
Understanding the intricate elements of fuel dispensing systems is essential for efficient operation and maintenance. Each component plays a crucial role in the overall functionality, contributing to the seamless transfer of liquid from storage to vehicle.
In this section, we will explore the various elements that constitute these systems. By familiarizing oneself with these components, operators can ensure optimal performance and address any issues that may arise during use.
Detailed knowledge of these individual elements aids in troubleshooting and repairs, leading to enhanced reliability and safety. Whether for professional use or personal knowledge, grasping the intricacies of these systems is invaluable.
This section aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the essential components that constitute the mechanism responsible for fuel delivery. Understanding the internal organization and functionality of these elements is crucial for efficient maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key components of this assembly include:
- Energy source
- Fluid management system
- Control interface
- Safety features
By examining each of these critical components, one can gain insight into how they work together to facilitate the process of fuel distribution, ensuring reliability and safety during operation.
Main Components of Gas Pumps
Understanding the essential elements of fuel dispensing systems is crucial for both functionality and maintenance. These systems comprise various key components that work in unison to ensure efficient operation and accurate delivery of fuel.
Dispensing Unit: This is the main interface where users interact to select fuel types and initiate the fueling process. It often features a digital display for transaction details.
Hoses: Flexible tubes that transfer fuel from the storage tanks to the dispensing unit. They are designed to withstand pressure and prevent leaks.
Flow Meter: A critical device that measures the amount of fuel dispensed. It ensures accurate billing and maintains system integrity by providing real-time data on fuel flow.
Storage Tanks: Underground containers that hold the fuel until it is needed. These tanks are equipped with safety features to prevent leaks and spills.
Control System: This electronic component manages the operation of the entire fueling system, coordinating tasks such as monitoring fuel levels and controlling the dispensing process.
Filtration System: A vital component that removes impurities from the fuel before it reaches the dispensing unit, ensuring that the fuel delivered is clean and of high quality.
Functionality of Each Pump Part
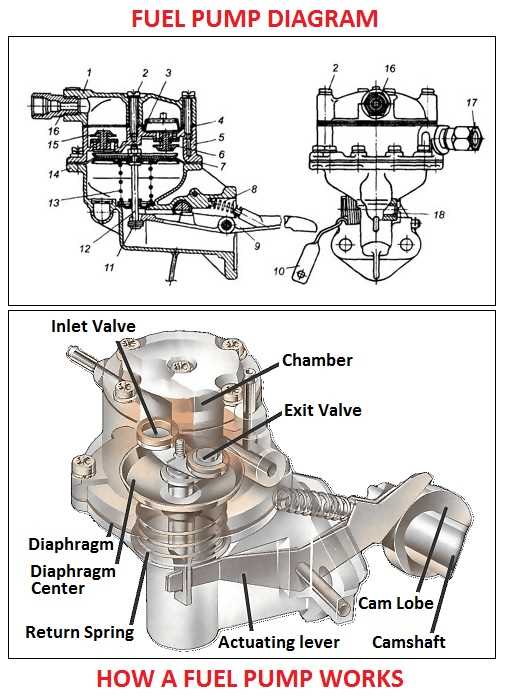
This section delves into the roles and responsibilities of various components within a fuel delivery system. Understanding how each element operates is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key Components and Their Roles
- Motor: Provides the necessary energy to drive the entire assembly, ensuring efficient operation.
- Controller: Regulates the flow and pressure, allowing for precise dispensing of the liquid.
- Hoses: Facilitate the transfer of fuel from the storage tank to the delivery nozzle.
- Nozzle: Ensures controlled release of the liquid, equipped with safety mechanisms to prevent spillage.
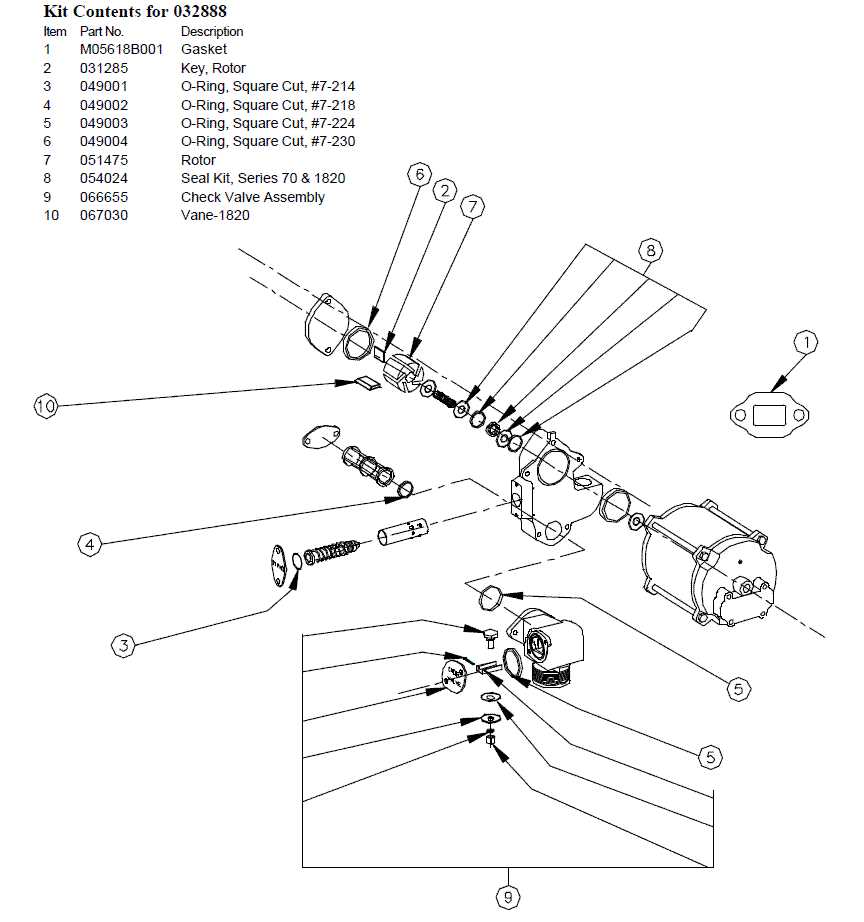
Supporting Elements
- Filters: Remove impurities from the liquid to protect other components from damage.
- Valves: Control the direction and flow rate, ensuring the system operates smoothly.
- Sensors: Monitor performance metrics, providing real-time data for better management.
- Chassis: Provides structural integrity, housing all components securely for optimal operation.
Identifying Common Gas Pump Issues
Understanding frequent complications that arise in fuel dispensing systems is crucial for maintaining their efficiency and reliability. Identifying these problems early can prevent operational disruptions and ensure a smooth refueling experience.
| Issue | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| Low Flow Rate | Insufficient fuel dispensing speed, affecting user experience. | Clogged filters, malfunctioning valves, or improper calibration. |
| Leaks | Unwanted fuel escape, leading to safety hazards. | Worn seals, loose fittings, or damaged hoses. |
| Erratic Readings | Inconsistent volume measurements during fueling. | Faulty sensors, electrical issues, or software glitches. |
| Noise | Unusual sounds during operation, indicating potential issues. | Worn components, loose connections, or lack of lubrication. |
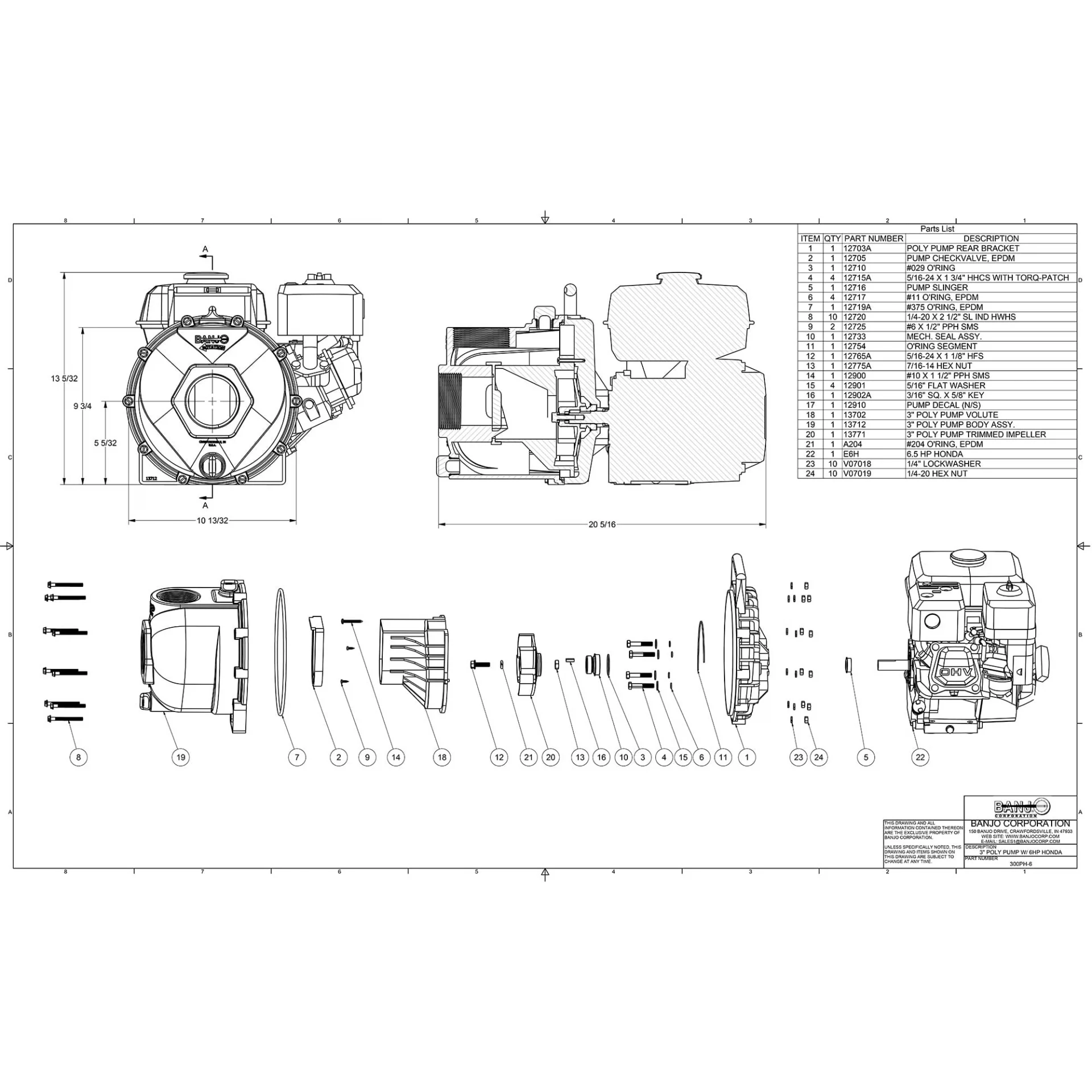
How to Read a Parts Diagram
Understanding a schematic representation of components is essential for effective maintenance and repair. This guide provides insights into interpreting such illustrations, allowing users to identify each element and its function.
Start by familiarizing yourself with the overall layout. Each section typically represents a specific area, often labeled for clarity. Look for reference numbers or letters that correspond to accompanying descriptions or lists, which explain the role of each item.
Pay attention to the connections between components. Lines and arrows usually indicate how parts interact with one another, illustrating the flow of operation. Recognizing these relationships is crucial for troubleshooting and ensuring proper assembly.
Lastly, consult the manufacturer’s documentation for additional details. Often, schematics will include notes or legends that provide further context, enhancing your comprehension of the entire system.
Maintenance Tips for Gas Pumps
Regular upkeep of fueling systems is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Implementing effective maintenance strategies ensures that these systems operate smoothly and reduces the risk of unexpected breakdowns.
Routine Inspections: Conduct frequent evaluations to identify wear and tear. Check for leaks, corrosion, and any signs of malfunctioning components.
Cleaning Procedures: Maintain cleanliness by regularly removing debris and contaminants. This prevents blockages and enhances overall efficiency.
Fluid Levels: Monitor and replenish fluids as necessary to ensure proper functioning. Maintaining appropriate levels helps in minimizing friction and overheating.
Training Personnel: Ensure that operators are well-trained in handling and maintaining the systems. Knowledgeable staff can quickly address minor issues before they escalate.
Scheduled Maintenance: Establish a maintenance schedule that includes thorough checks and necessary repairs. Adhering to this plan can greatly extend the life of the equipment.
Repairing Damaged Pump Components
Ensuring the functionality of essential equipment requires addressing any wear or harm that may occur over time. This section focuses on methods for restoring compromised elements, promoting longevity and optimal performance.
Before starting the repair process, consider the following steps:
- Assessment: Inspect the affected areas to determine the extent of damage and identify the specific components that require attention.
- Cleaning: Remove any debris, residue, or contaminants that could interfere with the repair process.
- Replacement: For severely damaged elements, replacement may be necessary. Ensure that new components are compatible with existing equipment.
- Sealing: Use appropriate sealants to ensure that all joints and connections are tight and leak-free.
- Testing: Once repairs are made, conduct thorough testing to ensure that the equipment operates as intended.
Regular maintenance and prompt repairs can significantly enhance the durability of crucial machinery, minimizing downtime and improving efficiency.
Upgrading Parts for Improved Performance
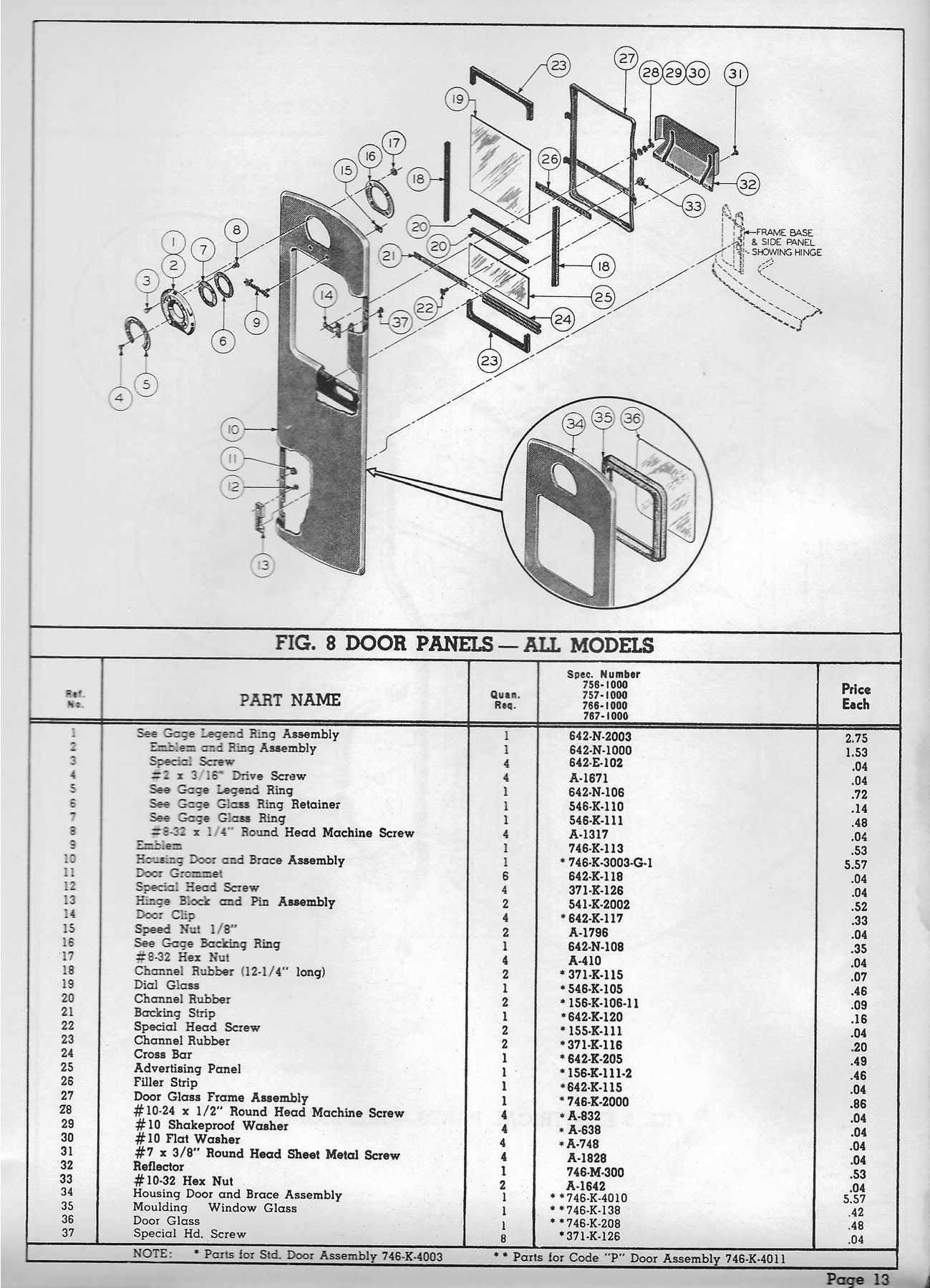
Enhancing the functionality of mechanical systems often involves replacing or improving key components. By selecting upgraded elements, it is possible to achieve smoother operation, increased durability, and better overall efficiency. This process can significantly extend the lifespan of the equipment and reduce the need for frequent repairs.
Advanced Materials: Using modern, high-quality materials in crucial areas can minimize wear and tear, leading to longer-lasting performance. Innovations in material science offer components that withstand harsher conditions and provide improved resistance to friction and corrosion.
Precision Engineering: Upgraded components designed with precision engineering principles ensure a more seamless interaction between moving parts. This reduces energy loss and maximizes operational output, resulting in a more reliable and powerful system.
Whether through material upgrades or refined design, these improvements contribute to a more efficient and cost-effective mechanical setup, ultimately delivering better results and performance in demanding environments.
Safety Precautions with Fuel Dispensers
When operating fuel dispensing systems, it is crucial to follow essential precautions to ensure personal safety and prevent potential hazards. By adhering to recommended practices, users can minimize risks associated with refueling processes and the handling of flammable substances.
Ensure Proper Grounding: Always verify that the vehicle and the dispenser are properly grounded to prevent static discharge, which can ignite fuel vapors. Use the grounding cable if provided.
Keep Flammable Objects Away: Avoid using electronic devices or open flames near the fueling station. Sparks from these sources can lead to dangerous situations.
Pay Attention to Warnings: Signage and audible alerts provided at the station should never be ignored. These serve as reminders of specific actions to avoid or follow during the refueling process.
Following these precautions contributes to maintaining a safe environment for all users.
Industry Standards for Gas Pump Parts
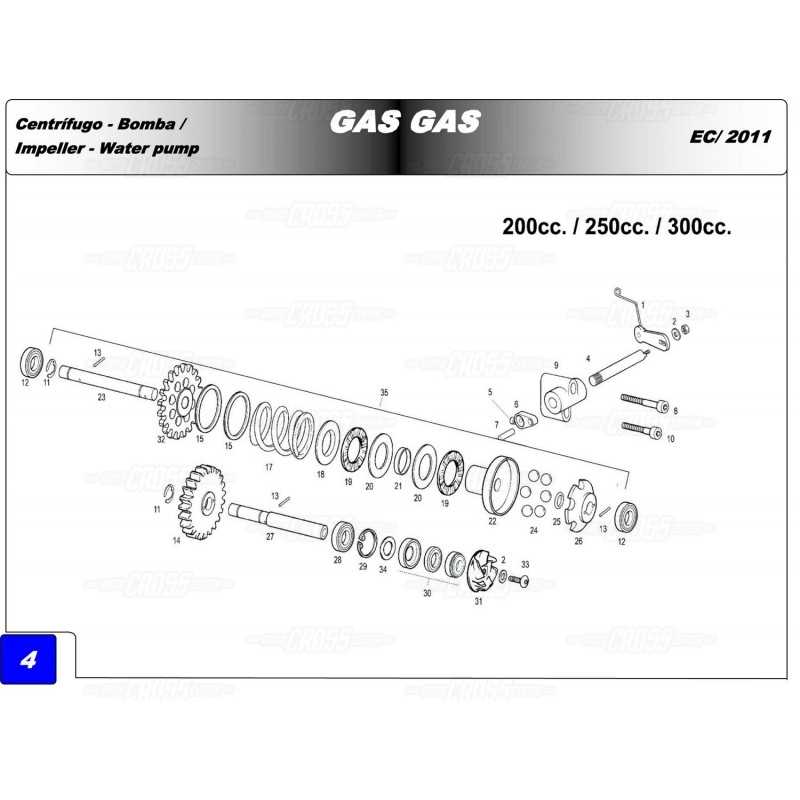
In the fluid dispensing industry, various regulations ensure the quality and safety of equipment components. These standards are developed to promote consistency, reliability, and efficiency across different models and manufacturers. Compliance with these rules is essential for maintaining operational effectiveness and meeting legal requirements.
Certification bodies play a crucial role in setting these guidelines, ensuring that every component meets rigorous testing criteria. Materials used in manufacturing must adhere to specific safety protocols to ensure durability under challenging conditions, including extreme temperatures and pressures.
Additionally, parts must conform to environmental and energy efficiency standards to reduce waste and minimize the environmental impact. Adopting best practices in component design and production helps maintain the safety and reliability of the entire system.
Resources for Further Learning
To expand your knowledge and gain a deeper understanding of various mechanical systems, there are numerous educational materials available. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced technician, these sources can provide valuable insights into the principles and components that make up complex equipment.
Online Courses and Tutorials
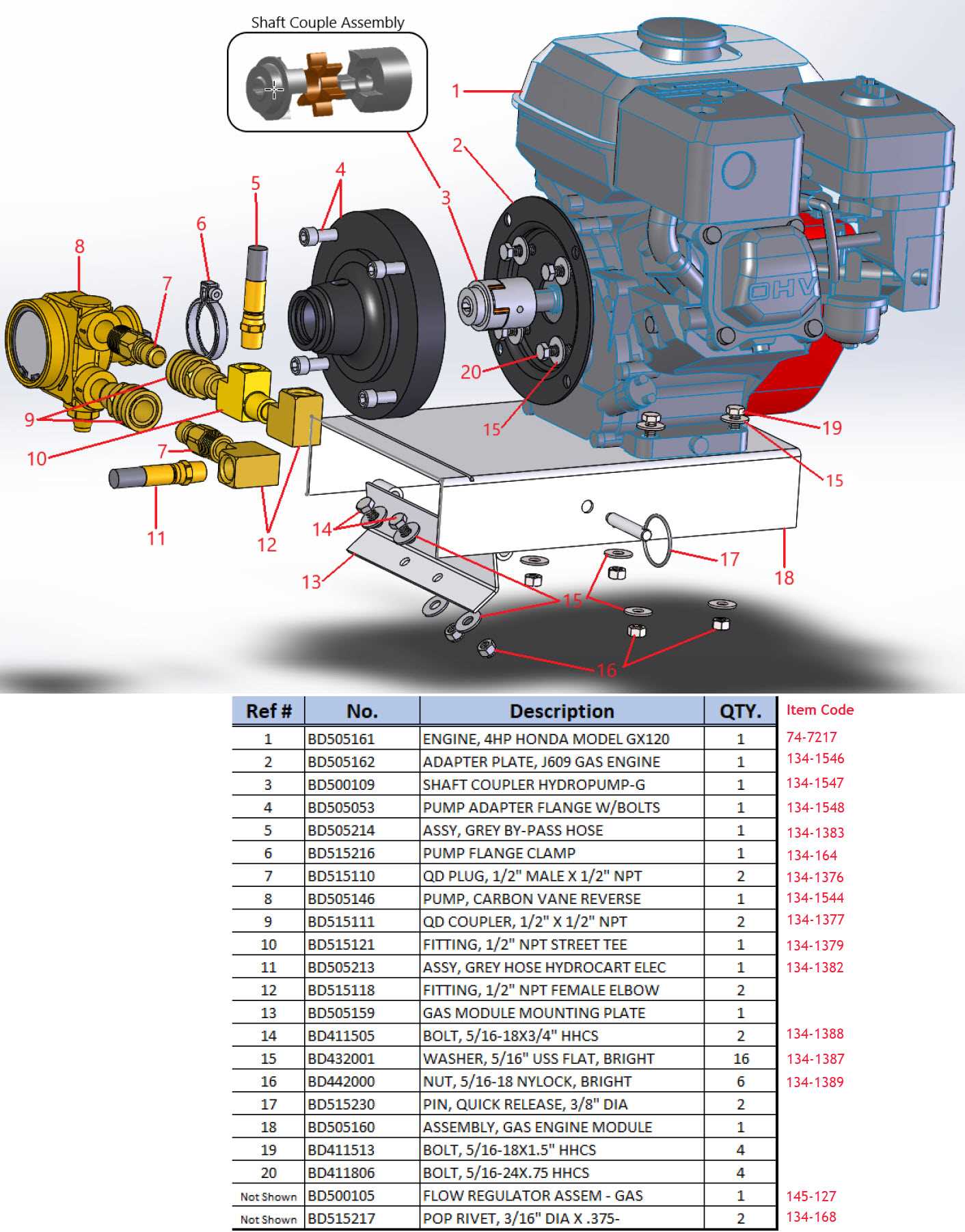
A wide range of online platforms offer courses and step-by-step tutorials. These can help you explore various aspects of machinery, from basic operations to advanced troubleshooting techniques. Many of these courses include visual aids and practical exercises to enhance your learning experience.
Technical Manuals and Guides
Detailed technical guides and manuals are also invaluable resources. These publications often break down complex systems into understandable segments, allowing you to study individual mechanisms in a structured way. Many of these resources can be accessed through specialized websites or obtained from manufacturers.