When it comes to maintaining a reliable marine engine, knowing the structure and arrangement of various elements is essential. This knowledge ensures smooth operation and effective troubleshooting, whether you’re an experienced technician or a boat owner. Each element, from the power system to the cooling mechanisms, plays a crucial role in overall functionality.
To keep your engine running efficiently, it’s important to be familiar with the internal organization of its components. Recognizing how each piece fits together helps to optimize performance and extend the lifespan of your equipment. By thoroughly understanding this system, you can identify potential issues early and address them before they become serious problems.
In this guide, we will explore the key elements that make up the engine, offering an in-depth look at their positioning and function. This knowledge will empower you to maintain, repair, and enhance your engine’s capabilities with confidence.
Comprehensive Overview of Marine Engine Components
This section provides an in-depth exploration of the various mechanical elements and systems that form the core of a high-performance inboard engine. These components work together to deliver exceptional power, reliability, and efficiency, ensuring optimal performance for marine vessels. Understanding the key elements of this engine is essential for maintaining and troubleshooting.
Main Engine Systems

- Fuel System: Responsible for delivering fuel to the engine in a precise manner, ensuring smooth and efficient combustion.
- Cooling System: Regulates the engine temperature by circulating water or coolant to prevent overheating.
- Lubrication System: Ensures that all moving parts are well-lubricated, reducing friction and wear.
Additional Essential Components
- Exhaust System: Manages the
Understanding the Engine Structure
The internal organization of an engine is a complex system of interconnected components that work together to ensure smooth and efficient performance. Each element within this structure has a distinct role, contributing to the overall function and reliability of the engine. By understanding how these components interact, one can gain a clearer perspective on engine maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Block: The foundation that houses various key elements, offering support and alignment for other parts.
- Cylinder: The chamber where the combustion process occurs, producing the power needed for motion.
- Pistons: Components that move within the cylinder, converting fuel into mechanical energy.
- Crankshaft: Transforms the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion, driving the machinery.
- Valves: Regulate the intake of fuel and the expulsion of exhaust gases, ensuring proper engine breathing.
Main Internal Parts of the Mercruiser 6.2
The inner workings of this engine model consist of various essential components that work in harmony to ensure smooth operation and efficient performance. These key elements contribute to the engine’s overall power output, durability, and functionality under different conditions. Below is a breakdown of the primary internal elements that play a crucial role in the motor’s functioning.
- Cylinders and Pistons: These are responsible for the combustion process, where fuel ignites and powers the system. The precise movement of the pistons within the cylinders generates the force necessary for propulsion.
- Crankshaft: Converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotational force. This part ensures that the energy created is transmitted effectively to the drive system.
- Camshaft: Regulates the timing of the valves
Fuel System Elements and Functionality
The fuel system plays a critical role in ensuring optimal engine performance by efficiently delivering fuel for combustion. Each component of the system is designed to handle specific tasks, ensuring smooth operation and reliable power output. Proper fuel management is essential for maintaining efficiency and longevity of the engine.
Main Components Overview
The key components of the fuel system include the fuel tank, fuel pump, injectors, and filtration elements. These parts work together to ensure that fuel is delivered at the correct pressure and cleanliness, preventing contamination and ensuring the engine receives the proper amount of fuel for various operational conditions.
Functional Importance of Each Element
Each element within the fuel system has a distinct function. The fuel pump ensures a consistent flow of fuel from the tank to the injectors, which precisely spray fuel into the combustion chambers.
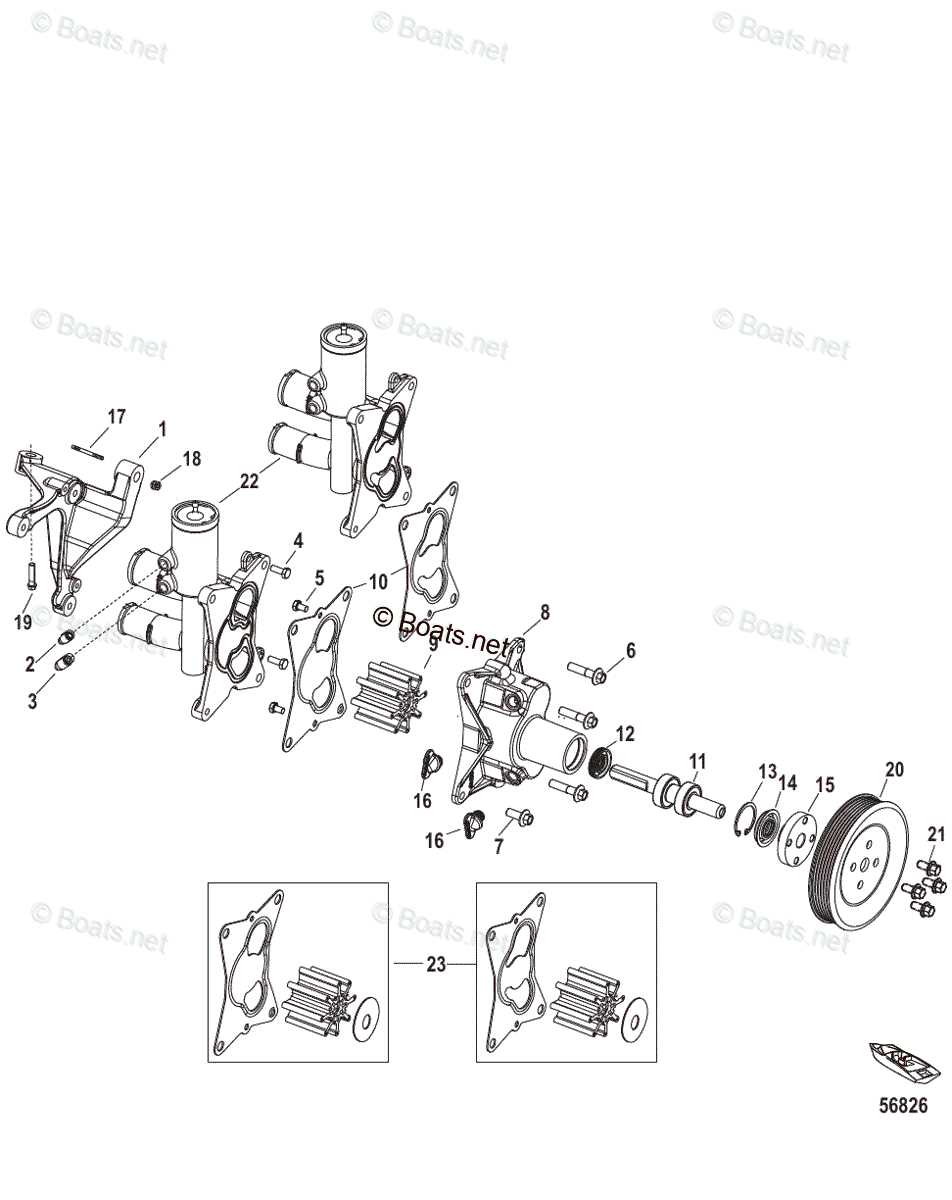
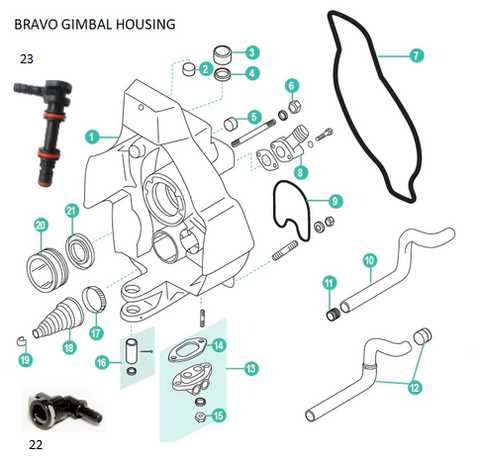
Cooling System Parts and Their Role
The cooling mechanism is vital for ensuring that the engine maintains an optimal operating temperature, preventing overheating and ensuring smooth performance. It involves various interconnected elements that work together to regulate and dissipate heat effectively.
- Water Pump: This component circulates coolant throughout the system, allowing the heat to be carried away from the engine block to maintain a stable temperature.
- Thermostat: A temperature-sensitive valve that controls the flow of coolant based on the engine’s needs, ensuring that it warms up efficiently and stays within the desired range.
- Heat Exchanger: Acts as a medium for transferring excess heat from the coolant to the external environment, helping to prevent the engine from overheating during prolonged use.
- Hoses and Connections: Flexible tubes that transport coolant between different components, ensuring consistent flow and proper pressure within the
Ignition Components and Their Importance
The ignition system plays a crucial role in the overall performance and reliability of marine engines. It is responsible for generating the spark needed to ignite the air-fuel mixture within the combustion chamber. Understanding the various components that make up this system can help boat owners maintain optimal engine efficiency and prevent potential failures.
Key Components of the Ignition System
Several essential elements work together to ensure effective ignition. These include the spark plugs, ignition coils, distributor, and wiring harnesses. Each component contributes to the system’s functionality, with spark plugs creating the actual spark and ignition coils providing the necessary voltage to initiate combustion.
Importance of Regular Maintenance

Regular inspections and maintenance of the ignition components are vital for ensuring the engine operates smoothly. Faulty spark plugs or worn-out coils can lead to misfires, reduced power output, and increased fuel consumption. By keeping these parts in good condition, boaters can enhance their vessel’s performance and longevity.
Lubrication System Breakdown
The lubrication system is a crucial component of any engine, ensuring smooth operation and longevity by minimizing friction and wear between moving parts. A well-designed lubrication system contributes to optimal performance and efficiency.
Understanding the key elements of this system is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting. The primary functions include:
- Reducing friction between engine components.
- Cooling critical parts through oil circulation.
- Cleaning contaminants from the engine interior.
- Providing a seal between piston rings and cylinder walls.
Typically, a lubrication system consists of the following components:
- Oil Pump: Responsible for circulating oil throughout the engine.
- Oil Filter: Removes contaminants from the oil to maintain purity and efficiency.
- Oil Cooler: Helps regulate the temperature of the oil to prevent overheating.
- Oil Reservoir: Stores the engine oil and allows for easy access for maintenance.
- Oil Lines: Connects all components, ensuring proper flow and distribution.
Regular inspection and maintenance of the lubrication system are vital for preventing potential engine damage and ensuring reliable performance. Proper oil levels, timely filter changes, and monitoring for leaks contribute significantly to the overall health of the engine.
Exhaust System Components Explained
The exhaust system plays a crucial role in the performance and efficiency of marine engines. It is responsible for directing harmful gases away from the engine while minimizing noise and ensuring optimal operation. Understanding the various elements that comprise this system is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
At the heart of the exhaust system are the manifolds, which collect exhaust gases from the engine’s cylinders. These manifolds are designed to withstand high temperatures and pressures, facilitating the efficient flow of gases. Attached to the manifolds are the risers, which elevate the exhaust gases above the waterline, preventing backflow and potential water intrusion.
Connecting the risers to the exhaust outlets are the exhaust pipes, which channel the gases to the outside environment. The design and diameter of these pipes are critical in maintaining proper back pressure, which can significantly impact engine performance. Additionally, some systems incorporate mufflers to reduce noise levels, providing a more pleasant experience on the water.
Furthermore, the cooling system often works in tandem with the exhaust setup. Coolant circulates through specific components to lower the temperature of the exhaust gases, preventing overheating and enhancing overall efficiency. This interplay ensures that the engine runs smoothly and reliably under various conditions.
In summary, the exhaust system is a complex assembly of parts that work together to promote engine efficiency and safety. Regular inspections and maintenance of these components are vital to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the marine engine.
Electrical System Overview

The electrical system plays a crucial role in the overall functionality of marine engines, providing power for various components and ensuring optimal performance. It encompasses a variety of elements that work in harmony to support the engine’s operation, from starting and ignition to powering electronic accessories.
Key Components
This system includes essential parts such as the battery, alternator, and wiring harnesses. The battery serves as the primary energy source, while the alternator replenishes the battery during operation. Proper connections and high-quality wiring are vital for maintaining efficiency and reliability.
Maintenance Considerations

Regular checks and maintenance of the electrical system are necessary to prevent failures. Inspecting connections, ensuring the battery is charged, and testing the alternator’s output can help identify potential issues before they escalate. Keeping these components in good condition is essential for smooth operation and longevity.
Key Differences in Mercruiser 6.2 Models
When examining various engine configurations within this category, it’s essential to recognize the distinctions that set each version apart. These differences can significantly impact performance, fuel efficiency, and overall suitability for specific applications. Understanding these variations helps in making informed decisions regarding maintenance and upgrades.
Model Variation Power Output Torque Fuel System Cooling System Base Model 350 HP 400 lb-ft Multi-Point Fuel Injection Raw Water Cooling High-Performance Variant 420 HP 450 lb-ft Direct Fuel Injection Closed-Loop Cooling Eco-Friendly Version 300 HP 350 lb-ft Electronic Fuel Injection Freshwater Cooling Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Ensuring the durability and performance of your marine engine requires regular upkeep and attention to detail. Implementing a systematic maintenance routine can significantly enhance the lifespan of your equipment and improve its efficiency.
- Regular Inspections: Conduct frequent checks on all critical components to identify any wear or damage early. Pay special attention to hoses, belts, and electrical connections.
- Fluid Changes: Change engine oil and filters as recommended to keep the engine running smoothly. Fresh fluids help in minimizing friction and reducing wear.
- Cooling System Maintenance: Ensure the cooling system is functioning optimally. Regularly check coolant levels and inspect for leaks.
- Battery Care: Keep the battery clean and fully charged. Corrosion on terminals should be cleaned to ensure efficient operation.
- Propeller Checks: Regularly inspect the propeller for damage or debris that could affect performance. Proper alignment is also crucial for optimal function.
Following these guidelines not only helps in maintaining peak performance but also prolongs the overall life of your marine equipment, ensuring enjoyable and trouble-free outings on the water.
Common Part Replacements and Upgrades
In the world of marine engines, certain components often require attention due to wear and tear or the pursuit of enhanced performance. Understanding which elements are commonly replaced or upgraded can help ensure a smoother operation and extended lifespan for your vessel.
Frequently Replaced Components
- Fuel Pumps: Essential for optimal fuel delivery, these can degrade over time.
- Water Pumps: Critical for cooling, ensuring that the engine maintains a safe operating temperature.
- Gaskets and Seals: Often replaced to prevent leaks and maintain efficiency.
- Ignition Components: Spark plugs and coils may need regular replacements for effective combustion.
- Belts and Hoses: These wear out due to exposure to heat and fluids, necessitating periodic checks.
Performance Enhancements
- Upgrading to High-Performance Fuel Injectors: Improves fuel efficiency and power output.
- Installing Aftermarket Exhaust Systems: Enhances exhaust flow and engine sound.
- Revising the Ignition System: Higher-performance coils and spark plugs can significantly boost engine responsiveness.
- Adding a Supercharger or Turbocharger: Provides substantial power increases for demanding applications.