The intricate composition of the lower extremities plays a crucial role in supporting the body’s weight and facilitating movement. Each component within this complex arrangement contributes to overall mobility, stability, and balance, allowing individuals to perform various activities with ease.
Exploring the various elements that constitute this anatomical region reveals a fascinating interplay between form and function. From the foundational structures that support the body’s weight to the more delicate components responsible for intricate movements, every element has a specific role to play.
By delving into the details of these structures, one can gain a deeper appreciation for their significance in everyday activities. Understanding their arrangement not only enhances knowledge of human anatomy but also provides insights into the importance of maintaining the health and functionality of these essential elements.
This section provides an overview of the intricate structure found in the lower extremities, emphasizing the various elements that contribute to mobility and support. Understanding these components is essential for comprehending their functions and interactions within the overall skeletal and muscular systems.
1. Introduction to Lower Limb Structure
The foundation of movement is rooted in the complexity of the lower limb structure. This introductory section will explore the fundamental concepts that define this region.
2. Bones of the Lower Extremity
- Tarsal bones
- Metatarsal bones
- Phalanges
3. Muscles Involved in Movement
- Intrinsic muscles
- Extrinsic muscles
4. The Role of Tendons
Tendons play a crucial role in connecting muscles to bones, facilitating movement and stability.
5. Ligaments and Joint Stability
- Structure of ligaments
- Impact on joint function
6. The Plantar Arch
This section examines the curvature of the underside, which is vital for shock absorption and weight distribution.
7. Common Injuries and Conditions
- Plantar fasciitis
- Sprains and fractures
8. Importance of Footwear
Choosing appropriate footwear is essential for maintaining optimal health and function of the lower extremities.
9. Impact of Aging on Structure
This section highlights how aging affects the overall anatomy and function of the lower limb.
10. Preventive Measures for Injury
- Strengthening exercises
- Proper stretching techniques
11. Rehabilitation and Recovery
Insights into effective rehabilitation practices can aid in recovery from injuries affecting the lower extremities.
12. Conclusion
A comprehensive understanding of the lower limb structure enhances appreciation for its complexity and importance in daily activities.
Overview of Foot Structure
This section delves into the intricate framework that constitutes the lower extremities of the human body. Understanding this composition is essential for grasping how these components work together to facilitate movement and provide support during various activities.
Anatomy of the Lower Extremities
The lower extremities consist of numerous elements that collaborate to maintain balance and enable mobility. These components include bones, tendons, ligaments, and muscles, each playing a pivotal role in the overall functionality and stability of the structure.
Functionality and Support
Each element contributes uniquely to the mechanics of movement. The bones serve as the rigid framework, while tendons and ligaments provide flexibility and stability. The muscular system, in turn, generates the necessary force for movement, ensuring smooth and coordinated actions.
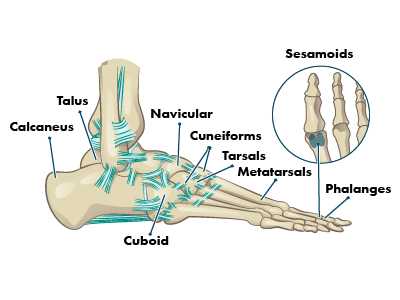
Key Bones in the Foot
The intricate structure of the lower extremity is supported by a variety of essential skeletal elements. These components work together to provide stability, mobility, and support for the entire body. Understanding their arrangement and function is vital for grasping how movement is achieved and maintained during daily activities.
Major Skeletal Elements
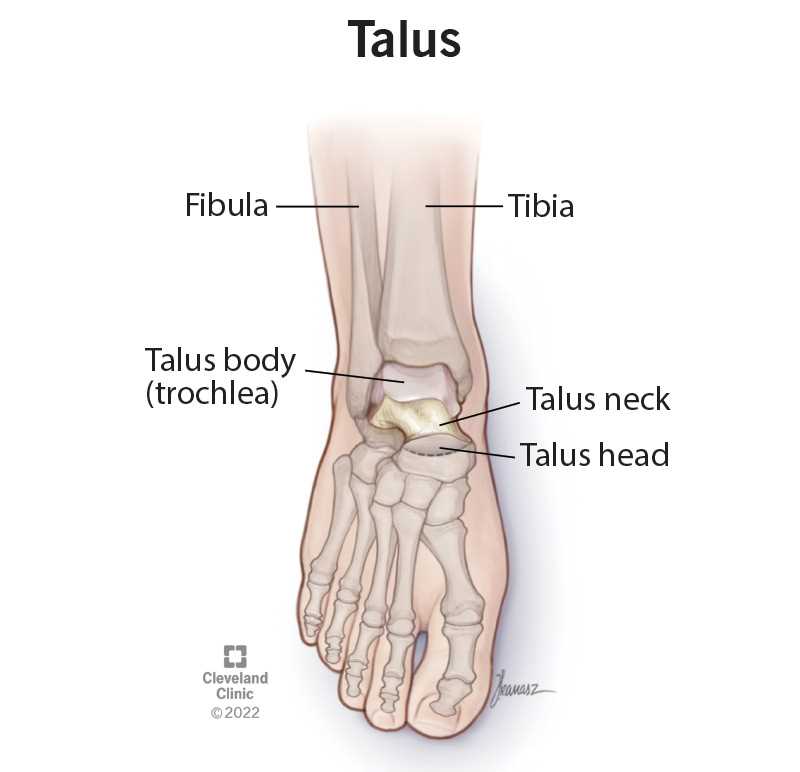
Among the numerous components, several key structures play a pivotal role. The calcaneus, often referred to as the heel bone, serves as the foundation for the posterior segment. Meanwhile, the talus acts as a crucial link between the leg and the remaining skeletal framework, facilitating smooth articulation during movement.
Supporting Structures
In addition to the primary bones, a network of smaller yet significant elements contributes to the overall functionality. The metatarsals and phalanges enable fine motor control, allowing for diverse movements such as gripping and balancing. Together, these elements ensure the lower extremity can adapt to various surfaces and activities.
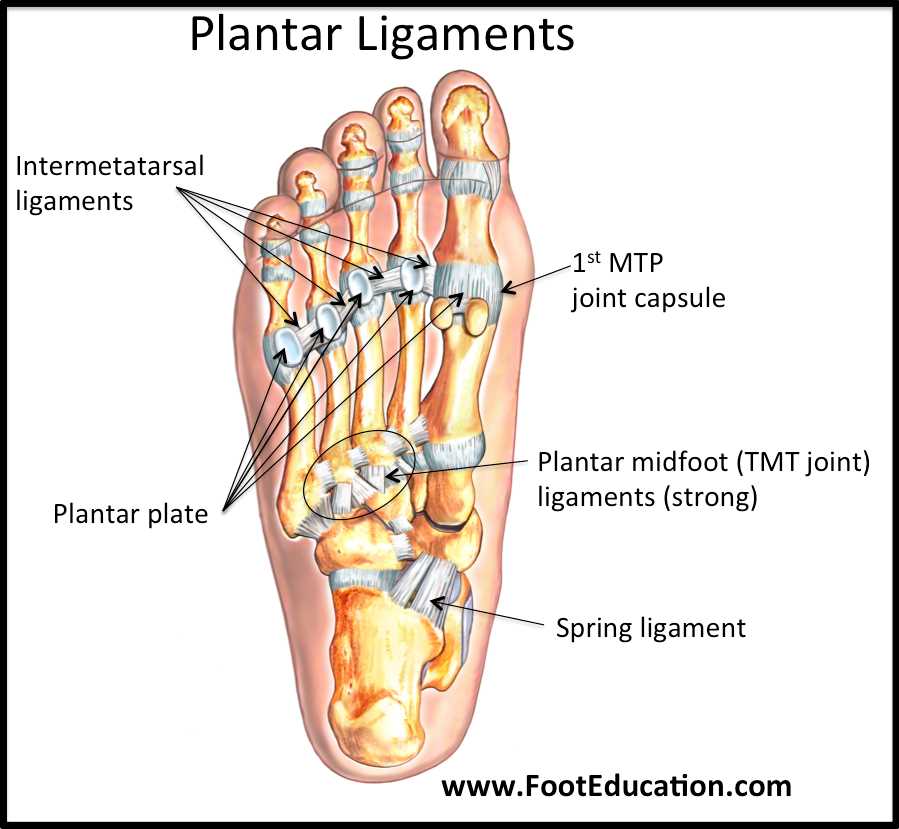
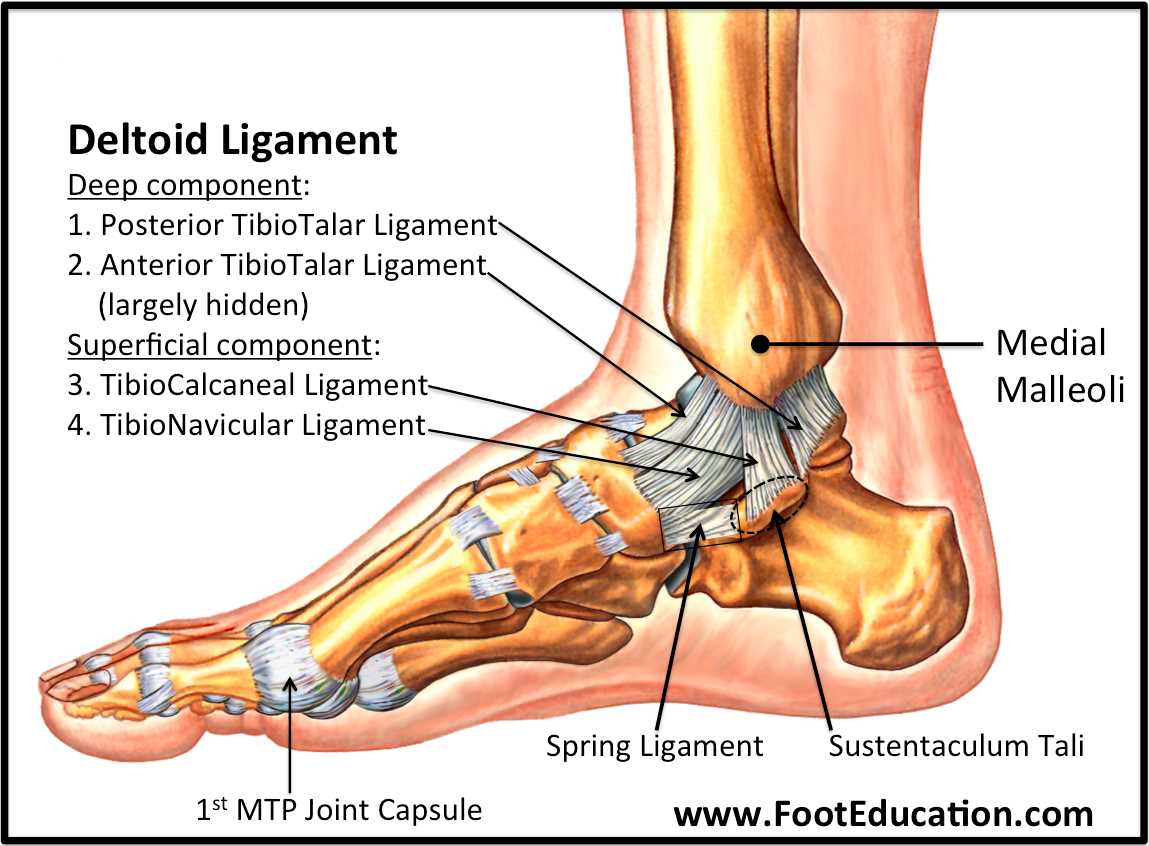
Major Ligaments and Tendons
The structural integrity and functionality of the lower limb are significantly influenced by various connective tissues. These components play a crucial role in facilitating movement, providing stability, and supporting weight-bearing activities. Understanding these elements is essential for comprehending how the body maintains balance and agility.
Key Connective Structures
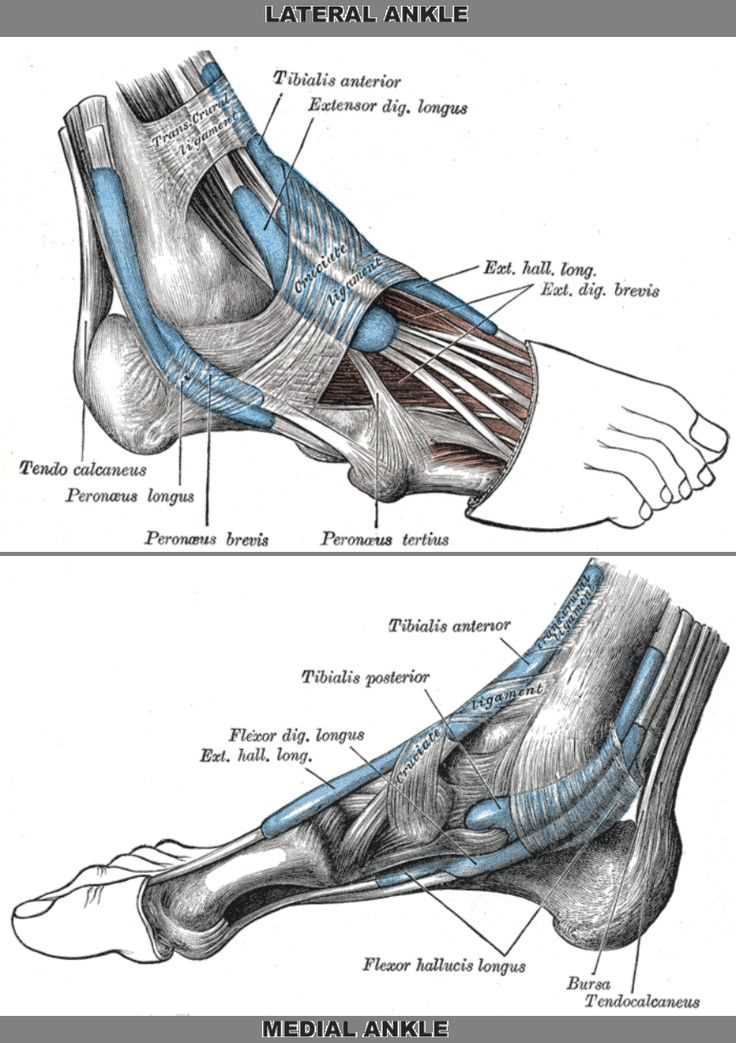
- Ligaments: These fibrous tissues connect bones to other bones, ensuring joint stability.
- Tendons: Tendons attach muscles to bones, enabling movement through muscle contractions.
Notable Examples
- Anterior Talofibular Ligament: Important for stabilizing the ankle during lateral movements.
- Achilles Tendon: The largest tendon in the body, vital for walking, running, and jumping.
- Plantar Fascia: A key ligament that supports the arch and absorbs shock during activities.
Common Foot Disorders Explained
The lower extremities play a crucial role in mobility and overall well-being. Various conditions can affect these structures, leading to discomfort and impaired function. Understanding these ailments is essential for effective management and prevention.
Types of Common Ailments
- Plantar Fasciitis: Inflammation of the tissue that connects the heel to the toes, causing heel pain, especially with the first steps in the morning.
- Achilles Tendinitis: An overuse injury affecting the Achilles tendon, leading to pain and stiffness at the back of the ankle.
- Bunions: A bony bump that forms at the base of the big toe, resulting in misalignment and discomfort.
- Neuromas: Thickening of tissue around nerves leading to pain and tingling, often between the toes.
Preventive Measures and Treatment Options
- Wear appropriate footwear that provides adequate support and cushioning.
- Engage in regular stretching and strengthening exercises for the lower limbs.
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce stress on the lower extremities.
- Consult a healthcare professional for persistent discomfort to explore treatment options such as physical therapy or orthotics.
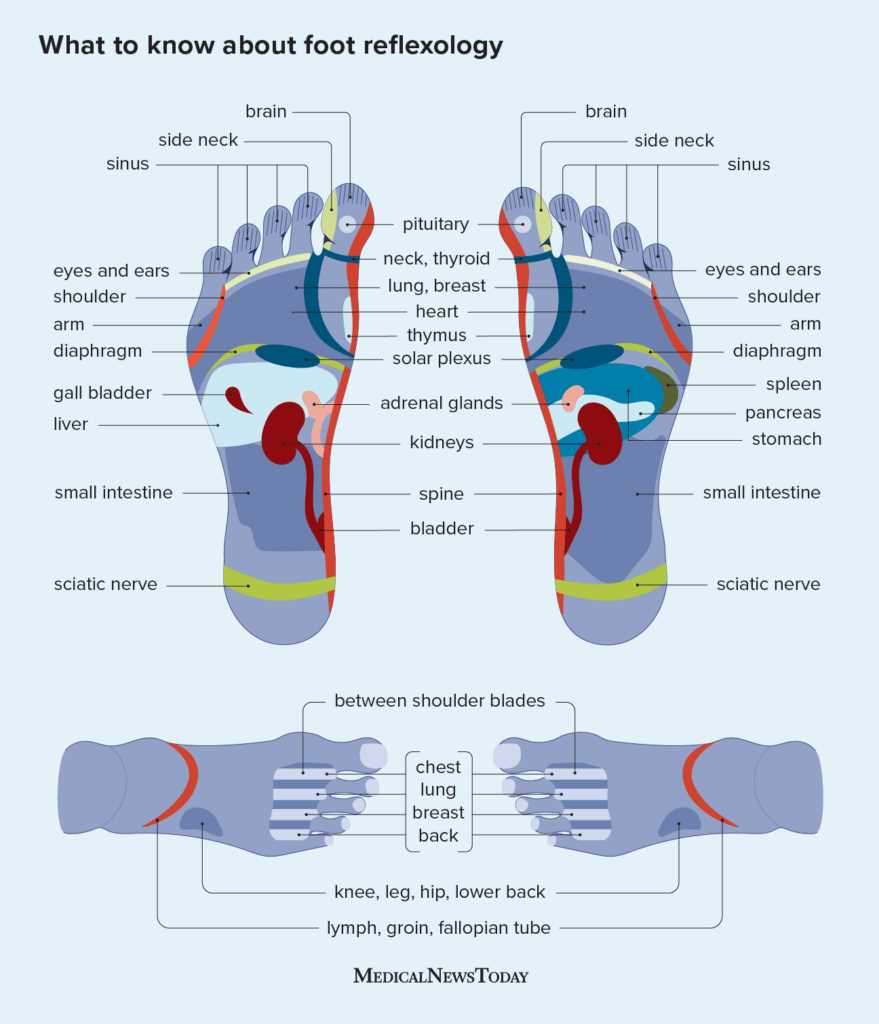
Foot Parts and Their Functions
This section explores the various components that contribute to the structure and movement of the lower extremities. Each element plays a crucial role in ensuring stability, balance, and mobility, allowing individuals to perform daily activities with ease.
Toes are essential for maintaining balance while standing and walking. They provide a gripping mechanism that enhances traction on various surfaces.
Arch serves as a shock absorber, distributing weight evenly and reducing strain on other areas. This curvature helps in adapting to different terrains and supports overall posture.
Heel acts as the primary point of contact during walking and running. Its robust structure aids in absorbing impact and providing support while propelling the body forward.
Ankle connects the lower leg to the foot, enabling a wide range of motion. It plays a pivotal role in stability and balance, facilitating various movements such as twisting and turning.
Ball of the foot acts as a pivot point during activities like running and jumping. This area is designed to bear weight and provide flexibility, contributing to an efficient stride.
Understanding these components and their functions is vital for appreciating the complexity of the human locomotor system and addressing any potential issues that may arise.
Diagram of Foot Muscles
This section explores the intricate network of muscles located within the lower extremity, emphasizing their crucial roles in movement and stability. Understanding the layout and function of these muscles is essential for appreciating their contributions to overall mobility and balance.
Overview of Muscle Groups
The muscles in this area can be categorized based on their locations and functions:
- Intrinsic Muscles: These muscles originate and insert within the structure, primarily responsible for fine motor control and stability.
- Extrinsic Muscles: These originate in the lower leg and extend down to the structure, aiding in more significant movements and force generation.
Key Functions of Muscles
The various muscle groups perform essential functions that facilitate movement:
- Flexion and Extension: These actions allow for bending and straightening of the toes and the arch.
- Abduction and Adduction: These movements enable the toes to spread apart and come together, essential for balance.
- Stabilization: Maintaining posture and stability while standing or moving is critical for preventing falls and injuries.
Role of Arches in the Foot
The structural formations within the lower extremity play a crucial role in providing support and balance during movement. These formations help distribute weight evenly across the entire structure, enhancing stability and overall function.
One of the primary functions of these arches includes:
- Weight Distribution: They assist in evenly spreading the body’s weight during various activities.
- Shock Absorption: These formations absorb impact, reducing stress on joints and tissues during activities like walking and running.
- Balance Maintenance: They contribute to overall equilibrium, enabling efficient movement on different surfaces.
In addition to their functional benefits, the structural integrity of these formations can also influence overall posture and alignment. Proper alignment is vital for minimizing discomfort and preventing potential injuries.
Understanding the significance of these formations is essential for maintaining optimal mobility and health. Ensuring their proper function can lead to enhanced performance in various physical activities.
Importance of Proper Footwear
Choosing the right footwear is crucial for overall well-being and comfort. Appropriate shoes can significantly influence mobility, posture, and even health. They serve not just as a fashion statement but as essential support for various activities, whether it’s walking, running, or standing for extended periods.
Health Benefits
Wearing suitable footwear helps to prevent injuries and alleviate discomfort. Quality footwear can reduce the risk of conditions such as plantar fasciitis and bunions. Proper cushioning and support promote better alignment and stability, ensuring that individuals can maintain an active lifestyle without undue strain.
Performance Enhancement
In sports and physical activities, the right shoes can enhance performance. Specialized designs provide the necessary grip and support, allowing individuals to excel in their respective activities. Investing in the right pair can lead to improved results, making every step count.
Foot Care and Maintenance Tips
Proper attention to your lower extremities is essential for overall well-being and comfort. Regular care can prevent discomfort, enhance mobility, and promote good health. Here are some valuable insights on how to keep your lower limbs in optimal condition.
Daily Hygiene Practices
Maintaining cleanliness is crucial. Ensure you wash your lower extremities daily with mild soap and warm water. Thoroughly dry the area, particularly between the toes, to prevent moisture buildup and fungal infections. Applying a suitable moisturizer can help keep the skin soft and prevent cracking.
Choosing the Right Footwear
Wearing appropriate shoes is vital for comfort and support. Select footwear that fits well and provides adequate cushioning. Avoid tight or ill-fitting options, as they can lead to various issues, including blisters and calluses. Consider using insoles for extra support and stability during daily activities.
Impact of Foot Alignment
Proper orientation and positioning of the lower extremities play a crucial role in overall body mechanics and function. Misalignment can lead to various issues, affecting not only the lower limbs but also other areas, such as the knees, hips, and spine. Understanding how these alignments influence physical performance and health is essential for prevention and rehabilitation.
Effects on Posture
Alignment discrepancies can significantly alter an individual’s posture. When the lower limbs are not correctly positioned, it may lead to compensatory mechanisms in the body. This can result in muscle imbalances, overuse injuries, and chronic pain, affecting daily activities and overall quality of life. Maintaining correct alignment is vital for sustaining a healthy posture and reducing the risk of injury.
Influence on Mobility
The orientation of the lower extremities directly impacts mobility and movement efficiency. Improper positioning can cause alterations in gait patterns, leading to fatigue and decreased performance during physical activities. Ensuring optimal alignment allows for better weight distribution and enhances agility, enabling individuals to move with greater ease and confidence.
Foot Parts and Their Measurements
This section provides an overview of various components of the lower limb and their respective dimensions. Understanding these elements is crucial for fields such as anatomy, orthopedics, and footwear design. Accurate measurements are essential for ensuring comfort and functionality in various applications.
Component Overview
The structure of the lower limb consists of several key elements, each serving unique functions and requiring precise measurements for proper assessment. These components play a significant role in biomechanics and the overall balance of the body.
Measurement Table
| Component | Measurement (cm) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Heel | 2.5 | The back part of the structure, crucial for shock absorption. |
| Arch | 3.0 | The curved structure providing support and flexibility. |
| Forefoot | 7.0 | The front part, responsible for propulsion during movement. |
| Width | 8.5 | The horizontal measurement across the widest part. |
| Length | 24.0 | The total distance from the heel to the tip of the forefoot. |
Comparing Human and Animal Feet
This section explores the structural and functional similarities and differences between the extremities of humans and various animals. Both species have evolved unique adaptations to navigate their environments, providing insights into their lifestyles and habitats.
Humans possess a specialized design that supports bipedal locomotion, characterized by an arch system that enables efficient walking and running. This configuration allows for balance and weight distribution while facilitating various movements.
In contrast, many animals exhibit different adaptations based on their modes of travel. For instance, quadrupeds typically have limbs designed for stability and speed, with structures that enable quick turns and acceleration. Some species, like birds, have developed lightweight and aerodynamic forms to aid in flight.
Furthermore, the claws and pads seen in numerous mammals provide traction and grip, essential for survival in diverse terrains. Understanding these variations helps appreciate how different species have adapted their extremities to thrive in their respective environments.