
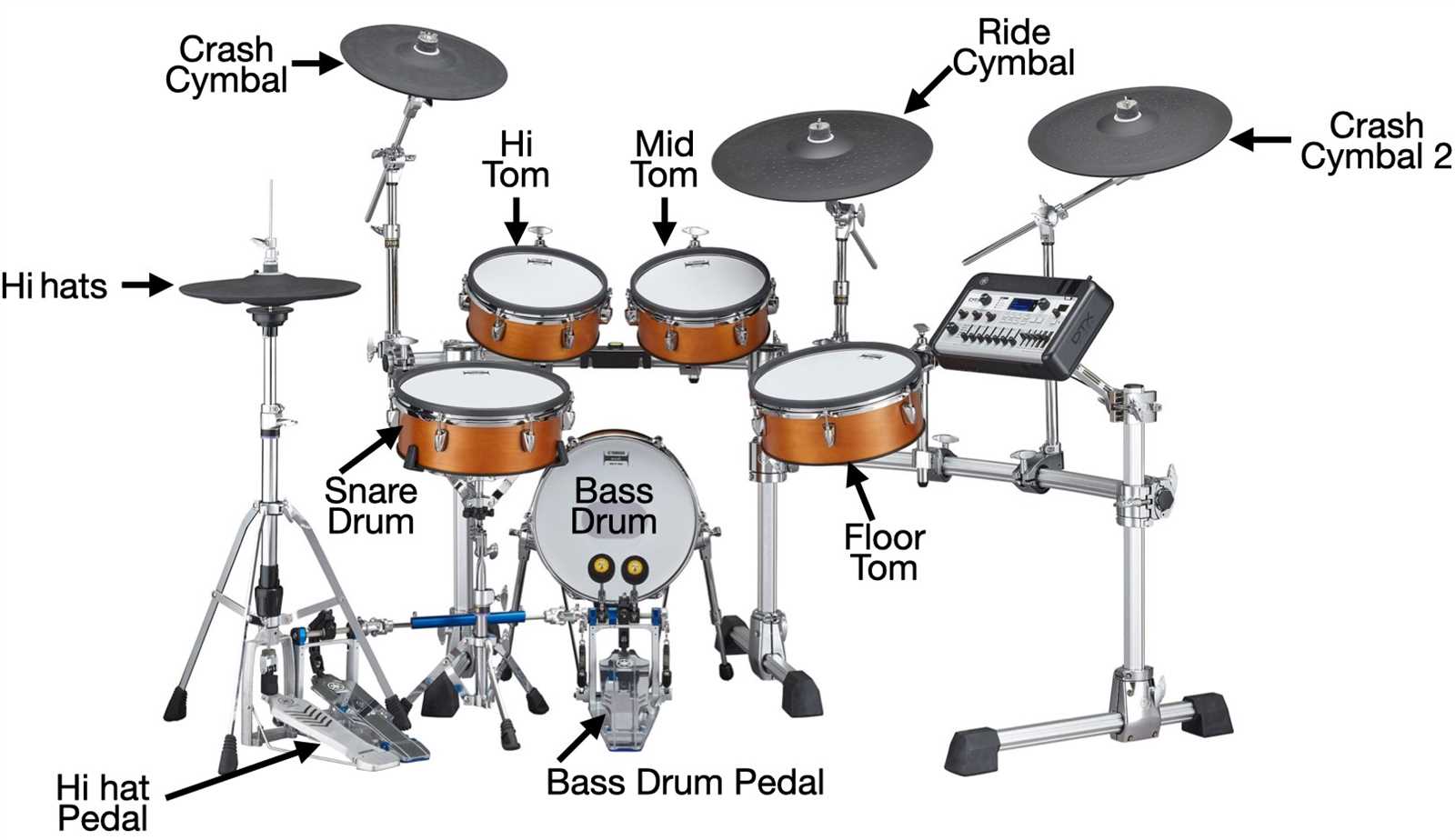
In the world of music, the foundation of rhythm is built upon an intricate assembly of various elements. These elements work harmoniously to produce captivating beats that resonate with audiences. Exploring the essential features of this ensemble unveils the complexity and creativity involved in crafting rhythmic sounds.
The configuration of these instruments showcases a diverse range of tones and dynamics, allowing for a multitude of musical expressions. Each component plays a vital role, contributing to the overall performance and enhancing the auditory experience. Whether it’s through striking, brushing, or rolling techniques, the interaction between these elements is crucial for creating engaging rhythms.
Familiarity with the arrangement and functionality of these instruments not only enriches one’s appreciation for music but also aids aspiring musicians in their journey. Understanding how each element contributes to the collective sound offers valuable insights into performance and composition. This exploration reveals the artistry behind rhythmic music, encouraging both players and listeners to delve deeper into the captivating world of percussion.

This section delves into the essential elements that comprise a percussion ensemble. Understanding these components is crucial for both performers and enthusiasts alike, as each element contributes to the overall sound and functionality of the ensemble. This overview will highlight the various features and their significance within the musical context.
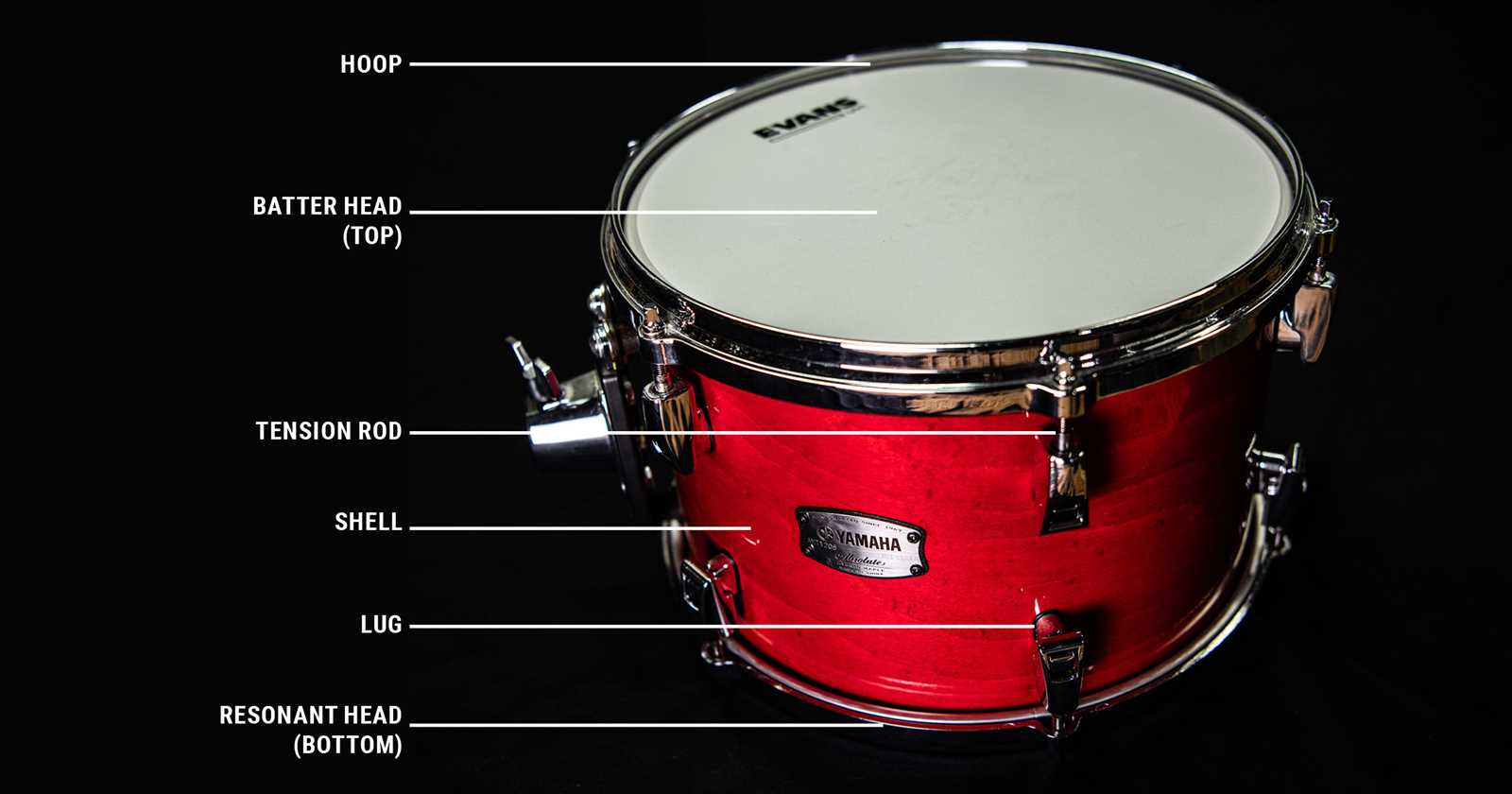
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Shell | The main body that produces sound, varying in size and material for tonal differences. |
| Heads | Stretched membranes that create vibrations, affecting pitch and tone when struck. |
| Hoops | Rings that hold the heads in place, influencing the overall tuning and sound projection. |
| Lugs | Hardware that secures the hoops and allows for tension adjustments on the heads. |
| Pedal | A mechanism used to strike a specific component, providing rhythmic accents. |
| Hardware | Supports and stabilizes the entire ensemble, including stands and mounts for various elements. |
Understanding the Bass Drum Functionality
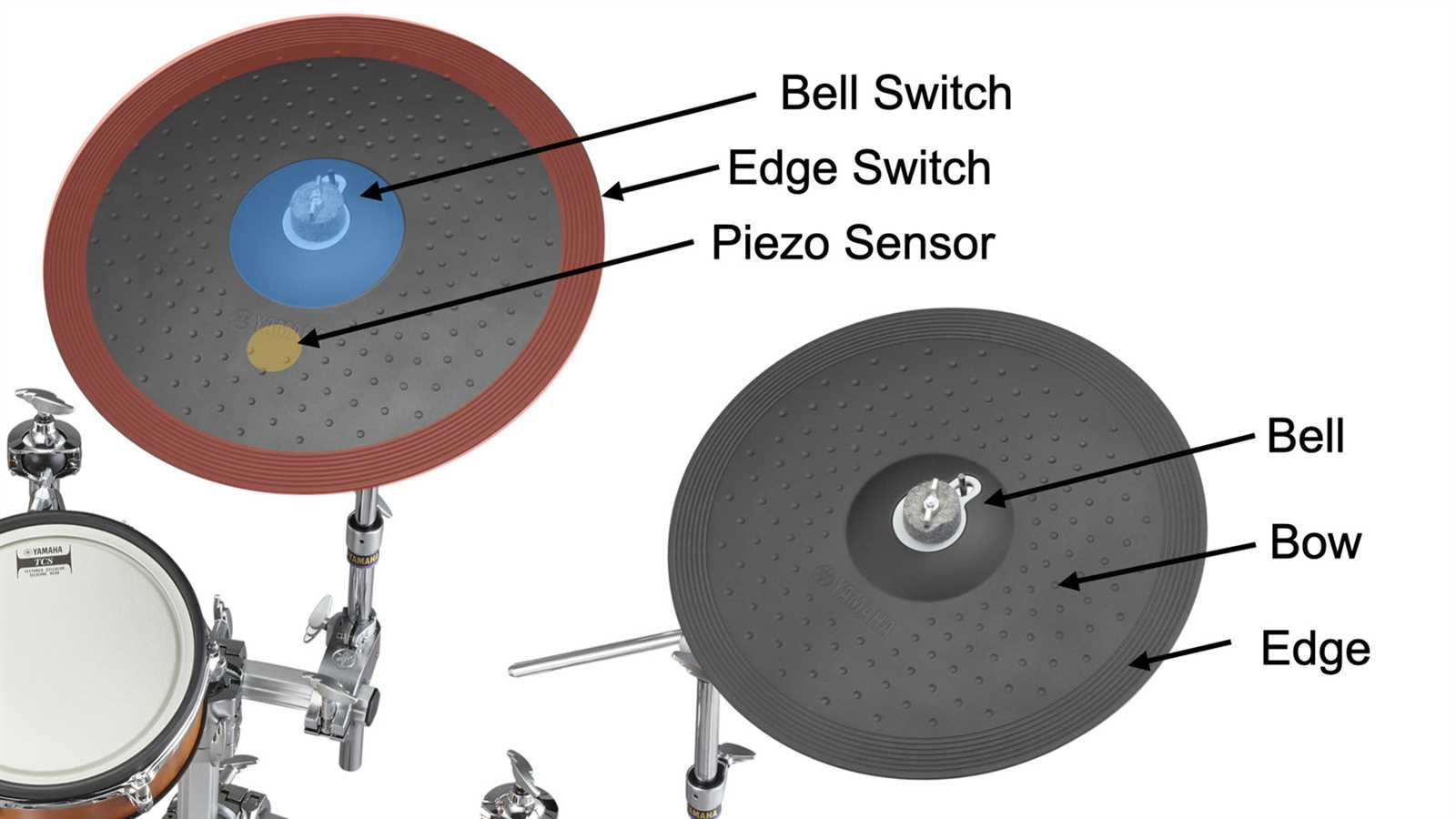
The bass component of a percussion ensemble serves a vital role in establishing the foundation of rhythm and harmony. This essential element produces deep, resonant tones that anchor musical passages, allowing other instruments to weave intricate patterns above it. The interaction between this element and various techniques creates a dynamic soundscape that enhances the overall musical experience.
Typically played with a foot-operated device, this foundational element allows the performer to maintain a steady pulse while freeing up their hands for other rhythmic tasks. The distinctive sound produced can vary significantly based on playing style, tension of the surface, and the materials used in its construction. In various musical genres, the function of this essential component may shift, from providing a simple pulse to executing complex rhythmic patterns that engage listeners.
In summary, understanding the role of this key component is crucial for both performers and composers. Its unique capabilities not only support the musical framework but also contribute to the expressive quality of the overall performance.
The Role of the Snare Drum
The snare is a crucial element in rhythmic ensembles, providing a sharp, cutting sound that serves as the backbone of many musical styles. Its unique timbre and ability to produce a quick, crisp attack make it an indispensable instrument in various genres, from jazz to rock. The placement of this component in a formation allows it to accentuate beats and add complexity to the overall rhythm, contributing significantly to the energy and drive of a performance.
This component is typically played using sticks, brushes, or mallets, each technique yielding different textures and dynamics. It interacts harmoniously with other components, enhancing the overall soundscape. Understanding the significance of this instrument can deepen appreciation for its role in musical arrangements.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Sound | Crisp and bright, cutting through other frequencies |
| Function | Provides backbeat and rhythmic structure |
| Techniques | Played with sticks, brushes, or mallets |
| Genres | Commonly used in rock, jazz, pop, and more |
Types of Tom-Toms Explained
Understanding the various types of tom-toms can enhance your musical experience. These components play a vital role in shaping the overall sound and rhythm, each contributing uniquely to a performance. Whether you are a beginner or a seasoned performer, knowing the distinctions among them is essential.
Categories of Tom-Toms
Tom-toms can be classified based on several factors, including their size, sound quality, and intended use. Here are the primary categories:
- Rack Tom-Toms: Typically mounted above the bass unit, these provide higher pitch and quick response.
- Floor Tom-Toms: Larger in size, these are positioned on the floor and offer deeper, resonant sounds.
- Concert Tom-Toms: Designed for orchestral settings, these are usually available without bottom heads, creating a more focused tone.
- Octobans: These are narrow and tall, offering unique tonal qualities, often used for specialized effects.
Choosing the Right Type

Selecting the appropriate tom-tom depends on your musical style and preferences. Consider the following factors when making your choice:
- Sound Quality: Assess how each type resonates and fits within your desired sound.
- Size: Larger units provide deeper tones, while smaller options yield higher pitches.
- Playing Style: Consider your technique and the genre of music you primarily perform.
By familiarizing yourself with these variations, you can make informed decisions that enhance your rhythmic expression.
Hi-Hat: A Critical Element
The hi-hat plays an indispensable role in the rhythmic landscape of music. It serves not only as a timekeeping device but also adds texture and dynamics to performances. Musicians utilize this element to create a variety of sounds that enhance the overall auditory experience.
Typically positioned to the left of the main performer, this component consists of two cymbals mounted on a stand, operated by a foot pedal. This unique setup allows for a wide range of articulations, making it a favorite among many genres.
Key characteristics of the hi-hat include:
- Versatility: It can produce sharp, cutting sounds or soft, subtle accents.
- Control: The pedal mechanism allows players to open and close the cymbals for varying effects.
- Rhythmic Foundation: It often sets the groove, providing a solid backbeat.
Different styles of playing can dramatically change the impact of this element within a musical piece. Here are some common techniques:
- Closed Hi-Hat: A crisp sound achieved by keeping the cymbals together.
- Open Hi-Hat: A sustained sound produced when the cymbals are apart.
- Chick Sound: A quick, sharp note created by tapping the foot pedal without striking the cymbals.
Ultimately, the hi-hat is a fundamental feature that enriches rhythm and expression, making it a critical element for any performance.
Cymbals: Varieties and Uses
Cymbals are essential elements in percussion ensembles, adding texture and character to musical compositions. These versatile instruments come in various forms, each designed to produce distinct sounds and effects, making them crucial for enhancing rhythm and dynamics in performance.
Types of Cymbals include ride, crash, splash, and hi-hat. Each variety serves a unique purpose, catering to different musical styles and genres. For instance, ride cymbals provide a steady pulse, ideal for maintaining tempo, while crash cymbals deliver sharp accents that can elevate climactic moments in a piece.
Usage in Music varies significantly based on the desired sound. Musicians may choose specific cymbals to achieve particular tonal qualities, such as bright and cutting or dark and warm. Moreover, the choice of cymbals can influence the overall feel of a performance, contributing to everything from jazz and rock to orchestral arrangements.
Understanding the various types and their applications allows percussionists to make informed choices, enhancing their playing experience and the overall musical presentation.
Drum Shells and Materials

The construction of the resonating components significantly influences the overall sound and performance of percussion instruments. Various substances and designs contribute to the tonal characteristics, volume, and projection. Understanding these materials is essential for selecting the right type for any musical setting.
Common Materials Used
- Wood: Offers a warm and rich tone, often preferred for its natural resonance. Common species include birch, maple, and mahogany.
- Metal: Provides a bright and cutting sound, commonly made from steel, aluminum, or brass, suitable for various genres.
- Acrylic: Known for its striking appearance and ability to produce a focused sound, often used in modern settings.
- Composite: A mix of different materials that can enhance durability and sound quality, appealing to versatile playing styles.
Impact on Sound

The choice of material directly affects the sonic properties:
- Resonance: Wooden structures generally provide warmer tones, while metal offers brighter, more cutting sounds.
- Volume: Thicker and denser materials can increase projection, making them ideal for louder environments.
- Durability: Some materials resist damage better, influencing longevity and maintenance needs.
Hardware: Stands and Accessories
The framework and supplementary elements play a vital role in enhancing the overall performance and functionality of a musical assembly. These components provide stability, adjustability, and convenience, ensuring that every musician can achieve the best possible sound.
Several types of equipment are essential for supporting various elements of the musical arrangement:
- Support Structures: These are crucial for holding various components securely in place, preventing unwanted movement during play.
- Adjustable Stands: Allowing for customization in height and angle, these stands enable musicians to position their instruments optimally for comfort and accessibility.
- Mounting Hardware: This includes clamps and brackets designed to attach different elements securely, facilitating a seamless setup.
- Foot Pedals: Essential for controlling sound and rhythm, these accessories enhance the versatility and dynamics of a performance.
- Carrying Cases: Protective gear is necessary for transporting equipment safely, ensuring longevity and durability.
Incorporating high-quality hardware and accessories not only improves the setup but also significantly impacts the sound quality and overall experience of the musician.
Exploring Drumheads and Their Types
Understanding the surfaces that produce sound in percussion instruments is essential for both musicians and enthusiasts. These elements significantly influence the tonal quality and resonance, shaping the overall auditory experience. Various types of coverings offer distinct characteristics, making it important to recognize their unique features and applications.
Common Types of Drumheads
- Coated Heads: Known for their warm, mellow tone, these coverings provide a textured surface that enhances stick control and reduces overtones.
- Clear Heads: Offering a brighter sound, these smooth coverings allow for a more pronounced attack and greater sustain.
- Mesh Heads: Typically used for practice, these provide a quieter playing experience while maintaining a realistic feel.
Choosing the Right Type
Selecting the appropriate covering depends on various factors, including musical style, desired sound, and playing technique. Here are some considerations:
- Genre: Different styles may require specific tonal qualities.
- Technique: Consider how your playing style affects sound production.
- Durability: Assess how often you perform and practice to determine the longevity needed.
Setting Up a Drum Kit
Arranging a percussion assembly is a crucial step in achieving optimal sound and playability. Each component needs to be positioned thoughtfully to enhance comfort and performance during practice or live sessions. This guide will provide insights on how to create an efficient and effective layout.
Choosing the Right Location
Selecting an appropriate space is essential for sound quality and ease of access. Ideally, the area should have sufficient room for movement while allowing the musician to reach all elements effortlessly. Consider the acoustics of the environment, as this can significantly affect the overall sound output.
Adjusting Heights and Angles

Once the location is determined, focus on the elevation and tilt of each component. Ensure that the seating arrangement is comfortable, allowing for a natural posture. Drumsticks should meet surfaces at a suitable angle to facilitate fluid playing. Make necessary adjustments based on individual preferences and playing styles, which can greatly enhance the overall experience.
Common Drum Set Configurations
Musical ensembles often feature various arrangements of percussive instruments, tailored to different genres and playing styles. These configurations can vary significantly, depending on the desired sound and the performance context. Understanding these common layouts can enhance both playing technique and overall musicality.
Each arrangement typically includes a combination of components designed to create a cohesive auditory experience. Below are some widely recognized configurations used by performers:
| Configuration Type | Instruments Included | Ideal Genre |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | Kick, snare, hi-hat, toms, cymbals | Rock, Pop |
| Jazz | Kick, snare, hi-hat, ride, floor tom | Jazz, Swing |
| Marching | Snare, bass, cymbals, tenors | Marching Band, Parades |
| Electronic | Drum machine, sampler, pads | Electronic, Dance |
| Fusion | Kick, snare, toms, electronic pads | Fusion, Progressive Rock |
These configurations serve as a foundation for creating diverse rhythmic patterns and enhancing musical expression. Each layout can be customized further based on individual preferences and performance requirements.
Care and Maintenance Tips

Maintaining your percussion equipment is essential for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Regular attention to various elements can prevent unnecessary wear and enhance the overall sound quality.
Start by cleaning the surfaces regularly to remove dust and grime. Use a soft, damp cloth for gentle cleaning, and avoid abrasive materials that could cause scratches. Pay special attention to areas that may accumulate dirt or residue from playing.
Check for any signs of wear or damage periodically. Loose components should be tightened to maintain structural integrity, while any damaged pieces should be repaired or replaced promptly to avoid further issues.
Proper storage is also vital. Keep your gear in a dry, temperature-controlled environment to prevent warping or degradation. Using protective cases can shield against dust and accidental impacts when not in use.
Lastly, consider regular professional inspections or servicing. Experienced technicians can provide valuable insights and maintenance that may not be evident during casual check-ups, ensuring your equipment remains in top condition for years to come.
History of the Drum Set
The evolution of percussion ensembles has been a fascinating journey, reflecting cultural shifts and technological advancements. This collection of instruments has transitioned from simple, hand-played tools to complex arrangements utilized in various musical genres. Understanding this progression provides insight into how rhythm has shaped and continues to influence music across the globe.
Early Beginnings
In ancient times, rhythm-making devices were integral to ceremonial and social events. Early forms emerged in various cultures, with each society crafting unique variations. These instruments often featured animal skins and natural materials, highlighting the connection between music and daily life.
Modern Developments
The 19th century marked a significant turning point with the introduction of mechanized components. Innovations such as foot-operated pedals and metal hardware transformed traditional instruments into more versatile tools. This transformation laid the groundwork for contemporary performance, enabling musicians to explore new styles and techniques.