
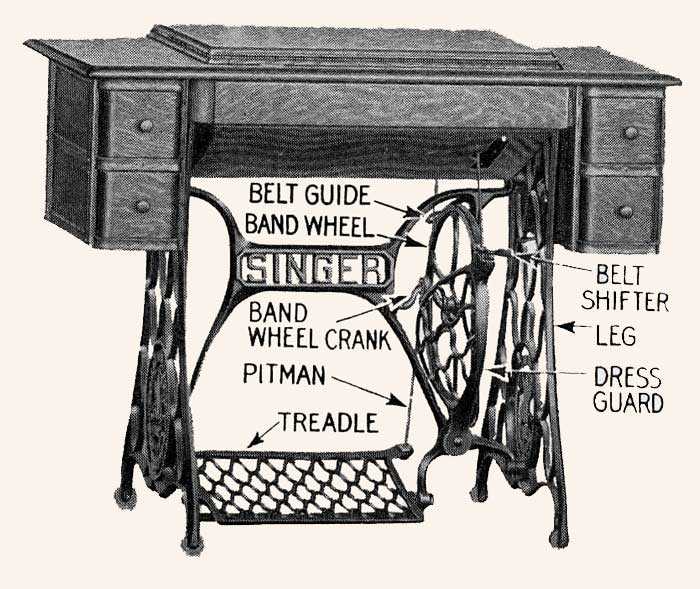
The world of sewing machines is intricate and fascinating, encompassing a variety of elements that work together to create beautifully crafted garments. Each machine consists of numerous components, each serving a specific purpose, contributing to the overall functionality and efficiency of the equipment. By delving into the mechanics behind these devices, one can appreciate the craftsmanship involved in sewing.
Recognizing how these elements interact is crucial for both beginners and experienced users alike. Whether it’s troubleshooting an issue or simply understanding the machine better, familiarizing oneself with the internal mechanisms enhances the sewing experience. A clear comprehension of these components can empower users to make informed decisions when it comes to maintenance and operation.
Furthermore, having a visual representation of the various components can be incredibly beneficial. It allows users to easily identify each part and understand its role in the sewing process. Such insights pave the way for more effective use of the machine, ultimately leading to improved results in various sewing projects.
Comprehensive Guide to Sewing Machine Components

The intricate world of textile machinery encompasses a variety of essential elements that work harmoniously to facilitate the art of stitching. Understanding these components is crucial for both novice and experienced users, as each part plays a pivotal role in the overall functionality of the equipment.
Key Elements of Textile Machinery
Among the fundamental components, the motor serves as the powerhouse, driving the movement of the needle and ensuring smooth operation. The needle assembly is another critical aspect, responsible for piercing the fabric and creating precise stitches. Additionally, the feed mechanism controls the movement of the fabric, allowing for even stitching as the material progresses through the machine.
Maintenance and Care
Regular maintenance of these parts is essential for optimal performance. Lubrication of moving components reduces friction and wear, while periodic cleaning prevents lint accumulation that can hinder functionality. By familiarizing oneself with the machinery’s elements and their maintenance needs, users can enhance the longevity and reliability of their sewing equipment.
Understanding the Internal Mechanics of Sewing Machines
Exploring the intricate workings of stitching devices reveals a fascinating interplay of components that harmoniously collaborate to create fabric masterpieces. These mechanisms are engineered to perform precise movements, facilitating the sewing process with remarkable efficiency and accuracy.
At the heart of any sewing apparatus lies a robust assembly of gears, levers, and needles. Each element is meticulously designed to fulfill specific functions, ensuring the seamless operation of the entire system. Understanding these components not only enhances the user experience but also aids in troubleshooting and maintenance.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Needle | Penetrates the fabric to create stitches. |
| Bobbin | Holds the lower thread, working with the needle. |
| Feed Dogs | Move the fabric through the machine during stitching. |
| Motor | Powers the machine, enabling movement of components. |
| Tension Control | Regulates the thread tightness for even stitches. |
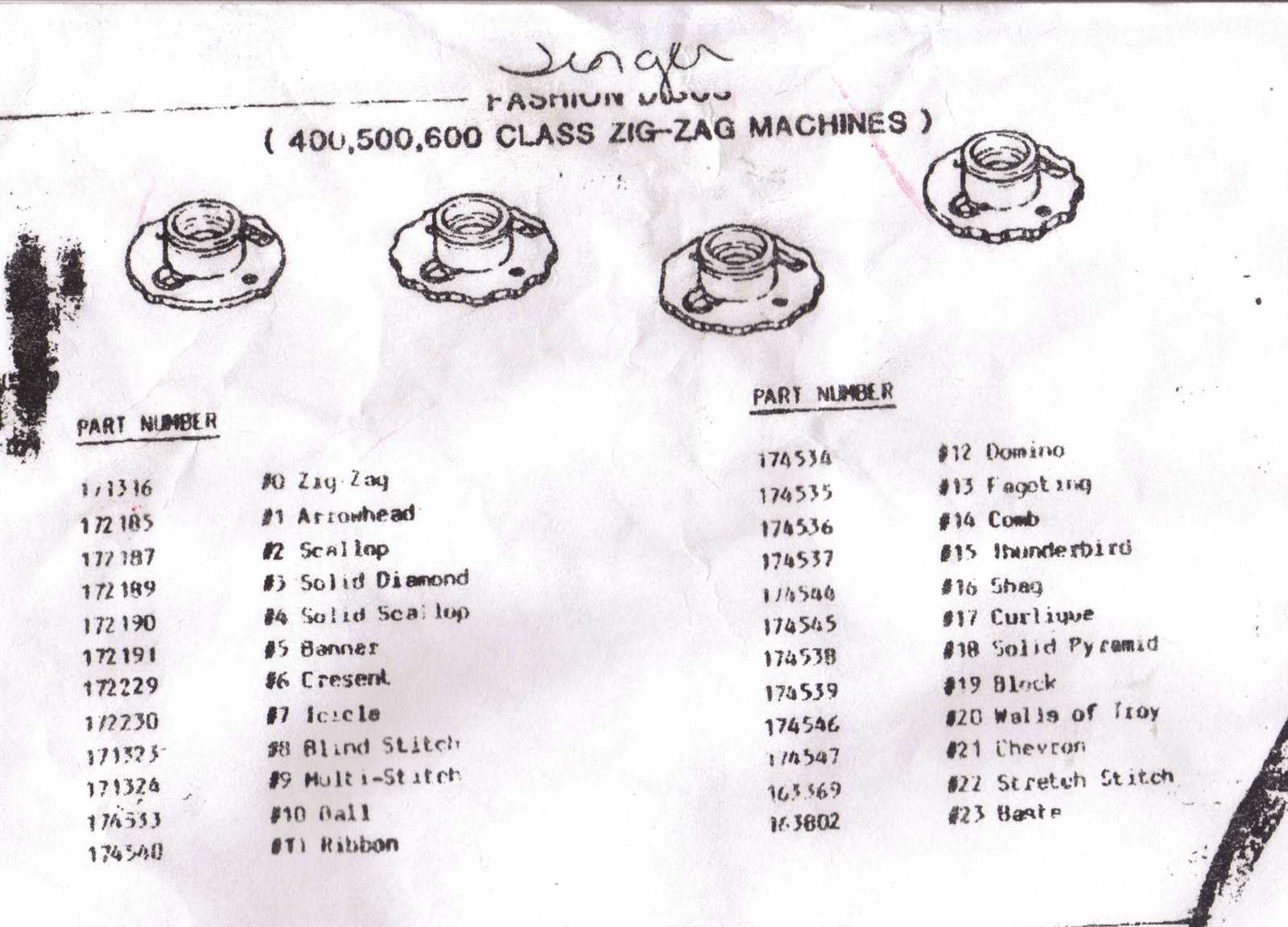
Key Features of the Singer 201-2 Model

This remarkable sewing machine boasts several attributes that set it apart from its competitors. Designed with both functionality and user-friendliness in mind, it caters to a variety of sewing needs, making it suitable for both beginners and experienced users.
One of the standout characteristics is its robust construction, ensuring durability and stability during operation. The machine is equipped with a powerful motor that allows for smooth stitching on various fabric types, enhancing performance and efficiency.
Additionally, it features a straightforward threading system, simplifying the setup process. Users appreciate the adjustable stitch lengths and widths, providing versatility for different sewing projects. The presence of various built-in stitch patterns enables creativity, allowing individuals to explore their artistic side while working on garments or home décor.
Moreover, this model is known for its quiet operation, making it ideal for environments where noise may be a concern. Overall, the combination of quality craftsmanship and practical design elements makes this machine a valuable tool for any sewing enthusiast.
How to Identify Essential Sewing Machine Parts
Understanding the crucial components of a stitching device is vital for effective usage and maintenance. Each element plays a specific role, contributing to the machine’s overall functionality and performance. Familiarity with these parts can enhance the sewing experience and streamline troubleshooting efforts.
Main Components of a Sewing Machine
- Needle: This is the sharp element that pierces the fabric, allowing thread to pass through.
- Presser Foot: It holds the fabric in place while sewing, ensuring smooth operation.
- Feed Dogs: These are the small teeth located under the needle plate that help move the fabric as you sew.
- Bobbin: This small spool holds the thread that forms the stitch on the underside of the fabric.
- Thread Tension Control: This mechanism adjusts the tightness of the thread, affecting stitch quality.
Understanding the Function of Each Element
Recognizing how these components interact will enable better handling of the sewing machine. Regular inspection and understanding of each part’s function can prevent common issues:
- Needle Maintenance: Replace needles regularly to ensure smooth stitching and avoid fabric snags.
- Cleaning the Feed Dogs: Keep these free of lint and dust for optimal fabric movement.
- Checking Thread Tension: Adjust as needed to achieve balanced stitches on both sides of the fabric.
Exploring the Functionality of Machine Bobbins

Bobbins are crucial components in the world of sewing machines, serving as the foundation for creating stitches that hold fabric together. Their design and functionality significantly influence the efficiency and quality of the sewing process. Understanding how these small yet essential items work can enhance the overall sewing experience and ensure that projects are executed flawlessly.
The Role of Bobbins in Stitch Formation
The primary purpose of a bobbin is to provide the lower thread that interlocks with the upper thread, forming a secure stitch. This interaction is vital for various sewing techniques. Key aspects include:
- Thread Tension: Proper tension is essential for achieving balanced stitches.
- Thread Type: Different materials and weights of thread can affect stitch quality.
- Bobbins Size: Using the correct size ensures compatibility with the machine and prevents jams.
Maintenance Tips for Bobbins
To keep bobbins functioning optimally, regular maintenance is necessary. Consider the following practices:
- Check for damage or wear before each sewing session.
- Clean the bobbin case to prevent lint buildup.
- Store bobbins in a dedicated case to avoid tangling.
By understanding the role and maintenance of these small components, sewists can ensure smoother operation and improved results in their sewing projects.
Maintenance Tips for Long-lasting Sewing Equipment

Proper care and attention are essential for ensuring that your sewing tools remain in optimal condition. By implementing a few straightforward maintenance practices, you can significantly extend the lifespan of your equipment and enhance its performance.
Regular Cleaning and Oiling
Cleaning your sewing machine frequently helps prevent dust and lint buildup, which can hinder functionality. Use a soft brush or cloth to remove debris from the machine’s exterior and interior parts. Additionally, applying oil to moving components as recommended by the manufacturer can ensure smooth operation and reduce wear over time.
Proper Storage Practices
Storing your sewing equipment in a dry, dust-free environment is crucial for its longevity. Consider using a protective cover or a dedicated storage case to shield it from environmental factors. Also, ensure that the workspace is organized, keeping tools and accessories in designated areas to prevent damage.
Troubleshooting Common Issues in Vintage Models

Addressing problems in older sewing machines can be a rewarding yet challenging experience. Understanding the typical issues that arise with these classic devices allows users to effectively maintain and restore their functionality.
Common difficulties include:
- Thread Jamming: Often caused by incorrect threading or using unsuitable thread types.
- Needle Breakage: This may occur due to dull needles or improper installation.
- Stitch Quality Issues: Inconsistent stitches can result from incorrect tension settings or dirty components.
- Motor Problems: Electrical issues may lead to the machine not powering on or running slowly.
To resolve these issues, consider the following steps:
- Check and re-thread the machine to ensure proper thread placement.
- Inspect the needle for damage and replace it if necessary.
- Adjust the tension settings according to the fabric type being used.
- Clean and lubricate the machine regularly to prevent build-up of lint and debris.
- Examine electrical connections and test the motor for functionality.
By following these guidelines, users can enhance the performance of their beloved vintage models, ensuring they remain reliable tools for years to come.
Cleaning and Oiling Your Sewing Machine
Regular maintenance of your stitching device is essential for its longevity and performance. Keeping the machine clean and well-lubricated ensures smooth operation and prevents potential issues that can arise from dust and debris accumulation.
Begin by removing the needle and presser foot to access the internal components easily. Gently brush away any lint or thread remnants using a soft brush or cloth. Pay special attention to the feed dogs and bobbin area, as these spots tend to collect the most debris.
After cleaning, it’s time to apply oil. Use a suitable lubricant specifically designed for sewing machines. A few drops in designated areas will help maintain moving parts. Refer to your device’s guidelines to identify the correct spots for oil application. This process will enhance performance and ensure that all mechanisms function smoothly.
Finally, reassemble your device, replacing the presser foot and needle. Regular cleaning and oiling should be part of your routine, ideally after every few projects, to keep your machine running efficiently.
The Role of Tension Adjustments in Stitch Quality

Correct tension settings play a crucial role in achieving optimal stitch quality in sewing projects. Proper adjustments ensure that threads are evenly balanced, resulting in neat, consistent stitches. Understanding how tension influences stitch formation can significantly enhance the overall quality of the finished product.
Impact of Thread Tension
Thread tension affects several aspects of sewing, including:
- Stitch appearance: Well-balanced tension results in straight, uniform stitches.
- Fabric integrity: Proper tension prevents fabric puckering or distortion.
- Thread breakage: Correct adjustments minimize the likelihood of thread snapping during operation.
Adjusting Tension Settings
To achieve ideal tension, consider the following tips:
- Test on scrap fabric before starting your project.
- Observe stitch quality and make incremental adjustments as needed.
- Ensure that both upper and lower thread tensions are balanced for the best results.
By carefully managing tension, sewists can significantly improve the quality of their work, leading to more satisfying results and professional-looking finishes.
Detailed Overview of Needle and Presser Foot Mechanisms
The intricate interplay between the needle and presser foot is fundamental to the functionality of a sewing device. These components work in harmony to ensure precise fabric handling and stitching accuracy. Understanding their mechanisms reveals how they contribute to the overall sewing process, enhancing the user’s experience.
The needle serves as the primary instrument for penetrating the fabric, creating stitches as it moves up and down. Its design, often featuring a tapered point and a groove, facilitates smooth entry into various materials. A well-aligned needle not only affects the quality of stitches but also minimizes the risk of damage to the fabric.
Complementing the needle, the presser foot plays a critical role in guiding the fabric through the machine. It exerts pressure on the fabric, ensuring consistent feed while preventing slipping or bunching. Various types of presser feet are available, each tailored for specific tasks, such as quilting, zipper application, or decorative stitching.
Moreover, the height and pressure settings of the presser foot can be adjusted, allowing for versatility when working with different fabric thicknesses. This adaptability enhances the machine’s capability to accommodate a wide range of sewing projects, from delicate silks to heavy denim.
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of the needle and presser foot mechanisms provides valuable insights into achieving high-quality sewing results. Mastery of these components not only improves stitching precision but also elevates the overall sewing experience.
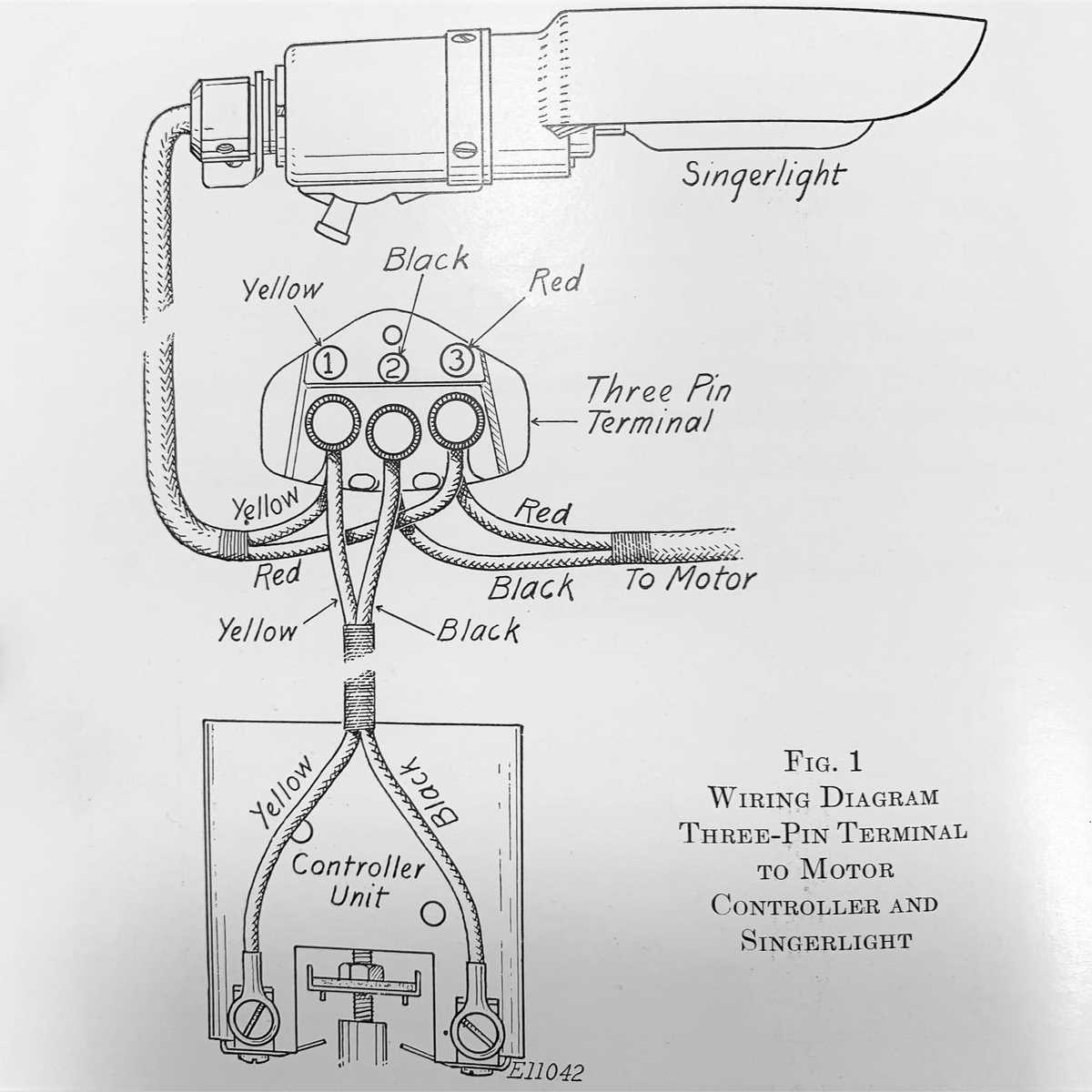
Exploring Power and Foot Control Systems
This section delves into the mechanisms that govern the operation of sewing machines, focusing on the energy transmission and user interface aspects. Understanding these systems is essential for enhancing performance and ensuring seamless operation.
At the core of most sewing machines lies a robust power system, responsible for delivering the necessary energy to operate various components. This system typically consists of a motor, which converts electrical energy into mechanical motion. The efficiency of this energy transfer plays a crucial role in the overall functionality of the device.
Foot control mechanisms serve as a vital interface between the user and the machine, allowing for precise regulation of speed and power. By employing a foot pedal, users can easily adjust the machine’s operation according to their needs, providing a more intuitive and responsive sewing experience. The design of these controls often emphasizes ergonomics and accessibility, ensuring that users can maintain comfort during prolonged use.
Overall, a comprehensive understanding of power and foot control systems can significantly improve one’s ability to operate sewing equipment effectively, leading to better results and greater satisfaction in the crafting process.