The complexity of the human anatomy is fascinating, particularly when it comes to the central support structure of the body. This intricate system plays a crucial role in mobility and overall health, allowing individuals to perform daily activities with ease. By examining the various components, one can gain insight into how they function together harmoniously.
Within this exploration, it becomes essential to recognize the distinct regions that contribute to both stability and flexibility. Each section has unique characteristics and functions, which are vital for maintaining balance and posture. Understanding these regions can lead to better care and prevention of injuries.
Moreover, a comprehensive look at this structure can enhance knowledge about common ailments and promote a healthier lifestyle. By delving into the specifics, individuals can appreciate the ultimate importance of this essential framework in their everyday lives.
Anatomy of the Human Back
The structure of the human dorsal region is intricate, comprising various elements that contribute to its functionality and stability. Understanding this complexity is crucial for grasping how movement and support are achieved, as well as recognizing the significance of maintaining its health.
Major Components
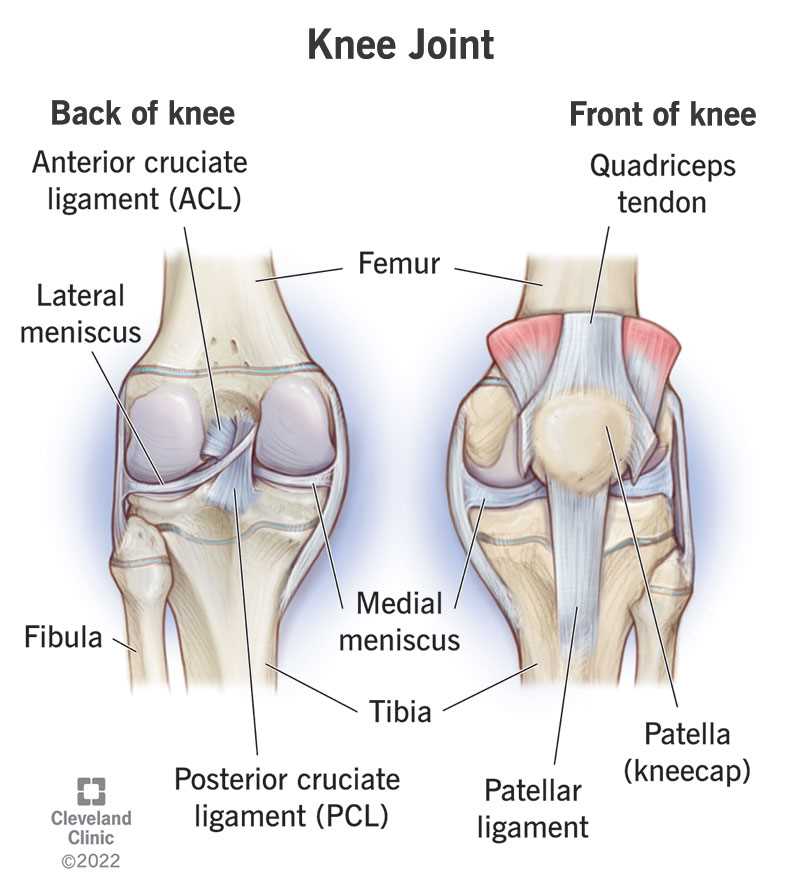
- Vertebral Column: A bony structure that serves as the backbone, providing support and protecting the spinal cord.
- Muscles: Groups of fibers that facilitate movement and maintain posture, working in coordination to allow flexibility.
- Ligaments: Strong connective tissues that connect bones, offering stability and limiting excessive motion.
- Nerves: Vital pathways that transmit signals between the brain and the rest of the body, essential for movement and sensation.
Functionality
- Support: The structure provides a framework that sustains the body’s weight.
- Movement: Muscles enable a range of motions, from bending to twisting.
- Protection: The vertebral column shields the spinal cord from injury.
- Posture: Maintaining an upright position relies on the balance of various elements within this region.
A comprehensive understanding of this area enhances awareness of its importance in daily activities and overall well-being.
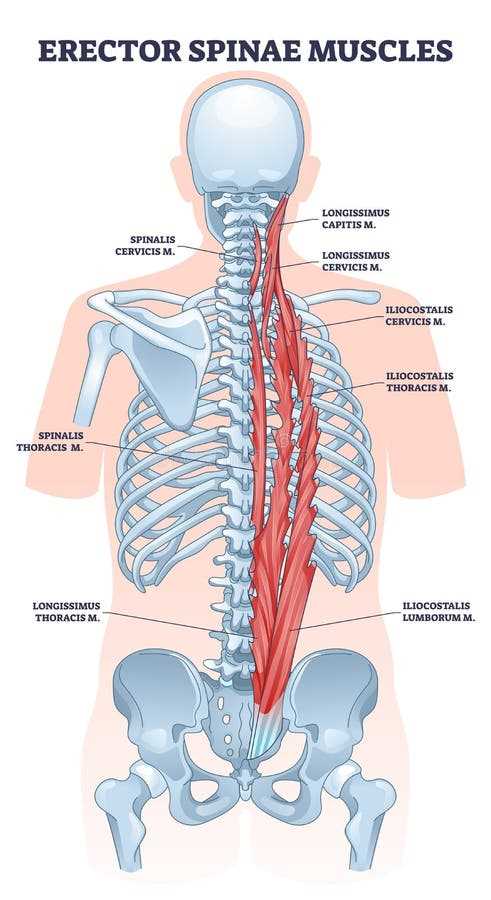
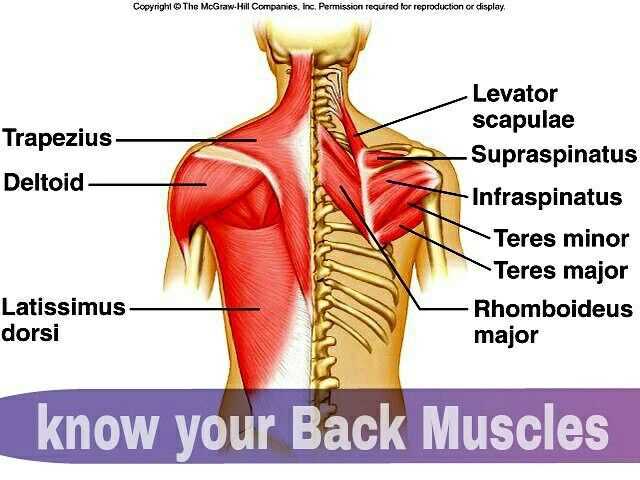
Major Muscles in the Back
The musculature of the posterior region plays a crucial role in supporting movement, maintaining posture, and facilitating various physical activities. Understanding these key muscle groups is essential for anyone interested in anatomy, fitness, or rehabilitation.
Here are the primary muscle groups located in this area:
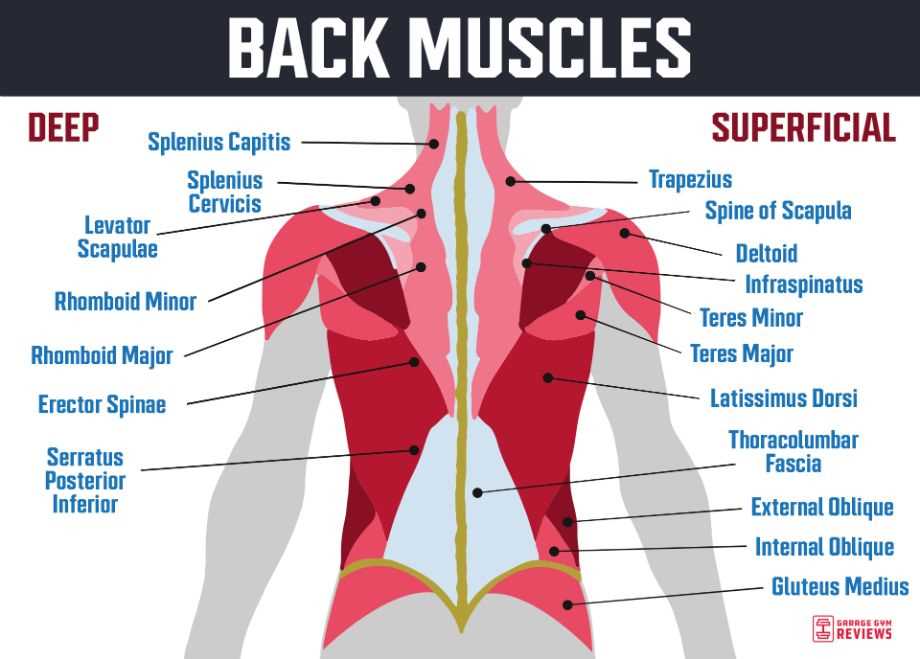
- Latissimus Dorsi: A large muscle that spans the lower and middle sections, contributing to arm movement and rotation.
- Trapezius: This muscle extends from the neck to the middle of the back and is responsible for shoulder elevation and retraction.
- Rhomboids: Located between the shoulder blades, these muscles help retract and stabilize the scapulae.
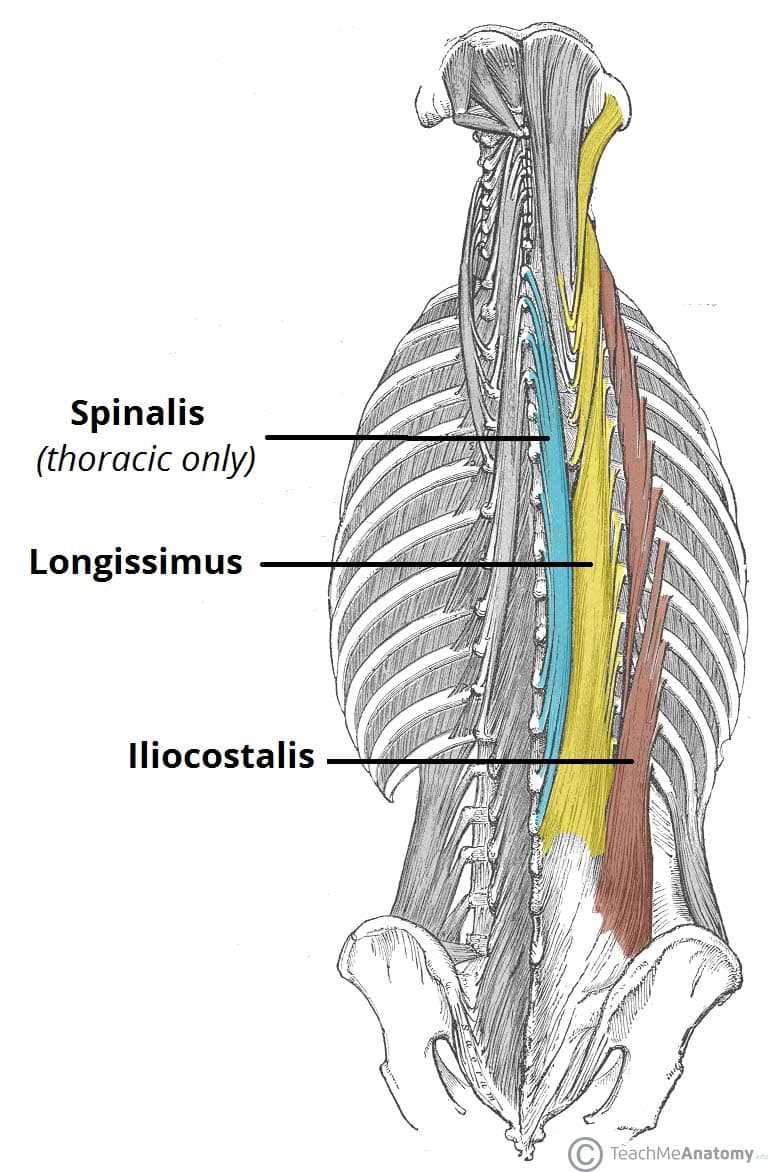
- Erector Spinae: A group of muscles that runs along the spine, essential for extending and rotating the torso.
- Quadratus Lumborum: Found in the lower section, this muscle aids in lateral flexion and stabilization of the pelvis.
Each of these muscle groups contributes to the overall function and strength of the posterior region, highlighting their importance in daily activities and athletic performance.
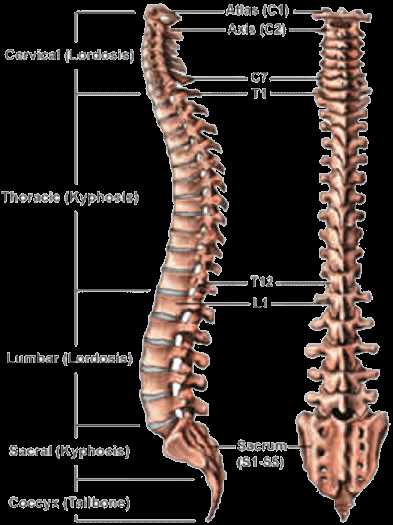
Understanding Spinal Structure
The spine serves as a critical framework for the human body, providing both support and flexibility. Its intricate design allows for a range of movements while protecting essential structures within. By exploring its components, one can gain deeper insights into overall health and mobility.
Key Components of the Spine
The spinal column consists of several regions, each playing a distinct role in maintaining balance and function. These areas work together harmoniously to facilitate various activities.
| Region | Function |
|---|---|
| Cervical | Supports the head and allows neck movement |
| Thoracic | Anchors the ribs and protects the heart and lungs |
| Lumbar | Provides lower back support and allows bending |
| Sacral | Connects the spine to the pelvis |
| Coccygeal | Forms the tailbone and supports pelvic structures |
Importance of Spinal Health
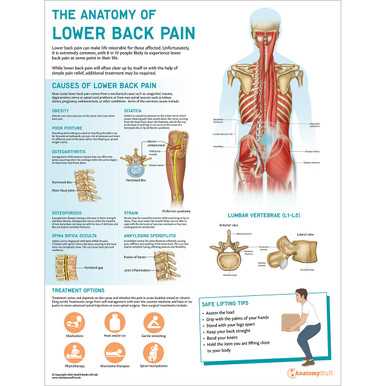
Common Back Pain Causes
Understanding the frequent origins of discomfort in the spinal area is crucial for effective management. Various factors contribute to this widespread issue, often intertwining lifestyle choices, physical strain, and underlying health conditions.
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Poor Posture | Slouching or improper alignment during daily activities can lead to strain. |
| Injury | Acute injuries from accidents or falls may result in significant pain. |
| Muscle Strain | Overexertion or lifting heavy objects improperly can cause muscle damage. |
| Herniated Disc | When discs in the spine protrude, they can compress nearby nerves, causing discomfort. |
| Arthritis | Degenerative conditions can lead to inflammation and stiffness in the spinal area. |
Importance of Back Flexibility
Flexibility in the spinal region plays a crucial role in overall mobility and physical well-being. Enhanced range of motion not only facilitates daily activities but also contributes to better performance in various sports and exercises. Maintaining suppleness in this area can prevent injuries and alleviate discomfort, promoting a healthier lifestyle.
Several factors highlight the significance of achieving and maintaining this flexibility:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Injury Prevention | Improved elasticity reduces the risk of strains and sprains during physical activities. |
| Enhanced Posture | Increased flexibility contributes to better alignment of the spine, promoting a healthier stance. |
| Improved Circulation | Flexibility exercises can enhance blood flow, aiding recovery and reducing muscle soreness. |
| Better Performance | A greater range of motion can lead to improved performance in various athletic pursuits. |
Incorporating flexibility routines into a regular fitness regimen can lead to significant long-term benefits, making it an essential aspect of physical health and activity. Emphasizing flexibility training helps individuals achieve a more dynamic and resilient physique.
Ergonomics for Back Health
Maintaining a well-aligned structure is essential for overall well-being, particularly when engaging in daily activities. By implementing thoughtful design principles, individuals can reduce discomfort and promote a healthier posture, minimizing strain on various regions of the body. This section explores strategies to enhance comfort and prevent injury through mindful adjustments in the workplace and at home.
Key Principles of Ergonomic Design
Effective ergonomic practices focus on aligning workstations to fit the individual’s needs. This includes selecting the right furniture, such as adjustable chairs and desks, which allow for a neutral position while sitting or standing. Additionally, positioning screens at eye level and keeping frequently used items within easy reach can significantly decrease the risk of tension and stress.
Daily Habits for Improved Posture
Incorporating specific movements and breaks into daily routines can greatly enhance alignment and alleviate discomfort. Regular stretching and strengthening exercises contribute to greater flexibility and stability. Moreover, being mindful of posture during activities, whether sitting, standing, or lifting, plays a crucial role in sustaining a healthy framework and preventing long-term issues.
Impact of Posture on Spine
The alignment of the body significantly influences overall well-being, affecting both physical health and comfort. Proper positioning can alleviate discomfort, enhance mobility, and prevent long-term complications.
Effects of Poor Alignment
- Increased strain on muscles and ligaments
- Higher risk of developing chronic pain
- Negative impact on respiratory function
Benefits of Proper Positioning
- Improved circulation and nutrient delivery
- Enhanced flexibility and range of motion
- Reduction in fatigue and tension
Exercises for Strengthening the Back
Building a strong foundation in the torso is crucial for overall stability and mobility. Engaging in targeted movements not only enhances posture but also supports daily activities and athletic performance. Below are effective routines designed to fortify the muscles in this region.
Key Exercises
- Deadlifts: This compound movement engages multiple muscle groups, promoting strength throughout the entire torso.
- Pull-Ups: An excellent way to develop upper body strength, focusing on the latissimus dorsi and trapezius.
- Rows: Bent-over or seated variations help improve muscle balance and stability.
- Supermans: A simple bodyweight exercise that targets the lower muscles effectively.
- Planks: A fundamental exercise that reinforces core stability, which is essential for overall strength.
Routine Recommendations
- Start with a warm-up to increase blood flow.
- Incorporate 3-4 sets of each exercise, with 8-12 repetitions.
- Focus on form to prevent injury and maximize effectiveness.
- Allow adequate rest between sets.
- Gradually increase weights or resistance as strength improves.
Consistency in performing these exercises will lead to noticeable improvements in strength and endurance over time. It is essential to listen to the body and modify routines as necessary to suit individual needs and fitness levels.
Back Injuries and Prevention Tips
Injuries affecting the spine region can significantly impact daily activities and overall well-being. Understanding common issues and implementing preventive measures is crucial for maintaining a healthy posture and mobility.
- Regular exercise to strengthen core muscles.
- Practice proper lifting techniques to avoid strain.
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the spine.
- Incorporate stretching routines to enhance flexibility.
- Use ergonomic furniture to support good posture.
By adopting these strategies, individuals can minimize the risk of injuries and promote lasting health in the spine area.
Role of the Nervous System
The nervous system serves as a complex communication network, orchestrating various functions throughout the body. It is essential for processing sensory information, coordinating responses, and maintaining homeostasis, enabling organisms to interact with their environment effectively.
One of the primary functions of this system is to relay signals between different parts of the body. It facilitates the transmission of messages from sensory receptors to the brain, allowing for perception and interpretation of stimuli. This interaction is crucial for initiating appropriate reactions, whether it be a simple reflex or a more complex behavior.
Additionally, the nervous system plays a vital role in regulating bodily functions, such as heart rate, digestion, and muscle movement. Through intricate pathways and connections, it ensures that various systems work harmoniously, adapting to changes and maintaining equilibrium within the organism.
Moreover, it supports cognitive functions, influencing memory, learning, and emotional responses. The interplay between different components fosters not only physical but also mental well-being, underscoring the significance of this intricate network in everyday life.
Maintaining a Healthy Back
Ensuring optimal wellness in this vital area is crucial for overall functionality and comfort. Regular care and mindful habits can significantly enhance strength and flexibility, ultimately preventing discomfort.
- Exercise Regularly: Engage in activities that strengthen muscles and improve posture.
- Stay Hydrated: Adequate fluid intake supports tissue health and aids in flexibility.
- Mind Your Posture: Maintain an ergonomic setup when sitting or standing to reduce strain.
Incorporating these practices into daily life can lead to a sustainable improvement in well-being.