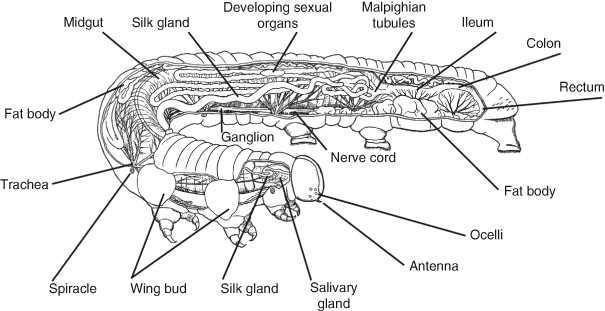
Understanding the structure of tiny organisms opens the door to comprehending their behavior and survival strategies. These creatures, often unnoticed, possess a fascinating and intricate physical framework that allows them to thrive in various environments.
The external body of such a creature can be divided into several segments, each serving a unique function. The design of these sections supports everything from movement to interaction with the environment, showcasing an incredible level of specialization.
By examining the physical layout and the roles each section plays, we can gain deeper insights into how these small beings adapt to their surroundings. Each part is a critical component in the complex puzzle of their survival and interaction with the world.
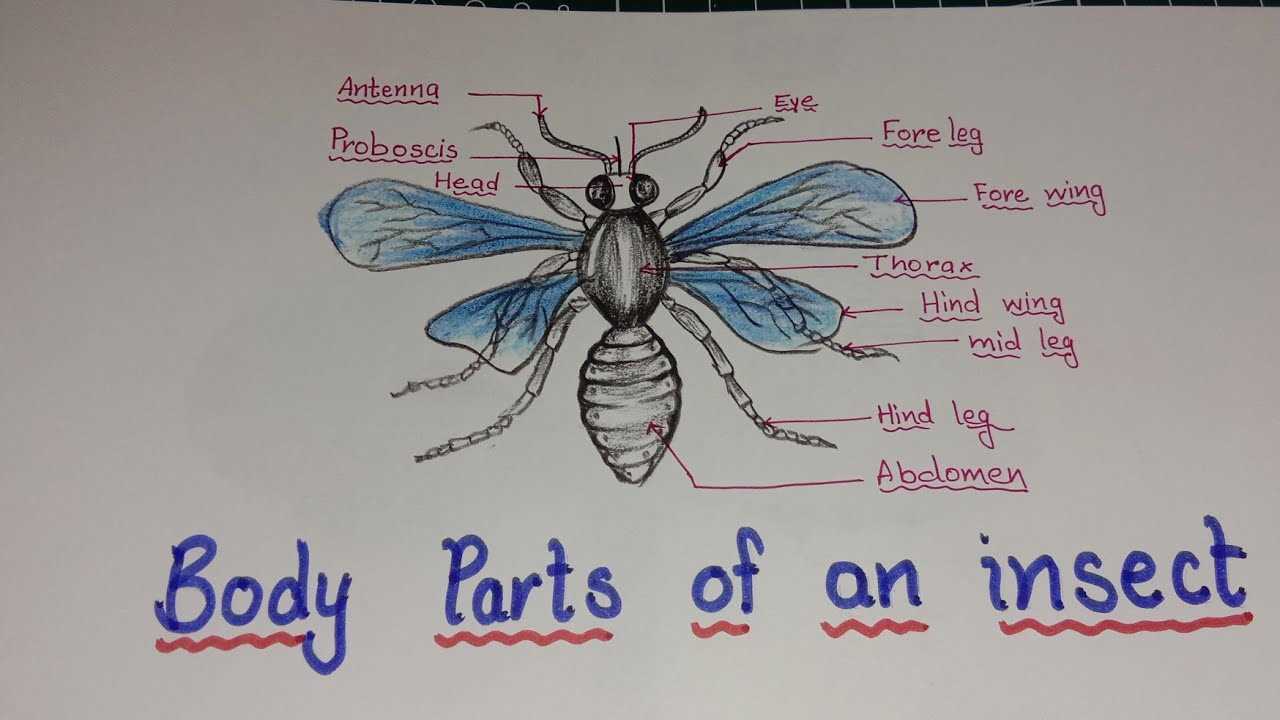
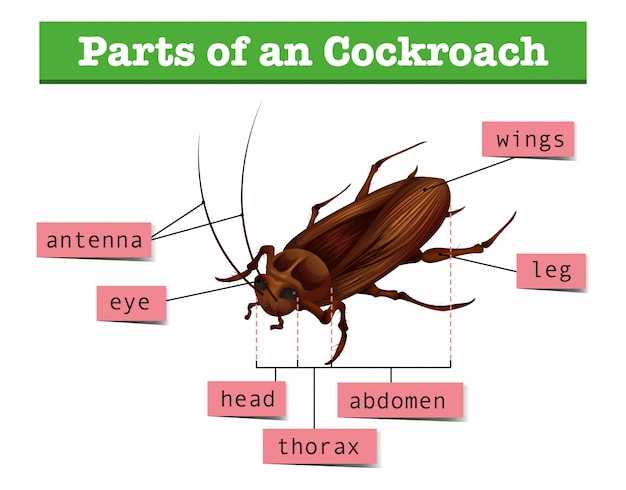
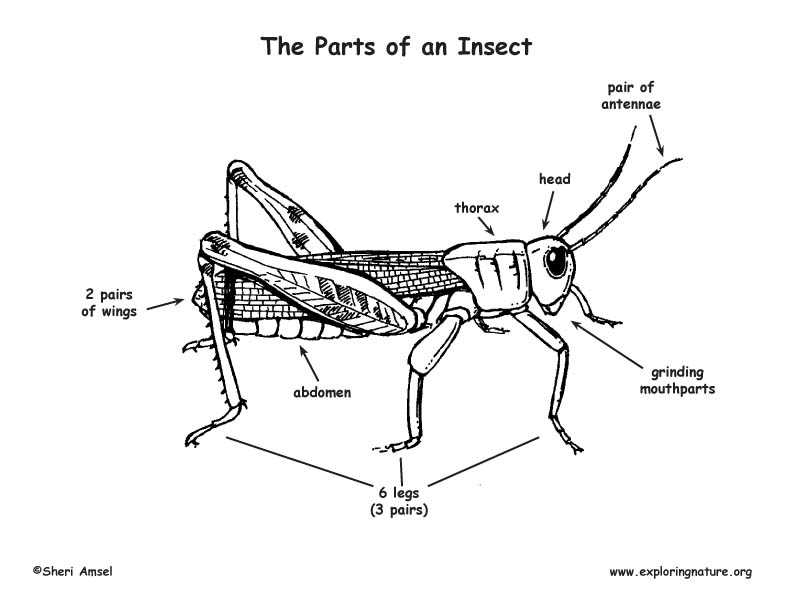
Anatomy Overview of an Insect
The structure of these small creatures is highly specialized, allowing them to adapt to various environments. Their bodies are organized in distinct regions, each responsible for different essential functions. Understanding this organization provides insights into how these organisms interact with their surroundings.
Key areas include:
- The first region, which houses the central control center and sensory organs.
- A middle segment dedicated to movement, featuring critical components that enable mobility.
- The final section, responsible for crucial biological processes necessary for survival and reproduction.
This complex arrangement ensures that these creatures can efficiently perform all necessary tasks for survival and adaptation in diverse habitats.
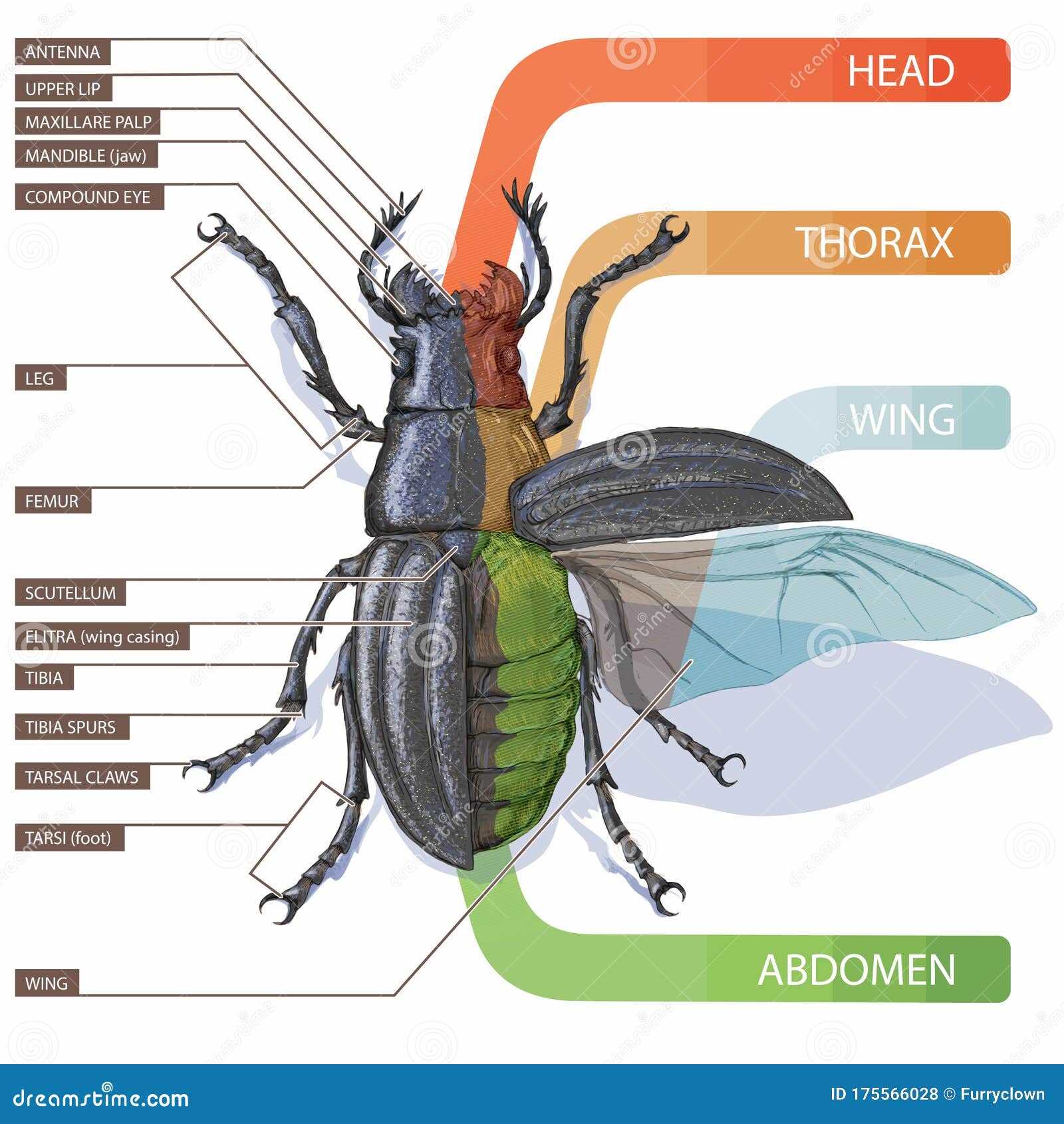
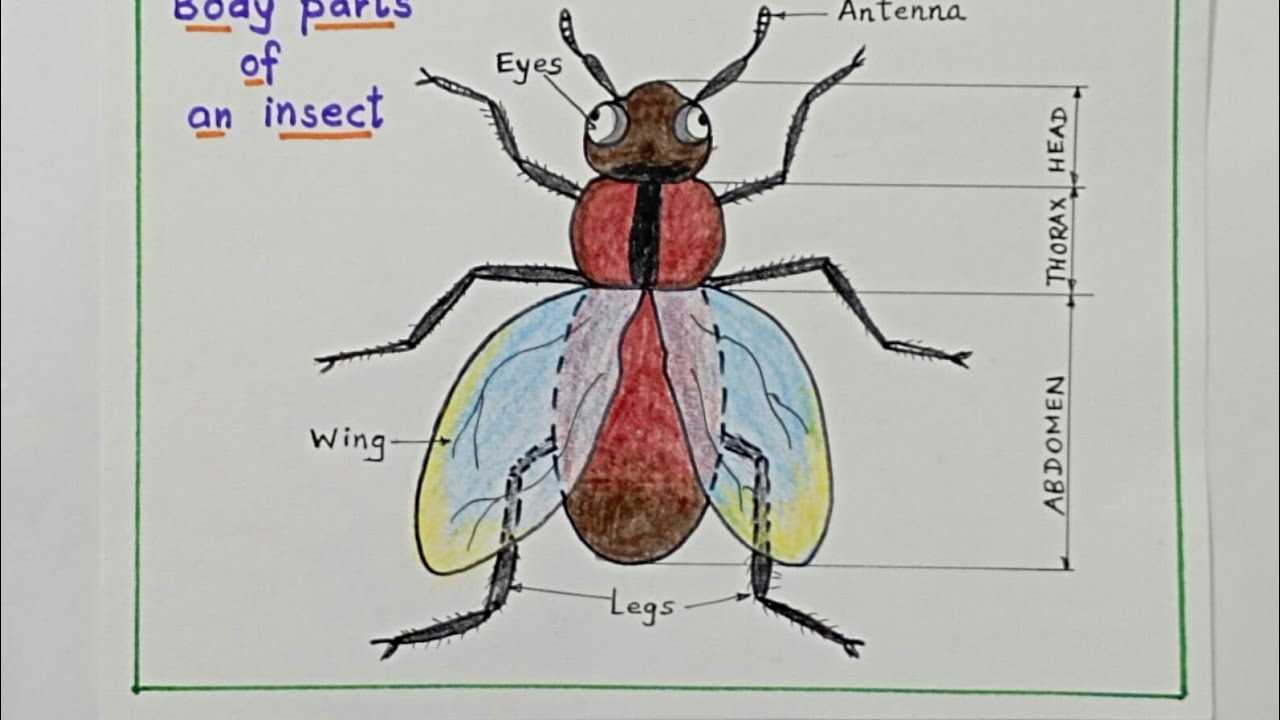
External Body Structure of Insects
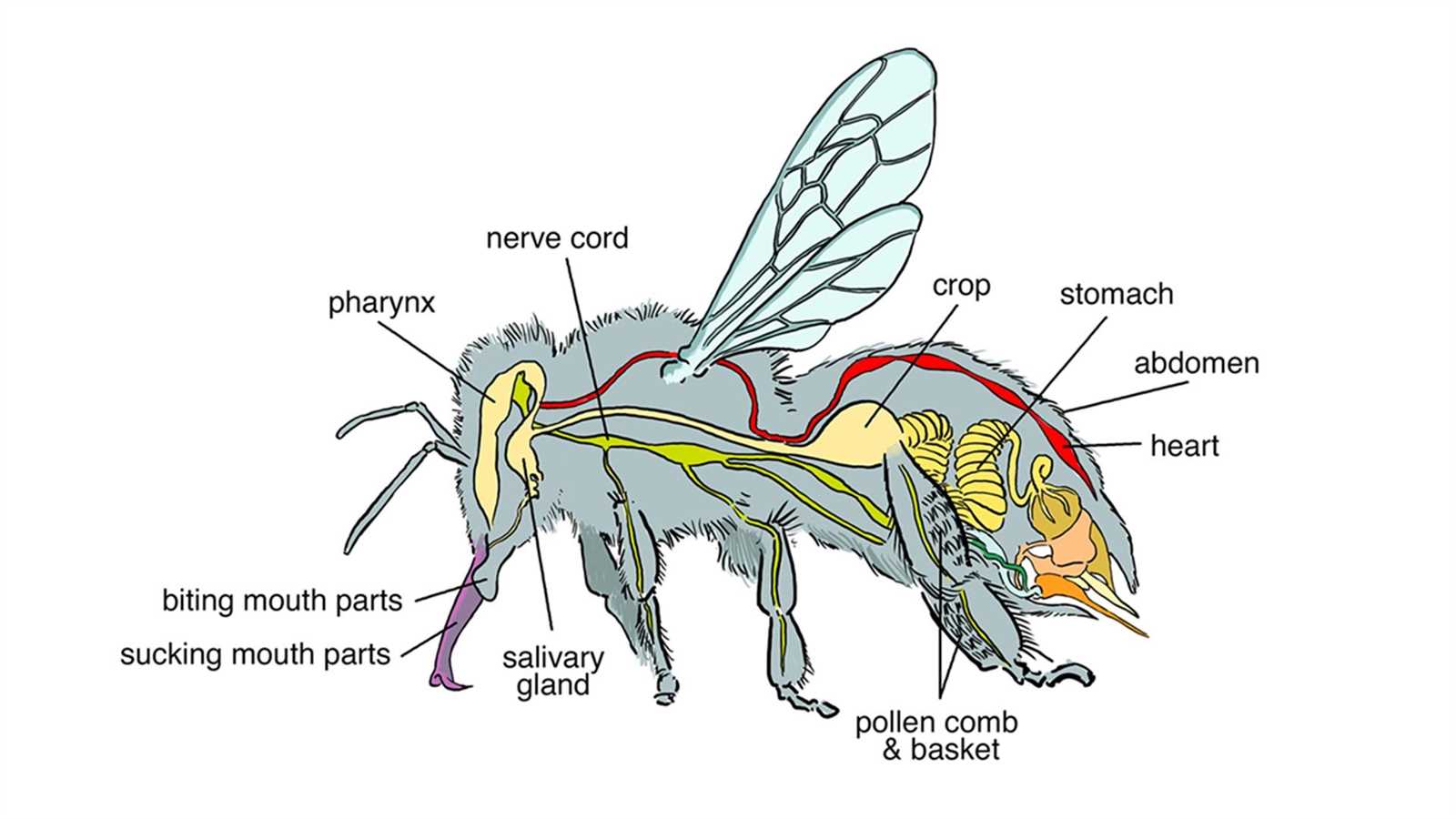
The outer appearance of small arthropods is characterized by a complex design that serves various vital functions. The external framework provides protection and support, while also enabling movement and interaction with the environment. This structure is a key aspect of their survival, adapting to their diverse habitats and life strategies.
The outer covering is typically divided into three main sections. Each section has its unique role, contributing to different abilities such as locomotion, sensory input, and feeding. This segmentation allows these creatures to perform specialized tasks effectively, ensuring their adaptability and evolutionary success.
Additionally, the surface may be covered with fine hairs or other extensions, which enhance their sensitivity to environmental changes. This intricate design not only defines their appearance but also plays a crucial role in their interaction with the world around them.
Function of Antennae in Insects
The antennae play a crucial role in the daily survival and activities of various species. These sensory organs help in gathering essential information from the surrounding environment, aiding in navigation, communication, and even locating food sources.
Sensing the Environment
Antennae serve as sensitive receptors for detecting chemical signals, temperature changes, and humidity. Through their ability to sense vibrations and airborne particles, they allow creatures to respond quickly to potential dangers or opportunities in their surroundings.
Communication and Navigation
These organs are also essential for communication between individuals, especially during mating seasons. They enable species to identify each other and their locations, assisting in both short-range and long-distance navigation.
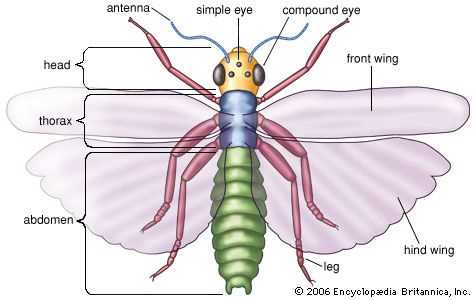
Insect Eyes: Structure and Purpose
The visual organs of many small creatures are highly specialized and adapted to their environment. These fascinating visual tools serve various functions, from detecting movement to discerning shapes and light. Understanding their structure helps reveal how these creatures interact with the world around them.
Compound Eyes
One of the key features of these visual systems is the presence of compound eyes, which are composed of numerous small units called ommatidia. Each ommatidium functions as an individual light receptor, allowing for a wide field of view and sensitivity to movement. This design gives certain species remarkable abilities in detecting even the slightest shifts in their surroundings.
Ocelli and Their Role
In addition to compound eyes, many species possess simpler visual organs known as ocelli. These organs primarily detect light intensity and are essential for stabilizing flight and navigation. Though less complex, ocelli contribute to maintaining orientation and reacting to environmental changes.
Role of Wings in Insect Mobility
Wings play a significant part in the movement capabilities of many small creatures. They serve not only for flight but also enhance their agility and responsiveness in various environments. The structure, shape, and function of these appendages determine the creature’s ability to move efficiently through the air, helping it navigate, evade predators, and search for food.
Functions of Wings in Movement
- Flight: Wings are essential for aerial mobility, allowing rapid travel over long distances.
- Maneuverability: They provide control during flight, enabling quick turns and changes in direction.
- Speed and Distance: Depending on wing design, creatures can achieve high speeds or cover vast areas in search of resources.
Adaptations in Wing Structure
Various species exhibit unique adaptations in their wings that contribute to their movement efficiency. These modifications help the
The Functionality of Insect Legs
The limbs of these small creatures serve various vital purposes that contribute to their survival and adaptability. They are not merely for movement; instead, they play crucial roles in multiple activities essential for life.
Locomotion and Mobility
One of the primary functions of these limbs is to enable swift and efficient movement across diverse terrains. Their structure allows for a range of motions, from walking and running to jumping and climbing. This versatility enhances their ability to escape predators and pursue prey.
Interaction with Environment
Beyond mobility, these appendages are instrumental in interacting with the surroundings. They aid in grasping, digging, and manipulating objects, which is vital for feeding and nesting. Additionally, some species have adapted specialized limbs for unique tasks, further showcasing the evolutionary significance of these structures.
How Insects Use Their Mouthparts
The specialized feeding structures of these creatures play a vital role in their survival and ecological interactions. These adaptations allow them to exploit a wide range of food sources and environments, showcasing the diversity of feeding strategies in the animal kingdom.
For instance, some species possess elongated structures that facilitate the extraction of nectar from flowers, making them essential pollinators. Others have strong mandibles suited for biting and chewing, enabling them to consume plant material or even prey. Additionally, certain varieties have evolved to use their mouthparts for siphoning liquids, allowing them to feed on substances like blood or decaying organic matter.
Overall, the functionality of these mouth structures reflects the ecological niches that different species occupy, highlighting the intricate relationships between these organisms and their environments.
Significance of the Insect Thorax
The thorax serves as a crucial region in the anatomy of these remarkable creatures, playing a vital role in their overall functionality and movement. This segment is primarily responsible for housing essential structures that enable various activities, including locomotion and the operation of appendages.
Role in Locomotion
This section is equipped with the legs and, in some species, wings, facilitating diverse modes of travel. The design and strength of these components allow for a wide range of movements, from walking and running to flying, showcasing the adaptability of these organisms in various environments.
Support and Protection
Beyond mobility, this region also provides structural support for vital organs and systems. It offers a protective casing that safeguards internal components from environmental hazards, ensuring the survival and efficiency of these creatures in their respective habitats.
The Abdomen and Its Role in Insects
The posterior segment of these creatures plays a crucial role in their overall functioning and survival. It houses essential systems and structures that contribute to various biological processes, enabling these organisms to thrive in diverse environments.
Key Functions of the Abdomen
One of the primary functions of this segment is to facilitate digestion and nutrient absorption. Inside, specialized organs work together to break down food, allowing for efficient energy extraction. Moreover, the posterior part is integral to the reproductive system, housing organs that ensure the continuation of the species.
Adaptations and Survival
Additionally, this area may possess adaptations that enhance survival. Some species have evolved features such as protective coverings or specialized appendages that assist in movement or defense. These modifications highlight the importance of this segment in the organism’s interaction with its habitat.
Understanding the Exoskeleton of Insects
The outer covering of certain arthropods plays a crucial role in their survival and adaptation. This structure not only serves as a protective barrier but also contributes to various functions essential for the organism’s life. Its unique composition and design enable these creatures to thrive in diverse environments.
Composition and Functionality
This protective layer is primarily made of chitin, a resilient and flexible substance. It provides strength and durability, allowing these organisms to withstand environmental pressures. Additionally, the exoskeleton aids in moisture retention, preventing dehydration in various habitats.
Adaptations and Variations
Different species exhibit a range of adaptations in their outer coverings to suit their lifestyles. For instance, some may possess a hard shell for defense, while others might have a softer, more pliable exterior to facilitate movement and growth. These variations highlight the evolutionary ingenuity of these creatures in overcoming challenges within their ecosystems.
The Importance of Insect Spiracles
Spiracles play a crucial role in the respiratory system of many arthropods. These specialized openings are essential for the exchange of gases, allowing oxygen to enter and carbon dioxide to exit. Their design and positioning contribute significantly to the efficiency of respiration, adapting to the needs of various species.
These structures are strategically located along the body, providing optimal access to the environment. The ability to open and close helps regulate moisture loss and protect against harmful substances. This function is vital for survival, particularly in diverse habitats where conditions can change rapidly.
Moreover, the spiracles’ role extends beyond mere respiration. They influence the overall physiology of these organisms, impacting growth and development. Understanding their significance can provide insights into the broader ecological roles that these creatures play in their ecosystems.
Function of Compound Eyes in Insects
The compound visual organs of certain arthropods play a crucial role in their ability to navigate and interact with their surroundings. These unique structures allow for a wide field of vision, enabling creatures to detect movement and changes in light from multiple angles simultaneously.
Structure and Mechanism
These organs are composed of numerous individual units, each contributing to the overall perception of the environment. Each unit functions independently, capturing light and images, which are then processed collectively. This architecture allows for:
- Wide-angle vision, minimizing blind spots.
- Rapid detection of motion, essential for evading predators.
- Color differentiation, aiding in foraging and mating behaviors.
Advantages for Survival
The ability to perceive a broad spectrum of stimuli offers significant advantages in the natural world:
- Enhanced awareness of potential threats.
- Improved navigation during flight or movement.
- Increased efficiency in locating food and mates.
Overall, these visual organs are vital for the survival and adaptability of various species, shaping their behaviors and interactions within ecosystems.
Exploring the Segments of Insect Legs
The anatomy of the limbs found in various arthropods showcases a remarkable complexity that contributes to their adaptability and functionality in diverse environments. Understanding the structure of these extremities reveals the intricate mechanisms that enable movement and interaction with their surroundings.
Typically, the limbs are divided into several distinct regions, each serving a unique purpose. The coxa connects to the body, providing a stable base for movement. Following this is the trochanter, which acts as a pivot point, enhancing the range of motion. The femur follows, often the largest segment, which plays a critical role in locomotion. The next component is the tibia, usually elongated and crucial for support and propulsion. Finally, the tarsus, consisting of multiple smaller segments, allows for intricate movements and manipulation of the environment.
Each of these sections is equipped with specialized features that enhance their functionality, such as spines or claws that aid in grasping and climbing. This division of the limbs into segments not only illustrates the evolutionary adaptations of these creatures but also highlights their ecological significance.