
Understanding the inner workings of home appliances helps users maintain and extend their longevity. Familiarity with key components allows for smoother troubleshooting when unexpected issues arise, saving both time and money. This section focuses on essential elements, providing insights into the design and layout of a well-known kitchen device.
Each element within such equipment plays a critical role, from cooling systems to control mechanisms. Recognizing how these parts interact ensures better performance and helps address common maintenance needs. Whether dealing with mechanical issues or electrical faults, having a reference to the layout becomes indispensable.
This guide offers a detailed overview of the primary sections and functional modules within the device. By exploring these areas, users will gain a deeper understanding of its structure and operation, facilitating easier repair and upkeep.
Overview of Internal Components
Understanding the arrangement and role of various internal elements is essential for ensuring smooth operation and extending the lifespan of appliances. Each section within the system serves a specific purpose, contributing to its overall performance and functionality.
Main Functional Units
The key sections are designed to manage cooling, storage, and control functions. These include chambers responsible for maintaining temperature, along with mechanisms that regulate airflow to ensure consistent performance. Control modules help monitor and adjust internal conditions based on user settings.
Connectivity and Supporting Structures
Additional elements work behind the scenes to enable seamless interaction between various sections. Electrical connections, sensors, and valves coordinate operations, while the supporting frame provides stability and protection for all internal modules. Together, these components create a well-balanced system.
Refrigeration System Structure

The cooling mechanism in modern appliances is designed to maintain optimal temperatures for food storage. This structure involves multiple interconnected elements working in harmony to regulate airflow, moisture levels, and energy consumption, ensuring efficient preservation. Understanding these components provides insight into how the system achieves consistent cooling performance.
Key Functional Units

A typical cooling system includes a compressor responsible for circulating refrigerant, transferring heat from the interior to the external environment. The evaporator coil cools the air by absorbing heat, while the condenser coil releases it outside. Each unit plays a critical role in maintaining the desired temperature range.
Air Circulation and Control
Proper airflow management ensures even temperature distribution throughout the compartments. Fans move air across the coils, and sensors work with control modules to adjust settings based on current conditions. This dynamic interaction helps reduce frost buildup and keeps stored items fresh over extended periods.
Arrangement of Electronic Controls
The organization of internal modules ensures smooth functionality by coordinating various elements involved in the system’s operations. These components are positioned strategically to optimize interaction and provide efficient control over essential functions.
Control boards serve as the primary hubs, managing signals and responses between the system’s circuits. Their placement minimizes latency, ensuring quick adjustments to user inputs and environmental changes.
Connectors and wiring paths are carefully routed to prevent interference and maintain signal integrity. This arrangement supports reliable communication between essential modules, extending the longevity and performance of the system.
Grouping key components within accessible sections also simplifies maintenance and troubleshooting, allowing technicians to quickly address potential malfunctions and replace worn elements without disrupting the entire setup.
Cooling Mechanism Layout
The design of a cooling system plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal performance. By carefully organizing the airflow, heat exchange, and temperature control elements, this structure ensures consistent operation and energy efficiency. Understanding how each segment interacts helps in troubleshooting and optimizing functionality.
Core Components Overview
- Air Circulation Pathways: These channels guide the airflow to remove excess heat and distribute cool air evenly.
- Heat Exchangers: Critical surfaces that transfer heat away from sensitive areas, improving energy regulation.
- Temperature Sensors: These sensors monitor internal conditions and adjust cooling levels dynamically.
Flow Regulation and Control
- Fan System: Rotating units positioned to direct airflow through key sections, ensuring adequate ventilation.
- Cooling Medium: A specialized substance or gas circulates within the sealed areas to absorb and dissipate heat.
Ice Maker Assembly Breakdown
The inner workings of the ice production unit involve several interconnected elements, each playing a specific role in ensuring smooth operation. Understanding these individual components and their cooperation helps maintain performance and troubleshoot issues effectively.
Water Inlet System: This section controls the flow of water into the system, ensuring that the right amount is delivered for ice creation. A valve regulates the input, preventing overflow or underfilling.
Freezing Tray: Water is dispensed into a mold where it solidifies under controlled temperatures. The shape and layout of the tray impact the size and quality of the frozen pieces.
Ejection Mechanism: Once the ice hardens, a release arm or motorized ejector pushes the pieces out of the mold, ensuring a smooth transfer to the storage area.
S
Water Filtration System Design
The design of an effective water purification mechanism is crucial for ensuring the delivery of clean and safe drinking water. This process involves a combination of physical, chemical, and biological methods to remove impurities and harmful contaminants from the water supply.
To achieve a well-functioning purification system, several key components must be carefully considered:
- Pre-filtration: Initial removal of larger particles and sediments to protect downstream components.
- Filtration Media: Selection of appropriate materials, such as activated carbon or sand, that effectively capture smaller particles and chemicals.
- Membrane Technology: Implementation of advanced filtration techniques, like reverse osmosis, for thorough purification.
- Post-filtration Treatment: Additional processes, such as UV light treatment, to eliminate any remaining microorganisms.
Each stage of the system should be designed to work in harmony, ensuring maximum efficiency and longevity. Regular maintenance and monitoring are also essential to adapt to changes in water quality and consumption needs.
By focusing on a holistic approach to the design, it is possible to create a robust water purification system that meets the requirements of various applications, from residential to industrial use.
Storage Compartments Configuration
The arrangement of storage areas within a refrigeration unit plays a crucial role in maximizing efficiency and convenience. Understanding how these compartments are organized can help users better utilize their appliance, ensuring optimal storage for various food items and beverages. Different sections are designed to accommodate specific types of products, making it easier to access and manage contents.
Main Storage Area

The primary storage section is typically designed for larger items, allowing for versatile arrangements. This compartment often features adjustable shelving, which can be customized to fit various heights of containers and packages. Such flexibility enhances the overall organization and accessibility of stored goods.
Compartment Type Features Recommended Items Main Storage Area Adjustable shelves, spacious Large containers, beverages, leftovers Crisper Drawers Humidity control, separate compartments Fruits, vegetables Door Bins Varied sizes, easy access Condiments, small jars, drinks Door Gasket Placement
Ensuring a proper seal around the entryway is essential for maintaining optimal energy efficiency and preventing moisture ingress. The positioning of the flexible lining plays a vital role in the overall performance of the cooling appliance.
To achieve an effective seal, begin by aligning the gasket carefully along the frame. It is important to ensure that the material is free from any twists or folds that could compromise its function. Press the gasket firmly into place, making certain that it adheres evenly across all contact points.
Regular inspection of the gasket is recommended to identify any signs of wear or damage. If any irregularities are detected, replacement should be considered to maintain peak performance and efficiency.
Lighting System Distribution
The distribution network for illumination within an appliance plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal functionality and aesthetics. This system facilitates the even spread of light throughout the interior, enhancing visibility and user experience. Understanding how this distribution works can help in maintaining and troubleshooting the overall efficiency of the lighting setup.
Components of the Illumination Network
The primary elements of the illumination network include various fixtures, circuits, and control mechanisms. These components work together to regulate the flow of energy and maintain the desired brightness levels. Proper integration of these parts ensures that the entire system operates smoothly, preventing issues such as flickering or uneven lighting.
Importance of Effective Distribution
Efficient distribution of light is essential for both functionality and energy conservation. When light is evenly distributed, it reduces the strain on individual fixtures and minimizes the risk of burnout. Furthermore, an effective system contributes to energy savings, making it an essential consideration for users aiming to lower operational costs while enhancing performance.
Shelf and Drawer Setup
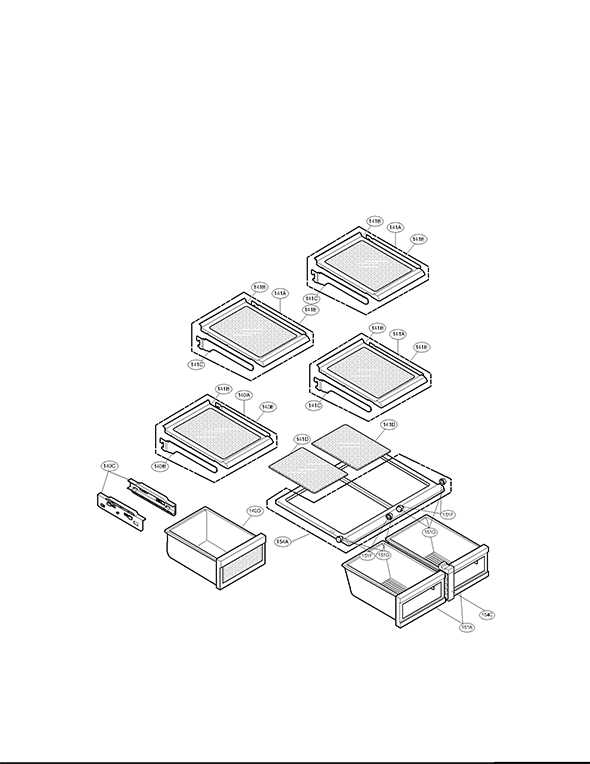
This section provides insights into organizing and configuring the various storage compartments and surfaces within the appliance. Proper arrangement not only enhances accessibility but also optimizes space utilization, allowing for efficient storage of food and beverages.
When setting up the shelving and drawers, consider the types of items you plan to store. Adjustable shelves can accommodate varying heights, while dedicated drawers are ideal for specific categories of items such as fruits, vegetables, or dairy products.
Storage Component Optimal Use Adjustment Features Top Shelf Ideal for non-perishable items or infrequently accessed goods Fixed position Middle Shelves Best suited for everyday essentials like beverages and leftovers Adjustable height for flexibility Bottom Shelf Perfect for larger containers and bulk items Fixed position Vegetable Drawer Designed for storing fresh produce Humidity control for freshness Dairy Drawer Specifically for dairy products to maintain optimal temperature Fixed position Compressor and Condenser Layout
The arrangement of the refrigerating unit plays a crucial role in the efficiency and functionality of cooling systems. Understanding the positioning and interaction between the compressor and condenser components is essential for effective operation and maintenance. This section explores the layout and integration of these key elements, highlighting their importance in the overall performance of the appliance.
Compressor Positioning
The compressor serves as the heart of the cooling mechanism, responsible for circulating the refrigerant through the system. Typically situated in a designated compartment, its placement allows for optimal airflow and heat exchange. Ensuring adequate space around the compressor is vital for preventing overheating and ensuring efficient operation. Regular checks on the compressor’s condition can prevent costly repairs and extend the lifespan of the entire cooling apparatus.
Condenser Arrangement
Located adjacent to the compressor, the condenser facilitates the dissipation of heat from the refrigerant. Its layout is designed to maximize exposure to airflow, aiding in the cooling process. Proper installation of the condenser ensures effective heat transfer, which is critical for maintaining the desired temperature within the unit. Cleaning and maintaining the condenser coils are essential tasks that contribute to the efficiency and longevity of the cooling system.
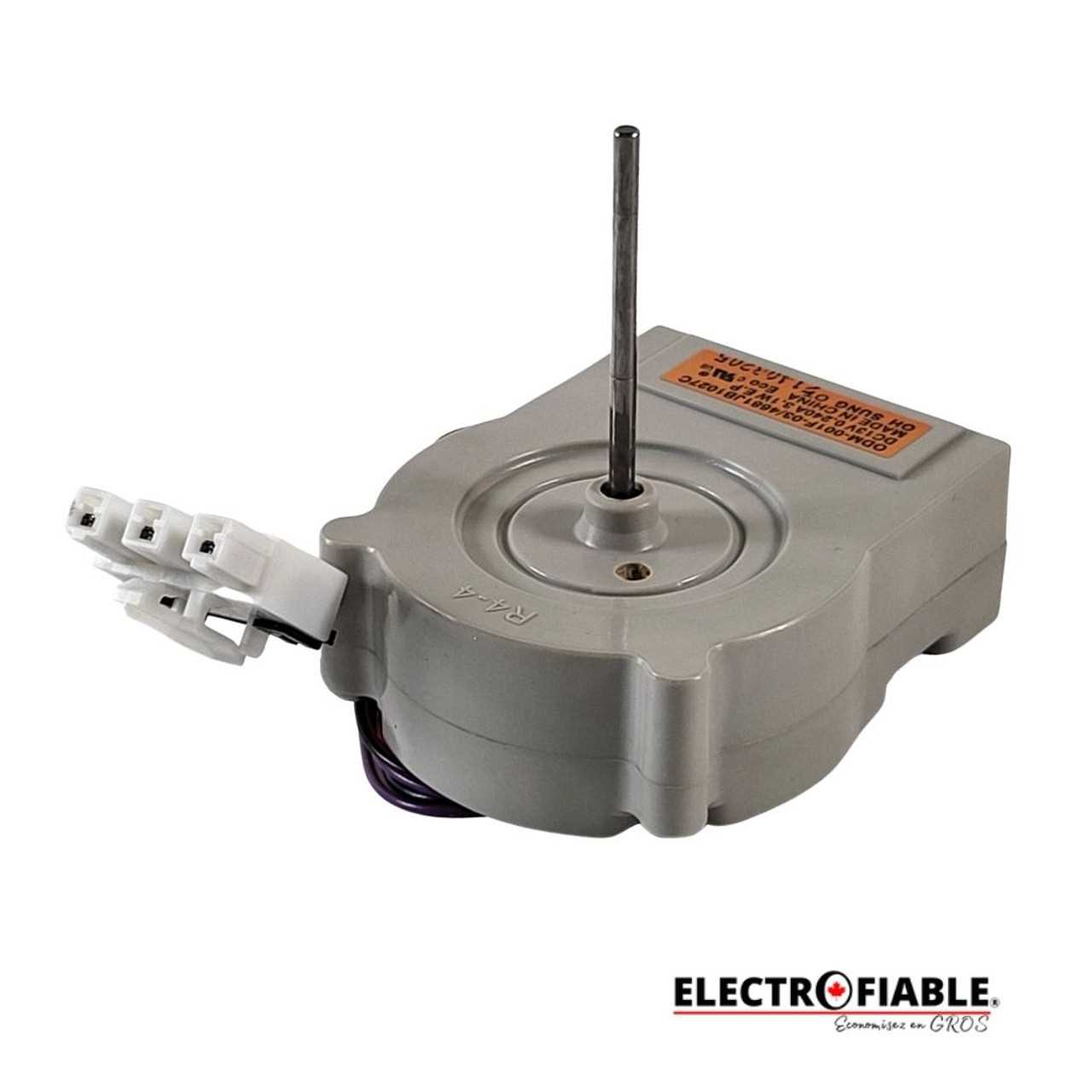
Fan Motor and Ventilation Path
The efficiency of cooling systems in modern appliances greatly relies on the design and functionality of the airflow mechanisms. A key component in this setup is the motor responsible for driving the air circulation. This motor ensures optimal temperature management and prevents overheating, contributing to the overall performance of the device.
Importance of Proper Airflow
Effective ventilation is crucial for maintaining a balanced environment within the unit. Proper airflow not only aids in cooling but also helps in removing excess humidity. This process protects internal components from potential damage and enhances the lifespan of the appliance.
Role of the Fan Motor
The fan motor plays a pivotal role in the movement of air throughout the system. By continuously rotating the fan blades, it creates a consistent flow that promotes even temperature distribution. An efficient motor reduces energy consumption while ensuring the necessary cooling effect is achieved. Regular maintenance of this component is essential to avoid operational failures and ensure long-term reliability.