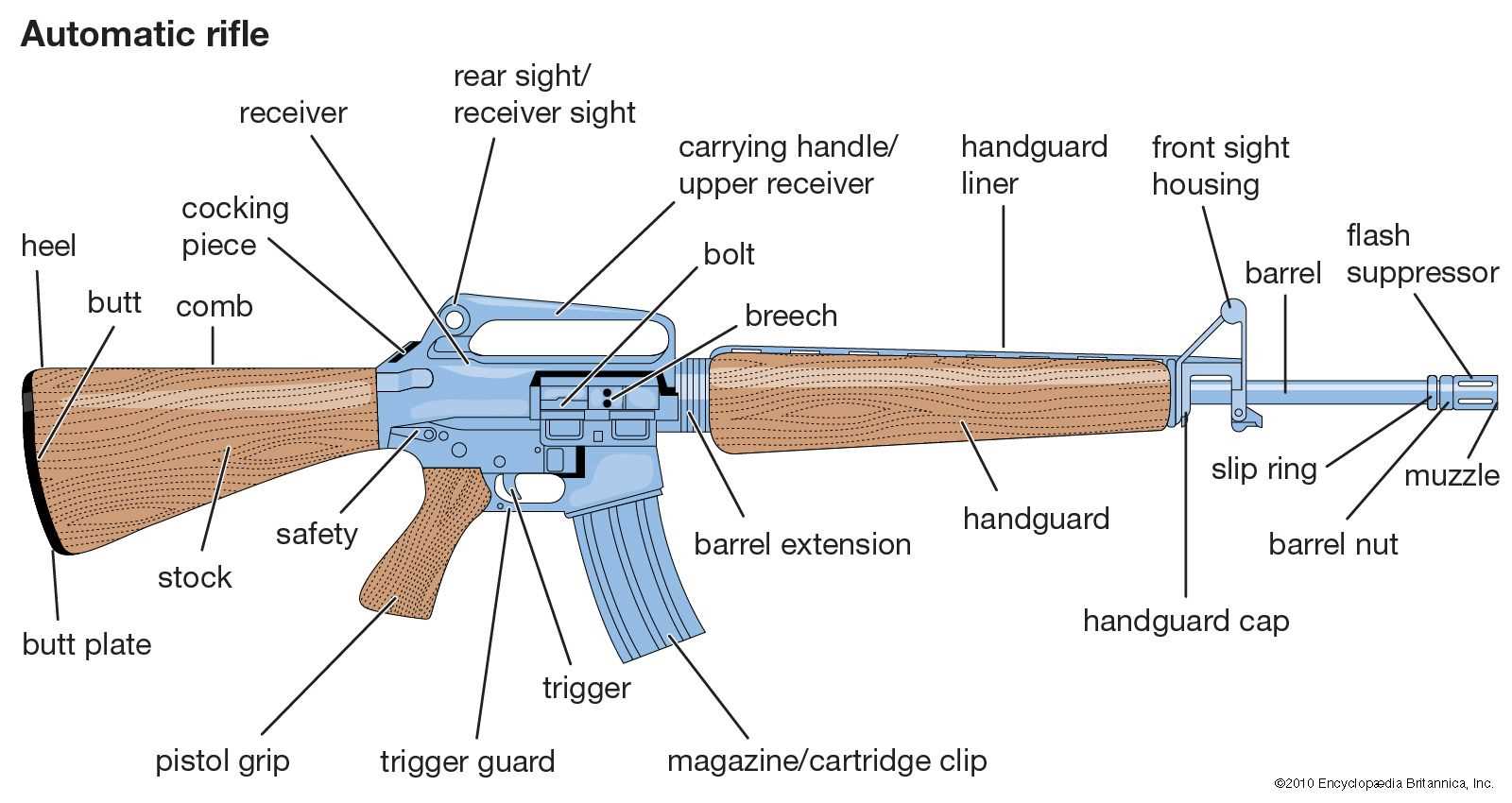
The widely recognized M4 platform stands as a benchmark in modern firearms engineering, offering versatility and reliability across various applications. This overview delves into its essential elements, providing a clear understanding of its structure and functionality. Each piece works in unison to create a cohesive and efficient mechanism that ensures performance in the field.
By examining the major segments of this system, it becomes easier to appreciate how these elements contribute to overall accuracy, durability, and ease of use. Whether you’re maintaining the weapon or looking to enhance its capabilities, a thorough knowledge of its framework is crucial for optimal operation.
This guide offers insight into the inner workings of the platform, focusing on
Overview of the M4 Carbine Components
The structure of this widely used firearm is made up of various essential elements that work in harmony to ensure reliable operation. Understanding these elements provides insight into its functionality, making it easier to perform maintenance, upgrades, or repairs. Each component has a distinct role, contributing to both the performance and durability of the system.
Key Structural Elements
The system is divided into several primary sections, including the framework responsible for housing the internal mechanisms and the moving parts that facilitate operation. These sections are designed for easy handling, offering both versatility and efficiency in various scenarios.
Operational Mechanisms
Key Internal Mechanisms of the Rifle
The inner workings of a modern rifle are intricate and finely tuned, ensuring its reliability and precision. Understanding these mechanisms is essential for maintaining optimal performance and ensuring the safe operation of the weapon. Below, we explore the core components that drive the internal functionality, focusing on how they work together to manage firing, cycling, and reloading.
Action and Cycling Mechanism
The action mechanism is responsible for the rifle’s ability to load, fire, and eject rounds. This involves a series of components that work in harmony to ensure smooth cycling. Key elements include:
- Chamber: The area where a round is held prior to firing.
- Construction Materials: Magazines are commonly made from materials such as aluminum, polymer, and steel. Each material offers distinct advantages in terms of weight, durability, and resistance to corrosion.
- Design Variations: Different configurations exist to accommodate specific operational needs, including:
- Standard magazines
- Extended versions for increased ammunition capacity
- Drum magazines that offer high round counts
- Capacity Ranges: Typical capacities vary widely, with options including:
- 10-round
- 20-round
- 30-round
- High-capacity magazines exceeding 30 rounds
- Feeding Mechanism: A reliable feeding mechanism is crucial for seamless operation. Features include:
- Follower design for smooth ammunition feeding
- Spring tension for consistent performance
- Compatibility: Ensuring that the magazine is compatible with the specific model of the firearm is vital for function and safety.
- Carrier: The main housing that facilitates the movement of other components and interacts with the upper receiver.
- Bolt: The piece that locks into the chamber and ensures proper alignment during firing.
- Firing Pin: Responsible for striking the primer of the cartridge, igniting the propellant.
- Cam Pin: A critical connector that aids in the rotation of the bolt during the locking and unlocking process.
- Extractor: The component that grips the spent cartridge case to eject it from the chamber.
- Ejector: Works in conjunction with the extractor to ensure spent cases are removed from the firearm effectively.
External Attachments and Their Functions
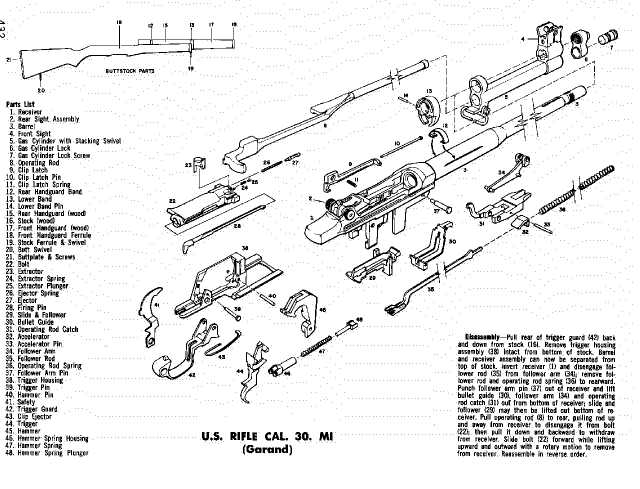
External attachments enhance the functionality and versatility of modern equipment. These add-ons are designed to improve handling, accuracy, and overall performance by offering various practical uses for different scenarios. Whether for tactical, recreational, or professional use, they provide flexibility in adapting to specific needs.
One commonly used accessory is the handguard. It serves as a protective barrier, allowing the user to handle the item safely without exposure to heat, while also offering mounting options for additional tools. Another key attachment is the optics system, which improves precision by aiding in target acquisition at various distances. Users can choose from a variety of sights and scopes depending on their requirements.
Additional features may
Understanding the Barrel and Its Role
The barrel is a key component in the performance of any firearm. Its primary function is to guide and stabilize the projectile, ensuring accuracy and velocity. Without a well-designed barrel, the precision of the weapon would suffer, impacting its overall effectiveness. Its internal dimensions and materials are crucial factors in determining the quality of shots fired, as well as the reliability of the firearm over time.
The construction and characteristics of this element significantly influence how the firearm handles heat, pressure, and wear during use. The materials chosen for the barrel, its length, and internal rifling pattern all play a role in enhan
Stock Adjustments for Optimal Performance

Ensuring the perfect fit of your firearm’s shoulder support is crucial for achieving maximum efficiency and accuracy. The right adjustments can significantly enhance stability, comfort, and control during use. By fine-tuning this component, users can adapt to various shooting positions and personal preferences, leading to improved performance.
Key considerations for optimizing shoulder support include length adjustments, cheek riser settings, and material choice. Each aspect plays a vital role in the shooter’s overall experience.
| Adjustment Type | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Length Adjustment | Modifying the overall length to suit individual reach. | Enhances comfort and control. |
| Cheek Riser | Altering the height for optimal eye alignment. | Improves sight picture and reduces strain. |
| Material Choice | Selecting different materials for grip and weight. | Affects handling and recoil management. |
By carefully adjusting these elements, users can delve into their shooting technique and achieve the ultimate performance tailored to their needs.
Magazine Features and Capacity Details
The efficiency of a firearm is greatly influenced by the design and capacity of its ammunition storage system. Understanding these characteristics is essential for optimal performance and versatility in various scenarios.
In conclusion, understanding the various features and capacities of ammunition storage systems can significantly enhance the effectiveness of any firearm, providing users with greater flexibility and reliability in the field.
The Bolt Carrier Group Breakdown
The Bolt Carrier Group (BCG) is a critical assembly in modern firearms, serving as the heart of the operating mechanism. Understanding its components and functions is essential for anyone interested in firearm maintenance and performance. This section will delve into the various elements that constitute this assembly, explaining their roles and interactions.
Key components of the BCG include:
Each of these elements plays a vital role in the cycling process. The carrier moves back and forth, driven by gas pressure, while the bolt rotates to lock and unlock as necessary. This coordinated action ensures reliable operation and performance.
For proper functioning, regular maintenance and inspection of the BCG are crucial. Cleaning and lubricating each part can prevent malfunctions and prolong the lifespan of the assembly.
Rail System for Accessory Mounting
The integration of a mounting framework is crucial for enhancing the functionality of a firearm. This system allows users to customize their setup by attaching various accessories, thereby optimizing performance for specific applications.
Types of Mounting Systems
There are several configurations available, each designed to accommodate different accessories and user preferences. The most common systems include:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Picatinny Rail | A standard rail that provides versatility and compatibility with a wide range of accessories. |
| KeyMod | A modular system that allows for lightweight attachments and a streamlined profile. |
| M-LOK | An innovative system that offers a secure, adaptable platform for accessory mounting. |
Benefits of Rail Systems
Utilizing a rail system significantly increases the versatility of the firearm. Users can easily switch out accessories like optics, lights, and grips, tailoring their setup for the ultimate experience in performance and adaptability.
Trigger Mechanism and Fire Control System
The trigger mechanism and fire control system are integral components that govern the operation of a firearm, ensuring precise handling and response during use. These elements are designed to enhance user control and facilitate a reliable shooting experience, playing a crucial role in the overall functionality of the weapon.
Overview of the Trigger Mechanism
The trigger mechanism comprises various elements that interact to initiate the firing sequence. When the shooter applies pressure to the trigger, a series of components engage, ultimately releasing the firing pin. This process is engineered for both efficiency and safety, allowing for a smooth and predictable operation.
Fire Control System Functions
The fire control system encompasses the trigger, sear, hammer, and associated linkages that work together to enable different firing modes. This system can be configured for semi-automatic or fully automatic firing, depending on the design and intended use of the firearm. Understanding this system is vital for proper handling and maintenance.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Trigger | Initiates firing sequence |
| Sear | Holds the hammer in place until released |
| Hammer | Strikes the firing pin to ignite the cartridge |
| Disconnector | Prevents automatic firing during reset |
Grip and Handguard Designs for Stability
The design of the grip and handguard plays a crucial role in enhancing the overall stability and control of a firearm. These components not only influence the handling experience but also affect accuracy during use. A well-engineered grip and handguard can significantly reduce fatigue and improve shooting performance.
Ergonomic Features for Enhanced Control
Incorporating ergonomic shapes and textures into grips can provide users with a more secure hold. Features such as finger grooves and thumb shelves allow for natural hand positioning, minimizing the chance of slippage during operation. Additionally, materials that offer a non-slip surface can greatly enhance grip stability, especially in challenging conditions.
Adjustability and Customization
Adjustable handguards allow users to tailor their setup according to personal preferences and specific use cases. Options like removable panels or modular attachments enable shooters to modify their setup for improved comfort and functionality. This customization ensures that individuals can find the optimal configuration for their unique shooting style, further contributing to overall stability.
Gas System Operation and Maintenance
The gas system is a crucial component that significantly influences the functionality and reliability of a firearm. Understanding its operation and proper maintenance ensures optimal performance and longevity. This section outlines the essential aspects of how the gas mechanism works and the steps necessary to keep it in prime condition.
Operation of the Gas Mechanism
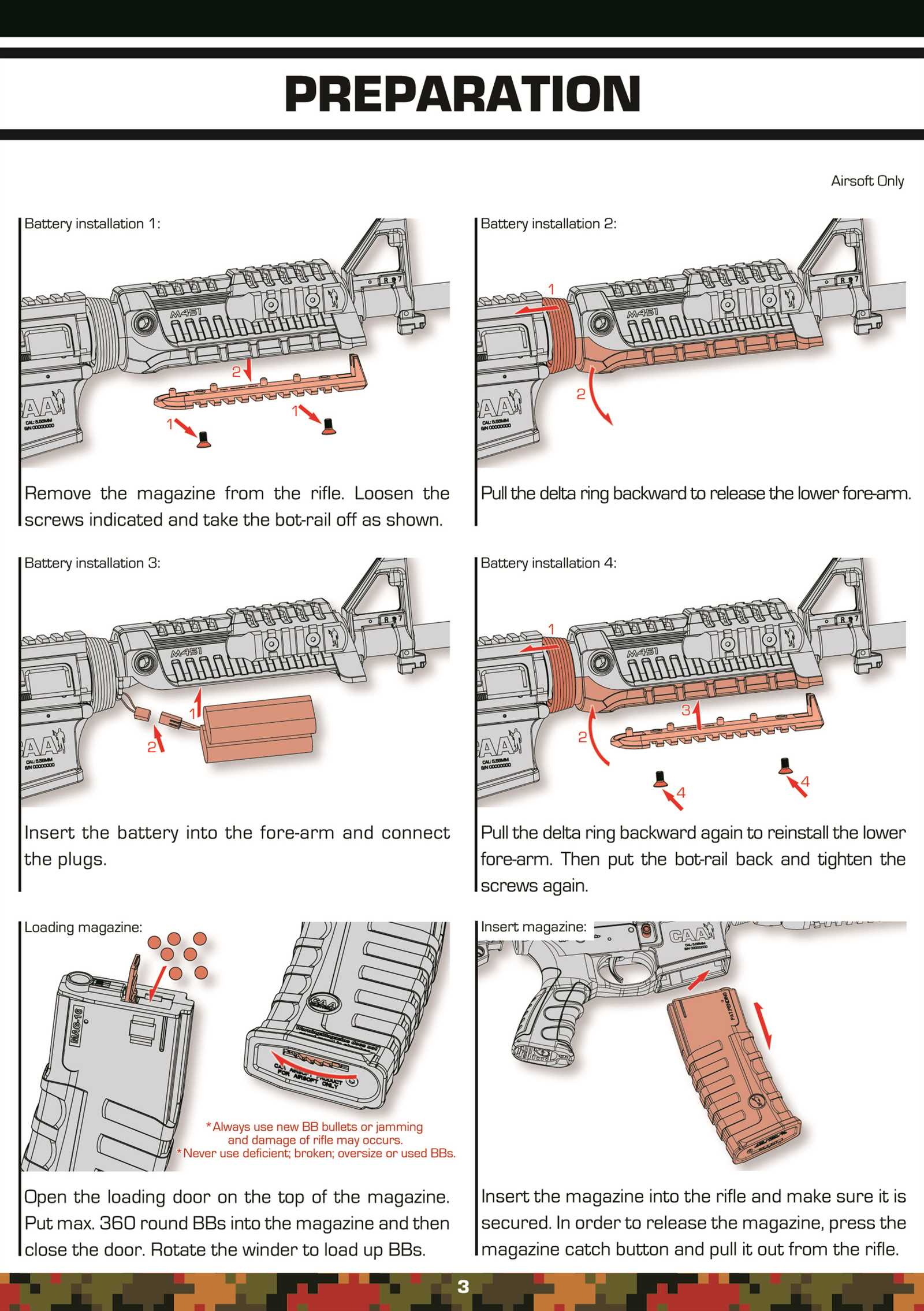
The gas system operates by utilizing the expanding gases produced during firing to cycle the action. This process involves several key steps:
- When a round is fired, gases are expelled from the chamber.
- These gases travel through a port into the gas tube.
- The gas then moves to the bolt carrier, forcing it rearward.
- This rearward motion ejects the spent cartridge and chambers a new round.
Understanding these stages is vital for diagnosing issues that may arise during operation.
Maintenance Practices
Regular maintenance of the gas system helps prevent malfunctions and enhances performance. Consider the following practices:
- Inspection: Routinely check the gas block and tube for obstructions or damage.
- Cleaning: Use appropriate solvents to remove carbon buildup from the gas tube and block.
- Lubrication: Apply a suitable lubricant to moving parts to ensure smooth operation.
- Testing: After maintenance, conduct function tests to confirm proper operation.
By following these guidelines, users can maintain the integrity of the gas system, ensuring reliable and effective performance. Regular attention to these components will significantly contribute to the overall functionality of the firearm.
Sight Options
When it comes to enhancing target acquisition and overall shooting accuracy, the choice of optical systems plays a pivotal role. Various sighting mechanisms are available, each offering distinct advantages that cater to different shooting styles and environments. Selecting the right type can significantly impact performance, making it essential to understand the available options.
Traditional iron sights provide a reliable and durable solution, ideal for shooters who prefer a lightweight setup. These sights are simple in design and require no batteries, making them suitable for various conditions. Alternatively, red dot sights offer rapid target engagement with a clear point of aim, perfect for close to medium-range engagements. Their ease of use and quick adjustments make them a popular choice among many enthusiasts.
For those seeking precision at longer distances, magnified optics deliver exceptional clarity and accuracy. These scopes allow for fine adjustments and improved target identification, catering to both competitive shooters and hunters alike. Additionally, some advanced systems combine both magnification and reticle illumination, providing versatility in diverse lighting conditions.
Finally, holographic sights represent a modern approach, featuring a unique reticle that remains visible even in bright sunlight. This technology allows for both speed and accuracy, making it a favored option for tactical applications. Each sighting method has its unique characteristics, making it crucial for users to evaluate their specific needs before making a selection.