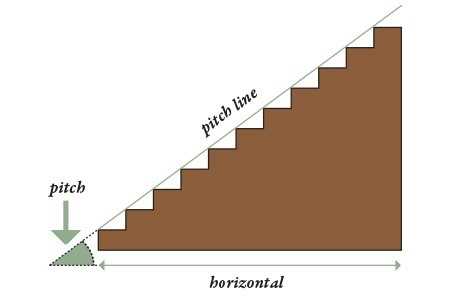
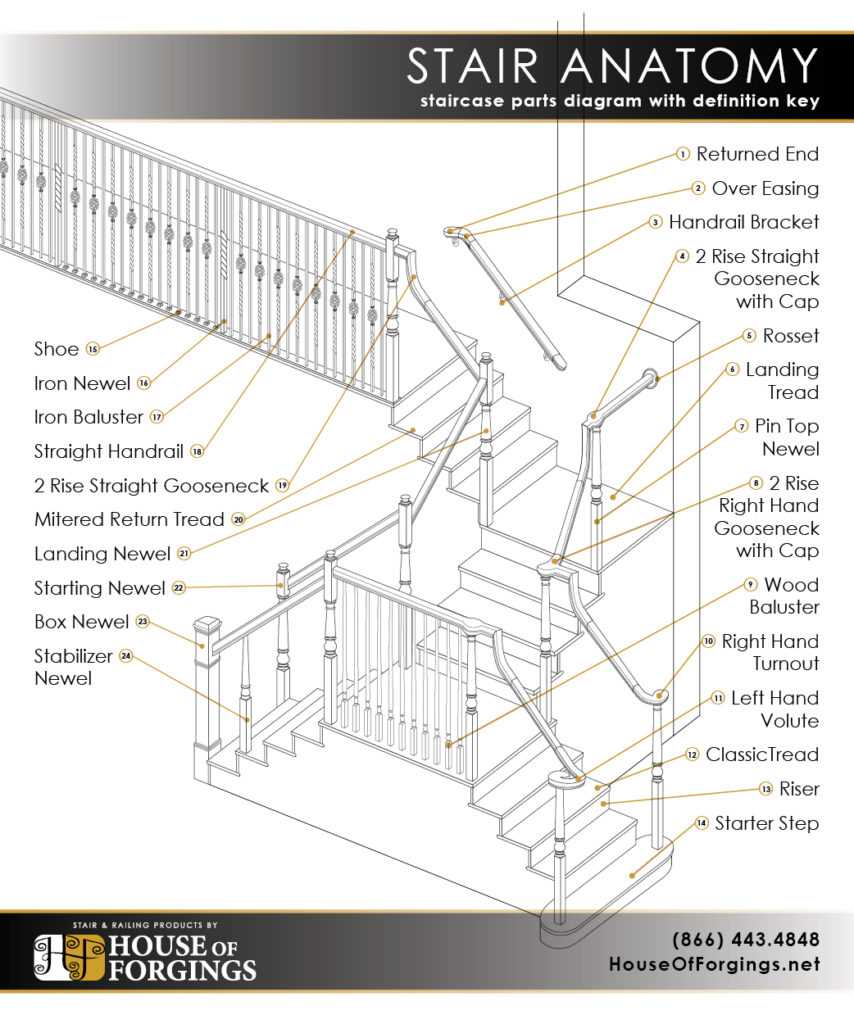
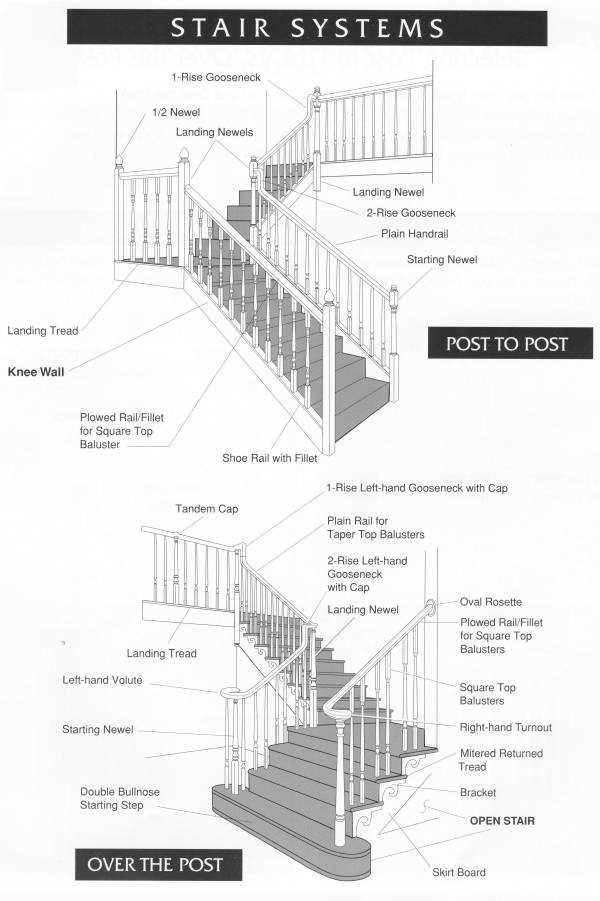
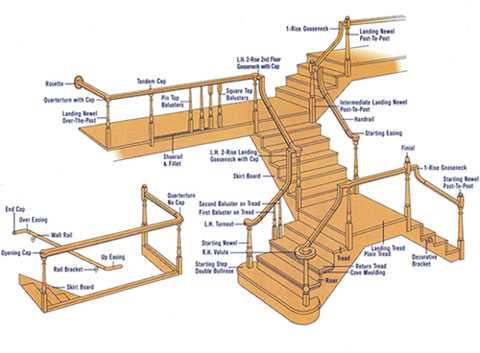
The construction of a vertical ascent encompasses various elements that contribute to its overall functionality and aesthetic appeal. Recognizing the significance of each component helps in appreciating the craftsmanship involved in designing these architectural features. A well-constructed set of steps not only ensures safety but also enhances the visual charm of any space.
Each segment plays a vital role in supporting both the users and the structure itself. From the base to the top, every section is designed to provide stability and comfort. Whether it is the inclination, the tread, or the rise, understanding these segments leads to better design decisions and enhances the user experience.
Moreover, the interplay between different elements creates a harmonious flow that is essential for effective navigation. A thoughtful arrangement ensures that movement is both safe and fluid. By examining these individual aspects, one can gain insights into the intricate balance of form and function inherent in this essential architectural feature.
The construction of a vertical ascent involves essential components that contribute to both functionality and safety. These elements work in harmony to provide support and accessibility for individuals moving between different levels.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
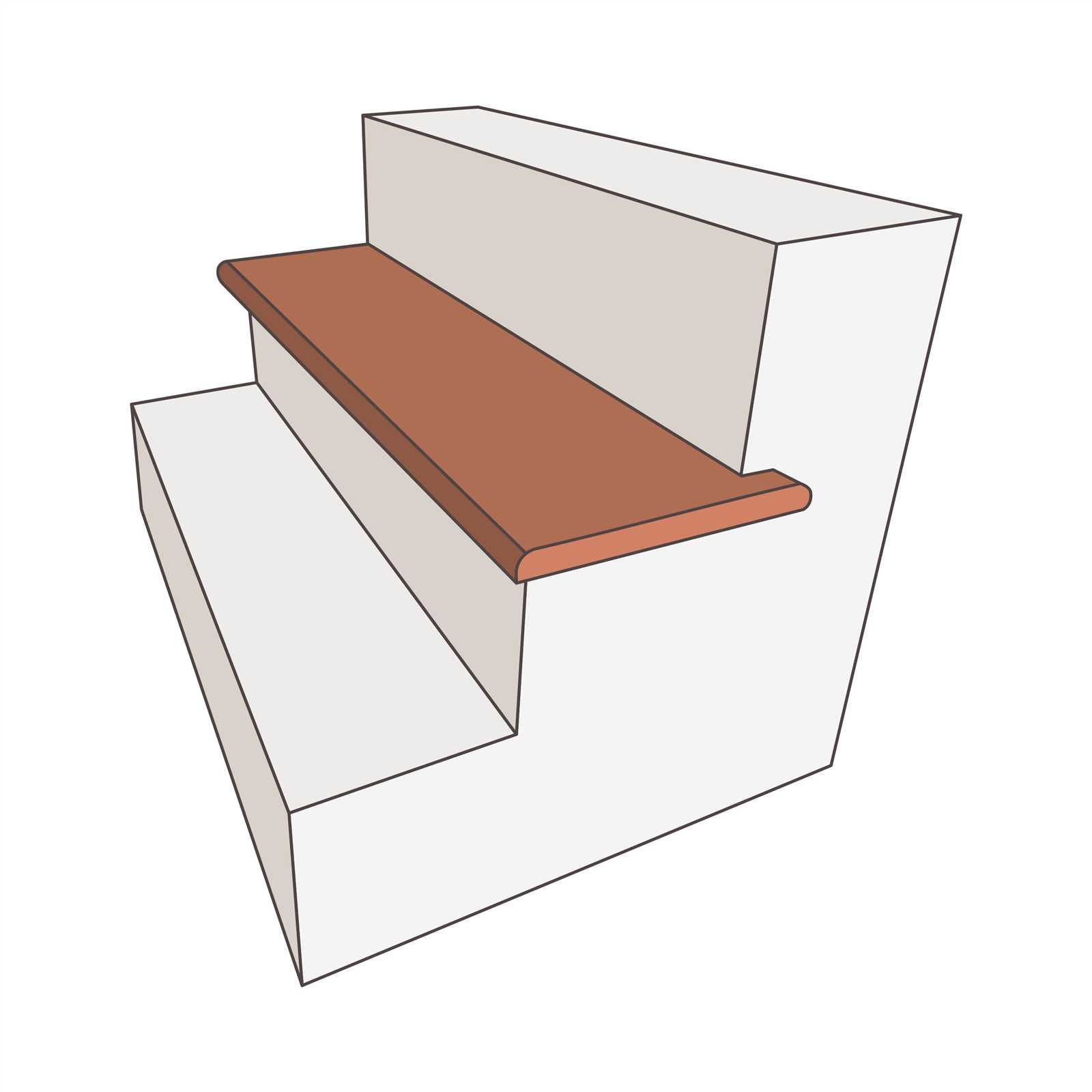
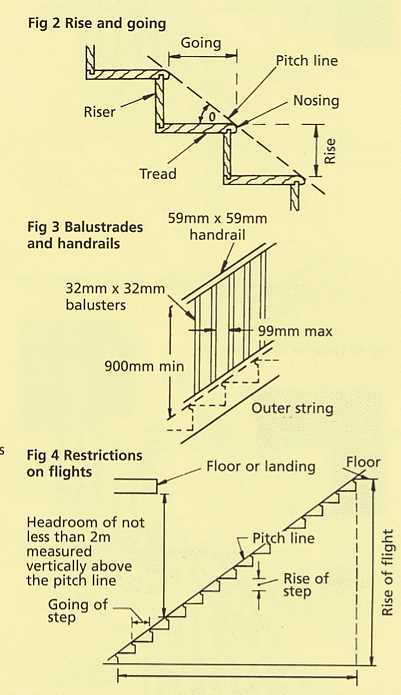
| Tread | The horizontal surface where one steps. It is crucial for ensuring stability and comfort when ascending or descending. |
| Riser | The vertical section that connects two consecutive treads. It plays a significant role in the overall height of each step and aids in maintaining balance. |
Understanding the relationship between these two components is vital for effective design and safety. The correct measurements and materials contribute to a secure and pleasant experience for users.
Handrails: Function and Design
Handrails serve a vital role in enhancing safety and providing support in elevated structures. Their design can greatly influence both functionality and aesthetics, making them an essential element in any elevated environment.
Beyond merely offering assistance to individuals as they navigate changes in elevation, handrails contribute to the overall visual appeal of a space. The selection of materials, shapes, and finishes allows for a wide range of styles that can complement various architectural themes.
| Functionality | Design Considerations |
|---|---|
| Provide support for stability | Material choice (wood, metal, etc.) |
| Enhance safety for users | Style compatibility with surroundings |
| Guide movement along pathways | Color and finish selection |
| Increase accessibility for all | Ergonomic height and grip |
Common Staircase Materials
When it comes to constructing elevated structures, the choice of substances plays a crucial role in both aesthetics and functionality. Various materials offer unique benefits and can significantly impact the overall look and durability of the ascent.
- Wood: A classic option that provides warmth and character. It can be customized in different finishes and types, such as oak, maple, or pine.
- Concrete: Known for its strength and durability, this material is often used in modern designs. It can be molded into various shapes and finished with different textures.
- Metal: Typically used for railings and supports, metal offers a sleek, contemporary look. Options include steel, aluminum, and wrought iron.
- Stone: This timeless choice adds elegance and can withstand heavy use. Common types include granite, marble, and slate.
- Composite: Made from a blend of materials, composites offer durability and low maintenance. They can mimic the appearance of wood or stone without the drawbacks.
Choosing the right material depends on various factors, including budget, desired style, and the overall design of the structure. Each option brings its own unique qualities to the table, allowing for diverse designs and finishes.
Importance of Staircase Measurements
Accurate dimensions are crucial when designing or constructing a multi-level structure. Proper measurements ensure safety, functionality, and aesthetic appeal. Neglecting these factors can lead to numerous issues, affecting both the usability and overall design of the space.
Safety Considerations
One of the primary reasons to focus on precise dimensions is safety. Miscalculations can lead to:
- Inconsistent height and depth of steps, increasing the risk of trips and falls.
- Insufficient landing areas, creating hazards during ascent or descent.
- Non-compliance with building codes, which can result in legal consequences.
Functional Efficiency
Well-measured structures enhance the efficiency of movement between levels. Key factors include:
- Proper rise and run ratios that promote comfortable navigation.
- Space optimization that accommodates furniture and traffic flow.
- Aesthetic harmony that complements the overall architectural style.
Safety Features for Stairs
Ensuring the security of vertical transitions within structures is essential to prevent accidents and injuries. Various enhancements can be implemented to create a safer environment for users. From illumination to tactile surfaces, these elements play a crucial role in maintaining safety during navigation.
Handrails and Guardrails
Handrails provide vital support for individuals while ascending or descending, reducing the risk of falls. Properly installed guardrails offer additional protection, especially in elevated areas, ensuring that users remain secure within designated pathways.
Anti-Slip Surfaces
Utilizing anti-slip materials is an effective way to enhance grip and stability. Textured finishes or adhesive strips can be applied to surfaces, significantly decreasing the likelihood of slipping, particularly in wet conditions.
Architectural Considerations for Stairs

Designing an elevated pathway involves various factors that impact functionality and aesthetics. It is essential to integrate these elements harmoniously to ensure safety and comfort while enhancing the overall architectural appeal of the structure.
Key Factors in Design
- Safety Regulations: Compliance with local building codes is crucial to prevent accidents and ensure user safety.
- Dimensions: The width, height, and depth of each step must be carefully calculated to accommodate various users.
- Materials: The choice of materials affects durability, maintenance, and the visual character of the installation.
- Lighting: Proper illumination can enhance visibility and reduce the risk of slips and falls.
- Accessibility: Consideration for individuals with mobility challenges is vital for inclusivity.
Aesthetic Integration
- Style: The design should reflect the overall architectural theme of the building.
- Color Palette: Choosing colors that complement the surrounding environment can create a cohesive look.
- Finishing Touches: Decorative elements, such as railings and landings, should enhance both functionality and visual interest.
Staircase Aesthetics and Styles
The visual appeal of elevated structures plays a crucial role in enhancing the overall ambiance of a space. Various designs contribute uniquely to the character of a room or corridor, influencing both functionality and beauty. This section explores diverse styles that can elevate the aesthetic quality of any environment.
Contemporary Designs

Modern frameworks often embrace minimalism, featuring sleek lines and open concepts. Glass and metal are popular materials, providing a sense of spaciousness and sophistication. The integration of these elements can create a striking contrast against traditional decor.
Traditional Elegance
Classic styles typically incorporate rich woods and ornate detailing. The use of handcrafted elements adds a touch of charm, making these structures timeless. Curved shapes and intricate balustrades enhance the grandeur, appealing to those who appreciate a more historical aesthetic.
Innovative Staircase Designs Today
Modern architectural approaches have redefined the concept of vertical transitions within spaces. Designers now emphasize not only functionality but also aesthetics, creating features that serve as focal points in residential and commercial environments. This evolution has led to the emergence of unique configurations that blend creativity with structural integrity.
Materials and Techniques
The choice of materials plays a pivotal role in contemporary constructions. Designers experiment with a variety of substances, including glass, metal, and sustainable wood, to enhance the visual appeal and functionality of these transitions. Innovative techniques such as cantilevering and spiral formations challenge traditional concepts while ensuring safety and comfort.
Customization and Personalization
Today’s designs often reflect the personality and preferences of the users. Customization options allow individuals to create solutions tailored to their needs and styles. This trend encourages a harmonious blend of form and function, resulting in unique creations that enhance the overall ambiance of any space.
| Design Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Floating Steps | Steps that appear to hover, providing a modern and airy feel. |
| Spiral Forms | Circular designs that save space while adding an artistic touch. |
| Glass Railings | Clear barriers that maintain open sight lines and enhance safety. |
| LED Lighting | Integrated lighting for safety and ambiance, highlighting the design. |