
When exploring the mechanical structure of a youth all-terrain vehicle, it’s essential to gain a clear understanding of how its various elements come together to ensure optimal performance and safety. Each mechanical unit plays a role in ensuring smooth operation, durability, and ease of maintenance. Familiarity with the layout helps users maintain their vehicle effectively, ensuring it remains in top condition over time.
The breakdown of individual systems, such as the engine, suspension, and transmission, reveals the complexity of these off-road machines. Recognizing the interconnections between these systems can significantly aid in diagnosing potential issues and performing routine checks. Having a detailed overview can also be beneficial when it comes to replacing specific mechanical elements.
By understanding the structure and how different elements fit together, users can improve their overall knowledge of youth ATVs. This not only enhances their ability to care for the vehicle but also promotes a deeper appreciation of the engineering behind these machines.
Essential Components of the Polaris Outlaw 50
Understanding the key elements of a youth ATV is crucial for maintaining performance and safety. The main structure is composed of various interconnected elements, each playing an important role in the vehicle’s operation. By identifying these critical components, riders can ensure smooth functionality and address potential issues early on.
Engine and Transmission
- The motor powers the vehicle, providing the necessary force for movement.
- The transmission system allows for smooth shifting and control of speed.
Suspension and Braking
- The suspension absorbs shocks, making for a comfortable ride on uneven terrain.
- Cylinder: The core part of the engine where the combustion process takes place, transforming fuel into power.
- Piston: Moves within the cylinder, compressing air and fuel, allowing combustion to occur.
- Crankshaft: Converts the up-and-down motion of the piston into rotational movement, driving the vehicle forward.
- Camshaft: Controls the opening and closing of the valves, timing the intake and exhaust strokes precisely.
- Valves: Regulate the flow of air and fuel into the
Examining the Suspension System
The suspension system plays a crucial role in enhancing the vehicle’s stability and overall performance. By absorbing shocks from uneven surfaces and maintaining wheel contact with the ground, it ensures a smoother ride and greater control. Understanding how different components interact within the suspension is key to ensuring both rider comfort and vehicle safety.
Component Function Shock Absorbers Reduce impact from rough terrain Springs Provide support and manage weight distribution Control Arms Connect the wheels to the frame, allowing controlled movement Braking Mechanism Overview
The braking system is a crucial component ensuring the safety and control of the vehicle during operation. It is responsible for managing the speed and bringing the vehicle to a complete stop when needed. Understanding the key elements and how they work together helps in maintaining optimal performance and ensuring safe usage over time.
Main Components of the Braking System
The braking system consists of several interconnected parts that work in unison to reduce the speed effectively. These include the brake lever, pads, and discs. Each element has a specific role that contributes to the overall functioning of the system, ensuring consistent and reliable stopping power.
How the Mechanism Functions
When the operator applies pressure to the brake lever, a hydraulic or mechanical action is triggered, causing the brake pads to press against the discs. This friction generates the necessary force to slow down or stop the vehicle. The system is designed for quick responsiveness and to withstand repeated use without significant wear.
Component Function Brake Lever Initiates the braking process when pressed by the operator. Wheels and Tires: Key Features The wheels and tires play a significant role in ensuring stability, traction, and performance in off-road vehicles. These components are designed to withstand various terrains, offering durability and control under challenging conditions. Understanding their core features helps in maintaining optimal functionality.
Tire Composition and Durability
Off-road tires are crafted from specialized materials that provide resistance to punctures, cuts, and wear. Their construction ensures that they can handle rough surfaces without compromising performance. The tread patterns are designed to offer maximum grip, enhancing both maneuverability and control on uneven terrains.
Wheel Structure and Compatibility
The wheel structure is equally important in supporting the vehicle’s weight and ensuring smooth rotation. The rims are designed to be lightweight yet strong enough to handle impacts. Compatibility with the tire size is essential to maintain balance and prevent any unnecessary strain on the suspension system.
Handlebars and Control Layout
The handlebars and control arrangement play a crucial role in the overall functionality and maneuverability of a compact all-terrain vehicle. This section delves into the various components and their placements, ensuring optimal control for the rider.
Key elements found in the control layout include:
- Handlebar Grips: Designed for comfort and a firm hold, enhancing the riding experience.
- Throttle Control: Typically located on the right side, it allows the operator to adjust speed easily.
- Brake Lever: Positioned on the left side, essential for managing speed and stopping safely.
- Headlight Switch: Often integrated within reach, it provides quick access to lighting controls.
- Ignition Switch: Located for easy access, ensuring the vehicle can be started and stopped with minimal hassle.
Understanding the arrangement and functionality of these components enhances the overall riding experience, providing both safety and convenience on various terrains.
Fuel System Parts and Functions
The fuel system is crucial for the efficient operation of any motorized vehicle. It ensures that the engine receives the appropriate amount of fuel necessary for combustion, enabling optimal performance. Understanding the various components of this system and their specific roles can help in maintaining and troubleshooting any issues that may arise.
Key Components
At the heart of the fuel system is the fuel tank, which stores the gasoline or alternative fuel. Attached to the tank is the fuel pump, responsible for moving the fuel to the engine. The fuel filter plays a vital role in maintaining the cleanliness of the fuel by removing contaminants before they reach the engine.
Fuel Delivery Mechanism
The fuel is then delivered through a series of fuel lines that connect the tank to the engine. The carburetor or fuel injector mixes the fuel with air to create an optimal air-fuel ratio for combustion. Each component works in harmony to ensure the engine operates smoothly and efficiently.
Electrical Components and Wiring
Understanding the electrical system is essential for maintaining and optimizing performance. The electrical components play a critical role in ensuring the efficient operation of various functions. This section will explore the key elements involved in the wiring and electrical systems.
- Battery: The power source that supplies energy to all electrical components.
- Wiring Harness: A network of wires that connects different electrical parts, facilitating communication and power distribution.
- Fuse Box: A protective unit that houses fuses, safeguarding the electrical system from overloads and short circuits.
- Ignition System: The setup responsible for starting the engine, which includes spark plugs and ignition coils.
- Lights and Indicators: Components that provide visibility and convey information to the rider regarding the vehicle’s status.
- Control Switches: Devices that allow the rider to operate various functions such as lights, horn, and starting the engine.
Proper maintenance and troubleshooting of these components are vital to ensure reliability and safety. Regular checks can prevent unexpected failures and enhance the overall riding experience.
Transmission System Breakdown
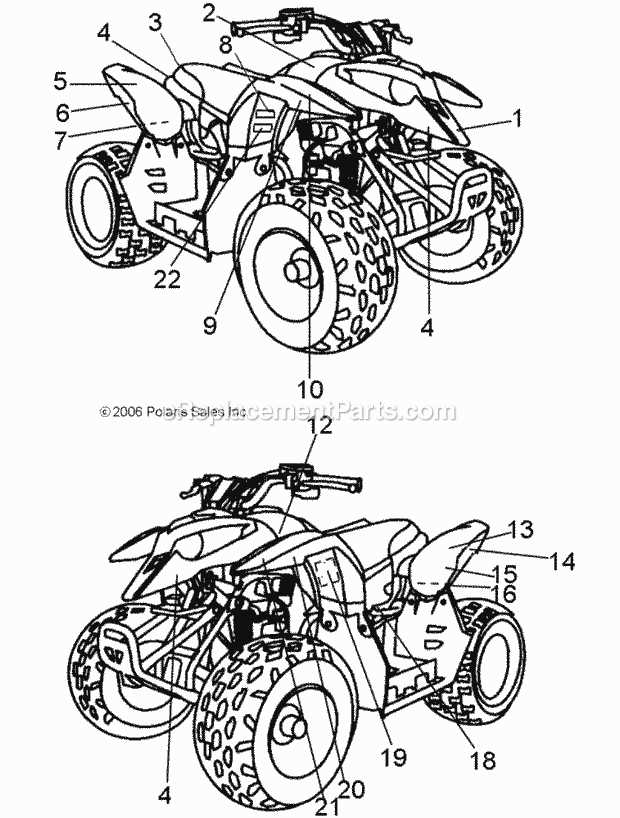
The transmission system is a crucial component in any vehicle, facilitating the transfer of power from the engine to the wheels. Understanding its various elements and their functions is essential for optimal performance and maintenance.
This section will delve into the key components of the transmission system, providing insights into their roles and interconnections:
- Transmission Housing – Encloses and protects the internal mechanisms while providing structural support.
- Gear Set – Comprises various gears that alter torque and speed, allowing the vehicle to adapt to different driving conditions.
- Clutch Assembly – Engages and disengages the engine from the transmission, facilitating smooth gear shifts.
- Output Shaft – Transfers the power generated by the engine to the wheels, playing a vital role in propulsion.
- Fluid System – Utilizes hydraulic fluid to operate various components, ensuring effective gear changes and cooling.
Regular maintenance of the transmission system is vital for ensuring longevity and efficiency. This includes fluid checks, gear inspections, and timely repairs. Understanding these components will help in diagnosing issues and making informed decisions about maintenance and upgrades.
Exhaust System Design
The design of an exhaust system plays a crucial role in enhancing the performance and efficiency of any vehicle. It ensures the effective expulsion of combustion gases, minimizes noise, and contributes to overall engine functionality. A well-engineered exhaust system can significantly impact the driving experience and longevity of the machine.
Key components of a typical exhaust system include:
- Muffler: This element reduces noise produced by the engine while allowing exhaust gases to exit smoothly.
- Headers: Headers connect the engine’s cylinders to the exhaust system, improving gas flow and performance.
- Exhaust Pipes: These pipes transport gases from the engine to the rear of the vehicle, typically designed to minimize restrictions.
- Catalytic Converter: This component converts harmful emissions into less harmful substances before they exit the system.
When designing an exhaust system, various factors must be considered:
- Material selection for durability and weight efficiency.
- Pipe diameter for optimal gas flow and performance.
- Layout to avoid unnecessary bends, which can restrict exhaust flow.
- Integration of emissions control devices to meet environmental regulations.
In conclusion, a thoughtfully designed exhaust system is essential for maximizing engine performance and ensuring compliance with emission standards. It plays a pivotal role in the overall functionality and efficiency of the vehicle.
Frame and Structural Elements
The framework and supporting components of a vehicle play a crucial role in its overall functionality and stability. These elements not only provide structural integrity but also contribute to the design and handling characteristics. Understanding the various components that form the backbone of an all-terrain vehicle is essential for maintenance and repair.
Main Framework
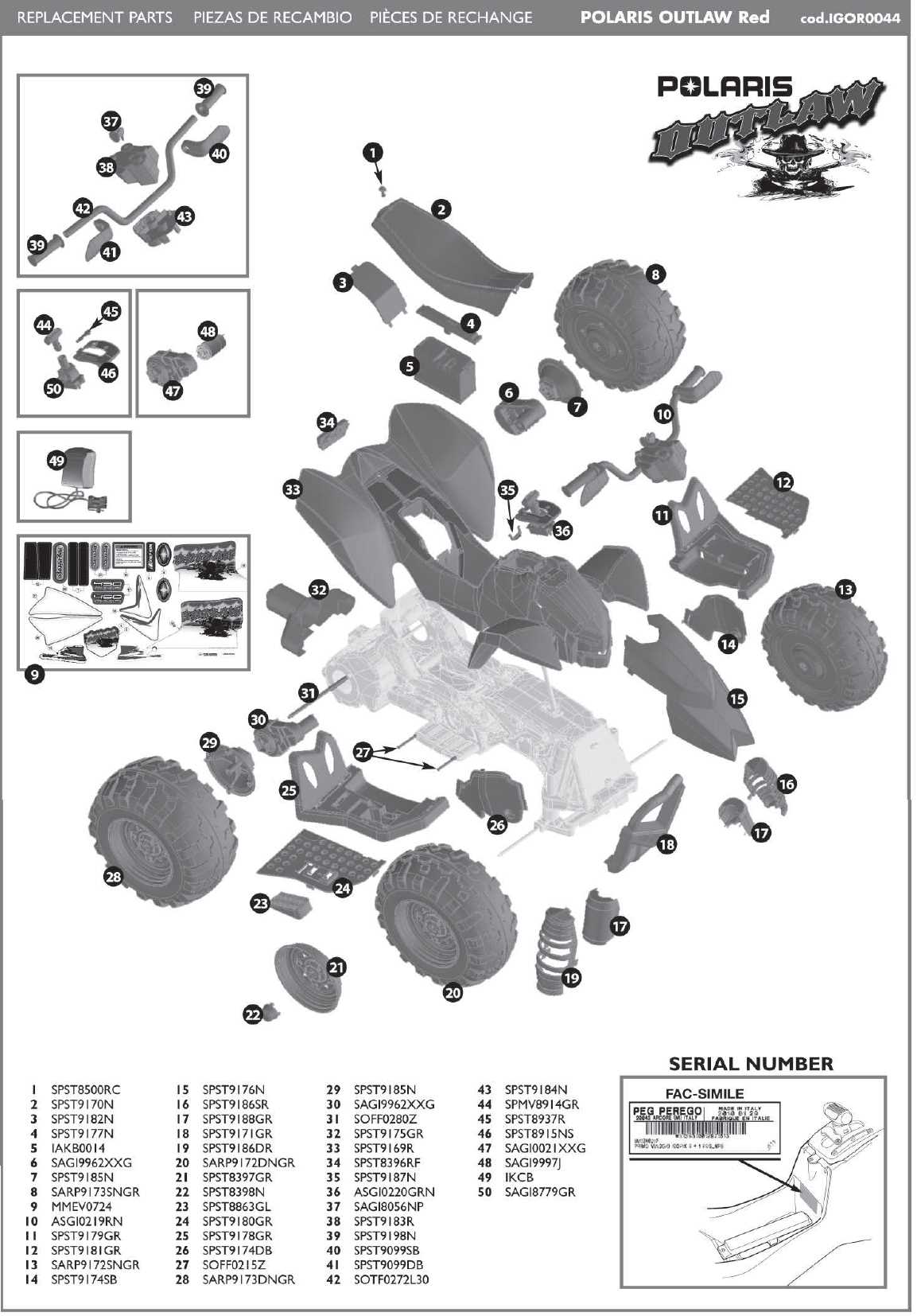
The primary structure consists of several key elements that work together to support the entire assembly. Key aspects include:
- Chassis: The main supporting structure that houses various systems.
- Subframe: Additional framework that supports specific components such as the engine or suspension.
- Mounting Points: Locations designed to secure other parts, ensuring everything is held in place.
Reinforcement and Support
To enhance durability and performance, various reinforcement elements are integrated into the design. These components include:
- Cross Members: Structural pieces that provide additional support across the chassis.
- Brackets: Specialized supports that attach different systems to the main framework.
- Suspension Links: Components that connect the suspension system to the main structure, allowing for flexibility and movement.
Understanding the Engine Assembly
The engine assembly is the heart of any vehicle, consisting of multiple interconnected components that work together to convert fuel into mechanical energy. Understanding how these elements interact is essential for maintaining and improving performance.