In the realm of human biology, the intricacies of female physiology play a crucial role in health and well-being. A comprehensive exploration of these structures not only enhances knowledge but also promotes awareness regarding reproductive health and personal care.
Visual representations serve as effective tools for understanding the complex relationships between various systems. By examining these illustrations, individuals can delve deeper into the unique features and functions that define female anatomy.
Ultimately, gaining insight into this subject fosters empowerment, enabling individuals to make informed decisions about their health and lifestyle. Through education and awareness, we can break down barriers and encourage open conversations about women’s health.
Understanding Female Anatomy
The intricacies of female physiology encompass a variety of structures and systems that play crucial roles in overall health and reproductive function. A comprehensive understanding of these elements can enhance awareness and contribute to well-being. This section aims to explore the fundamental components that define the female form, focusing on their significance and interrelationships.
Key Structures
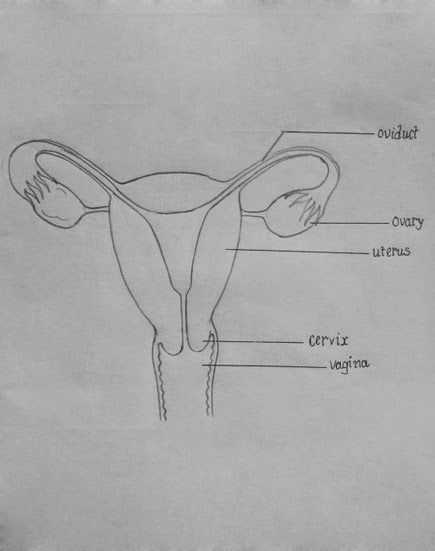
- Reproductive System: This complex system includes organs that are essential for reproduction, such as the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, and vagina.
- Endocrine System: Hormones produced by glands like the ovaries and pituitary are vital for regulating various bodily functions, including the menstrual cycle.
- Pelvic Floor: A group of muscles that support the pelvic organs and play a key role in bladder and bowel control.
Health Considerations
- Regular Check-Ups: Routine examinations can help detect any irregularities early.
- Understanding Menstrual Health: Awareness of menstrual cycles can provide insight into overall health.
- Pelvic Health: Exercises aimed at strengthening pelvic muscles can improve support for internal organs.
Understanding the complexity of these anatomical features empowers individuals to take charge of their health and fosters a deeper appreciation for the female body.
Overview of Reproductive System
The reproductive system is a complex network essential for procreation, encompassing various organs that work in harmony to facilitate the continuation of species. This system not only plays a critical role in reproduction but also influences hormonal balance and overall health.
Major Components
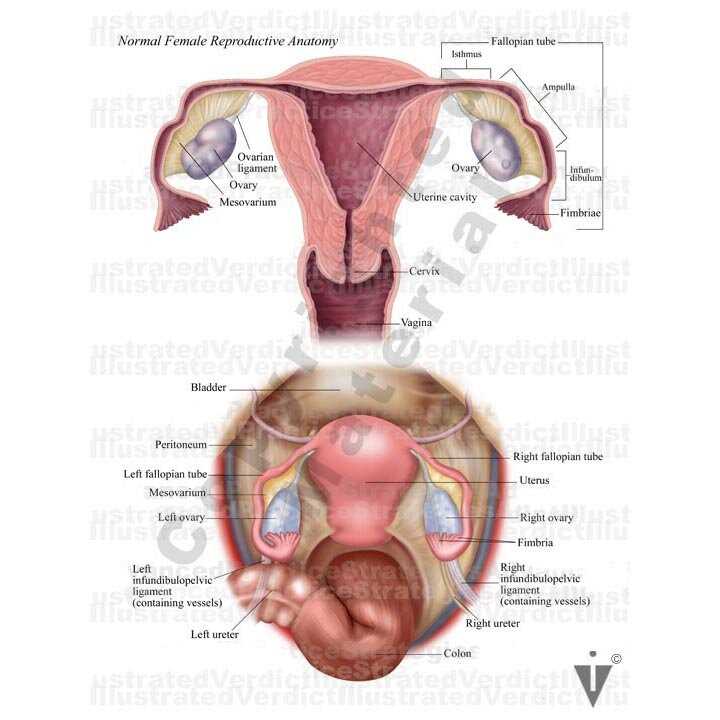
Key elements of this system include the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, and vagina, each serving distinct functions. The ovaries produce eggs and hormones, while the uterus provides a nurturing environment for a developing embryo.
Functions and Processes
During the menstrual cycle, the body prepares for potential fertilization. If this does not occur, the cycle resets, demonstrating the system’s dynamic nature. Understanding these functions allows for a deeper appreciation of human biology and the intricate mechanisms at play.
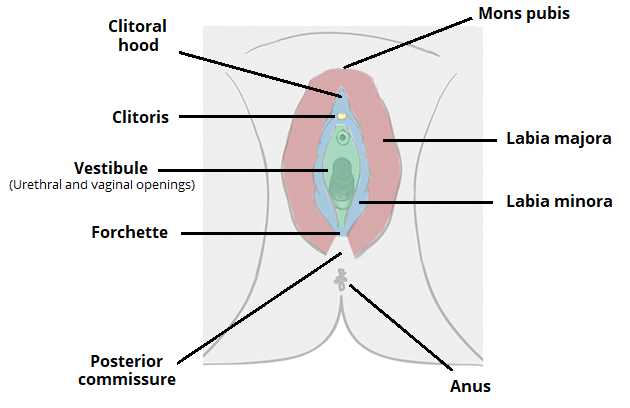
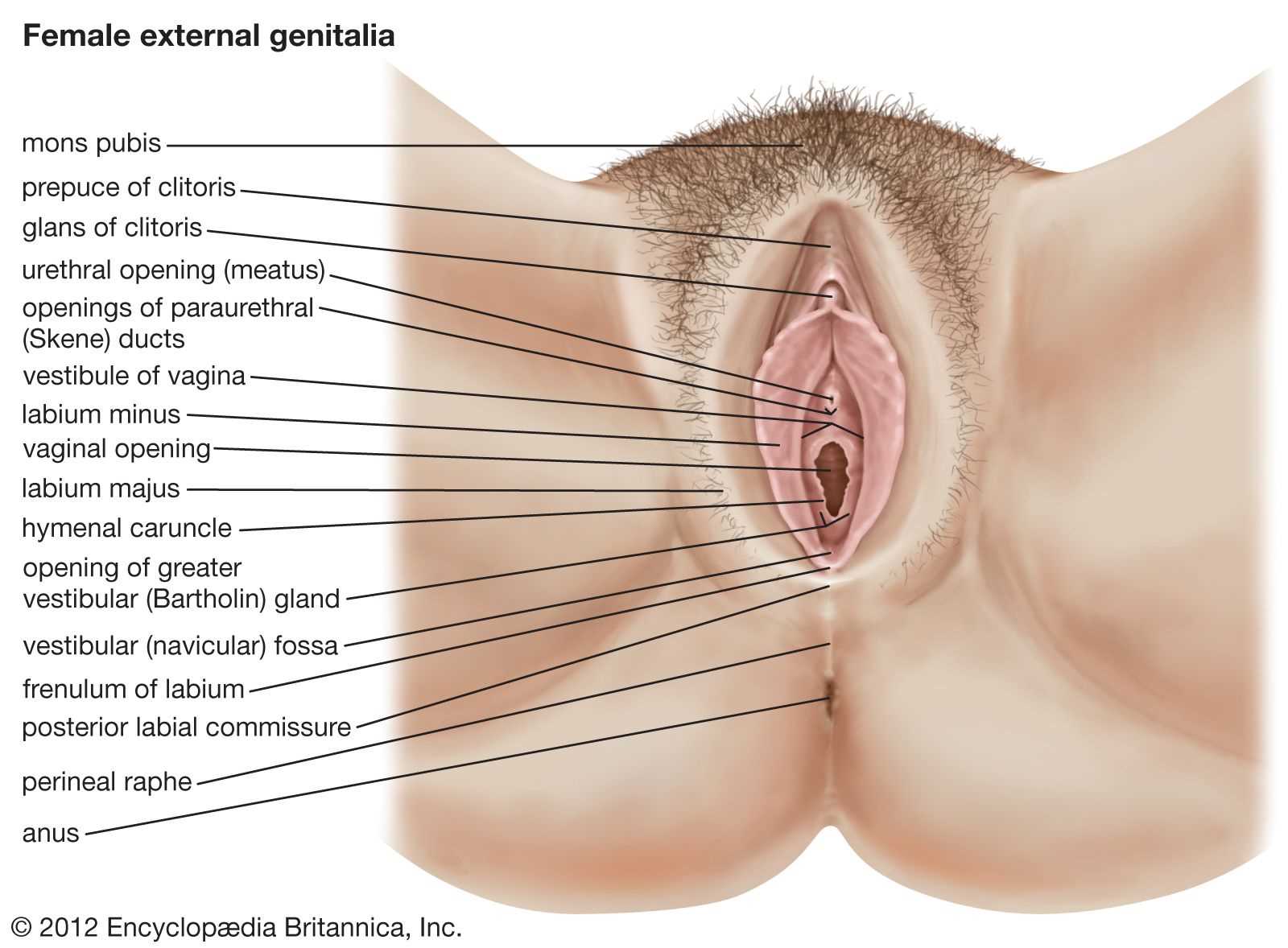
Anatomy of the Vulva
The external female genitalia play a vital role in sexual and reproductive health. Understanding this area is essential for recognizing its functions and maintaining overall well-being. Various components contribute to its structure and significance in human biology.
Key Structures
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Labia Majora | The outer folds of skin that protect the inner structures. |
| Labia Minora | The inner folds that surround the vaginal opening and urethra. |
| Clitoris | A highly sensitive organ crucial for sexual pleasure. |
| Vaginal Opening | The entry point to the vaginal canal. |
Functions and Importance
This region serves multiple purposes, including protection, sensation, and involvement in sexual response. A thorough comprehension of its anatomy can empower individuals in their health journeys.
Function of Ovaries Explained
The ovaries play a crucial role in the reproductive system, serving as the primary organs responsible for producing essential hormones and gametes. These structures are vital for maintaining overall hormonal balance and facilitating the processes of conception and menstruation.
Hormone Production: Ovaries secrete hormones such as estrogen and progesterone, which regulate the menstrual cycle, support pregnancy, and influence various physiological functions.
Gamete Production: They also generate ova, the female gametes, through a process known as oogenesis. This is essential for reproduction and occurs in a cyclical manner, typically releasing one egg per menstrual cycle.
Overall, the proper functioning of the ovaries is indispensable for female health, impacting not only reproduction but also other aspects of well-being.
Role of Fallopian Tubes
The fallopian tubes are essential conduits within the female reproductive system, facilitating the journey of the ovum and sperm. They play a pivotal role in the early stages of conception and are crucial for successful reproduction.
Transportation of Gametes
These tubes serve as the primary passage for the egg to travel from the ovaries to the uterus. During ovulation, an egg is released and captured by the fimbriae at the end of the tube, ensuring it moves toward potential fertilization.
Site of Fertilization
Beyond mere transportation, the fallopian tubes are the ultimate location where fertilization typically occurs. The union of sperm and egg within this environment sets the stage for embryo development, highlighting the tubes’ importance in reproductive health.
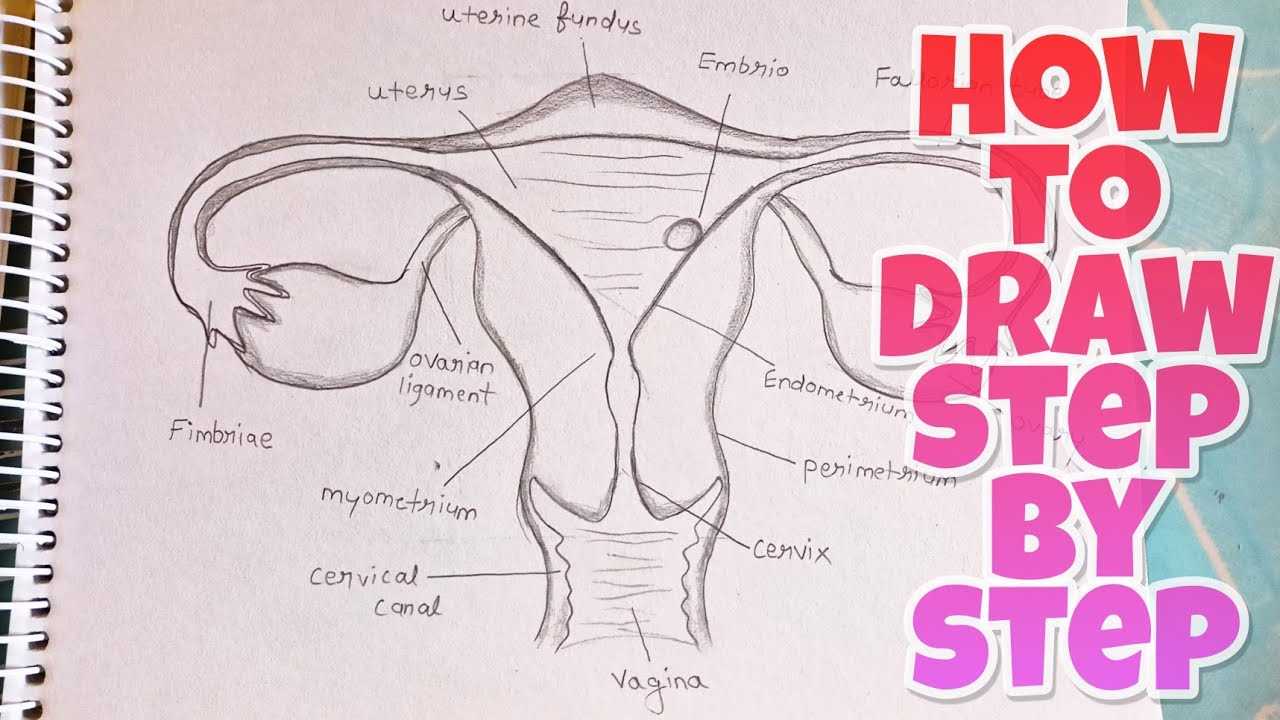
Insights on the Uterus
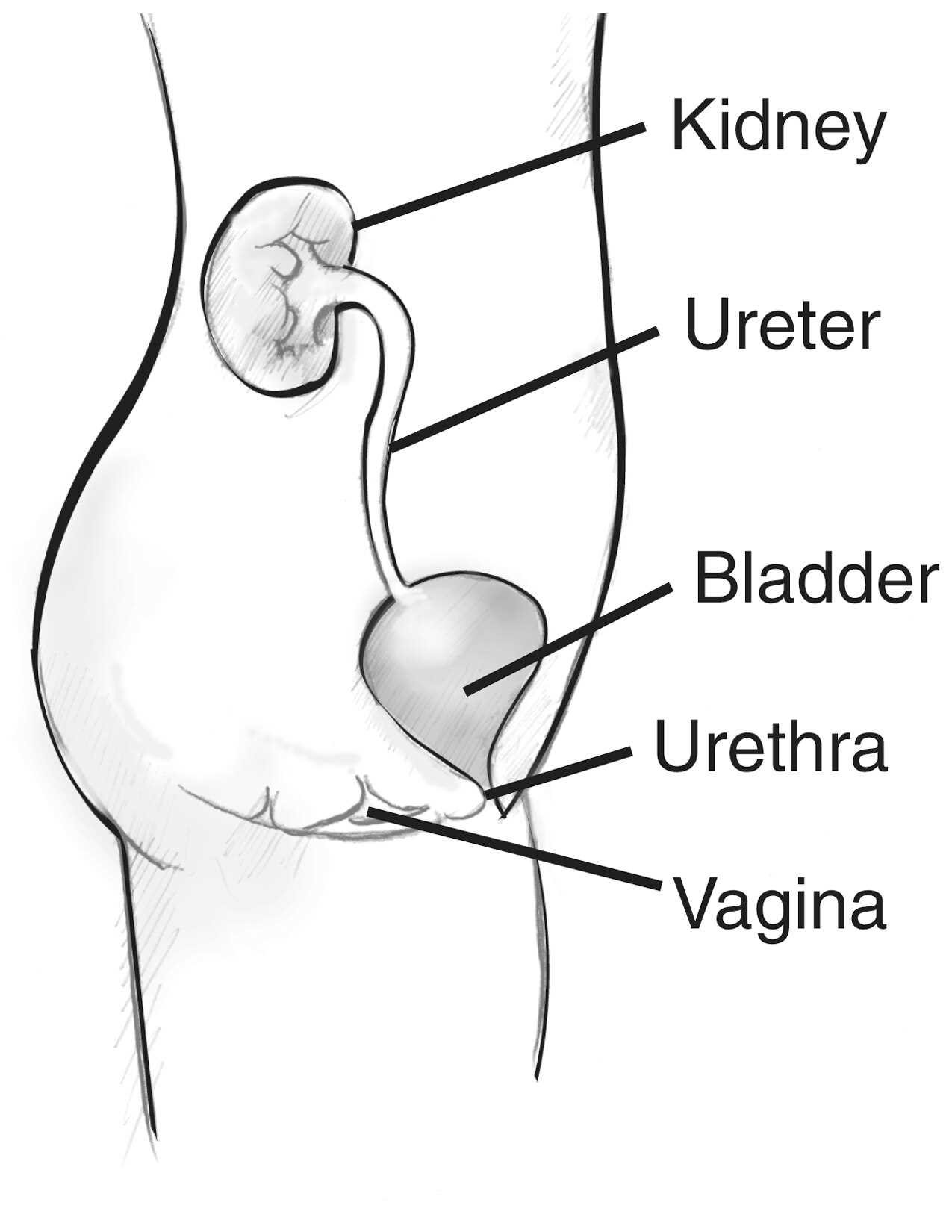
The uterus plays a vital role in reproductive health, serving as a central organ in various biological processes. Understanding its functions and structure can enhance awareness of overall well-being and health practices.
Structure and Function
This organ is characterized by several key features:
- Layers: Composed of the endometrium, myometrium, and perimetrium.
- Location: Positioned in the pelvic cavity, it is supported by ligaments.
- Role in Reproduction: Houses and nourishes a developing fetus during pregnancy.
Common Conditions
Various conditions can affect the uterus, including:
- Fibroids: Noncancerous growths that can cause discomfort.
- Endometriosis: A condition where tissue similar to the lining grows outside the uterus.
- Cancer: Uterine cancer can manifest in different forms and requires timely detection.
Cervix: Its Importance in Reproduction
The cervix plays a vital role in the reproductive system, acting as a gateway between different anatomical structures. Its function is crucial for several processes that contribute to fertility and the overall health of the reproductive system.
Here are some key functions of the cervix in reproduction:
- Barrier Function: The cervix serves as a protective barrier, regulating the passage of sperm into the uterus and preventing the entry of harmful pathogens.
- Mucus Production: Cervical mucus changes throughout the menstrual cycle, facilitating or hindering sperm movement depending on fertility signals.
- Support During Pregnancy: The cervix maintains its closed position during pregnancy, providing essential support to the developing fetus and preventing premature labor.
- Dilation During Labor: The cervix undergoes significant changes during childbirth, dilating to allow the passage of the baby.
Understanding the cervix’s functions highlights its importance in reproductive health and fertility. Any abnormalities or conditions affecting this structure can have significant implications for conception and pregnancy outcomes.
Vagina: Structure and Function
The vagina is a complex organ that plays a crucial role in female anatomy and health. It serves multiple purposes, including sexual reproduction, menstruation, and childbirth. Understanding its structure helps to appreciate its functions and significance in the reproductive system.
Anatomically, the vagina is a muscular tube that connects the external genitalia to the uterus. Its elasticity allows it to accommodate various activities, such as intercourse and the passage of a baby during delivery. The walls of this organ are lined with mucous membranes that maintain a balanced environment, supporting overall health.
Functionally, the vagina acts as a passageway for menstrual fluids and a receptacle for sperm during intercourse. Additionally, it plays a protective role by acting as a barrier against infections. The interplay between its structure and function highlights its importance in reproductive health and overall well-being.
Menstrual Cycle Overview
The menstrual cycle is a complex physiological process that plays a vital role in reproductive health. This cycle involves various hormonal changes that prepare the body for potential pregnancy, marking distinct phases with specific characteristics and functions.
Phases of the Cycle
The cycle is typically divided into several key stages: the follicular phase, ovulation, and the luteal phase. Each phase is orchestrated by hormonal fluctuations, influencing everything from mood to physical well-being.
Hormonal Regulation
Hormones such as estrogen and progesterone are crucial in regulating the cycle. During the follicular phase, estrogen levels rise, promoting the growth of follicles, while progesterone surges post-ovulation, preparing the lining of the uterus for a potential implantation.
Common Disorders of Female Anatomy
Understanding the various conditions that can affect the female reproductive system is crucial for maintaining health and well-being. These disorders can range from minor issues to significant health concerns, impacting quality of life and reproductive capabilities. Awareness of these conditions helps in early diagnosis and effective management.
Menstrual Disorders
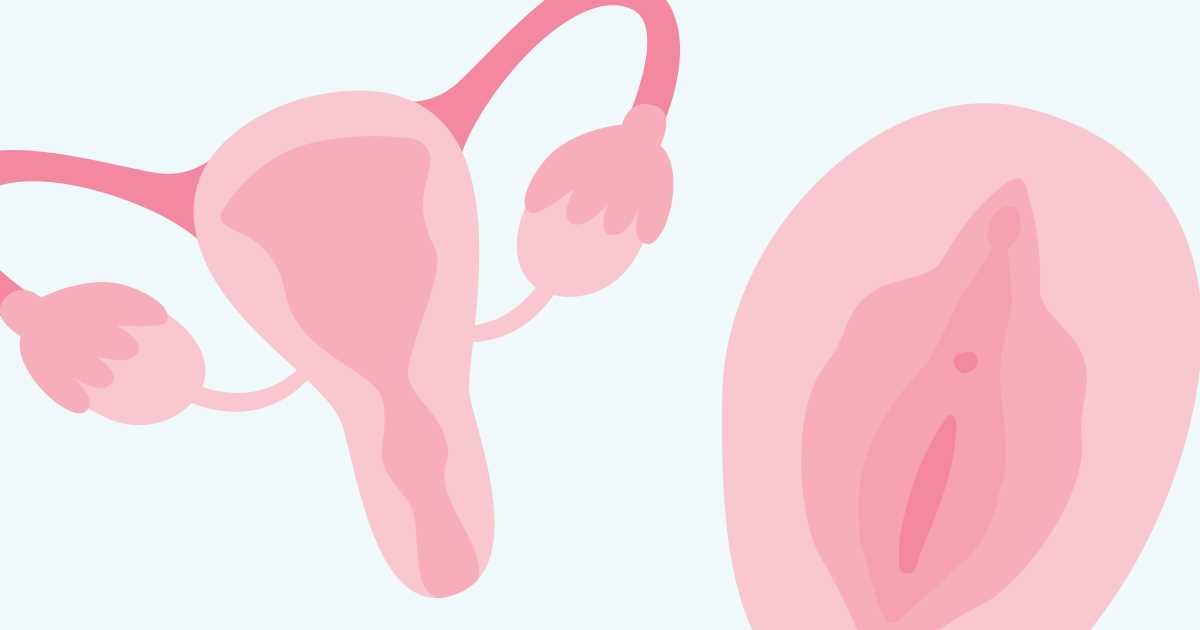
Menstrual disorders encompass a range of issues related to the menstrual cycle. Common conditions include amenorrhea, where menstruation is absent, and dysmenorrhea, characterized by severe menstrual pain. These conditions can arise from hormonal imbalances, lifestyle factors, or underlying health issues, requiring careful evaluation and treatment.
Pelvic Floor Disorders
Pelvic floor disorders affect the muscles and tissues supporting the pelvic organs. Common examples include prolapse, where pelvic organs descend due to weakened support structures, and incontinence, which involves involuntary leakage of urine. These disorders can significantly impact daily activities and overall well-being, necessitating specialized care and rehabilitation.
Importance of Regular Check-ups
Regular health assessments play a crucial role in maintaining overall well-being. These evaluations help identify potential issues early, allowing for timely intervention and prevention of serious conditions. By prioritizing routine visits, individuals can gain valuable insights into their health status and make informed decisions.
Consistent examinations can significantly enhance one’s quality of life. They not only foster awareness of personal health but also empower individuals to adopt healthier lifestyles. Regular check-ups can establish a trusting relationship with healthcare providers, facilitating open communication about concerns and treatment options.
Ultimately, making these assessments a routine part of life is essential for safeguarding health and ensuring long-term vitality. Embracing this proactive approach can lead to a more vibrant, fulfilling existence.
Educational Resources for Women
Access to comprehensive knowledge is crucial for women’s health and empowerment. Various platforms offer essential information, guidance, and support tailored to women’s unique needs. These resources aim to foster a deeper understanding and promote well-being throughout different life stages.
Online Courses: Many educational websites provide courses focused on health, wellness, and reproductive education. These programs encourage personal growth and informed decision-making.
Support Groups: Connecting with others can be invaluable. Numerous organizations offer forums where women can share experiences and seek advice in a safe environment.
Books and Publications: A wide array of literature exists, covering topics from anatomy to mental health. These texts serve as reliable sources for anyone wishing to delve into specific subjects.
Workshops and Seminars: Local communities often host events designed to educate women on health-related issues, fostering engagement and awareness.
Utilizing these resources can lead to the ultimate empowerment and enhanced quality of life for women everywhere.
Empowering Knowledge about Female Health
Understanding the complexities of women’s well-being is essential for fostering confidence and resilience. Gaining insight into the physiological and emotional aspects can lead to informed choices and improved quality of life.
Access to information empowers individuals to take charge of their health. By delving into various topics, such as reproductive processes, hormonal changes, and preventive care, one can uncover the ultimate strategies for maintaining balance and vitality.
Education is key to dismantling myths and stigmas surrounding female health. With the right knowledge, individuals can advocate for themselves, seek appropriate medical care, and support one another in their journeys toward well-being.