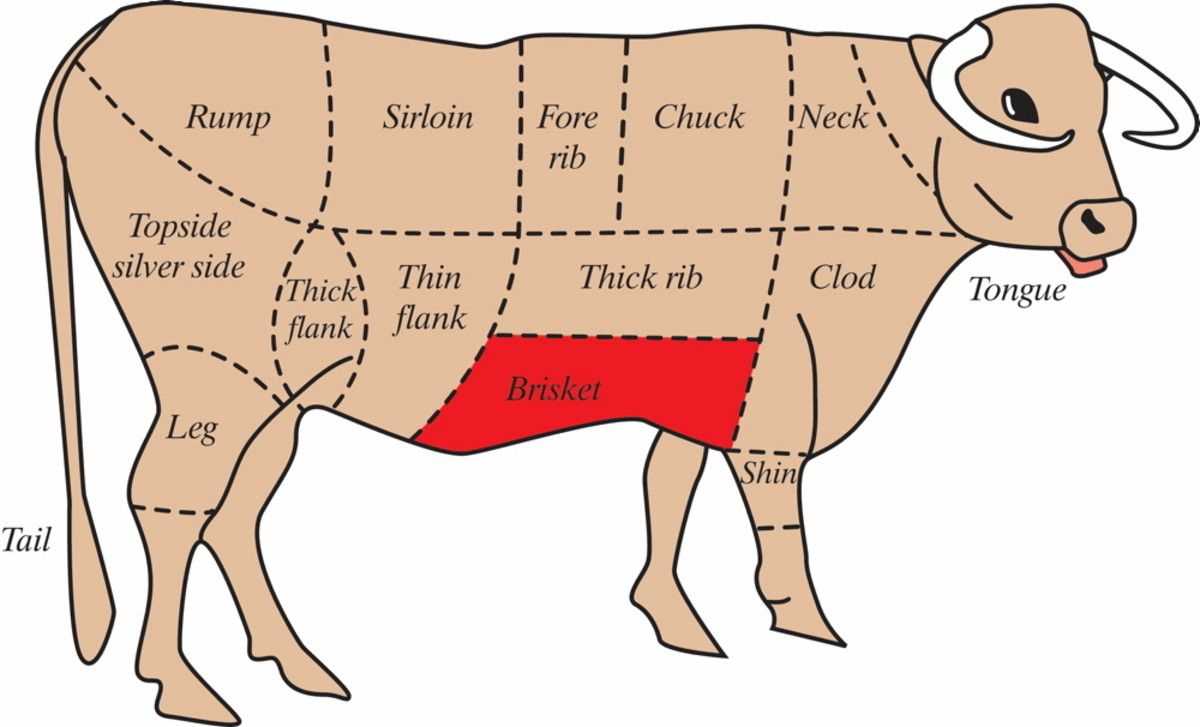
The exploration of different sections of livestock is essential for both culinary enthusiasts and professionals. Each segment possesses unique characteristics, flavor profiles, and textures, contributing to the overall dining experience. By familiarizing oneself with these divisions, one can make informed choices when selecting ingredients for various dishes.
In this section, we will delve into the various regions of the animal, highlighting their specific attributes and uses in the kitchen. Understanding these distinctions not only enhances culinary skills but also allows for a deeper appreciation of the food we consume. As we navigate through the diverse options available, the significance of quality sourcing and preparation methods will also come into focus.
Whether one is a seasoned chef or a home cook, grasping the intricacies of these divisions opens up a world of possibilities. By mastering the art of selecting and utilizing different sections, individuals can elevate their cooking and bring a greater sense of creativity to their meals.
This section aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of various segments derived from cattle. By exploring the unique characteristics and uses of each section, readers will gain insights into culinary applications, nutritional values, and preparation techniques.
- Introduction to Cattle Segmentation
An overview of how cattle are divided into distinct sections for various culinary uses.
- Understanding the Forequarter
Description of the front section and its typical cuts.
- Exploring the Hindquarter
Insights into the rear section and the types of cuts it offers.
- Premium Cuts Explained
Identification of high-value sections known for tenderness and flavor.
- Common Cuts for Roasting
Discussion on popular segments suitable for roasting preparations.
- Steaks and Their Origins
Detailing various steak cuts and their specific sources on the animal.
- Ground Meat Variations
Exploring the various sources for ground meat and their unique flavors.
- Using Tougher Cuts
Suggestions for utilizing less tender sections effectively in cooking.
- Traditional Cooking Techniques
Highlighting classic methods of preparing different sections.
- Pairing with Sides and Sauces
Recommendations for suitable accompaniments to enhance the meal experience.
- Conclusion and Summary
Recap of key points and the importance of understanding different sections.
Understanding Meat Classification
Meat classification plays a crucial role in the culinary world, providing a framework for understanding the various types of animal flesh available for consumption. This categorization aids in recognizing the distinct qualities and culinary applications of different varieties, which can vary significantly based on factors such as texture, flavor, and preparation methods.
Categories of Animal Flesh
Animal flesh can be broadly classified based on several criteria, including the source of the meat, the age of the animal at slaughter, and the type of muscle. These distinctions are essential for consumers and chefs alike, influencing not only flavor profiles but also cooking techniques and dish presentations.
Common Classifications
| Type of Flesh | Common Sources | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Red Meat | Cattle, Sheep, Goats | Rich flavor, firm texture, often requires longer cooking times. |
| White Meat | Poultry, Pork | Subtle flavor, tender texture, cooks quickly. |
| Processed Meat | Various | Includes cured or smoked options, often high in sodium and preservatives. |
Importance of Beef Quality Grades
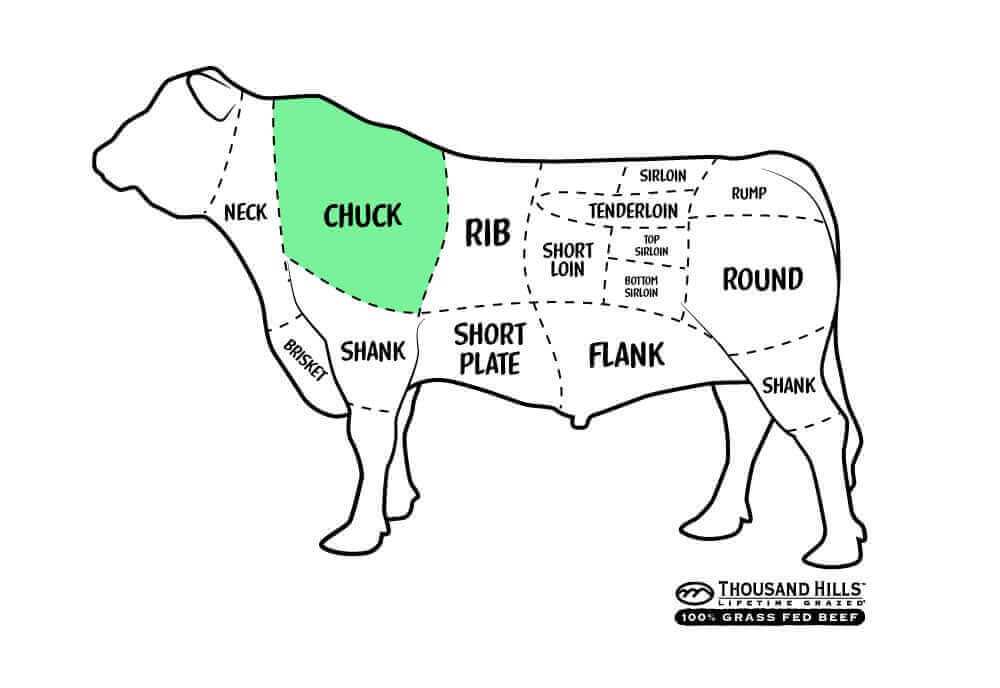
The evaluation of meat quality plays a crucial role in the culinary and agricultural industries. It serves as a benchmark for consumers and producers alike, influencing purchasing decisions and market dynamics. By assessing various characteristics, such as tenderness, flavor, and juiciness, this system provides insight into the overall value of the product.
Quality grades are essential for ensuring that consumers receive consistent and satisfactory products. These classifications help to standardize expectations, allowing buyers to make informed choices based on their preferences and budget. A clear understanding of these grades also facilitates better pricing strategies, enabling producers to position their offerings effectively in the market.
Moreover, these assessments contribute to the overall efficiency of the supply chain. By adhering to quality standards, producers can enhance their reputation and build trust with consumers. As a result, maintaining high quality is not just beneficial for individual businesses; it promotes a healthier market environment that prioritizes excellence and customer satisfaction.
Common Cuts and Their Uses
Understanding the various sections of meat can greatly enhance culinary experiences. Each section offers distinct flavors and textures, making them suitable for different cooking methods and recipes. Knowledge of these selections allows for better meal preparation and can elevate dishes from ordinary to extraordinary.
- Chuck: This area is known for its rich flavor and tenderness when cooked properly. Ideal for slow cooking, it is commonly used in:
- Beef stews
- Pot roast
- Ground beef
- Rib: Renowned for its marbling, this cut is juicy and flavorful, making it perfect for grilling or roasting. Popular preparations include:
- Ribeye steaks
- Prime rib
- Short ribs
- Loin: Known for tenderness, this section includes cuts that are excellent for quick cooking methods. It is often used for:
- Filet mignon
- New York strip steaks
- T-bone steaks
- Round: Leaner than other sections, cuts from this area are often used in roasts and can be flavorful when marinated. Common uses include:
- Beef jerky
- Roast beef
- Stir-fries
- Brisket: This cut is known for its rich flavor and is typically slow-cooked to enhance tenderness. It is often featured in:
- Barbecue
- Smoked dishes
- Beef sandwiches
phpCopy code
By selecting the right section for your recipes, you can create delicious meals that highlight the unique characteristics of each cut. Understanding these options empowers cooks to make informed decisions in the kitchen.
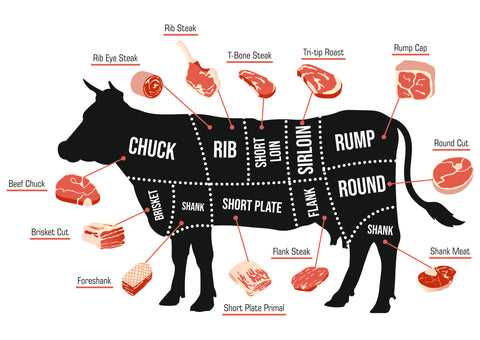
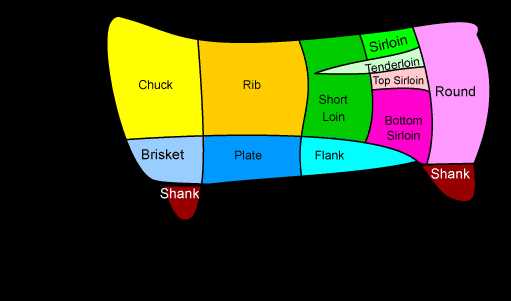
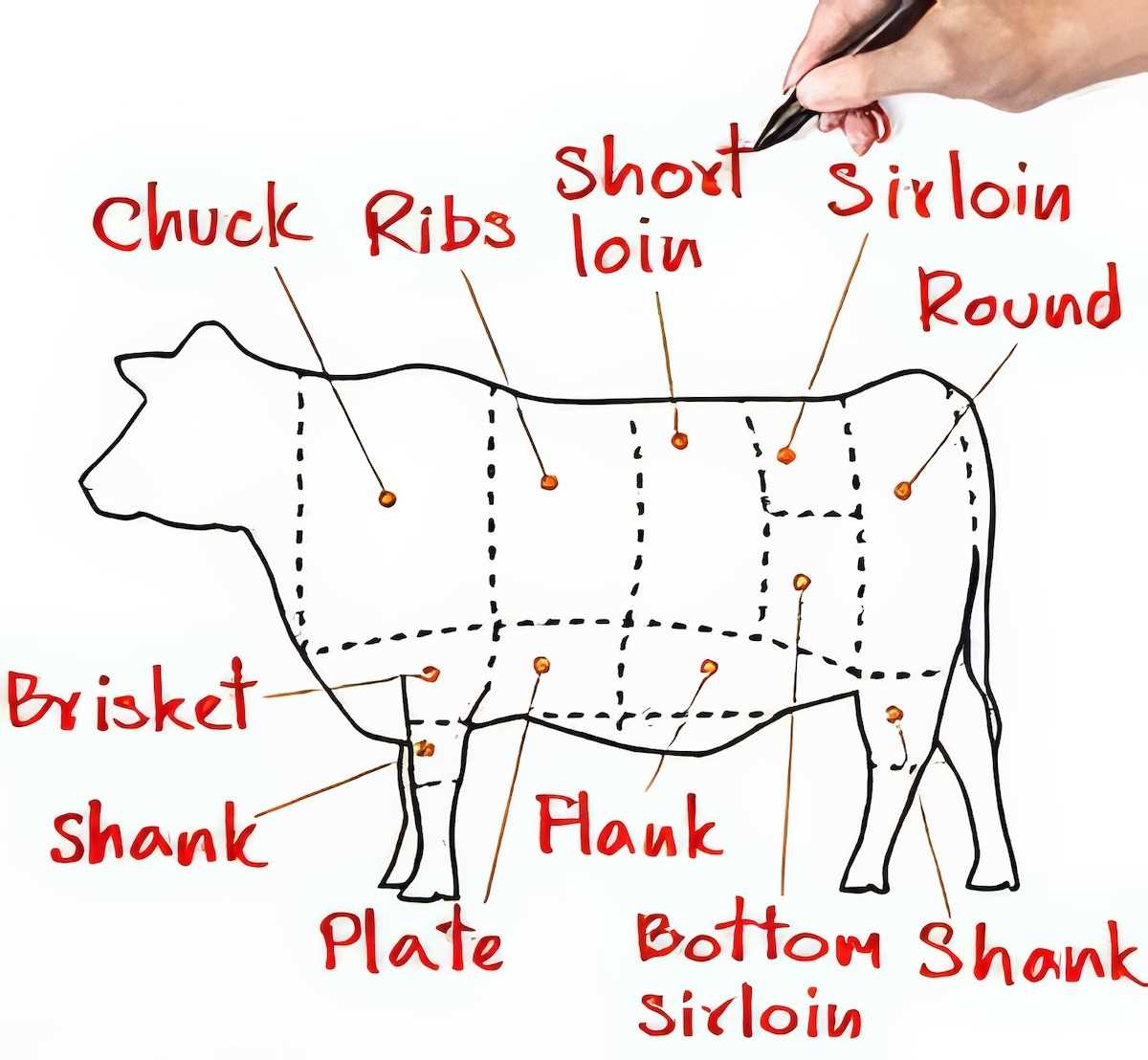
Location of Different Beef Parts
Understanding the various sections of the animal is essential for culinary enthusiasts and professionals alike. Each segment offers unique flavors and textures, making it crucial to know where they are situated. This knowledge enhances the cooking process and aids in selecting the right cuts for specific dishes.
Overview of Cuts
- Forequarter
- Hindquarter
- Brisket
- Round
- Chuck
- Rib
- Loin
Geographical Locations
- Forequarter: Located at the front of the animal, this area includes the shoulder and neck, providing cuts like chuck and brisket.
- Hindquarter: Situated at the rear, this section encompasses the loin and round, offering premium cuts such as tenderloin and sirloin.
- Brisket: Found in the chest area, this cut is known for its rich flavor and tenderness when cooked properly.
- Round: Positioned at the back leg, this region yields cuts that are typically lean and suitable for roasting or slow cooking.
- Chuck: Located near the neck and shoulder, this section is often used for hearty stews and ground meat.
- Rib: Located between the forequarter and hindquarter, this area is famous for its marbled cuts, ideal for grilling and barbecuing.
- Loin: Situated just behind the ribs, this region produces some of the most tender and sought-after cuts.
Popular Cooking Methods for Beef
When it comes to preparing succulent cuts of meat, various techniques can enhance flavor and tenderness. Understanding these methods allows culinary enthusiasts to explore a range of tastes and textures, ensuring a delightful dining experience. From quick preparations to slow-cooked masterpieces, each approach offers something unique to the table.
Grilling
Grilling is a favored technique that imparts a smoky flavor and creates an appealing char on the surface. This method involves cooking over direct heat, allowing the meat to sear quickly while retaining its juices. The result is a dish that boasts a deliciously caramelized exterior, complemented by a tender interior.
Slow Cooking

For those who appreciate rich flavors, slow cooking is an excellent option. This method involves cooking at low temperatures for extended periods, allowing the natural juices to meld and infuse the meat. The outcome is exceptionally tender and flavorful dishes that practically fall apart with a fork, making it a beloved choice for hearty meals.
How to Choose Quality Beef
Selecting high-grade meat is essential for achieving delicious and satisfying meals. When looking for prime cuts, it is important to consider various factors that influence the overall quality, including color, marbling, and texture. A keen eye and understanding of these characteristics can greatly enhance your culinary experience.
Visual Characteristics
One of the first things to observe is the color of the meat. Fresh cuts should display a rich, vibrant hue. A bright red shade indicates freshness, while darker tones may suggest aging. Additionally, the presence of marbling–tiny flecks of fat within the muscle–plays a significant role in determining flavor and tenderness. Well-marbled selections typically yield a juicier and more flavorful dish.
Texture and Smell
The texture of the meat can also provide insights into its quality. A firm and slightly springy feel is preferable, while any sliminess or excessive softness may signal spoilage. Finally, a subtle aroma is indicative of freshness. Any off-putting odors should raise a red flag regarding the meat’s condition.
Beef Processing Techniques Explained
The art of transforming raw meat into various culinary delights involves a series of intricate methods. Each stage in the processing journey plays a crucial role in determining the final quality, flavor, and presentation of the product. Understanding these techniques not only enhances appreciation for the craft but also informs consumers about the journey their food takes from farm to table.
At the outset, the initial step often includes meticulous examination and selection of the raw material. This ensures that only the finest cuts are chosen, establishing the foundation for quality. Following this, the processes of cutting and trimming are essential. These actions not only improve the aesthetic appeal but also influence cooking methods and flavor profiles.
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Slaughtering | The humane process of killing the animal, ensuring minimal stress and high-quality meat. |
| Butchering | Disassembling the carcass into specific sections, making it easier to handle and prepare. |
| Dry Aging | A technique where cuts are stored in a controlled environment to enhance flavor and tenderness. |
| Vacuum Sealing | Packaging method that removes air to preserve freshness and prevent freezer burn. |
| Cooking Methods | Various techniques such as grilling, roasting, and braising to develop unique flavors and textures. |
Each of these methods contributes to the overall experience, influencing not just taste but also texture and presentation. By exploring these techniques, one gains a deeper understanding of the culinary landscape and the craftsmanship involved in meat processing.
Regional Variations in Beef Cuts
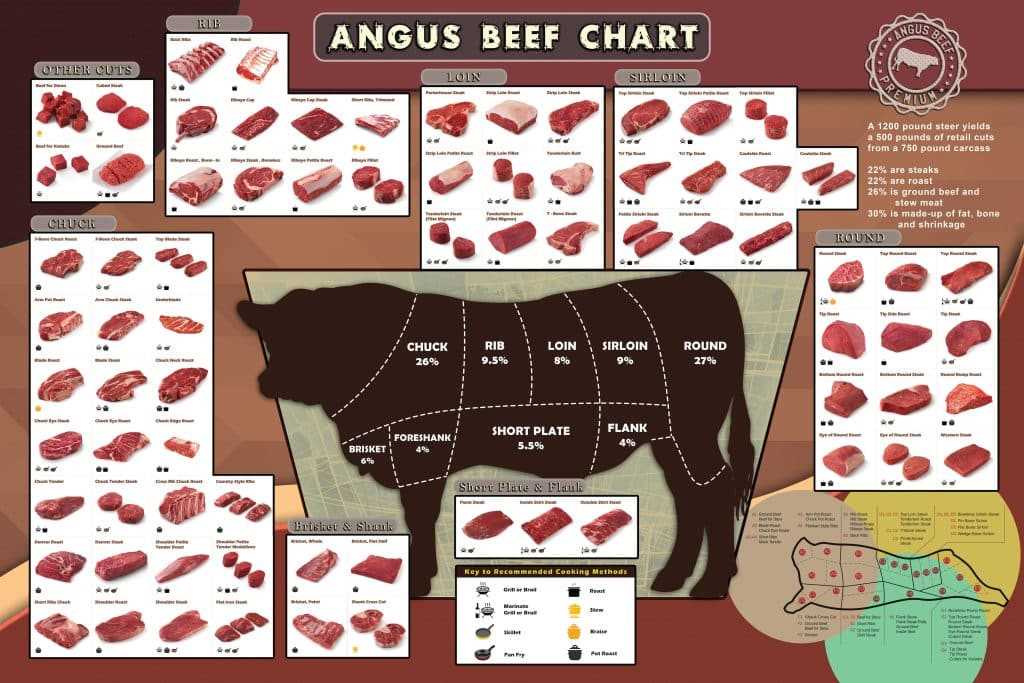
Different cultures and culinary traditions around the world influence how meat is divided and utilized in various cuisines. These regional adaptations not only reflect local tastes but also emphasize specific cooking methods and practices unique to each area.
In North America, for instance, the emphasis is often on larger, more recognizable sections, leading to popular cuts such as:
- Ribeye
- Sirloin
- Brisket
Conversely, in countries like Argentina, the approach tends to prioritize specific preparations for grilling, leading to the popularity of cuts such as:
- Asado
- Vacío
- Entrana
In Asian cuisines, the focus may shift to incorporating various cooking techniques that enhance the flavor and texture of smaller cuts. Notable examples include:
- Shabu-shabu slices in Japan
- Stir-fry strips in China
- Korean barbecue selections
Understanding these regional distinctions can enrich culinary practices and offer new insights into the diverse ways that meat can be enjoyed across different cultures.
Health Benefits of Consuming Beef
Incorporating red meat into one’s diet can provide numerous advantages for overall health and well-being. Rich in essential nutrients, this protein source plays a significant role in supporting various bodily functions and promoting a balanced diet.
Nutrient Density
This type of meat is an excellent source of high-quality protein, crucial for muscle development and repair. Additionally, it contains vital vitamins and minerals such as iron, zinc, and B vitamins, which contribute to energy production and immune function.
Support for Muscle Health
Regular consumption of this protein source can aid in maintaining muscle mass, especially in individuals who engage in regular physical activity. The amino acids present in red meat are instrumental in building and sustaining lean muscle tissue, enhancing physical performance and recovery.
Beef Industry and Sustainability Practices

The livestock sector plays a crucial role in global food systems, contributing to nutrition and economic stability. However, the environmental impacts of this industry have prompted a shift towards more sustainable practices. By adopting innovative approaches, stakeholders aim to balance production demands with ecological preservation and animal welfare considerations.
Various strategies have emerged to enhance sustainability within this sector. These practices not only address environmental concerns but also support the long-term viability of farming operations. Below is a summary of key methods implemented to promote a more sustainable approach:
| Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Rotational Grazing | This method involves moving livestock between pastures to allow for regrowth and reduce overgrazing, thereby improving soil health and biodiversity. |
| Feed Efficiency | Improving feed conversion ratios reduces waste and lowers greenhouse gas emissions, making production more resource-efficient. |
| Water Management | Implementing efficient irrigation and water conservation techniques helps to preserve water resources while supporting livestock needs. |
| Waste Management | Utilizing manure as fertilizer or energy source minimizes waste and enriches soil, creating a closed-loop system. |
| Animal Welfare | Ensuring humane treatment and optimal living conditions for livestock enhances overall health and productivity, aligning with consumer expectations. |
Through these initiatives, the industry strives to create a more resilient and responsible food system. The integration of sustainability practices not only benefits the environment but also enhances the quality and safety of food products.
Future Trends in Beef Consumption
The landscape of meat consumption is evolving, influenced by various factors such as health awareness, environmental concerns, and technological advancements. As consumers become more informed about their dietary choices, the demand for sustainable and ethically sourced options is on the rise. This shift is reshaping how meat products are produced, marketed, and consumed globally.
Health and Nutrition Awareness
One of the significant trends is the increasing focus on health and nutrition. Consumers are becoming more conscious of their dietary choices, leading to:
- Demand for leaner cuts and lower-fat options.
- Interest in grass-fed and organic varieties.
- Preference for meat alternatives and plant-based diets.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Another critical aspect shaping future consumption is the emphasis on sustainability. As environmental concerns grow, consumers are more likely to consider:
- Carbon footprint of livestock production.
- Support for regenerative farming practices.
- Reduction of food waste through innovative packaging and preservation techniques.
These trends suggest a transformative future for the meat industry, where consumer preferences drive changes in production methods and product offerings.