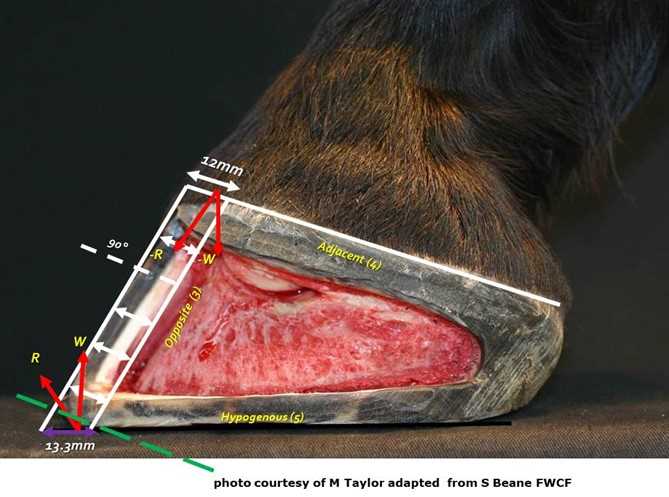
Exploring equine foot structure reveals intricate components crucial for overall health and performance. Each element plays a vital role in supporting movement and weight distribution.
Knowledge of these structures enhances appreciation for their function and importance in equine care. Understanding how they interact can lead to better management practices.
Delving into this subject not only aids in recognizing signs of distress but also fosters improved practices for maintenance and care. Awareness of these elements is essential for those involved in equine management.
Understanding the Horse Hoof Structure
A solid foundation is crucial for overall health and performance. This intricate structure plays a significant role in mobility and stability, providing support and protection to vital components within. Recognizing the complexities involved can enhance care practices and improve well-being.
- Outer layer: Acts as a protective shield.
- Inner components: Essential for shock absorption and weight distribution.
- Nutrition: Vital for maintaining strength and resilience.
Proper knowledge fosters better management practices and promotes optimal function. Attention to each element ensures longevity and performance in various activities.
External Parts of the Hoof
This section explores various visible components that contribute to the overall structure and functionality of equine feet. Understanding these elements is crucial for proper care and management.
The outer covering, known for its durability, plays a significant role in protection. It acts as a barrier against external elements while supporting weight and movement.
Function of the Hoof Wall
The outer structure plays a crucial role in protecting and supporting an animal’s weight. Its robust nature ensures durability while contributing to overall health and movement efficiency. Understanding its functions reveals its importance in daily activities and overall well-being.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Protection | Shields sensitive internal structures from injuries and environmental hazards. |
| Support | Distributes weight evenly, promoting balance during movement. |
| Flexibility | Allows for slight movement, aiding in shock absorption and comfort. |
| Growth | Continuously regenerates to maintain integrity and functionality. |
Exploring the Sole of the Hoof
Delving into this critical region reveals its essential role in support and balance. Understanding its structure can enhance care practices and overall well-being.
- Composition: This area consists of various layers, each contributing to durability and flexibility.
- Function: Acts as a shock absorber, protecting internal components from impact.
- Health Indicators: Changes in texture or color can signal underlying issues.
By examining this unique section, one can grasp its ultimate significance in ensuring soundness and comfort.
Role of the Frog in Movement
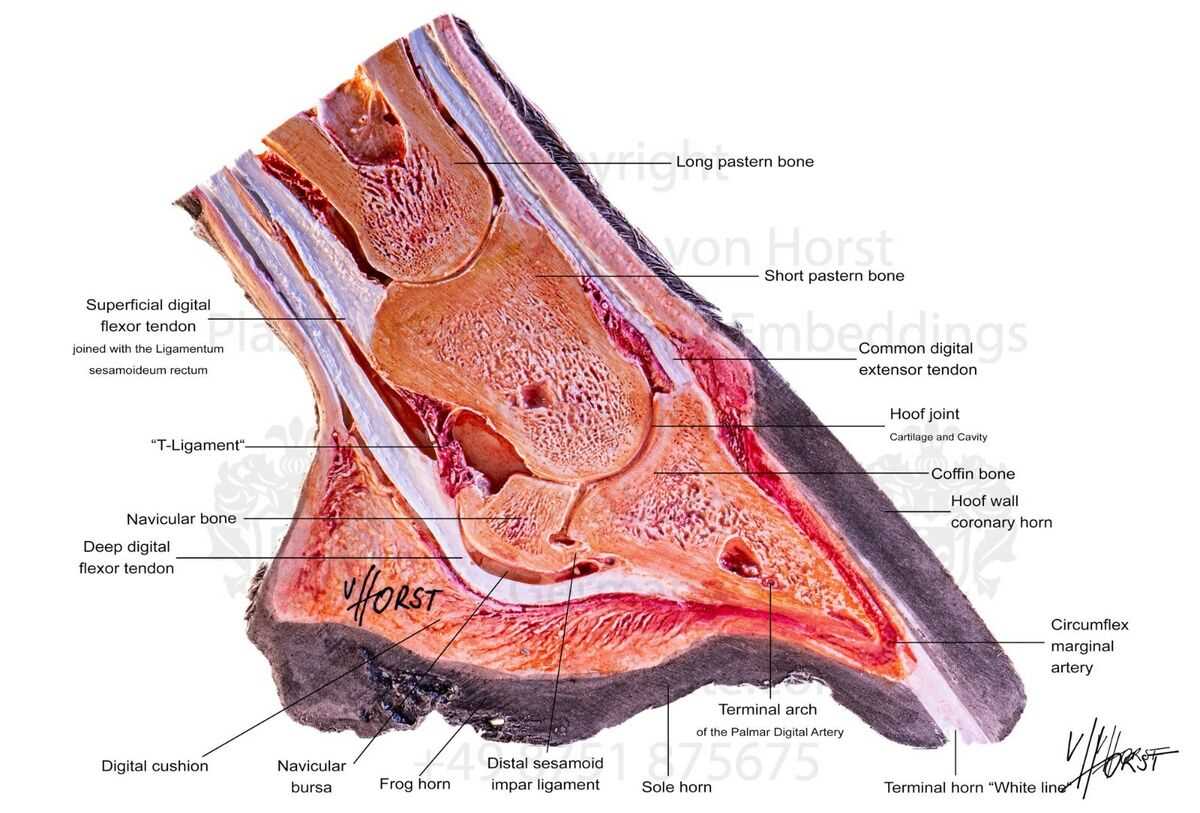
The frog serves a crucial function in locomotion, contributing to the overall mechanics of movement. This specialized structure enhances flexibility and provides necessary support during various activities. Its design allows for efficient shock absorption, promoting comfort and stability while navigating different terrains.
When a creature walks or runs, the frog aids in distributing weight evenly. This distribution minimizes stress on surrounding tissues, thereby reducing the risk of injury. The interaction between the frog and ground surfaces is vital for maintaining balance and traction, allowing for smooth transitions in gait.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Shock Absorption | Mitigates impact forces during locomotion, protecting structures. |
| Weight Distribution | Ensures even load sharing across the underside, promoting health. |
| Traction | Enhances grip on surfaces, improving stability and control. |
| Flexibility | Allows adaptation to varying ground conditions, facilitating smooth movement. |
Understanding the significance of this anatomical feature can lead to better care practices, ensuring optimal performance and well-being during various activities.
Importance of the Digital Cushion
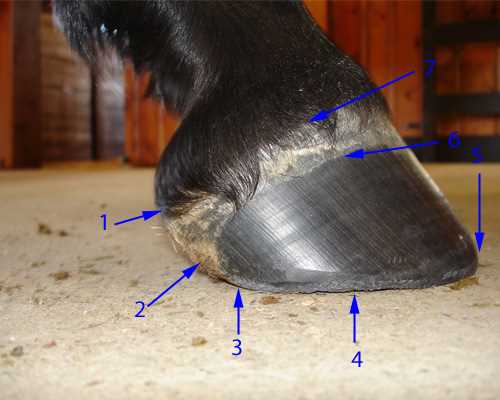

The digital cushion plays a crucial role in providing support and absorbing shock in equine locomotion. This unique structure contributes significantly to overall functionality and health.
- Shock Absorption: It mitigates impact during movement, reducing strain on bones and joints.
- Circulation: Enhances blood flow within the foot, promoting overall vitality.
- Support: Provides stability, aiding in balanced weight distribution.
- Protection: Shields delicate structures from external pressures and injuries.
Understanding this essential component can help in maintaining optimal conditions for performance and well-being.
Hoof Bulbs: What You Need to Know
Understanding the significance of these rounded structures at the back of the foot is essential for overall well-being. They play a critical role in cushioning, stability, and support during movement. Proper care and knowledge can prevent various issues that might arise if these areas are neglected.
Functions of Bulbs
- Cushioning impact during movement.
- Providing support and balance.
- Assisting in circulation within the foot.
Common Issues
- Injury or trauma leading to swelling.
- Infections that can cause pain and discomfort.
- Improper trimming affecting overall health.
Regular inspection and maintenance can significantly enhance comfort and performance, ensuring a healthy and active lifestyle.
The Significance of the Laminae
Laminae serve a crucial role in maintaining structural integrity and functionality of equine extremities. Understanding their importance is essential for promoting optimal health and performance.
Key Functions
- Support: They provide essential support by connecting sensitive and hard structures.
- Shock Absorption: Laminae help absorb impact during movement, reducing strain on surrounding tissues.
- Nutrient Exchange: They facilitate the transfer of nutrients and oxygen to the underlying tissues.
Health Implications
- Imbalances: Compromised laminae can lead to significant health issues, including laminitis.
- Preventive Care: Regular check-ups can help identify early signs of laminar stress.
- Nutrition: Proper diet supports laminar health and overall well-being.
Hoof Growth and Maintenance Tips
Healthy development and proper upkeep of equine extremities are crucial for overall well-being and performance. This section provides essential guidelines for ensuring optimal growth and maintenance, promoting strength and durability.
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Regular Trimming | Maintain a consistent trimming schedule to prevent overgrowth and cracking. Frequency may vary based on activity level and terrain. |
| Balanced Nutrition | Provide a well-rounded diet rich in vitamins and minerals to support strong and resilient structures. Focus on biotin and protein intake. |
| Hydration | Ensure access to fresh water, as hydration plays a key role in maintaining flexibility and preventing brittleness. |
| Clean Environment | Keep living spaces clean and dry to reduce the risk of infections and other issues. Regularly remove waste and debris. |
| Observation | Regularly inspect for signs of discomfort or irregularities, such as cracks or discoloration, to address issues promptly. |
Common Hoof Problems and Solutions
Numerous issues can affect the well-being of equines, leading to discomfort and potential complications. Recognizing these challenges early is essential for effective management and care.
- Cracks: Often caused by environmental factors or improper trimming.
- Thrush: A bacterial infection that thrives in damp conditions.
- Lameness: Can result from various underlying conditions, requiring thorough evaluation.
Solutions to these problems may include:
- Regular trimming and shoeing to maintain proper shape.
- Keeping living areas clean and dry to prevent infections.
- Consulting a veterinarian for persistent lameness or infections.
Tools for Hoof Care Professionals
Maintaining equine wellness requires specialized instruments that facilitate effective care. These essential implements enable practitioners to ensure optimal health and performance in their equine clients. Understanding various tools and their applications is crucial for achieving superior outcomes in hoof management.
Essential Instruments
Among the most vital tools are nippers, rasps, and knives. Nippers are designed for trimming excess growth, while rasps refine and smooth surfaces. Knives assist in precise adjustments, making these instruments indispensable for any expert.
Advanced Equipment
In addition to basic tools, some professionals utilize more advanced gear like hoof testers and radiography equipment. Hoof testers help assess sensitivity, while radiographs provide deeper insights into structural integrity. Employing such technology can significantly enhance diagnosis and treatment efficacy.
Understanding Hoof Anatomy for Owners
Gaining insight into equine foot structure is essential for caretakers seeking to ensure optimal health and performance. A solid grasp of this unique anatomy fosters better management practices, contributing to overall well-being. Recognizing key components empowers owners to make informed decisions regarding care, maintenance, and any potential issues.
Key Components of Equine Feet
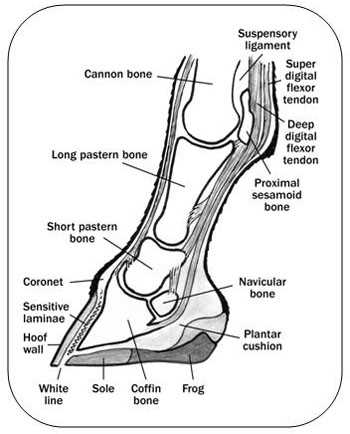
Within the structure, several crucial elements work together to provide support and function. The outer layer, known for its toughness, protects inner tissues while also playing a vital role in weight distribution. Beneath this protective covering, softer tissues are responsible for cushioning and absorbing shock, which is crucial during movement. Understanding these elements helps in identifying signs of distress or injury.
Importance of Regular Care
Routine maintenance, including trimming and cleaning, is vital for preventing common ailments. By regularly inspecting each section, caretakers can detect potential problems early, ensuring swift action can be taken. Furthermore, recognizing changes in behavior or movement may signal underlying issues related to foot health. A proactive approach to care not only enhances comfort but also supports longevity in activity.