
In the realm of residential climate control, the intricacies of heating mechanisms play a pivotal role in maintaining comfort during colder months. Grasping the layout and functionality of these essential elements can empower homeowners to enhance efficiency and address potential issues proactively.
By exploring the various segments of these systems, one can unlock the ultimate understanding of how each component contributes to overall performance. This knowledge not only aids in troubleshooting but also informs decisions regarding maintenance and upgrades.
As we delve into the specific configurations and connections within these systems, we uncover a wealth of information that can demystify the operation of heating solutions. Armed with this understanding, users can ensure their environments remain warm and inviting all season long.
Understanding Furnace Components
Grasping the essential elements of heating systems is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring optimal performance and safety. This section will explore the key features and functionalities that contribute to the overall efficiency of these systems.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Blower Motor | Responsible for circulating air throughout the space, ensuring consistent temperature distribution. |
| Heat Exchanger | Transfers heat from the combustion process to the air, allowing for efficient warming of the living area. |
| Thermostat | Controls the system’s operation based on the desired temperature set by the user, acting as a communication hub. |
| Ignitor | Initiates the combustion process by igniting the fuel, ensuring a steady and safe operation. |
| Flue Pipe | Ventilates exhaust gases outside, maintaining air quality and system safety. |
Understanding these components can empower homeowners to identify potential issues and take proactive measures to maintain their heating systems effectively.
Common Parts of Suburban Furnaces
Understanding the key components of heating systems is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. These elements work together to ensure efficient operation and comfort within residential spaces. Below are some of the frequently encountered elements in such systems.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Blower | Responsible for circulating air throughout the living area. |
| Heat Exchanger | Transfers heat from the combustion process to the air being heated. |
| Thermostat | Controls the temperature by signaling the system to activate or deactivate. |
| Ignitor | Initiates the combustion process, often using electric or hot surface technology. |
| Flue | Exhausts gases produced during the heating process safely outside. |
Importance of a Parts Diagram
Understanding the layout of components within a heating system is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. A visual representation allows users to easily identify each element, ensuring efficient repairs and optimal performance.
Enhanced Clarity
A clear illustration provides several advantages:
- Facilitates quick identification of components
- Reduces confusion during repairs
- Improves communication with technicians
Streamlined Maintenance
Regular upkeep is vital for longevity:
- Identifying wear and tear becomes straightforward.
- Planning replacements is more efficient.
- Helps in tracking system upgrades.
Identifying Key Furnace Elements
Understanding the essential components of a heating system is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. Familiarity with these elements allows homeowners to recognize issues early and ensure optimal performance during colder months. In this section, we will explore the primary features that contribute to the efficient operation of such systems.
Main Components Overview
At the core of any heating apparatus are several integral components, each serving a unique function. The burner ignites the fuel, while the heat exchanger transfers warmth to the air circulating through the dwelling. Additionally, the blower motor plays a vital role in distributing heated air effectively throughout the living space.
Control Mechanisms
Modern systems also incorporate sophisticated control mechanisms. The thermostat regulates temperature settings, providing comfort and energy efficiency. Meanwhile, safety switches are designed to prevent malfunctions, ensuring that the system operates safely and reliably.
How to Read a Diagram
Understanding a schematic representation is essential for effective troubleshooting and maintenance. By familiarizing yourself with the layout and symbols, you can quickly identify components and their relationships. This knowledge streamlines repairs and enhances your overall comprehension of the system.
Key Components
Each element in the representation serves a unique purpose. Pay attention to symbols, as they denote various functions and types of equipment. Familiarity with these will enable you to navigate the layout with confidence.
Interconnections
Look for lines that connect the symbols; these represent pathways or interactions between components. Recognizing these connections is crucial for understanding how the system operates as a whole, allowing you to pinpoint issues effectively.
Typical Issues with Furnace Parts
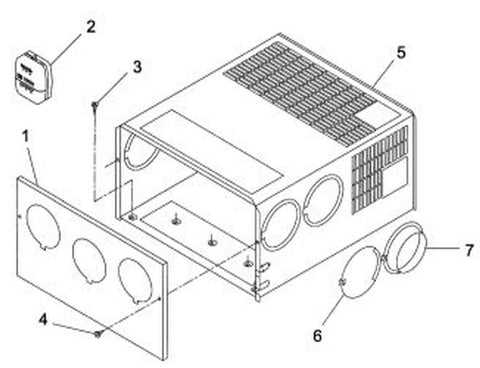
Understanding common challenges related to heating systems is essential for maintaining efficiency and safety. Various components can malfunction due to wear and tear, leading to inefficiencies or complete breakdowns. Recognizing these issues can help homeowners take timely action.
Common Problems
- Inadequate heating: Insufficient warmth may indicate issues with the heat exchanger or blower.
- Noisy operation: Unusual sounds often stem from loose elements or worn-out motors.
- Frequent cycling: Excessive on-and-off activity may suggest a faulty thermostat or clogged filters.
Signs of Malfunction
- Unusual odors: Burning smells or gas leaks should be addressed immediately.
- Increased energy bills: Higher costs can indicate reduced efficiency due to failing components.
- Error codes: Many systems display codes that can guide troubleshooting efforts.
Maintenance Tips for Long Life

Ensuring the longevity of your heating system requires regular attention and care. By following a few simple guidelines, you can enhance performance, reduce the risk of breakdowns, and extend the lifespan of your equipment. Consistent maintenance not only saves money in the long run but also contributes to a safer and more comfortable environment.
Regular Inspections
Conducting routine evaluations is crucial. Look for any signs of wear or damage that could indicate underlying issues. It’s advisable to schedule professional check-ups at least once a year to ensure everything operates efficiently. Timely detection of potential problems can prevent costly repairs and extend the overall functionality of your system.
Keep Components Clean
Accumulated dirt and debris can hinder performance and lead to inefficiencies. Regularly clean filters and other accessible components. Replacing filters at recommended intervals is essential for maintaining optimal airflow and improving indoor air quality. A clean system works more efficiently, consuming less energy and reducing your utility bills.
Safety Precautions When Servicing
Ensuring safety during maintenance tasks is essential to prevent accidents and injuries. Proper preparation and adherence to guidelines can significantly reduce risks associated with handling complex machinery. This section outlines crucial precautions to follow before, during, and after service activities.
Before Starting Work
- Disconnect power sources to avoid electric shock.
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves and safety goggles.
- Read the manufacturer’s instructions and safety warnings thoroughly.
- Ensure the work area is well-ventilated to avoid exposure to harmful fumes.
During Maintenance
- Keep tools organized and within reach to prevent unnecessary movement.
- Handle all components carefully to avoid damage and ensure safe operation.
- Be cautious of hot surfaces and allow adequate cooling time before touching any part.
- Stay focused and avoid distractions to maintain attention on the task at hand.
Following these precautions not only safeguards personal well-being but also ensures effective servicing, contributing to the longevity and reliability of the equipment.
Upgrading Your Furnace Components
Enhancing the efficiency and performance of your heating system can lead to improved comfort and reduced energy costs. This section will explore various components that can be upgraded to achieve better functionality and longevity. By investing in modern alternatives, you can ensure your system operates optimally and meets your heating needs more effectively.
- Blower Motor: Replacing an outdated blower motor with a variable-speed model can significantly improve air circulation and energy efficiency.
- Thermostat: Upgrading to a smart thermostat allows for greater control over your system, offering programmable settings and remote access for convenience.
- Heat Exchanger: A new heat exchanger can enhance heat transfer efficiency and ensure the safety of your system by preventing leaks.
- Filters: Investing in high-quality air filters will improve indoor air quality and reduce strain on your system.
- Ignition System: Transitioning to an electronic ignition can provide more reliable starts compared to older pilot light systems.
Consider consulting with a professional to assess which components would provide the most benefit based on your specific situation. Prioritizing these upgrades can lead to a more reliable and efficient heating system.
Resources for Finding Diagrams
When it comes to locating detailed schematics for heating systems, there are various avenues to explore. Whether you are seeking technical illustrations for repairs or upgrades, leveraging a mix of online and offline resources can greatly enhance your search. These resources can provide clarity and facilitate troubleshooting, ensuring that you have the necessary information at your fingertips.
Online Platforms
The internet is a treasure trove of information. Websites dedicated to home improvement often feature user-generated content, including diagrams and step-by-step guides. Specialized forums and social media groups can also serve as valuable communities where enthusiasts share their insights and resources. Additionally, manufacturers’ official websites frequently provide technical documentation, including comprehensive schematics for their products.
Print Resources
Books and manuals remain reliable sources for in-depth information. Local libraries and bookstores often have sections dedicated to home maintenance and repair. These publications typically include detailed illustrations that can aid in understanding complex systems. Furthermore, trade magazines may feature articles with relevant diagrams and tips, making them a useful addition to your resource collection.
Understanding Heating Efficiency Ratings
Heating efficiency ratings provide a crucial insight into how effectively a heating system converts energy into warmth. These ratings are essential for consumers looking to maximize comfort while minimizing energy costs. Understanding these metrics can help homeowners make informed decisions about their heating solutions.
There are several key efficiency ratings to consider when evaluating heating systems. Each rating serves a unique purpose and can influence both performance and operational costs.
| Rating | Description |
|---|---|
| AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency) | This percentage indicates how much fuel is converted into heat over the course of a year. A higher AFUE rating signifies greater efficiency. |
| HSPF (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor) | This rating measures the efficiency of heat pumps during the heating season. Higher HSPF values indicate better performance. |
| SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) | Primarily used for cooling systems, this ratio can also reflect heating efficiency in heat pump systems. A higher SEER means increased efficiency. |
| BTU (British Thermal Unit) | This measurement indicates the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit. It helps assess the capacity of heating units. |
By familiarizing yourself with these efficiency ratings, you can better assess your options and choose a heating system that meets your needs while being cost-effective and environmentally friendly.
Professional Help vs. DIY Repairs
When it comes to maintaining and fixing heating systems, homeowners often face the decision between seeking expert assistance and tackling the job themselves. Each approach has its own merits and drawbacks, and understanding these can help individuals make informed choices that suit their circumstances and skills.
Benefits of Professional Assistance
Engaging a trained technician offers several advantages. Professionals possess extensive knowledge and experience, allowing them to identify issues quickly and accurately. Moreover, they have access to specialized tools and parts, which can enhance the efficiency and safety of the repair process. Often, warranties and guarantees are provided, giving homeowners peace of mind.
Advantages of DIY Repairs
On the other hand, handling repairs independently can be rewarding and cost-effective. DIY enthusiasts can save money on labor costs and gain valuable skills in the process. Many find that taking on such projects fosters a deeper understanding of their systems, potentially preventing future issues. However, it is essential to recognize one’s limitations, as improper repairs can lead to more significant problems down the line.
| Criteria | Professional Help | DIY Repairs |
|---|---|---|
| Expertise | High | Varies |
| Cost | Higher (labor fees) | Lower (materials only) |
| Time | Usually quicker | Can be time-consuming |
| Safety | Ensured | Risky if untrained |