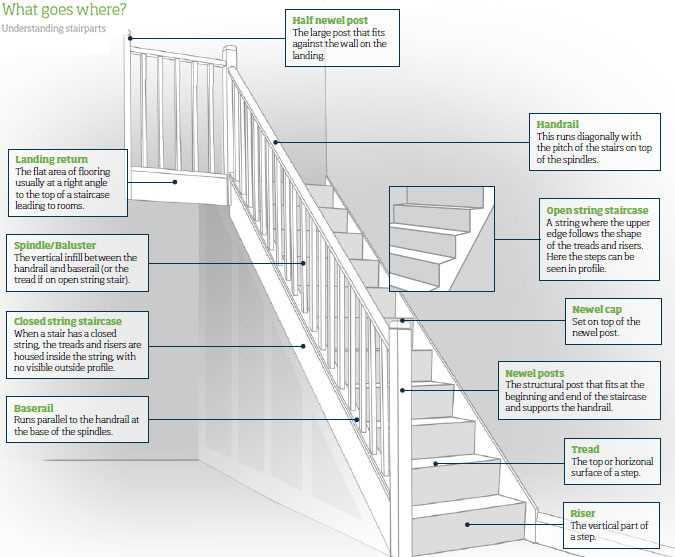
The construction of elevated pathways involves various crucial elements that contribute to both functionality and aesthetic appeal. These structures play a significant role in connecting different levels within a building or landscape, ensuring safe and efficient movement for users. A comprehensive overview of these components is essential for anyone looking to enhance their knowledge or skills in architectural design.
Each element serves a specific purpose, whether it be to provide support, enhance safety, or add visual interest. From the foundational supports to the finishing touches, understanding the role of each component can lead to better design choices and improved safety standards. Exploring these various elements allows for a deeper appreciation of the engineering principles involved.
As we delve into the individual components, we will uncover their unique characteristics and how they work together to create a cohesive and functional design. Recognizing the importance of each element not only aids in the design process but also fosters a greater respect for the craftsmanship involved in their creation.
This section aims to explore the fundamental elements that comprise a functional and aesthetically pleasing ascent within a building. Each component plays a critical role in ensuring safety, comfort, and style. By breaking down these elements, readers will gain insights into the various features that contribute to an effective design.
Key Elements of Elevation Systems
- Steps: The horizontal surfaces where individuals place their feet.
- Risers: The vertical sections that connect each step, providing height.
- Landings: The flat areas between flights that offer rest points.
Support Structures
- Stringers: The inclined beams that support the steps and risers.
- Post: The vertical supports that help stabilize the entire assembly.
- Handrails: The safety features that provide support and guidance.
Design Considerations
- Dimensions: Standard measurements that ensure safety and comfort.
- Materials: Various substances used to enhance durability and aesthetics.
- Style: The visual design that aligns with the overall architecture.
Safety Features
- Non-slip surfaces: Textures that prevent slips and falls.
- Lighting: Adequate illumination that enhances visibility.
- Guardrails: Additional barriers that protect users from accidental falls.
Basic Elements of Stair Design
The construction of vertical transitions in buildings involves several key components that ensure safety, functionality, and aesthetic appeal. Understanding these fundamental elements is essential for creating effective and user-friendly structures that facilitate movement between different levels.
Each component plays a critical role in the overall performance and appearance of the vertical transition. From the incline to the supporting structures, attention to detail is crucial in achieving a harmonious balance between form and function.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Riser | The vertical section that connects one step to the next, providing height and defining the transition’s profile. |
| Tread | The horizontal surface where individuals place their feet, crucial for stability and comfort. |
| Landing | A flat area at the top or bottom of a vertical transition, serving as a rest point and aiding in the transition between levels. |
| Handrail | A supportive bar typically mounted alongside the transition, enhancing safety and providing support for users. |
| Stringer | The structural framework that supports the treads and risers, essential for maintaining stability and integrity. |
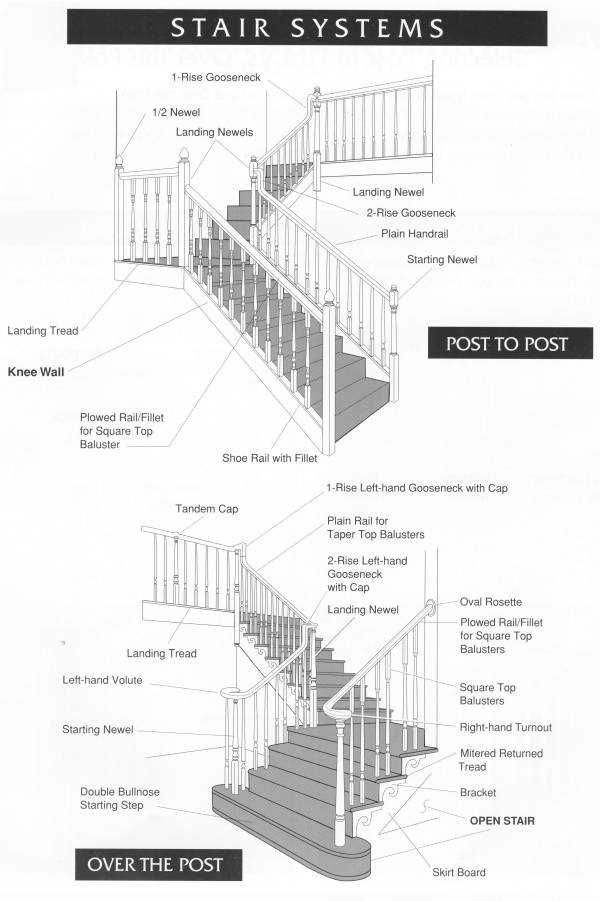
Types of Staircases Explained
In architectural design, various forms of elevation structures serve distinct purposes and aesthetic appeals. Each variant offers unique advantages, catering to different spatial requirements and design preferences. Understanding these configurations can aid in selecting the most suitable option for any given environment.
- Straight Configuration: This is the simplest form, characterized by a single, linear run without any turns. It provides direct access between levels.
- Curved Structure: Featuring a gentle arc, this design adds elegance to a space. It is often used in grand entrances and can save space compared to straight forms.
- Spiral Formation: Compact and visually striking, spiral types revolve around a central point. They are ideal for tight spaces and can serve as a statement piece in a room.
- L-Shaped Design: This version incorporates a turn, creating an L shape. It is effective for larger areas and offers a landing for rest or decoration.
- U-Shaped Configuration: Similar to the L shape, but with a return leg, this form creates a more substantial landing area. It enhances flow in spacious environments.
- Floating Style: This modern option gives the illusion of steps suspended in mid-air. It is visually appealing and often used in contemporary settings.
Choosing the right configuration involves considering factors such as space constraints, aesthetic preferences, and functional needs. Each style contributes differently to the overall ambiance of an area.
Dimensions and Measurements Overview
Understanding the various dimensions and measurements involved in construction is crucial for ensuring structural integrity and safety. This section provides an overview of key dimensions that play a vital role in designing and building effective vertical access solutions. Accurate measurements contribute to functionality, aesthetics, and compliance with regulations.
Essential Measurements
Key dimensions include overall height, width, and depth, which determine the overall footprint and usability of the structure. These measurements should align with user requirements and industry standards to ensure optimal performance. Additionally, riser height and tread depth are critical for creating a comfortable and safe user experience.
Importance of Accurate Dimensions
Precision in measurements cannot be overstated. Incorrect dimensions can lead to various issues, such as safety hazards and increased costs during construction. Regular checks and adherence to established guidelines can mitigate these risks, ensuring that the finished structure meets all necessary criteria.
Materials Used in Stair Construction
The choice of components in the creation of vertical access structures significantly influences their durability, aesthetic appeal, and functionality. Various materials can be utilized, each offering distinct advantages that cater to specific needs and preferences. Understanding the available options allows for informed decision-making in the construction process.
Wood is a traditional choice, renowned for its warmth and natural beauty. Common types include oak, maple, and pine, each providing a unique finish and grain pattern. Alternatively, metal such as steel or aluminum is often selected for its strength and modern appearance, making it suitable for contemporary designs. Concrete is another widely used material, offering excellent durability and the ability to mold into various shapes.
| Material | Advantages | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Wood | Natural beauty, warmth, ease of installation | Residential settings, traditional designs |
| Metal | Durability, modern look, low maintenance | Commercial buildings, contemporary styles |
| Concrete | Strength, longevity, design versatility | Industrial applications, outdoor structures |
Additionally, composite materials are gaining popularity due to their combination of strength and aesthetic appeal. They offer the look of natural wood while requiring less maintenance. Selecting the right combination of these materials plays a crucial role in achieving the desired functionality and visual impact of vertical access structures.
Load-Bearing Features in Stairs
Understanding the structural elements that contribute to the overall strength and stability of elevated platforms is crucial in architectural design. These features play a vital role in supporting weight and ensuring safety during use. Proper assessment and implementation of these components are essential to maintain the integrity of the entire construction.
- Risers: Vertical components that create height and support the steps.
- Treads: The horizontal surfaces that provide footing and distribute weight.
- Stringers: Diagonal supports that connect and hold the treads and risers in place.
- Landings: Flat areas that provide stability and transition between different sections.
- Bracing: Additional reinforcements that enhance the overall strength of the structure.
Each of these elements must be carefully designed and constructed to ensure they can withstand various loads and stresses. The selection of materials and construction techniques also significantly influences the performance and longevity of these features.
- Assess the intended load requirements.
- Choose appropriate materials for each component.
- Ensure accurate alignment and support during construction.
In summary, the load-bearing characteristics of elevated platforms are foundational to their functionality and safety. Understanding how these components work together can guide effective design and construction practices.
Safety Features and Codes
Ensuring the well-being of individuals in multi-level structures involves adhering to specific regulations and incorporating essential protective elements. These measures are designed to prevent accidents and enhance the overall functionality of access systems.
Regulatory compliance is crucial, as local and national building codes provide guidelines that must be followed. These codes outline minimum requirements for design, construction, and maintenance, ensuring that all components meet safety standards.
Key safety features include guardrails and handrails, which are vital for preventing falls. Proper installation and height specifications are dictated by codes to guarantee their effectiveness. Additionally, the clarity of markings and contrast in color are essential for visibility, particularly in low-light environments.
Regular inspections and maintenance are fundamental to uphold safety standards. Identifying and addressing wear or damage promptly can mitigate risks and ensure a secure environment for users.
Common Staircase Styles and Designs
When it comes to multi-level structures, the variety of configurations and aesthetics plays a significant role in enhancing both functionality and appeal. Understanding different approaches can help in selecting the right option for a particular environment, balancing style with practicality.
Traditional Styles often feature a classic look, emphasizing symmetry and elegance. These configurations may include features such as ornate railings and decorative newel posts, making them suitable for both residential and formal settings.
Modern Designs focus on minimalism, clean lines, and innovative materials. This approach often incorporates elements like glass and metal, creating a sense of openness and lightness, ideal for contemporary homes.
Spiral Configurations are perfect for compact spaces, offering a unique and space-efficient solution. These winding structures not only save room but also serve as striking visual elements that can enhance the overall design.
Floating Structures present a visually captivating option, appearing to hover without visible support. This style is often used in modern architecture to create an airy feel, making spaces look larger and more inviting.
In summary, choosing the right style can significantly influence the atmosphere and functionality of a space, making it essential to consider various options available in contemporary architecture.
Functionality of Stair Railings
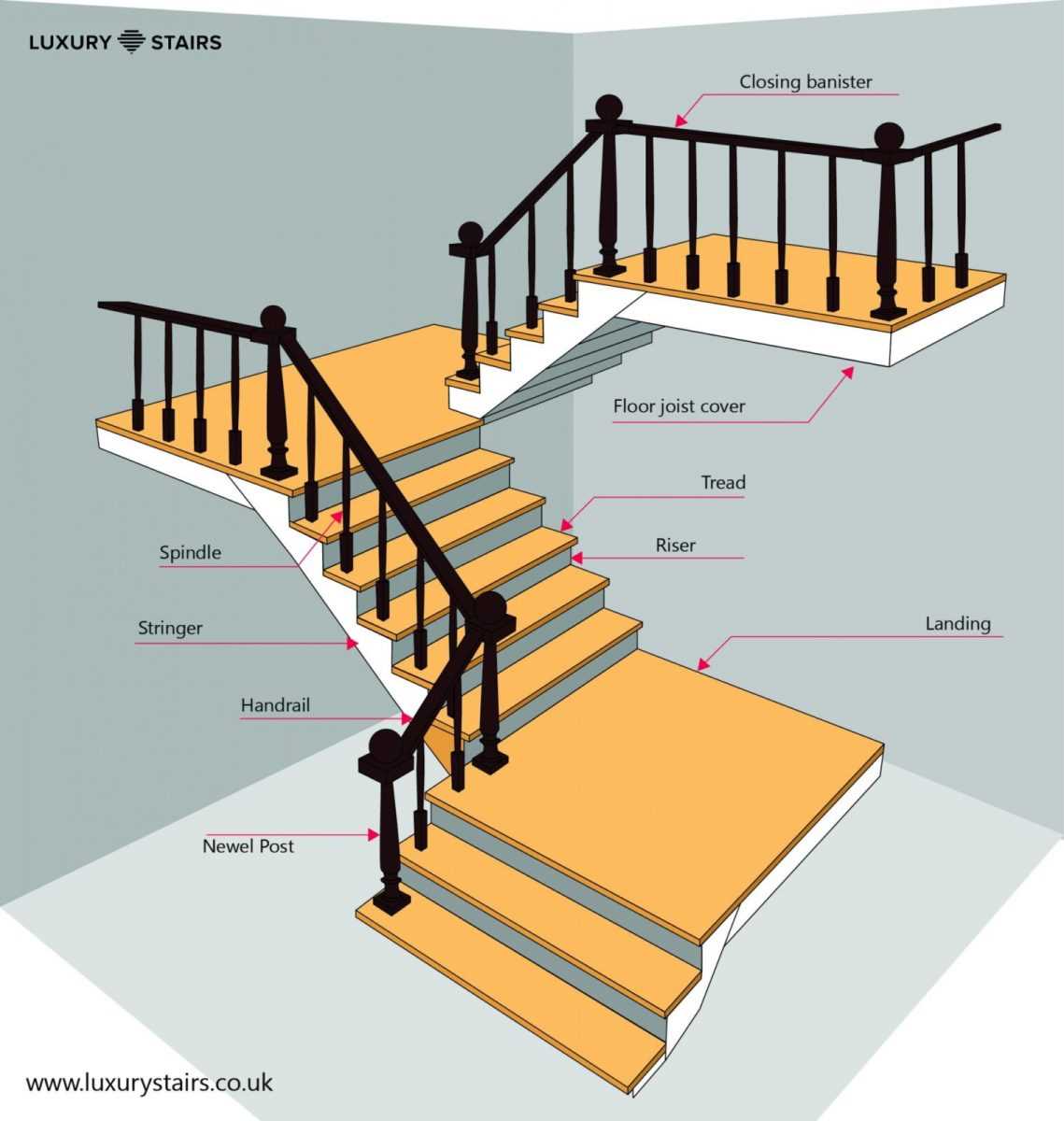
The significance of protective barriers in elevated structures extends beyond mere aesthetics. These elements serve crucial roles in ensuring safety and enhancing user experience in vertical transitions.
Safety is the primary function, as these barriers provide essential support for individuals navigating slopes. They prevent falls by offering a reliable grip, which is particularly vital for children and the elderly. Moreover, these installations can help guide users, making the journey more intuitive and less daunting.
In addition to safety, they contribute to the overall design of a space. With a variety of materials and styles available, they can complement the architectural theme, adding an element of elegance and sophistication. This aesthetic enhancement can significantly elevate the visual appeal of both residential and commercial environments.
Durability is another critical aspect. Quality materials used in these installations withstand the rigors of daily use, ensuring longevity and minimal maintenance. This resilience allows them to remain functional and visually appealing over time.
Furthermore, they can incorporate accessibility features, making it easier for individuals with mobility challenges to navigate different levels safely. This inclusivity is essential in public spaces, where accommodating diverse user needs is a priority.
In summary, protective barriers not only ensure safety but also enhance the design and functionality of multi-level structures, making them indispensable in modern architecture.
Maintenance Tips for Stairs
Regular upkeep is essential to ensure the longevity and safety of your elevated surfaces. Implementing a consistent maintenance routine can prevent wear and tear, enhance appearance, and reduce the risk of accidents.
Begin with a thorough inspection to identify any damages or loose components. Pay attention to cracks, splinters, or signs of deterioration. Addressing these issues promptly can prevent further complications.
Cleaning is vital to maintain a pristine look. Utilize a suitable cleaner for the material, ensuring that it effectively removes dirt and stains without causing damage. For wooden surfaces, consider using a soft cloth or a gentle scrub to avoid scratching.
Ensure that any railings or supports are securely fastened. Tighten loose screws or bolts to enhance stability and safety. Inspect for any corrosion or rust on metal components, treating them as necessary to prevent further deterioration.
Applying a protective finish can significantly extend the life of your surfaces. For wooden structures, consider using sealants or varnishes to shield against moisture and wear. Regularly reapplying these finishes will help maintain their appearance and integrity.
Lastly, be mindful of any environmental factors that may affect your elevated surfaces. Address any issues with moisture or extreme temperatures to prevent long-term damage. Regular maintenance is an investment in safety and durability, ensuring your elevated surfaces remain functional and appealing for years to come.
Visualizing Stairs with Diagrams
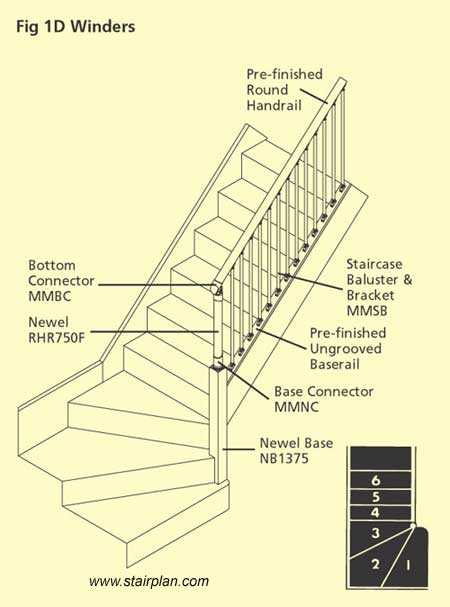
Illustrating structures that facilitate movement between different levels is essential for clarity and understanding. Utilizing visual representations can greatly enhance comprehension, enabling individuals to grasp the complexities of various components involved in these constructions.
Importance of Clear Illustrations
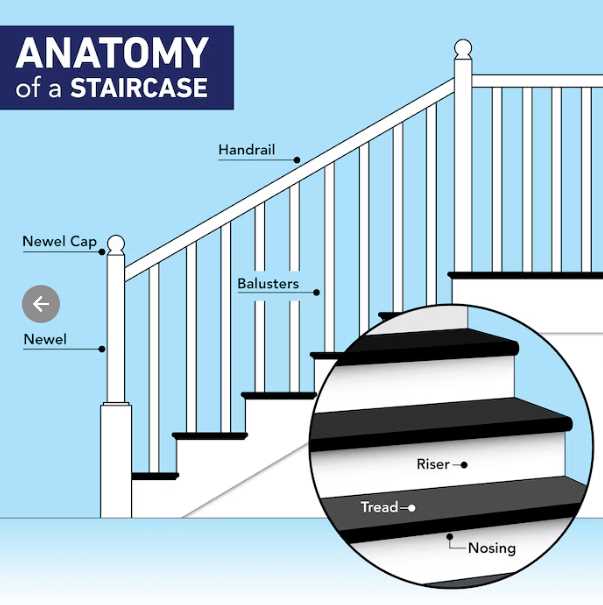
Effective visualizations play a crucial role in communicating ideas related to elevation changes. By providing detailed imagery, one can simplify complex concepts, making them accessible to a wider audience. This approach fosters better planning and execution, ultimately leading to improved safety and functionality.
Techniques for Effective Representation
Employing various methods, such as sketches or digital models, allows for a more comprehensive view of the entire system. Incorporating annotations and labels helps highlight critical elements, ensuring that the audience can easily interpret the information presented. A well-crafted visual tool can transform intricate designs into user-friendly formats, facilitating better decision-making.
Future Trends in Stair Design
The evolution of vertical movement solutions is paving the way for innovative concepts that prioritize both aesthetics and functionality. As architectural styles evolve, so do the methods of connecting different levels within a space. Future developments will likely focus on integrating sustainability, advanced materials, and smart technology into the design of these essential elements.
Emphasis on Sustainability
Environmental consciousness is shaping the future of design, with an increasing preference for eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient features. Utilizing recycled or sustainably sourced components not only enhances the appeal but also contributes to reducing the overall carbon footprint. Innovations such as integrated greenery can also be anticipated, allowing for a seamless blend of nature and structure.
Smart Integration and Customization
The incorporation of technology into movement solutions will likely gain momentum. Features like adjustable lighting, embedded sensors, and customizable configurations can enhance user experience and safety. Smart connectivity can allow users to control lighting or monitor usage patterns, making these elements more interactive and adaptable to the needs of their occupants.