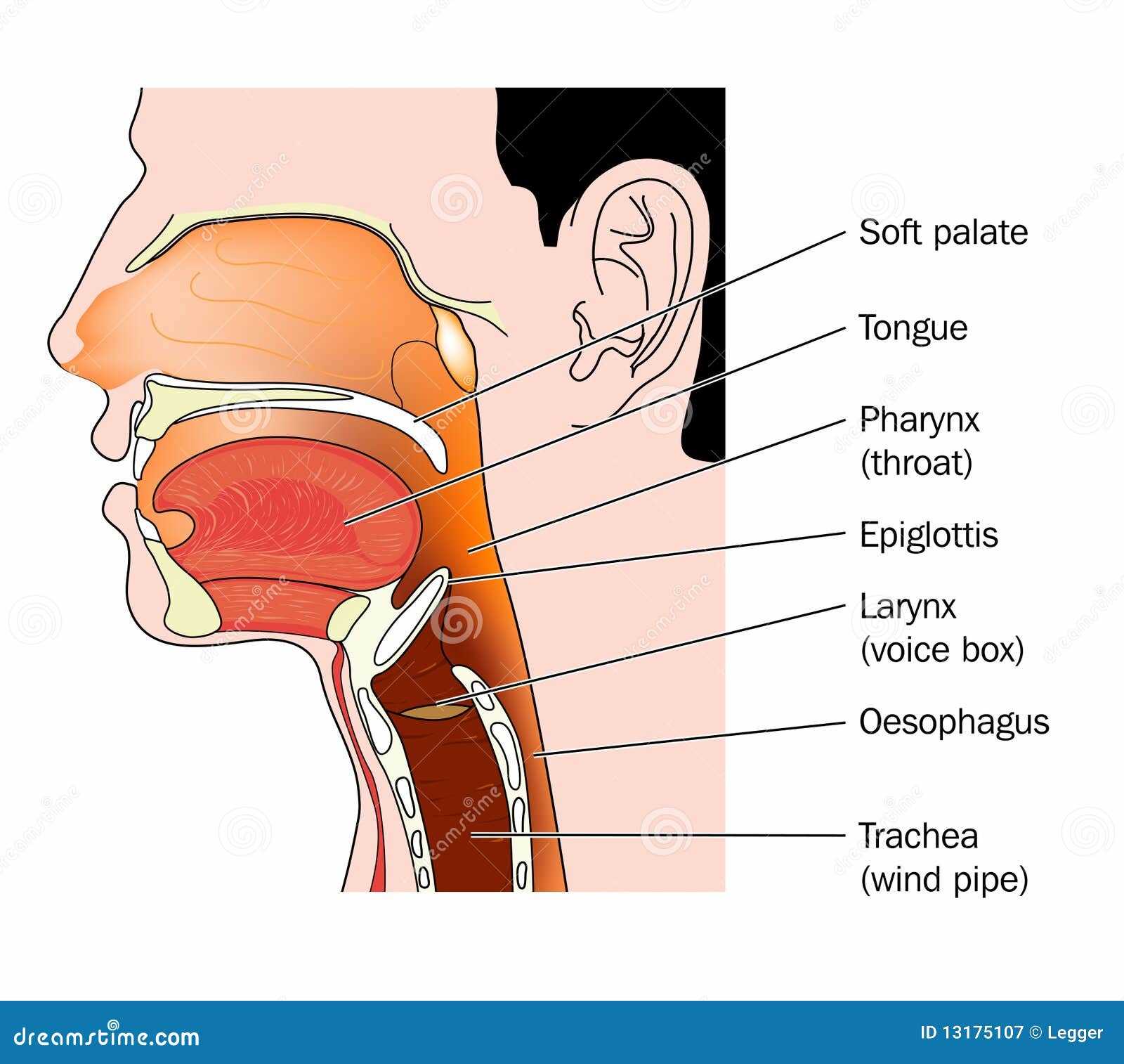
Exploring intricate structures within cervical area reveals essential functions vital for overall well-being. This complex region houses numerous components working harmoniously, playing crucial roles in various bodily processes. Gaining insight into this fascinating realm can enhance appreciation for human biology.
Detailed examination of anatomical features showcases relationships between different elements, offering clarity on their specific contributions. Each segment performs unique tasks that support essential activities, such as respiration, digestion, and communication. Understanding these connections deepens knowledge of bodily mechanics and underscores the significance of maintaining health in this area.
Visual representation aids comprehension, allowing for a clearer grasp of spatial arrangements. Recognizing how different elements interact enhances awareness of potential issues that may arise when complications occur. As a result, this knowledge can empower individuals to seek appropriate care and adopt healthy practices.
This section explores intricate anatomy located in the region between head and chest, emphasizing its significance in various bodily functions. By examining this complex system, one can appreciate the interplay of components that contribute to essential activities such as respiration, circulation, and communication.
Anatomical Overview
The region comprises several key elements that work together seamlessly. Each component plays a unique role, contributing to overall functionality and health. The following table summarizes these critical structures along with their primary functions:
| Structure | Function |
|---|---|
| Muscles | Facilitate movement and support posture |
| Nerves | Transmit signals between brain and body |
| Vessels | Transport blood and nutrients |
| Lymphatics | Support immune function and fluid balance |
Functional Significance
Understanding this region is crucial for recognizing how various health conditions can impact daily life. Awareness of potential issues allows for better preventative measures and appropriate responses to any anomalies that may arise.
Key Functions of Throat Components
Understanding essential roles of various elements within this anatomical region is crucial for grasping their significance in overall health and well-being. Each component contributes uniquely to vital processes that sustain life.
- Air Passage: Facilitates movement of air to lungs, ensuring efficient breathing.
- Food Transport: Aids in guiding ingested substances towards digestive system, preventing aspiration.
- Sound Production: Contributes to vocalization, allowing for communication and expression.
- Protection: Acts as a barrier against pathogens, safeguarding respiratory pathways from infections.
- Swallowing Mechanism: Coordinates muscle contractions to enable smooth passage of food and liquids.
Collectively, these functionalities highlight importance of this region in maintaining both respiratory and digestive processes, along with facilitating communication.
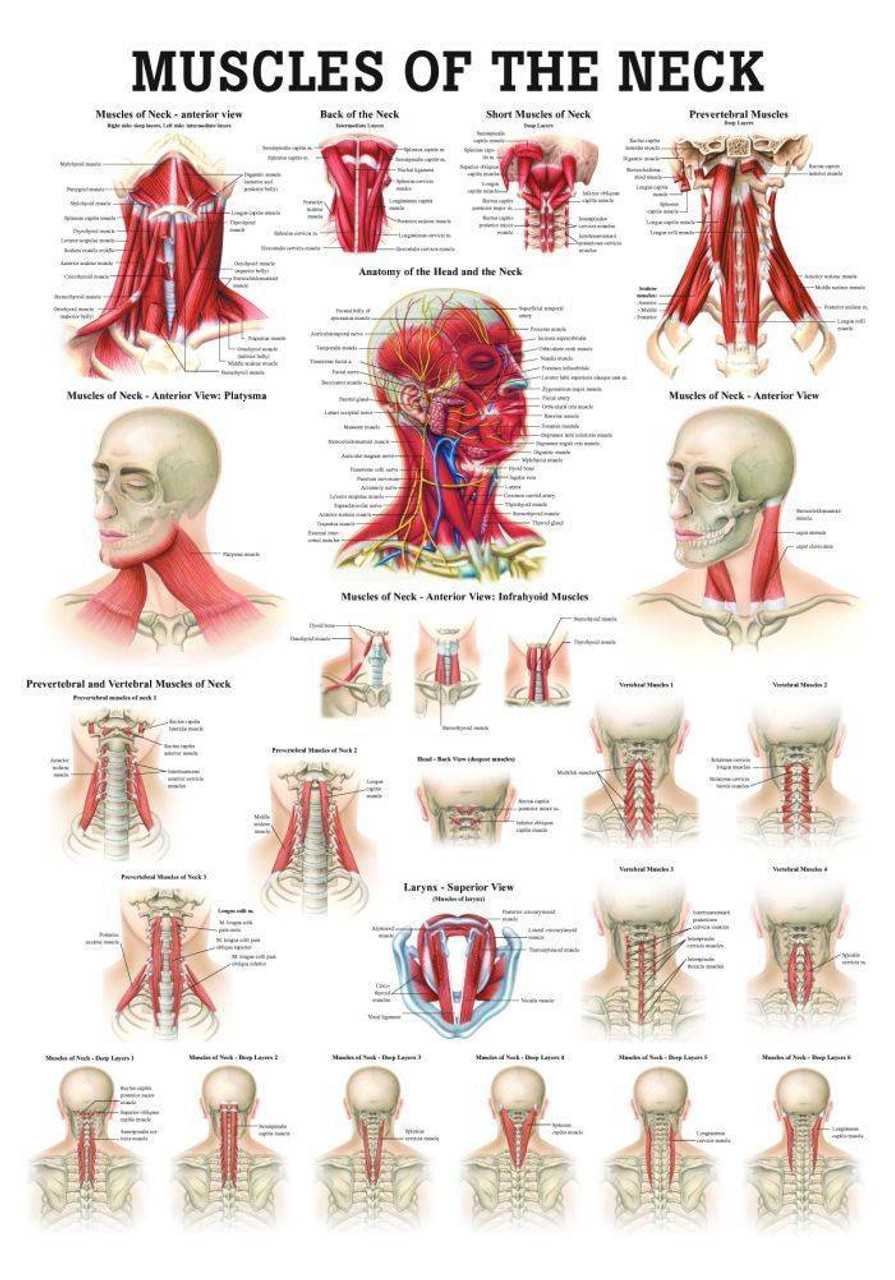
Muscles Involved in Neck Movement
Various muscle groups play a crucial role in facilitating movement in the region connecting head to torso. These structures enable a range of actions, including rotation, tilting, and flexing, contributing significantly to overall mobility and function.
Primary Muscular Contributors
Among the key players are sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles. The former assists in rotating and bending the head, while the latter supports shoulder elevation and extension of the cervical region. Together, they form a functional unit that enhances posture and dynamic movements.
Additional Supportive Muscles
In addition to the major contributors, several smaller muscles, such as splenius capitis and levator scapulae, provide essential support. These assist in finer adjustments and stabilization, ensuring smooth and coordinated actions during various activities.
Common Disorders of the Throat
Numerous issues can arise in this critical region of the body, affecting individuals of all ages. Understanding these ailments is essential for maintaining overall health. This section explores prevalent conditions that may cause discomfort, pain, or functional impairments.
Infections
Infections in this area are frequently encountered, with symptoms ranging from soreness to difficulty swallowing. Viral and bacterial pathogens can lead to conditions such as pharyngitis and tonsillitis. Early detection and appropriate treatment are vital to prevent complications.
Allergies and Irritations
Allergic reactions to various substances can trigger inflammation and discomfort. Common irritants include pollutants, smoke, and certain foods. Managing these triggers is crucial for alleviating symptoms and enhancing quality of life.
Importance of the Larynx
The larynx plays a crucial role in various essential functions of human physiology. It serves as a key structure for voice production, ensuring effective communication. This organ also acts as a protective mechanism for airways, preventing foreign substances from entering the respiratory tract.
Role in Voice Production
One of the primary functions of this organ is its involvement in sound generation. Through vibration of vocal cords, it enables individuals to produce a wide range of sounds, from speech to singing. The unique structure of the larynx allows for modulation of pitch and volume, making it vital for expressive communication.
Protective Function
In addition to its role in vocalization, the larynx provides essential protection for respiratory pathways. It closes during swallowing, ensuring that food and liquids do not enter the trachea. This reflexive action is vital for preventing choking and maintaining overall respiratory health.
Blood Supply to the Neck Region
The vascular network supplying this area plays a crucial role in maintaining health and functionality. This complex system ensures that essential nutrients and oxygen reach various structures, enabling their proper operation. Understanding this circulation is vital for grasping the overall physiology of nearby regions.
Major Arteries
Key arteries involved in providing blood to this area include the common carotid arteries and vertebral arteries. The common carotid arteries branch into internal and external segments, each serving distinct functions. The internal variant primarily nourishes the brain, while the external counterpart supplies the face and scalp.
Veins and Drainage
Veins play an equally important role in returning deoxygenated blood. The internal jugular vein is one of the primary vessels responsible for this process, collecting blood from various regions before directing it towards the heart. Understanding the pathways of these vessels aids in recognizing potential health issues.
Diagrammatic Representation of Structures
This section explores visual illustrations that capture various anatomical formations within the upper respiratory region. These representations provide a simplified overview, allowing for better understanding of complex biological systems. Through well-crafted images, intricate relationships among various components become more accessible, facilitating educational purposes and enhancing comprehension.
Importance of Visual Illustrations
Visual aids play a crucial role in conveying information effectively. They not only enhance retention but also make learning engaging. By utilizing diagrams, learners can quickly grasp spatial relationships, promoting an intuitive understanding of anatomy.
Applications in Medical Education
In medical education, visual representations serve as vital tools. They are instrumental in training professionals, enabling them to visualize procedures, identify structures, and enhance diagnostic skills. Comprehensive illustrations support the learning process, bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application.
Role of the Pharynx in Digestion
This muscular structure serves as a critical pathway for food, playing an essential role in processing nutrients. It connects oral cavity with esophagus, facilitating movement of ingested materials towards stomach. Its function is vital for ensuring efficient transit and initiating digestive processes.
Mechanism of Action
Upon swallowing, this structure contracts rhythmically, pushing food downwards through peristalsis. This involuntary action prevents aspiration, directing contents safely into the esophagus. It also plays a part in coordinating respiratory and digestive functions, demonstrating its importance in overall health.
Impact on Nutrient Absorption
While it primarily serves as a passageway, its role in preparing food for further digestion cannot be understated. By ensuring that food is adequately processed before entering stomach, it enhances nutrient absorption efficiency. Thus, maintaining optimal function of this region is crucial for digestive health.
Differences Between Adult and Child Anatomy
This section explores notable distinctions in anatomical structures between adults and children. Understanding these variations is crucial for healthcare professionals, educators, and anyone interested in human biology.
Size and Proportions
- Adults generally possess larger dimensions in both bone structure and soft tissues.
- Children have proportionally larger heads relative to their bodies, impacting their overall posture and alignment.
- The trachea and esophagus are shorter in younger individuals, leading to different respiratory and digestive dynamics.
Functional Considerations
- Young individuals often experience faster metabolic rates, influencing respiratory rates and heart function.
- Growth spurts can lead to temporary changes in function and comfort during activities such as eating or speaking.
- Developmental stages affect susceptibility to certain conditions, requiring tailored medical approaches.