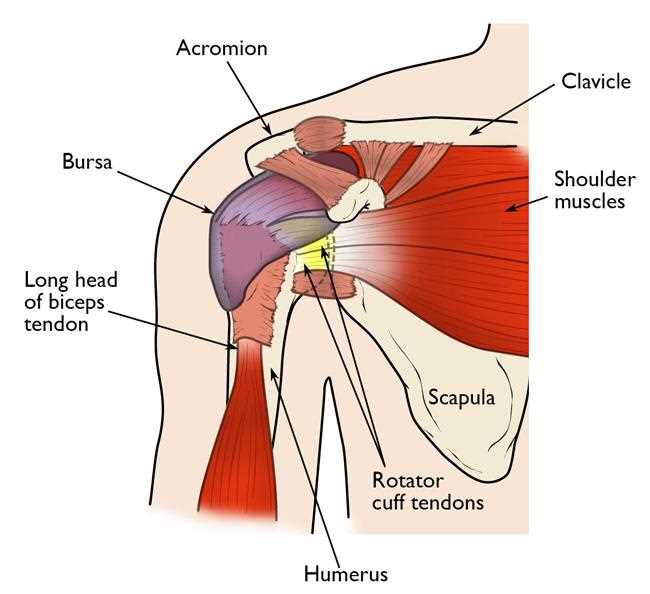
The complex structure located at the junction of the arm and torso plays a crucial role in human mobility and functionality. This region is characterized by a variety of components that work in harmony to enable a wide range of movements, from lifting and throwing to reaching and grasping. Gaining insight into this intricate arrangement can enhance our comprehension of both human anatomy and biomechanics.
Exploring the individual elements of this specific area reveals their distinct functions and contributions to overall movement. Each component, from the major joints to the supporting musculature, interacts to facilitate dynamic actions and stability. This interconnectedness underscores the importance of understanding how these features operate together to achieve seamless motion.
By examining the layout and relationships among these various elements, one can appreciate the remarkable design of the human body. This knowledge not only aids in anatomical education but also serves as a foundation for recognizing potential issues related to injury or strain in everyday activities.
Understanding Shoulder Anatomy
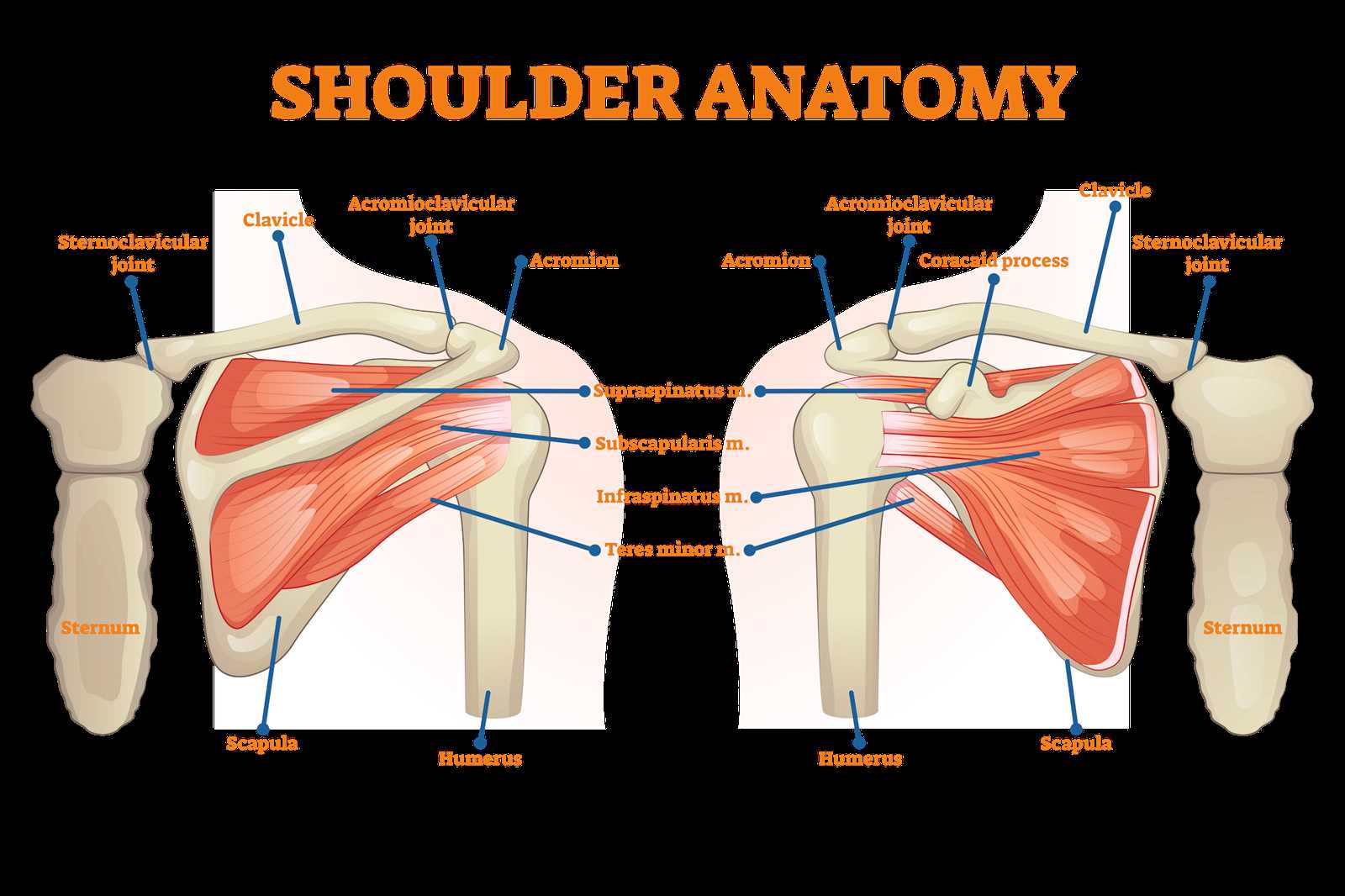
The upper limb region is a complex structure composed of various components that work together to provide mobility and strength. This area plays a crucial role in a wide range of activities, from simple movements to more complex tasks that require precision and coordination. A deeper comprehension of its anatomy enhances our appreciation of its functionality and significance in daily life.
Components of the Upper Limb Region
Within this region, several key elements contribute to its structure and movement. These elements can be categorized as follows:
- Bones: The framework consists of several bones that create stability and support.
- Muscles: Various muscles facilitate movement and enable the arm to perform diverse actions.
- Tendons: These connective tissues attach muscles to bones, allowing for the transmission of force.
- Ligaments: These structures connect bones to each other, providing stability and support.
- Nerves: A network of nerves controls movement and sensation in this area.
Functional Significance
The intricate arrangement of these components allows for a wide range of motions, including:
- Flexion and extension
- Abduction and adduction
- Internal and external rotation
Understanding these movements is essential for recognizing how injuries or conditions can affect functionality. Knowledge of the anatomy involved is crucial for healthcare professionals, athletes, and anyone interested in maintaining their physical well-being.
Key Functions of Shoulder Components
The upper limb structure plays a vital role in human mobility and functionality. Understanding the roles of its various elements is crucial for appreciating how they contribute to our everyday activities. This section explores the primary responsibilities of these components, highlighting their significance in maintaining movement and stability.
Mobility and Range of Motion
The primary function of these components is to enable a wide range of movements. This flexibility allows for various actions, including lifting, pushing, and rotating the arm. The intricate design of the structure facilitates seamless transitions between different motions, enhancing overall agility.
Stability and Support
Another essential role is providing stability and support to the upper limb. By maintaining proper alignment and balance, these elements ensure that the arm can bear weight without compromising integrity. Strong connections among the components are vital for preventing injuries during dynamic activities.
Common Shoulder Injuries Explained
Injuries affecting the upper arm region are prevalent among athletes and active individuals. Understanding these common ailments can aid in recognizing symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment. This section delves into some of the most frequent injuries that can occur in this area, highlighting their causes, symptoms, and potential management strategies.
-
Rotator Cuff Tear:
This condition involves the tearing of the muscles and tendons that stabilize the upper arm bone. It often results from repetitive overhead motions, leading to pain and limited mobility.
-
Impingement Syndrome:
This injury occurs when the tendons of the rotator cuff become irritated and inflamed due to compression during arm elevation. Symptoms include pain during activities that require lifting the arm.
-
Labral Tear:
The labrum is a cartilage ring that surrounds the socket of the upper arm bone. A tear can result from sudden injury or repetitive motion, causing pain and instability.
-
Dislocation:
A dislocation happens when the upper arm bone pops out of its socket. It can occur due to trauma, resulting in severe pain and a noticeable deformity.
-
Fracture:
Fractures in the upper arm area may arise from falls or direct impact. Symptoms typically include swelling, bruising, and an inability to move the arm normally.
Recognizing these injuries is crucial for timely intervention and effective rehabilitation. If symptoms persist, consulting a healthcare professional is recommended for a comprehensive evaluation and tailored treatment plan.
Importance of Joint Stability
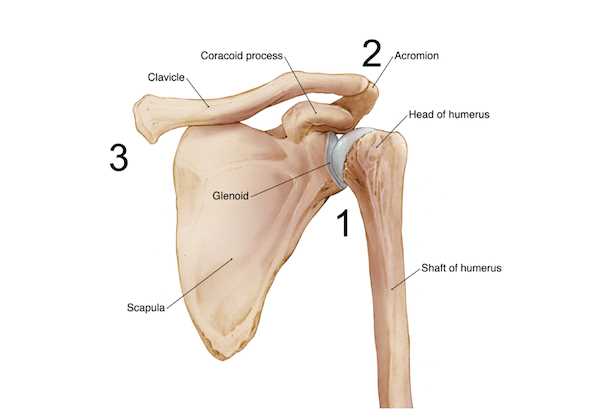
Maintaining stability in the body’s articulations is crucial for overall functionality and movement efficiency. A well-stabilized joint enables a range of motions while minimizing the risk of injuries. This stability is achieved through a combination of muscular support, ligamentous connections, and the structural integrity of the surrounding tissues. Understanding the significance of this stability can enhance performance in various physical activities and everyday tasks.
Role of Muscles and Ligaments
Muscles and ligaments work together to provide support and control over joint movements. Muscles generate the necessary force to execute actions while ligaments act as passive stabilizers, preventing excessive motion that could lead to injury. An imbalance in this dynamic can result in instability, increasing the likelihood of dislocations or strains.
Consequences of Instability
Joint instability can have several negative repercussions, affecting both physical performance and daily life. Individuals may experience pain, reduced range of motion, and a higher susceptibility to injuries. Proper rehabilitation and strength training can help restore stability and function.
| Stability Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Muscle Strength | Essential for dynamic support and control during movement. |
| Ligament Integrity | Helps maintain the joint’s structural stability and prevents excessive motion. |
| Proprioception | The body’s ability to sense its position, crucial for balance and coordination. |
| Neuromuscular Control | Involves the coordinated effort of nerves and muscles to stabilize the joint. |
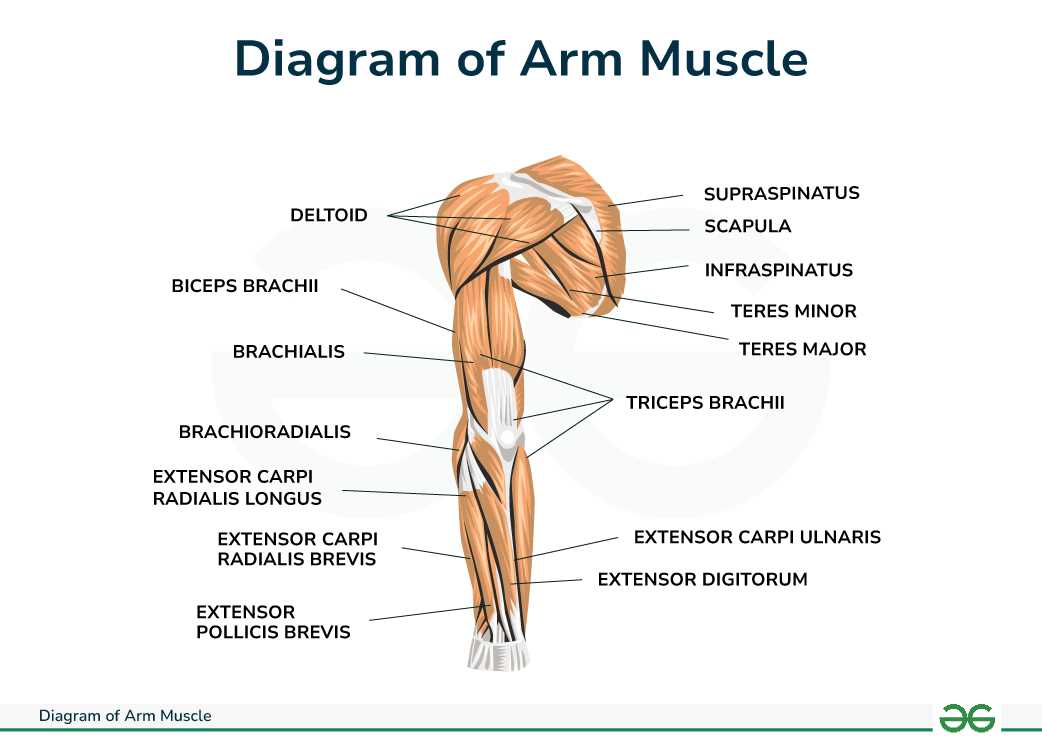
Muscles Involved in Shoulder Movement
The complex network of muscles around the upper limb plays a crucial role in enabling various movements. These muscles work in harmony to allow for a wide range of motion, contributing to both strength and flexibility in actions such as lifting, rotating, and reaching. Understanding these muscles is essential for comprehending how the upper limb functions and for preventing injuries.
Key Muscle Groups
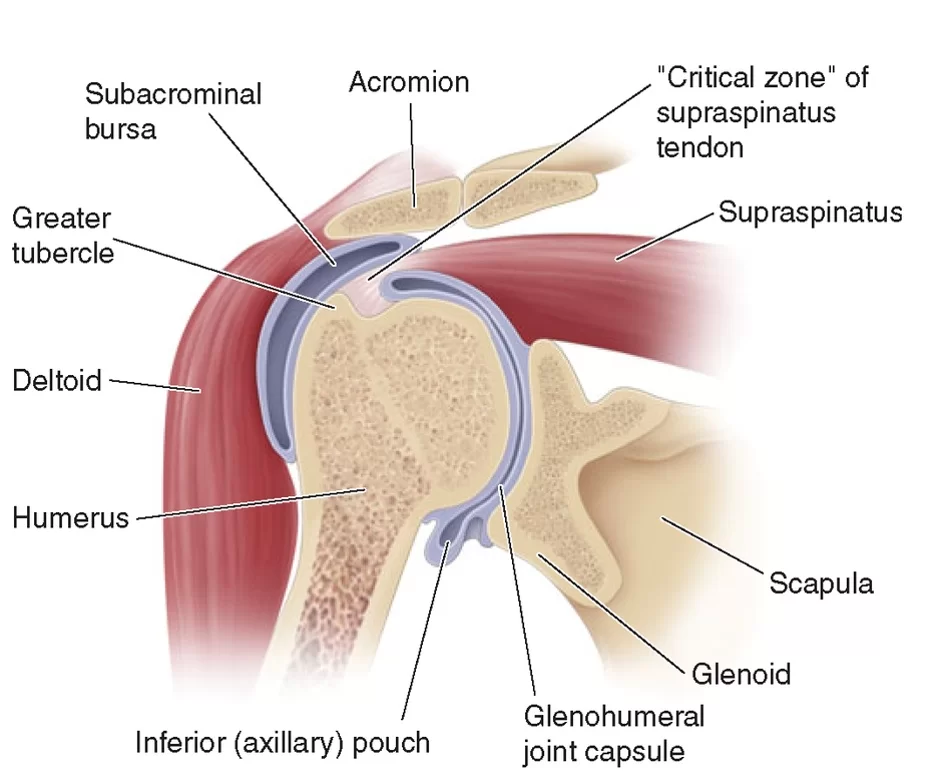
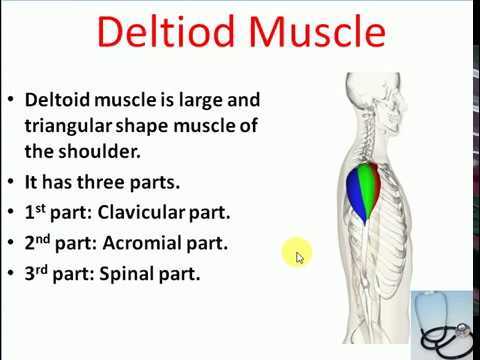
Several primary muscle groups facilitate movement in the upper limb. The deltoid, a prominent muscle, is responsible for lifting the arm and is divided into three distinct sections, each aiding in different types of motion. Additionally, the rotator cuff muscles stabilize the joint while allowing for rotation and elevation, making them vital for activities requiring precision.
Supporting Muscles
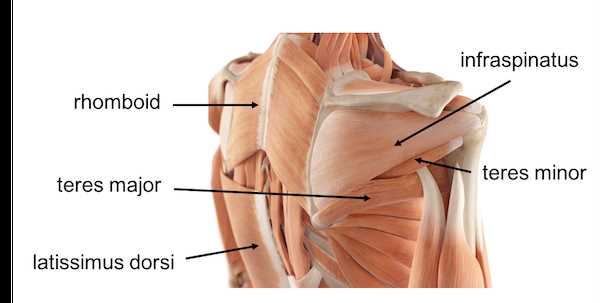
Other significant muscles contribute to the overall mobility and stability of the upper limb. The pectoralis major assists in adduction and flexion, while the trapezius and latissimus dorsi play vital roles in extension and lateral movements. Together, these muscles create a dynamic and functional system that supports various activities.
Role of Ligaments in Support
Ligaments play a crucial role in maintaining stability and integrity within the anatomical structure. These fibrous connective tissues serve as vital connectors between bones, ensuring that the joints function properly while preventing excessive movement that could lead to injury. By providing both support and flexibility, ligaments contribute significantly to the overall functionality of the musculoskeletal system.
Functions of Ligaments
Primarily, ligaments facilitate joint stability by limiting the range of motion. This control is essential in preventing dislocations and maintaining the alignment of the bones. Furthermore, they absorb stress during movement, acting as shock absorbers that protect surrounding tissues from potential damage. The resilience of these structures enables individuals to perform a wide range of physical activities while minimizing the risk of injury.
Importance of Ligament Health
Maintaining the health of ligaments is vital for optimal mobility and performance. Injuries to these connective tissues can lead to instability, pain, and restricted movement. Regular exercise, proper nutrition, and injury prevention strategies can help preserve ligament integrity, allowing for sustained physical activity and improved quality of life.
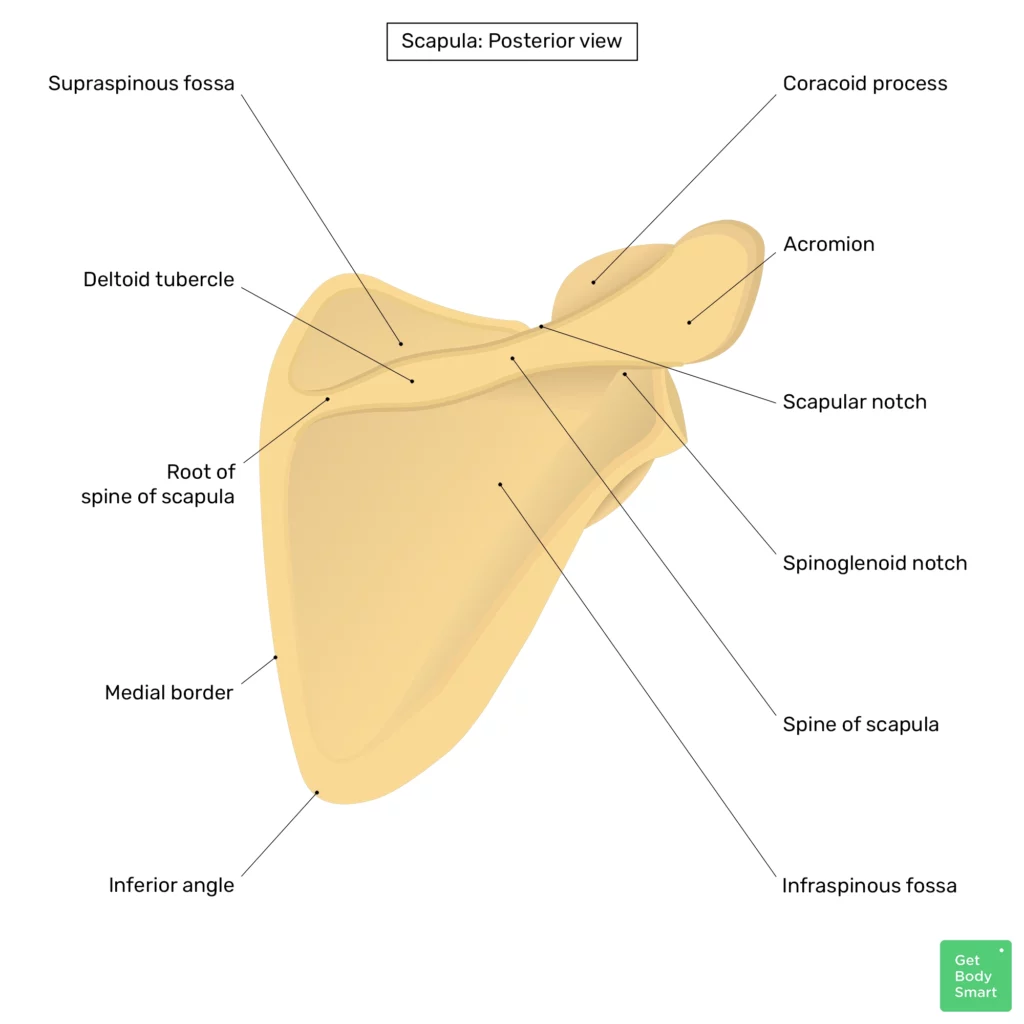
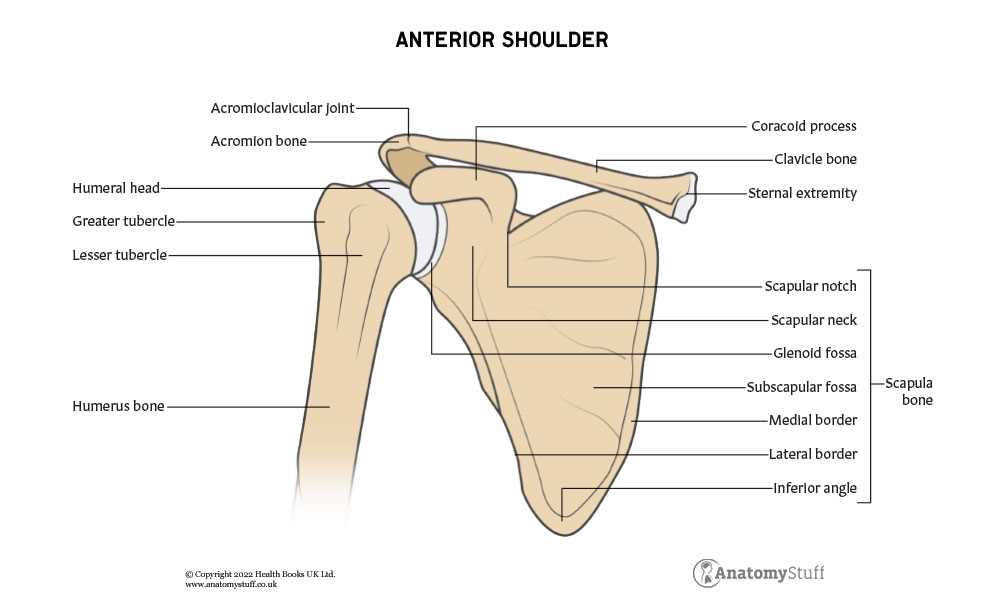
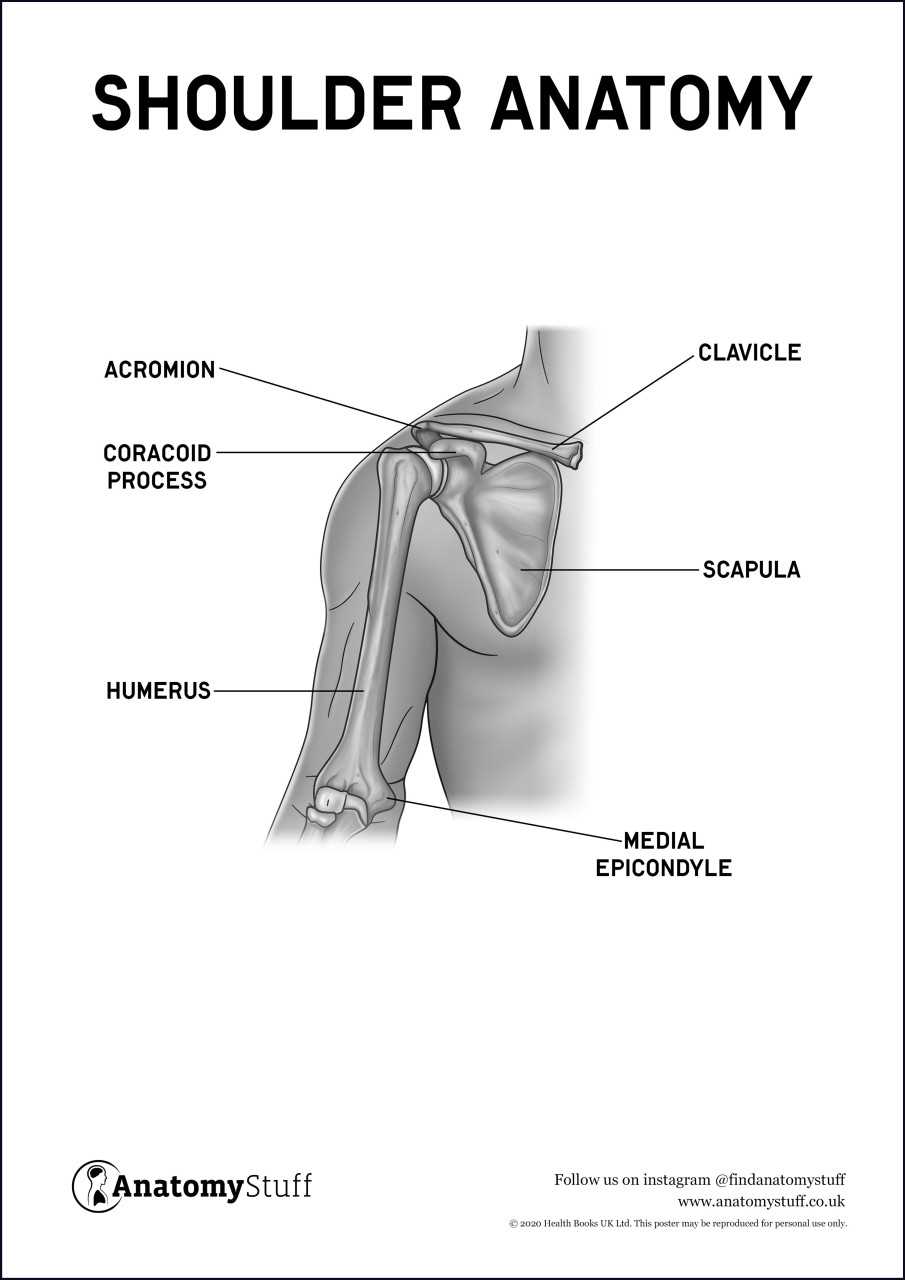
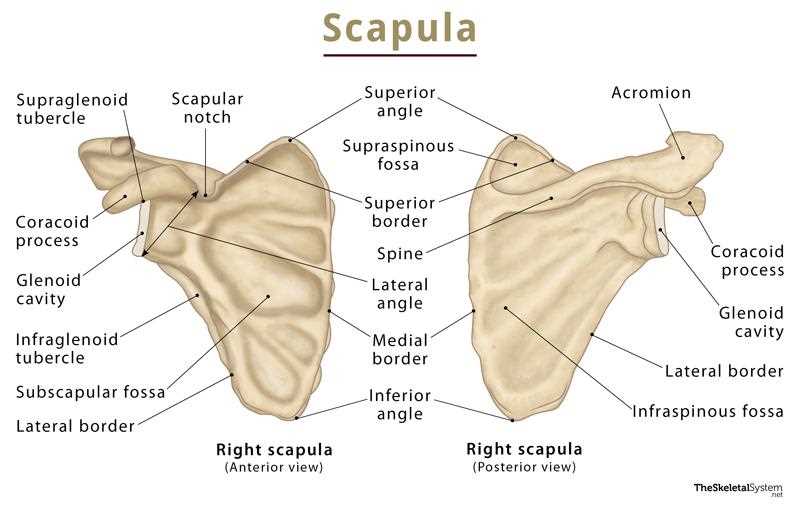
Visual Representation of Shoulder Parts
This section provides a comprehensive overview of the anatomical structure related to the upper limb’s joint area. A detailed illustration helps to enhance understanding of its various components and their relationships. By examining these elements visually, one can appreciate the complexity and functionality inherent in this region.
Highlighted Features: The graphical depiction emphasizes key elements that contribute to movement and stability. Each component serves a specific role, working in unison to facilitate a range of motions.
Importance of Visuals: Visual aids play a crucial role in anatomy studies. They allow learners to grasp spatial relationships and functional mechanics more effectively than text alone. This visual approach not only aids retention but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the intricacies of the human body.
Diagnostic Techniques for Shoulder Issues
Identifying complications in the upper limb involves a variety of assessment methods that can provide valuable insights into the underlying conditions. Each technique serves a distinct purpose, enabling healthcare professionals to accurately diagnose ailments and develop effective treatment plans. The combination of physical examinations, imaging studies, and functional assessments is crucial for obtaining a comprehensive understanding of the situation.
Common Assessment Methods
Several prevalent techniques are utilized in clinical settings to evaluate discomfort and dysfunction in the upper limb region. These approaches can help narrow down potential causes and inform subsequent interventions.
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical Examination | Involves palpation, range of motion tests, and strength assessments to evaluate the functionality of the limb. |
| X-ray Imaging | Provides a visual representation of bone structures, helping identify fractures, dislocations, and other abnormalities. |
| Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) | Utilizes magnetic fields to produce detailed images of soft tissues, ligaments, and muscles, aiding in diagnosing tears and inflammation. |
| Ultrasound | Employs sound waves to visualize soft tissue structures in real-time, useful for assessing fluid accumulation and soft tissue conditions. |
| Functional Testing | Assesses the capability of the upper limb through various movements, providing insight into limitations and pain triggers. |
Importance of Accurate Diagnosis
Accurate identification of issues within the upper limb is essential for effective management and rehabilitation. A comprehensive approach, incorporating various diagnostic techniques, ensures that clinicians can tailor treatments to individual needs, promoting recovery and restoring optimal function.
Rehabilitation Exercises for Shoulder Health
Maintaining optimal wellness in the upper limb is crucial for overall physical performance and daily activities. Engaging in targeted rehabilitation movements can significantly enhance strength, flexibility, and mobility, ensuring long-term vitality and resilience. These exercises are essential for those recovering from injuries, seeking to improve functionality, or preventing future issues.
Incorporating a variety of dynamic and static activities can help promote healing and restore range of motion. Focus on low-impact movements that engage the muscles surrounding the area, gradually increasing intensity as strength improves. Regular practice not only aids recovery but also fortifies the region against potential strains and discomfort.
Basic Exercises
Start with simple motions, such as arm circles and wall push-ups, to build foundational strength and coordination. These activities help enhance blood circulation and prepare the muscles for more challenging tasks.
Stretching Routines
Incorporate gentle stretching to improve flexibility and prevent stiffness. Hold each stretch for at least 15 seconds, focusing on breathing deeply to promote relaxation and increase range of motion.
Resistance Training
Once a comfortable baseline is established, introduce light resistance exercises using bands or small weights. Movements like lateral raises and front raises can effectively target the surrounding muscles, fostering endurance and stability.
Consistency and patience are key in any rehabilitation program. It is essential to listen to your body and adjust your routine as needed, seeking guidance from a healthcare professional when necessary.
Preventive Measures for Shoulder Injuries
Taking proactive steps to safeguard the upper limb’s well-being is crucial for avoiding discomfort and complications. Engaging in effective practices not only enhances physical performance but also minimizes the risk of strains and injuries.
Regular Strengthening Exercises: Incorporating targeted strengthening routines into your fitness regimen can significantly enhance the stability and resilience of the muscles supporting the joint. Focus on exercises that build the surrounding musculature, ensuring a balanced development that promotes overall support.
Proper Warm-Up Techniques: Prior to any physical activity, performing a thorough warm-up is essential. This practice prepares the body for exertion by increasing blood flow to the muscles and improving flexibility, which can help prevent injuries during intense activities.
Maintain Correct Posture: Being mindful of posture during daily activities and workouts can play a vital role in injury prevention. Adopting an ergonomic stance minimizes undue stress on the joints and surrounding muscles, fostering a healthier alignment.
Adequate Rest and Recovery: Allowing sufficient recovery time between workouts is critical for maintaining joint health. Overtraining can lead to fatigue and increase the likelihood of injuries, making it important to listen to your body and incorporate rest days as needed.
Seek Professional Guidance: Consulting with a healthcare or fitness professional can provide personalized insights into techniques and strategies that suit your individual needs. Tailored advice can enhance your understanding of safe practices and facilitate a more effective approach to injury prevention.