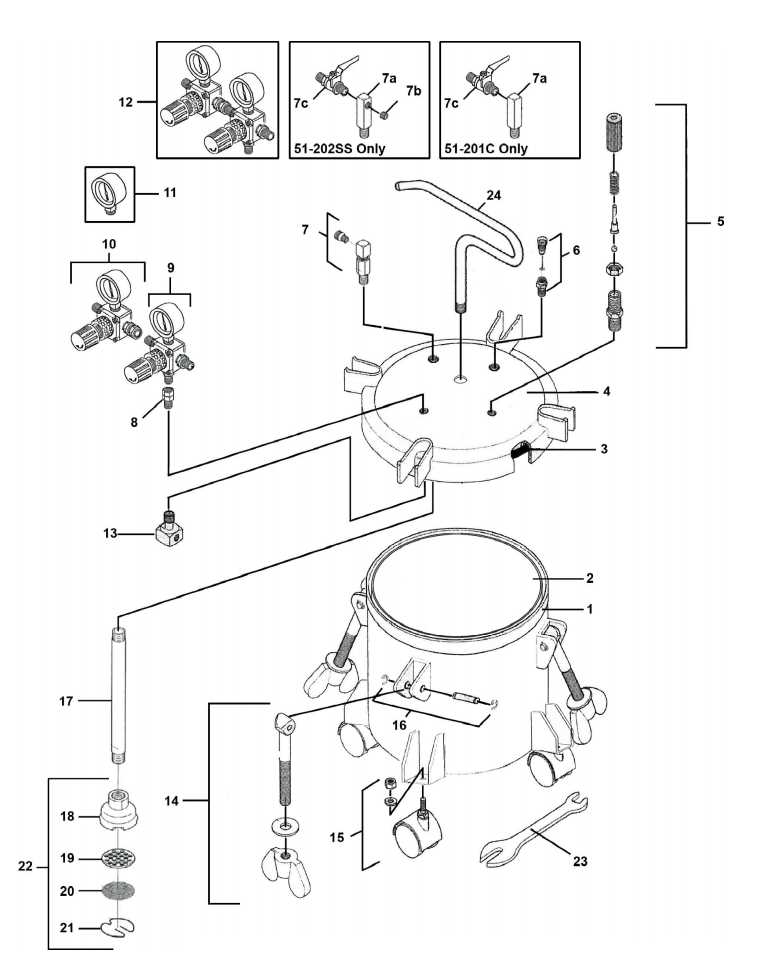
In the realm of machinery, comprehending the intricacies of various elements is crucial for optimal functionality. This section delves into the essential components that contribute to the effective operation of heavy-duty vehicles, highlighting their interconnectivity and roles within the overall system.
By exploring the configurations and functionalities of these essential components, one can gain valuable insights into maintenance and troubleshooting practices. A thorough understanding of how these elements interact fosters a deeper appreciation for the engineering behind robust vehicles and enhances their longevity.
Moreover, this knowledge empowers operators and technicians to identify potential issues swiftly, ensuring that machinery remains in peak condition. Familiarity with these critical elements ultimately leads to improved performance and efficiency in various operational settings.
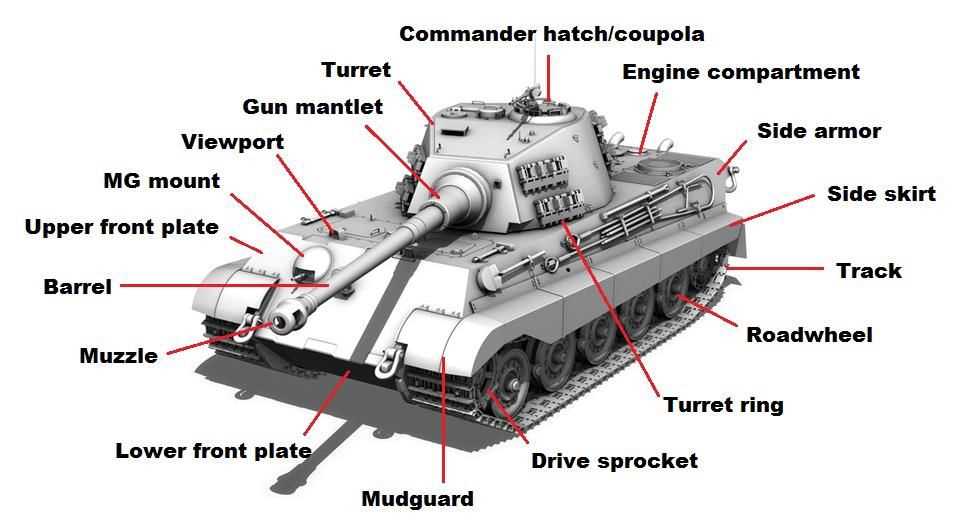
This section provides an overview of the weaponry and munitions utilized in armored vehicles, emphasizing their significance in enhancing combat effectiveness. Understanding the specifications and functionalities of these components is essential for optimizing performance and operational capabilities.
Weaponry Overview
Armored vehicles are equipped with various types of weapon systems, each designed to address specific combat scenarios. These systems can include cannons, machine guns, and missile launchers, contributing to both offensive and defensive strategies.
Ammunition Specifications
The munitions used in armored vehicles vary in type and caliber, influencing their effectiveness against different targets. Proper selection and understanding of these munitions are crucial for maximizing impact in engagements.
| Type of Weapon | Caliber | Ammunition Type | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main Gun | 120 mm | Armor-Piercing Fin-Stabilized Discarding Sabot (APFSDS) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Coaxial Machine Gun | 7.62 mm
Hydraulic Systems in Tank Operation
Hydraulic systems play a crucial role in the functionality and performance of armored vehicles. These systems utilize pressurized fluid to transmit force, enabling various movements and operations that are essential for effective maneuvering and combat capabilities. Efficiency and precision are key attributes of hydraulic mechanisms, allowing for smooth control of critical functions such as turret rotation, gun elevation, and suspension adjustments. The integration of hydraulic power enhances overall operational effectiveness, providing the necessary strength and agility to navigate challenging terrains and execute complex tasks. Furthermore, the design and maintenance of these fluid-based systems are vital for ensuring reliability during missions. Regular inspections and timely servicing can prevent potential failures, thereby ensuring that the vehicle operates at peak performance when it matters most. Importance of Tank Chassis LayoutThe arrangement of the framework in armored vehicles plays a crucial role in their overall performance and functionality. A well-designed structure not only enhances mobility and stability but also contributes significantly to the vehicle’s ability to withstand various battlefield conditions. Effective layout ensures optimal weight distribution, which is essential for maintaining balance and agility during maneuvers. This structural configuration also facilitates the integration of essential systems, such as propulsion and suspension, leading to improved operational efficiency. Moreover, a thoughtfully crafted framework can enhance crew safety and accessibility, allowing for quick repairs and maintenance in critical situations. Electrical Systems in Modern TanksThe electrical framework in contemporary armored vehicles plays a crucial role in their overall functionality and efficiency. This intricate network is responsible for powering various essential systems, enhancing communication, navigation, and combat capabilities. By integrating advanced technologies, these vehicles can perform complex tasks while ensuring crew safety and operational effectiveness. Components of the Electrical FrameworkThe electrical architecture comprises several key elements that work synergistically to support the vehicle’s operations. These components include power distribution systems, control units, sensors, and communication devices, all designed to enhance the performance and reliability of the armored vehicle.
Importance of Advanced Technologies
Modern advancements in electrical systems significantly improve the operational capabilities of armored vehicles. The incorporation of digital technologies, such as automated controls and sophisticated diagnostic tools, enhances the efficiency and responsiveness of these machines. Consequently, this leads to improved strategic advantages in various operational scenarios. Cooling Systems and Their Role
Effective thermal management is crucial for the longevity and performance of machinery. The cooling systems are designed to maintain optimal operating temperatures, preventing overheating and ensuring efficient functioning. These systems play a vital role in the overall health of mechanical equipment, contributing to its reliability and efficiency. Understanding the Components Cooling systems typically consist of various elements, including radiators, pumps, and hoses. Each component works in harmony to facilitate the transfer of heat away from the engine or core system. This process is essential for sustaining peak operational efficiency and prolonging the lifespan of the machinery. The Importance of Maintenance Regular maintenance of cooling systems is necessary to prevent issues such as coolant leaks or blockages. Neglecting these systems can lead to severe overheating, resulting in potential damage to critical components. Therefore, timely inspections and replacements of any worn or faulty parts are essential for optimal performance. Combat Features and Defense MechanismsThis section explores the essential capabilities and protective systems designed to enhance operational effectiveness and ensure crew safety in challenging environments. Understanding these attributes is crucial for evaluating overall performance and resilience during engagements. Key Combat FeaturesVarious advanced technologies contribute to the combat efficiency of modern vehicles. These include enhanced targeting systems, superior mobility, and the integration of automated systems, which collectively facilitate strategic advantage in diverse scenarios. Defensive SystemsProtection mechanisms are paramount in safeguarding personnel and critical components from enemy threats. Innovations in armor composition, active defense systems, and electronic countermeasures work in conjunction to mitigate risks and enhance survivability on the battlefield.
Maintenance of Tank Parts DiagramRegular upkeep of armored vehicle components is essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Proper care can prevent unexpected failures and enhance operational efficiency. This section outlines crucial practices for maintaining these critical systems, emphasizing systematic approaches and thorough inspections. Essential Maintenance Practices
Inspection and DocumentationRegular inspections play a vital role in the upkeep of these systems. Documenting findings helps track changes over time and informs future maintenance strategies. Consider the following steps:
|