braking system ensures safety and control. Important aspects include:
- Gearing: The choice of gears impacts the bike’s efficiency and adaptability to different inclines.
- Brakes: Options include hydraulic disc and mechanical brakes, each offering varying levels of stopping power and responsiveness.
- Chain and Crankset: These elements are essential for smooth pedaling and power transfer during rides.
Frame Structure and Materials

The framework of a bicycle plays a crucial role in its performance, stability, and overall ride quality. It serves as the backbone, supporting various components while ensuring structural integrity. Understanding the materials used in construction is essential for both durability and weight management, influencing the overall riding experience.
Typically, the frame is constructed from a variety of materials, each offering distinct advantages:
- Aluminum: Lightweight and resistant to corrosion, aluminum frames are popular for their balance of strength and weight. They provide good performance and are often more affordable than other materials.
- Carbon Fiber: Known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, carbon fiber offers a smooth ride due to its ability to absorb vibrations. This material is often favored by competitive riders for its performance benefits.
- Steel: Renowned for its durability and ease of repair, steel frames offer a classic ride quality. While heavier than aluminum or carbon fiber, they are often praised for their comfort and longevity.
- Ti (Titanium): This material combines lightweight characteristics with incredible strength. Titanium frames are resistant to corrosion and provide a unique ride feel, making them a premium choice for enthusiasts.
In addition to materials, the design of the frame is equally important. Key features to consider include:
- Geometry: The angles and lengths of the frame tubes influence handling and comfort, affecting how the bike responds to rider inputs.
- Tubing Diameter: Thicker tubes can enhance stiffness and strength, while thinner tubes often reduce weight, impacting overall performance.
- Welding Techniques: The method used to join frame components can affect both strength and aesthetics, with options ranging from traditional brazing to modern welding techniques.
Choosing the right combination of materials and design elements will ultimately define the riding characteristics and longevity of the bicycle, catering to various rider preferences and styles.
Suspension System Overview
The suspension framework of a bicycle is essential for providing stability and comfort during rides. It serves to absorb shocks from uneven terrain, ensuring that the rider maintains control and experiences minimal discomfort. A well-designed system enhances performance and allows for a smoother journey across various landscapes.
Typically, this mechanism comprises several components, including forks, shock absorbers, and linkages. Each element plays a vital role in managing the bicycle’s response to bumps and dips, ultimately influencing handling and speed. A correctly calibrated setup contributes significantly to both safety and enjoyment, making it crucial for any serious cyclist to understand its function and maintenance.
Moreover, advancements in technology have led to innovations in suspension systems, allowing for greater customization and improved efficiency. Riders can choose between various configurations, such as air or coil systems, based on their specific needs and riding styles. This flexibility enables enthusiasts to fine-tune their experience, optimizing performance for different conditions.
Brake Systems Explained
Understanding the mechanisms behind stopping a bicycle is essential for both safety and performance. The brake system is a critical component that ensures riders can halt their momentum effectively, providing control in various situations. Different types of braking technologies offer distinct advantages, catering to diverse riding styles and conditions.
Types of Brake Systems
There are several main categories of brake systems, each designed to meet specific needs:
- Disc Brakes: Known for their superior stopping power and modulation, disc brakes are favored in challenging terrain. They function using a rotor and caliper, allowing for consistent performance in wet conditions.
- Rim Brakes: These brakes operate by applying force to the outer rim of the wheel. While they are lighter and easier to maintain, their performance can be affected by weather conditions.
- Hydraulic Brakes: Utilizing fluid to transmit force, hydraulic systems provide smooth and powerful braking. They are often preferred for their responsiveness and ease of modulation.
- Cable-Actuated Brakes: These systems use cables to engage the brakes. They are generally simpler and more affordable, making them a popular choice for entry-level bicycles.
Key Components of Brake Systems
Regardless of the type, a brake system typically consists of several key components:
- Brake Levers: Located on the handlebars, these levers allow the rider to engage the brakes.
- Calipers: These are responsible for applying pressure to the braking surface, whether a rotor or rim.
- Brake Pads: The pads create friction against the rotor or rim, slowing down the wheel.
- Brake Cables or Hoses: In cable-operated systems, cables transmit the force from the levers to the calipers. In hydraulic systems, hoses carry the fluid that activates the brakes.
Gear and Drivetrain Configuration
The performance of a mountain bike is heavily influenced by its transmission system. This configuration determines how efficiently power is transferred from the pedals to the wheels, affecting speed, handling, and overall ride experience. A well-designed setup can enhance both climbing and descending capabilities, providing a balance between control and responsiveness.
Key components of this system include:
- Crankset: The primary assembly that converts pedal force into rotational movement.
- Chainrings: Attached to the crankset, they come in various sizes to adjust the gear ratio.
- Chain: The link that connects the crankset to the rear cassette, enabling movement across different gears.
- Derailleurs: Mechanisms that shift the chain between gears, allowing for smooth transitions and effective gear changes.
- Cassette: The cluster of sprockets at the rear wheel, providing multiple gearing options for different terrains.
When selecting components, consider the following factors:
- Gear Ratios: Higher ratios facilitate faster speeds on flat terrains, while lower ratios aid in climbing steep inclines.
- Durability: Components should withstand rough conditions and resist wear over time.
- Weight: Lighter components enhance overall bike performance, especially during uphill rides.
- Compatibility: Ensure that all components work seamlessly together to avoid mechanical issues.
Understanding these elements and how they interact is crucial for optimizing performance, tailoring the bike to individual riding styles, and ensuring an enjoyable experience on varied trails.
Wheel Size and Specifications
Understanding the dimensions and characteristics of wheels is essential for optimizing the performance and handling of a bicycle. The right wheel size not only affects the bike’s overall feel but also influences aspects such as stability, agility, and comfort during rides. Different models come with varying specifications to suit diverse terrains and riding styles.
When selecting the appropriate wheels for your ride, consider the following factors:
- Diameter: The wheel diameter is a crucial specification that impacts the bike’s rolling efficiency. Common sizes include 26″, 27.5″, and 29″. Each size has its advantages depending on the intended use.
- Width: The width of the rim plays a significant role in tire compatibility and overall ride quality. Wider rims can accommodate larger tires, enhancing traction and stability.
- Material: Wheel construction materials vary, affecting weight and durability. Common materials include aluminum and carbon fiber, each offering distinct performance benefits.
- Hub Type: The hub is central to wheel functionality. Options include quick-release and thru-axle designs, influencing ease of wheel removal and installation.
- Spoke Count: The number of spokes can affect wheel strength and weight. More spokes generally provide increased strength but can also add weight, while fewer spokes can reduce weight but may compromise durability.
Choosing the right specifications tailored to individual needs ensures an optimal cycling experience, whether for leisurely rides or challenging trails. Understanding these elements is key to making informed decisions about wheel selection and enhancing overall performance.
Handlebar and Stem Arrangement
The configuration of the handlebars and stem plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal control and comfort during rides. This setup significantly affects the rider’s posture and maneuverability, making it essential to choose the right dimensions and alignment based on personal preferences and riding style.
When arranging the handlebars and stem, several factors should be considered:
- Height: The height of the handlebars relative to the saddle influences back and shoulder positioning. Higher handlebars promote an upright position, while lower ones offer a more aggressive stance.
- Width: The width of the handlebars affects leverage and stability. Wider bars provide more control in rough terrain, while narrower options may enhance aerodynamics.
- Stem Length: The length of the stem can alter reach and handling. A longer stem increases distance to the handlebars, which can improve speed, while a shorter stem enhances maneuverability.
- Angle: The angle at which the stem is set can affect riding comfort. A positive angle elevates the handlebars, while a negative angle lowers them, influencing the rider’s center of gravity.
Adjusting these elements allows riders to fine-tune their setup, optimizing the bike for various terrains and personal preferences. Regular assessment and modifications may lead to improved performance and overall enjoyment during rides.
Seatpost and Saddle Features
The components that connect the rider to the frame play a vital role in overall performance and comfort. The design and functionality of these elements are essential for an enjoyable riding experience. An effective combination of these components enhances stability, allows for better weight distribution, and provides the necessary adjustability for different riding styles.
Seatpost Characteristics
- Material: Commonly made from aluminum or carbon fiber, each material offers unique benefits such as weight savings or enhanced durability.
- Adjustability: Many models feature a clamp mechanism that allows for easy height adjustments, accommodating various rider preferences.
- Diameter: Ensuring the correct diameter is crucial for a snug fit within the frame, which affects performance and comfort.
- Travel Options: Some posts are designed with internal mechanisms to provide adjustable travel, enabling greater control over riding dynamics.
Saddle Attributes
- Shape: Available in various shapes to cater to different riding styles and body types, affecting comfort and performance.
- Padding: Different levels of padding provide varying degrees of comfort; riders can choose between minimalist designs for efficiency and thicker padding for enhanced comfort on longer rides.
- Cover Material: Saddle covers are made from a range of materials, including synthetic fabrics and leather, impacting durability and grip.
- Rails: The saddle’s attachment mechanism often features steel or titanium rails that offer strength and weight advantages, contributing to overall performance.
Fork Options and Adjustments
Choosing the right suspension fork and making appropriate adjustments can significantly enhance the riding experience. Various factors, including terrain type, rider weight, and personal preferences, influence the decision-making process. Understanding the different features available allows cyclists to fine-tune their setup for optimal performance and comfort.
Types of Suspension Forks
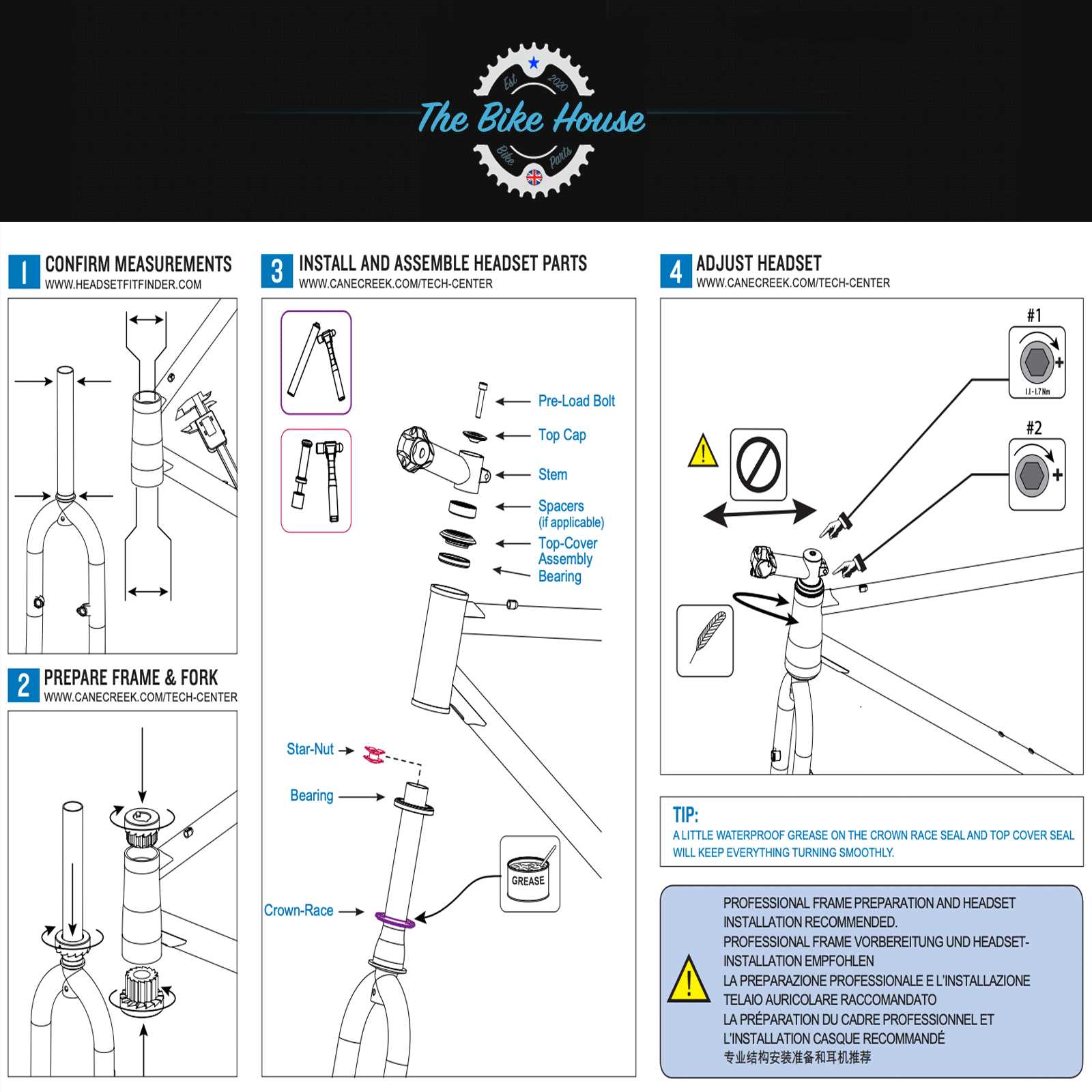
Suspension forks are generally categorized into two main types: coil and air. Coil forks utilize a spring mechanism that provides consistent performance, making them ideal for riders who prefer a plush feel. Conversely, air forks are lightweight and adjustable, offering the flexibility to adapt to varying conditions and rider weights. Selecting between these types depends on individual riding styles and the demands of specific trails.
Adjusting Your Fork

Proper adjustment of the suspension fork is crucial for achieving the desired balance between comfort and control. Key settings include preload, rebound, and compression. Preload affects the initial sag and ride height, while rebound controls the rate at which the fork returns after compression. Compression adjustments influence how the fork handles bumps and impacts. Riders should experiment with these settings to find the optimal configuration that suits their riding style and terrain.
Electrical Components in E-Mountain Bikes
Electric mountain bikes are equipped with a variety of electronic elements that enhance performance and user experience. These components work in harmony to provide power assistance, enabling riders to tackle challenging terrains with ease. Understanding the function and layout of these electrical systems is essential for anyone looking to maintain or upgrade their e-mountain bike.
Key Electrical Components
At the heart of any e-mountain bike is the battery, which stores energy and powers the motor. The capacity of the battery significantly impacts the bike’s range and performance. Another critical element is the motor, responsible for providing the necessary torque and speed. Different motor types, such as hub or mid-drive, can influence the bike’s handling and responsiveness.
Control Systems and Sensors
Control systems play a vital role in managing the power output of the motor. These systems often include a display unit, which allows the rider to monitor speed, distance, and battery level. Additionally, various sensors detect rider input and terrain conditions, enabling the bike to adjust its power delivery for optimal performance. Together, these components create a seamless riding experience, blending human effort with electric assistance.
Maintenance Tips for Giant Trance Parts
Regular upkeep of your bicycle’s components is essential for optimal performance and longevity. Proper care not only enhances the ride quality but also prevents potential issues that could arise from neglect. Below are some effective strategies to maintain your bike’s features.
- Inspect Regularly: Frequently check your bicycle for any signs of wear and tear. Look for frayed cables, worn tires, and loose bolts.
- Clean Components: Use a gentle cleaner and a soft cloth to wipe down frames, gears, and brakes. Regular cleaning helps prevent dirt buildup that can cause damage.
- Lubricate Moving Parts: Apply lubricant to the chain, derailleurs, and pivot points to ensure smooth operation. Avoid over-lubricating, as excess can attract dirt.
- Adjust Brakes and Gears: Ensure that brakes engage properly and that gears shift smoothly. Regular adjustments can improve performance and safety.
- Check Tire Pressure: Maintain the correct tire pressure for optimal traction and comfort. Under-inflated tires can lead to poor handling and increased wear.
- Inspect Wheel Alignment: Ensure that wheels are properly aligned to prevent uneven wear and handling issues. Regularly check for any wobbling or misalignment.
- Store Properly: Keep your bike in a dry and secure location. Avoid exposure to harsh weather conditions that can accelerate wear.
By following these maintenance tips, you can extend the life of your bicycle’s components and ensure a smooth and enjoyable riding experience.
Aftermarket Upgrades and Modifications

Enhancing the performance and aesthetics of your mountain bike can significantly elevate your riding experience. By incorporating aftermarket components, cyclists can tailor their bicycles to better suit their personal preferences and riding styles. This section explores popular enhancements and adjustments that can be made to improve functionality, comfort, and visual appeal.
One of the most sought-after modifications is upgrading the suspension system. Enhanced shocks can provide better control and comfort, especially on rugged terrains. Additionally, replacing standard wheels with lighter and more durable options can lead to improved handling and acceleration. Other noteworthy upgrades include fine-tuning the drivetrain for smoother gear shifts and better efficiency.
| Upgrade Type | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Suspension System | Upgrading to high-performance shocks and forks. | Improved control and comfort on rough trails. |
| Wheels | Switching to lightweight and durable rims and tires. | Better handling and faster acceleration. |
| Drivetrain | Enhancing gears and derailleurs for smoother operation. | Increased efficiency and reliability. |
| Brakes | Installing hydraulic disc brakes for superior stopping power. | Enhanced safety and control during descents. |
| Handlebars | Replacing with wider or adjustable options for comfort. | Improved ergonomics and handling precision. |
Incorporating these enhancements not only improves the bike’s performance but also allows riders to express their individuality through unique components. With the right modifications, cyclists can enjoy a personalized riding experience that caters specifically to their needs.