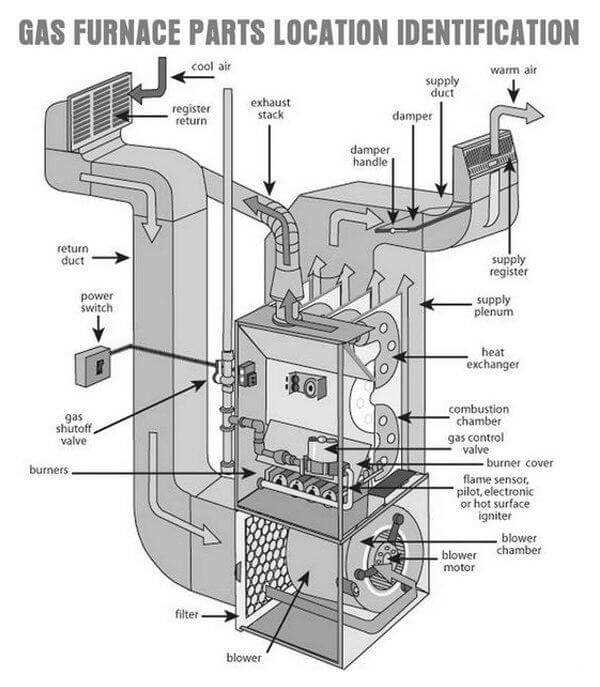
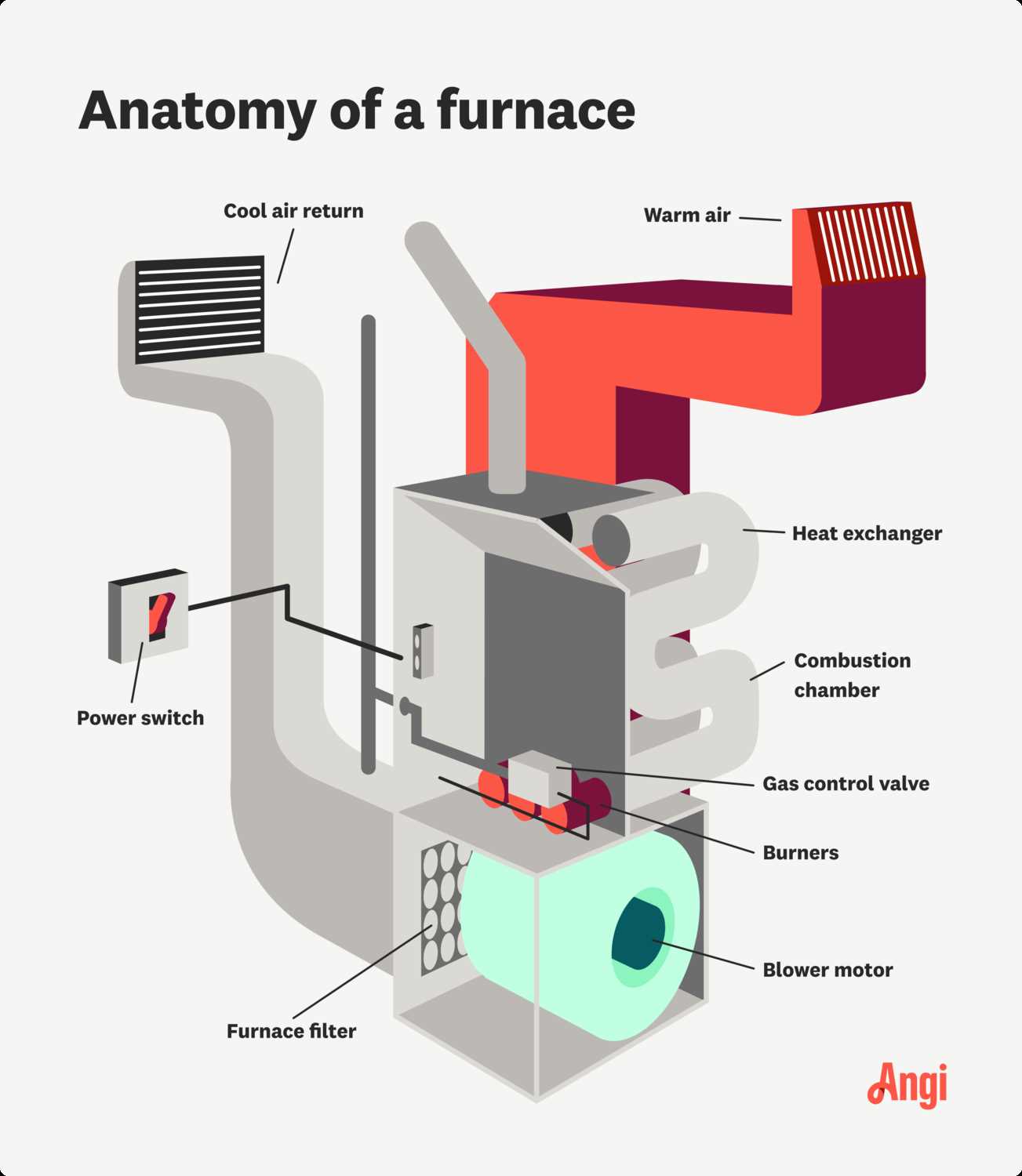
The design and functionality of modern home heating systems rely on a combination of advanced mechanisms that work together to ensure optimal comfort. These systems are composed of various interconnected elements, each playing a crucial role in maintaining indoor temperature and air quality. By recognizing the purpose of each section, homeowners can better appreciate how these systems provide warmth during cold months.
In this guide, we will explore the essential elements that form the core of heating units. Each component has been carefully designed to work in harmony, ensuring both safety and energy conservation. Knowing how these elements interact can help in troubleshooting and maintaining a reliable and effective heating system.
As we delve deeper, a clearer picture will emerge of how different sections collaborate to generate and distribute warmth. Whether you’re looking to enhance system performance or perform basic maintenance, understanding these components is key.
Key Components in a High-Efficiency Furnace
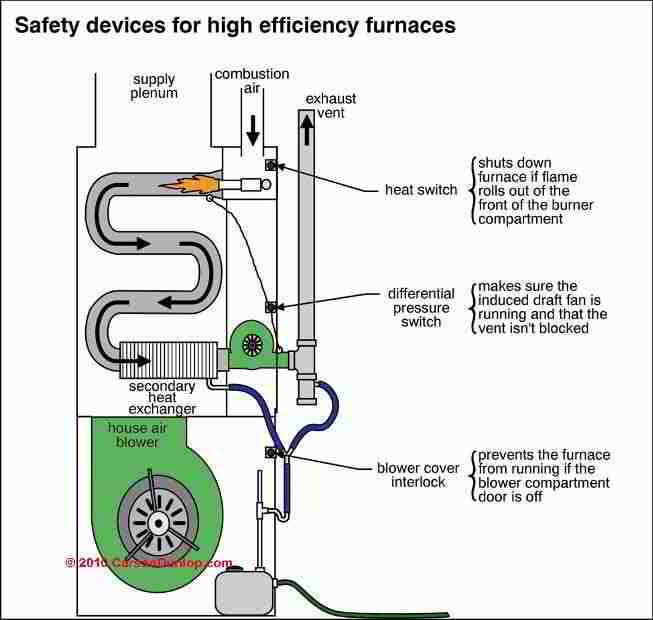
The system designed for optimal indoor heating relies on a set of specialized elements working together to ensure consistent performance and reduced energy consumption. Understanding the core pieces that make up this type of equipment is crucial for both effective maintenance and ensuring long-term durability.
Burner Assembly
The burner is where the ignition process begins, combining fuel with air to produce the heat necessary for the overall system. Proper maintenance of the burner ensures stable heating and efficient energy usage.
Blower Motor
The blower is responsible for distributing warm air throughout the living space. It ensures that heated air moves evenly across all rooms, contributing to a comfortable indoor environment.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Heat Exchanger | Transfers generated warmth to the air without mixing gases. |
| Inducer Motor | Removes exhaust gases, ensuring clean and safe operation. |
| Thermostat | Controls temperature, ensuring the system runs as needed. |
Understanding the Role of the Heat Exchanger
The heat exchanger is a vital component in many heating systems, responsible for transferring warmth from the energy source to the air or water that circulates through your home. This process allows the system to effectively generate and distribute heat while ensuring safety and efficiency.
To better understand its operation, it is important to explore its key functions:
- Heat Transfer: The primary job of the heat exchanger is to capture warmth and pass it on to the air or fluid that will be distributed throughout the space.
- Maintaining Safety: It acts as a barrier, preventing harmful gases from mixing with the air supply, ensuring a safe environment.
- Durability and Material Choice: Heat exchangers are often made from metals that withstand high temperatures, ensuring long-term performance.
In summary, the heat exchanger is a crucial component that ensures warmth is efficiently delivered while protecting the safety and reliability of the system.
Blower Motor Function and Efficiency
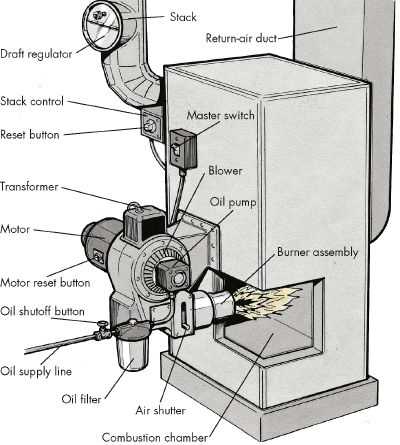
The blower motor plays a crucial role in regulating airflow within heating systems. It ensures that warm air circulates evenly through the vents, maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature. This component is designed to operate efficiently, providing consistent performance with minimal energy use.
Reliable airflow control is essential for the overall performance of any heating system. The motor adjusts the speed and intensity of air movement, responding to the specific needs of the system. This helps to optimize air distribution and prevent any uneven heating throughout the space.
Furthermore, the blower motor contributes to the longevity of the system. By maintaining consistent airflow, it reduces the strain on other components, ensuring a longer operational life and minimizing potential repairs. Proper maintenance and timely replacement of this part can prevent future issues.
The Importance of the Furnace Control Board
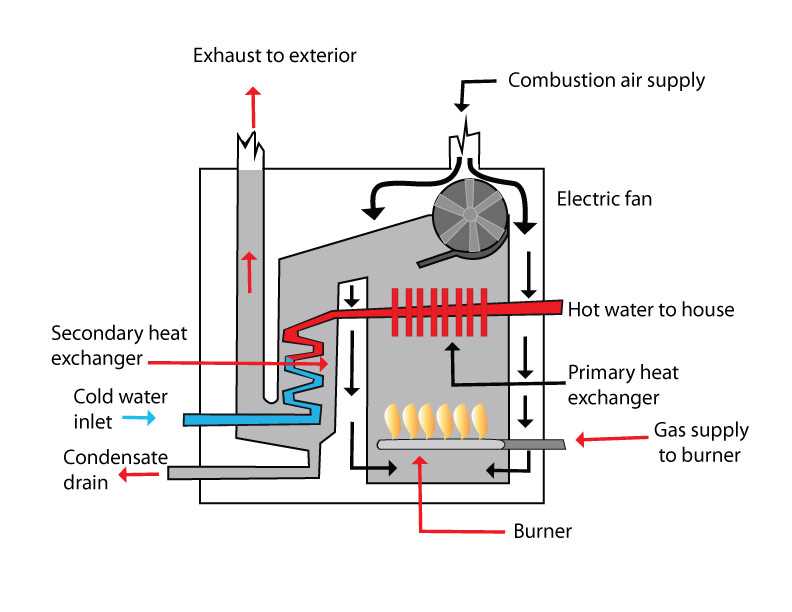
The control board plays a central role in ensuring smooth and coordinated operation of various components in heating systems. Acting as the “brain” behind the system, it manages and regulates processes to ensure safety and performance, preventing malfunctions and ensuring reliability.
How the Control Board Manages Operations
- It monitors input from various sensors to make real-time adjustments.
- The board coordinates the ignition, blower fan, and gas valve operation.
- It ensures that all safety features are working as intended.
Why It’s Essential for System Longevity
- Reduces the wear and tear of individual components by managing their use efficiently.
- Prevents potential failures by detecting early issues through built-in diagnostics.
- Improves energy use by optimizing the system’s runtime based on conditions.
Inducer Motor: How It Works
The inducer motor plays a crucial role in maintaining proper airflow and ensuring optimal operation within heating systems. It drives the movement of air through the venting system, preparing the way for combustion by clearing out any lingering gases. This component ensures that the process is safe and efficient, providing consistent operation throughout its cycle.
Key Function of the Inducer Motor
Once activated, the motor generates a strong draft, drawing air from the system into the exhaust vent. This process prevents harmful gases from lingering, creating a safe environment for the combustion chamber to ignite. Without this airflow, the ignition process would be compromised, potentially leading to dangerous conditions.
Role in System Performance
The performance of the entire system heavily depends on the inducer motor. By ensuring the proper removal of gases, it enables smoother and more reliable operation. Regular maintenance of this motor can prevent breakdowns and improve the longevity of the overall heating system.
How Flame Sensors Ensure Safety
Flame sensors play a critical role in maintaining the safe operation of heating systems. These devices detect the presence of a flame and ensure that combustion occurs properly. If a flame goes out unexpectedly, the sensor triggers safety measures to prevent potential hazards, such as gas leaks or explosions.
When the heating mechanism is activated, the flame sensor monitors the combustion process. In the event that the flame is extinguished, the sensor sends a signal to the control system, which promptly shuts off the gas supply. This immediate response is vital for preventing dangerous situations, thereby safeguarding both equipment and occupants.
Regular maintenance of flame sensors is essential for optimal performance. Accumulation of dirt or corrosion can hinder their functionality, leading to false readings. Ensuring that these sensors are clean and properly calibrated not only enhances safety but also contributes to the overall effectiveness of the heating system.
Gas Valve Mechanism in Modern Furnaces

The gas control system is a vital component in contemporary heating appliances, ensuring safe and efficient operation. This mechanism plays a critical role in regulating the flow of fuel to the burner, directly impacting the heating performance and safety of the unit. Understanding its functionality and design can provide insights into how these systems maintain optimal conditions within the heating device.
Functionality and Operation
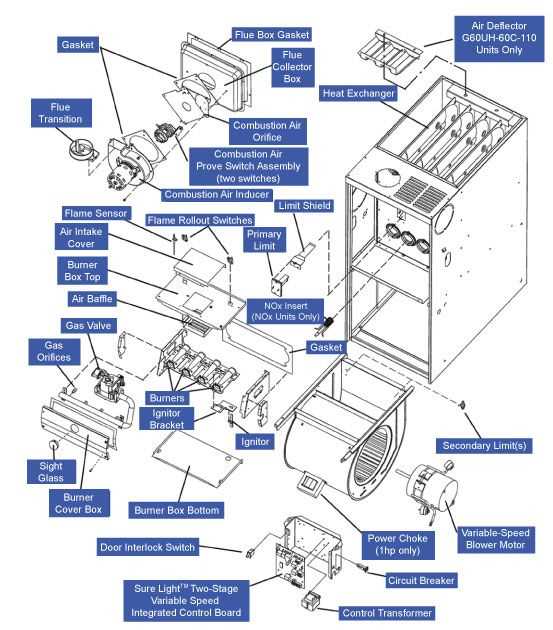
The operation of the gas control assembly involves a series of precise steps. When the thermostat signals the need for warmth, the control unit activates the valve, allowing gas to flow to the burner. Sensors within the system monitor pressure and temperature, ensuring that the right amount of fuel is delivered. This automated process enhances safety by preventing gas leaks and ensuring that combustion occurs only when necessary.
Types of Gas Control Valves
There are several varieties of gas valves used in modern heating systems, each designed for specific applications. Electronic valves provide quick response times and enhanced safety features, while mechanical valves may offer simplicity and reliability. Regardless of the type, all valves must comply with rigorous safety standards to prevent hazardous situations.
In summary, the gas control system is essential for the safe and efficient operation of heating devices. By understanding its mechanisms, users can appreciate the importance of regular maintenance and the role it plays in overall performance.
Pressure Switch: A Crucial Safety Feature
A pressure switch serves as a vital component in heating systems, ensuring safe operation by monitoring the pressure levels within the system. This device plays an essential role in preventing potential hazards that could arise from improper functioning or malfunctions. By responding to changes in pressure, it helps maintain optimal performance while safeguarding against risks.
When the pressure within the system deviates from the normal range, the pressure switch activates, signaling the system to shut down or take corrective action. This feature is particularly important in avoiding dangerous conditions that could lead to system failures or accidents. Understanding the significance of this safety mechanism contributes to better maintenance practices and overall system reliability.
Regular inspections and prompt replacements of faulty pressure switches are crucial for sustaining the safe operation of heating units. By ensuring that this component is functioning correctly, users can enjoy a dependable and secure heating experience, ultimately prolonging the lifespan of the entire system.
Thermostat Connection to Furnace Operation
The interaction between the temperature control unit and the heating system is essential for maintaining a comfortable indoor environment. Properly establishing this connection allows for efficient regulation of heat output, ensuring that the living space remains at the desired temperature. Understanding the role of the control unit in this process is crucial for effective system operation.
Key Components of the Connection
- Thermostat: This device measures the ambient temperature and sends signals to the heating unit when adjustments are necessary.
- Wiring: Conductors that transmit signals between the control unit and the heating mechanism.
- Control Board: The central unit that interprets the thermostat’s signals and regulates the operation of the heating system.
Steps for Connecting the Control Unit
- Ensure that power to the system is turned off for safety.
- Identify the appropriate terminals on both the control unit and the heating mechanism.
- Connect the wires according to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Secure all connections and restore power to the system.
- Test the system to confirm that the control unit is functioning correctly and communicating with the heating unit.
By following these steps, the connection can be established effectively, allowing for optimal performance of the heating system while maintaining a comfortable atmosphere within the space.
Air Filter Placement and Maintenance Tips
Proper positioning and upkeep of air filtration systems are essential for optimal performance and longevity of heating units. Ensuring that filters are correctly placed allows for maximum airflow while effectively trapping dust and debris, which can otherwise hinder functionality. Regular attention to these components can significantly enhance the overall atmosphere within your space.
Placement Considerations: When installing air filters, ensure they are oriented in the correct direction. Most filters have arrows indicating the intended airflow. Installing them backwards can lead to restricted air movement and decreased performance. Additionally, consider the location of your system; filters should be easily accessible for maintenance without obstructing other components.
Maintenance Guidelines: Routine checks and replacements of air filters are crucial for sustaining a clean environment. It is recommended to inspect filters monthly and replace them at least every three months, or more frequently if you have pets or allergies. Cleaning reusable filters according to the manufacturer’s instructions can also prolong their lifespan while maintaining air quality.
Conclusion: Proper placement and diligent maintenance of air filtration systems can lead to improved air quality and system efficiency. By following these tips, you can ensure that your heating apparatus operates smoothly and effectively, providing comfort in your living space.
Understanding the Role of Ignitors
Ignitors play a crucial role in the operation of heating systems by ensuring the efficient and reliable ignition of fuel. These components are essential for initiating combustion, which is vital for the generation of heat within the system. Without a properly functioning ignitor, the heating mechanism may fail to start, leading to inefficiencies and potential system malfunctions.
There are various types of ignitors utilized in heating appliances, each designed to suit specific operational needs. The following table outlines the common types of ignitors and their characteristics:
| Type | Description | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Hot Surface Ignitor | Made from ceramic materials, it glows red when heated to ignite the fuel. | Common in modern heating systems. |
| Intermittent Pilot Ignitor | Uses a small flame to ignite the main burner when needed. | Often found in older models. |
| Direct Ignition | Ignites the gas directly with a spark when the system is activated. | Typically used in high-efficiency units. |
Understanding the function and types of ignitors can help in maintaining and troubleshooting heating systems effectively. Regular inspections and timely replacements can prevent costly repairs and ensure a steady supply of warmth during colder months.
Condensate Drain Systems Explained
The management of byproducts generated during the combustion process is a crucial aspect of modern heating appliances. Properly designed drainage solutions are essential to prevent water damage and ensure the system operates optimally. These systems effectively handle the condensation that accumulates, diverting it away from sensitive components and maintaining efficiency.
Components of a condensate drainage system typically include a drain line, a pump, and a reservoir. The drain line channels the condensate away from the unit, while the pump assists in moving the water to a designated disposal area when gravity alone isn’t sufficient. The reservoir collects any excess fluid, ensuring that the system doesn’t overflow.
Regular maintenance of these systems is vital to avoid blockages and ensure smooth operation. Clogs can lead to water backing up, causing potential leaks and damage to the appliance and surrounding areas. Therefore, periodic inspections and cleanings can prolong the lifespan of the system and enhance overall performance.
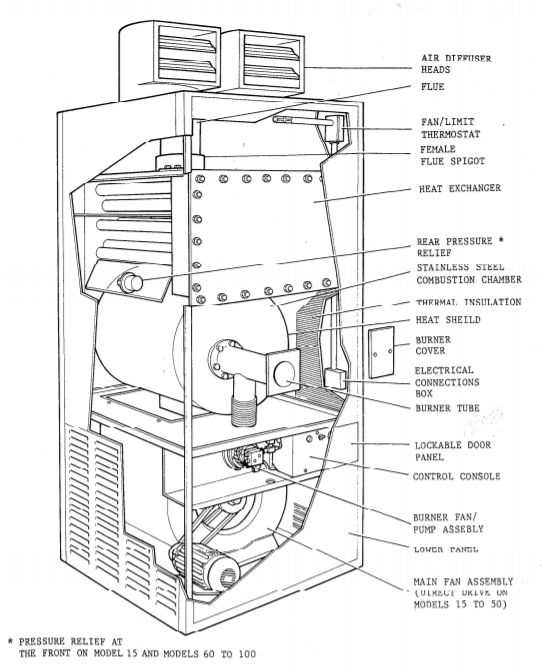
Flue Pipe: Ventilation and Safety
The flue pipe plays a critical role in the safe operation of heating appliances, ensuring that harmful gases are effectively expelled from the living space. Proper ventilation is essential not only for the performance of the system but also for the safety of the occupants. A well-designed flue system mitigates the risks associated with the buildup of toxic emissions, creating a safer indoor environment.
Importance of Proper Ventilation
Effective ventilation helps maintain optimal airflow, preventing any backdrafts that could lead to gas leakage. The design of the flue pipe must comply with local codes and regulations to guarantee safe exhaust. Regular inspection and maintenance are vital to ensure that there are no obstructions, such as debris or animal nests, which could hinder the flow of exhaust gases.
Safety Considerations
Safety is paramount when it comes to the installation and upkeep of the flue pipe. Proper sealing and insulation are necessary to avoid heat loss and potential hazards. Installation should be performed by qualified professionals to meet safety standards and ensure reliable operation. Regular checks for corrosion and wear will extend the lifespan of the system and enhance the overall safety of the heating solution.