
When it comes to maintaining household appliances, having a clear visual reference for their internal structures is essential. A comprehensive overview of the different elements within these machines can greatly aid in troubleshooting and repairs. Recognizing how each component functions together ensures efficient operation and extends the lifespan of the unit.
In this section, we will explore the intricate arrangement of various elements within the unit, emphasizing their roles and interconnections. By delving into the specifics of these components, you can gain a deeper understanding of how to address common issues and perform necessary maintenance. This knowledge not only empowers you as a user but also enhances your ability to engage with service professionals when repairs are required.
Whether you are a seasoned technician or a curious homeowner, familiarizing yourself with the layout of the essential components will prove beneficial. With this foundation, you can confidently navigate the complexities of your appliance, ensuring it operates at peak performance for years to come.
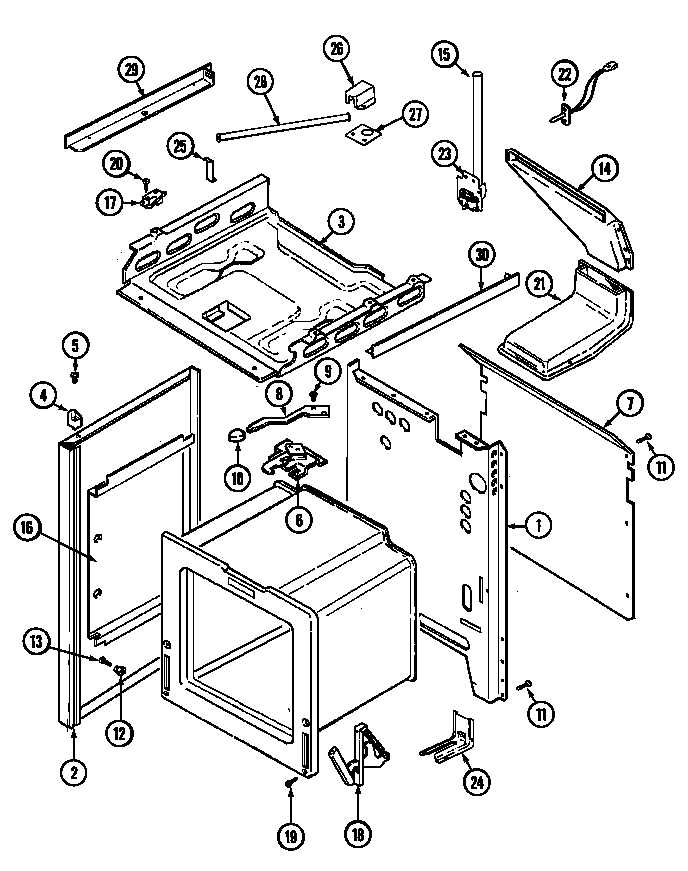
Understanding the intricacies of electrical connections within household appliances is crucial for maintenance and troubleshooting. Proper identification of wiring components can enhance safety and efficiency when addressing issues. This section provides guidance on recognizing and interpreting essential electrical elements.
Key aspects to consider when examining wiring configurations include:
- Color coding: Wires are typically insulated with specific colors, indicating their function, such as live, neutral, and ground.
- Connector types: Different connectors may be used for secure connections, each with its own identification method.
- Wire gauge: The thickness of the wire affects its capacity to carry current safely.
- Voltage ratings: Ensure that the components are rated for the correct voltage to prevent overloads and failures.
When inspecting the electrical layout, follow these steps:
- Turn off the power supply to avoid electrical shock.
- Remove any covers to access wiring safely.
- Document the current setup for future reference.
- Check for any signs of wear or damage on the wires.
- Use a multimeter to verify continuity and voltage levels.
By carefully examining these elements, one can effectively identify and address potential electrical issues, ensuring the smooth operation of the appliance.
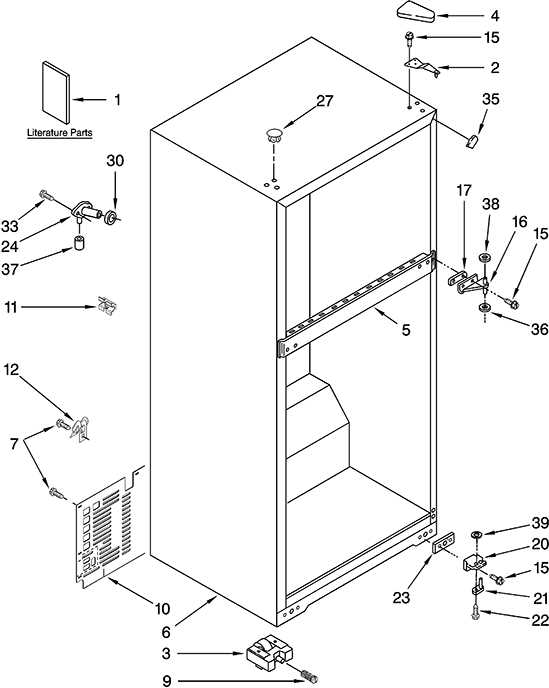
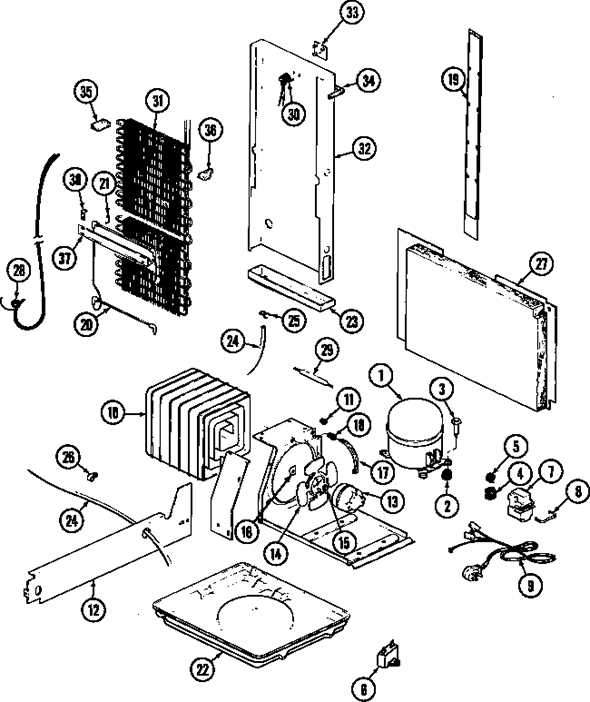
Common Replacement Components Overview
When dealing with household appliances, understanding the essential elements that may require substitution is crucial for maintaining functionality. This section highlights various components that often need to be replaced due to wear and tear or malfunction. Being familiar with these items can help in making informed decisions regarding repairs and replacements.
Key Components
- Compressors: Vital for circulating refrigerant throughout the system, ensuring proper cooling.
- Thermostats: Regulate the internal temperature, providing comfort and efficiency.
- Evaporator Coils: Absorb heat from the interior, playing a crucial role in the cooling process.
- Condenser Coils: Release heat outside, allowing the refrigeration cycle to continue.
- Fan Motors: Help in air circulation, essential for both cooling and temperature regulation.
Additional Components to Consider
- Door Seals: Prevent air leaks, maintaining energy efficiency and temperature stability.
- Water Filters: Ensure the purity of dispensed water, essential for health and taste.
- Light Bulbs: Provide illumination for visibility, enhancing user convenience.
- Drip Pans: Collect excess moisture, preventing leaks and maintaining cleanliness.
Being aware of these common elements will empower users to address issues effectively and maintain the longevity of their appliances.
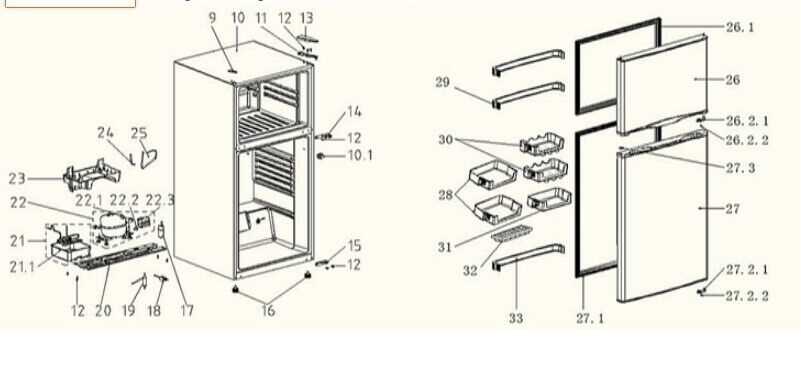
Assembly of the Door Mechanism
The assembly of the cooling unit’s entry system involves precise alignment and secure attachment of various components, ensuring smooth functionality. Proper positioning of these elements guarantees a tight seal, maintaining optimal temperature control and preventing air leakage. This process is crucial for preserving the internal environment of the storage area, contributing to efficiency and longevity.
Step-by-Step Process
Begin by attaching the hinges to the main structure, ensuring they are tightly fixed to provide stability. Align the upper and lower supports with the frame, ensuring smooth movement when opening and closing. Tighten all screws and bolts to prevent any play in the joints, which can affect the overall function.
Installing the Door Gasket
The gasket plays a vital role in maintaining an airtight closure. Position the seal evenly around the edges, pressing firmly to avoid any gaps. Check for uniformity along the corners to ensure a proper fit. This component aids in preserving the internal climate by blocking external air flow.
Final Adjustments
After assembling the mechanism, check the alignment of the entry panel. Adjust the tension on the hinges if necessary to ensure it swings smoothly without resistance. Perform a test to verify the sealing efficiency and en
Features of the Shelving System
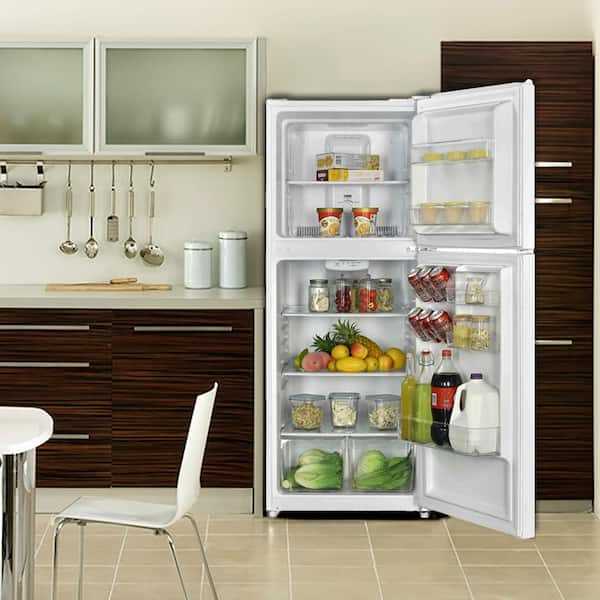

The organization within the cooling unit is greatly enhanced by its versatile storage arrangement. Designed to maximize space and accessibility, each level offers specific attributes that cater to a range of storage needs. This makes it easy to manage different items while maintaining an efficient flow of air circulation, contributing to optimal conditions for stored goods.
Adjustable Levels: The unit includes multiple tiers that can be repositioned to accommodate larger or oddly-shaped items. This flexibility ensures that users can adapt the space based on their changing needs, allowing for efficient use of every compartment.
Durable Materials: Constructed with high-quality materials, each section is designed to support heavy loads without warping. The structure remains stable over time, providing a reliable place for various contents while being easy to clean and maintain.
Specialized Compartments: Integrated compartments and door racks offer dedicated spaces for smaller items, keeping them separate from larger ones. These sections are especially useful for organizing bottles, jars, and similar items, making them easy to access without disrupting the rest of the arrangement.
With these features, the storage system not only enhances the organization but also ensures a seamless experience for users, maintaining order and making daily use more convenient.
Examining the Temperature Control Unit
The temperature control component plays a crucial role in managing the internal climate of cooling systems. It ensures that the conditions inside remain consistent, adjusting the cooling levels based on the user’s settings and the current environment. This section delves into the core mechanisms that allow this element to maintain the optimal conditions required for various stored items.
Key Functions and Adjustments
One of the main features of this module is its ability to respond to variations in internal conditions. It detects changes through sensors, allowing it to adjust the cooling output to maintain a stable environment. Users can often adjust the settings manually, offering flexibility to adapt to different needs. Such adjustments can extend the lifespan of stored items, preserving their quality over time.
Internal Mechanisms and Sensors

The unit relies on several internal mechanisms, including a set of sensors that monitor changes in temperature. These sensors communicate with the control board, signaling when to activate or reduce the cooling cycle. By ensuring that the internal environment remains within the desired range, these mechanisms prevent fluctuations that could affect performance and efficiency.
Role of the Condenser and Evaporator
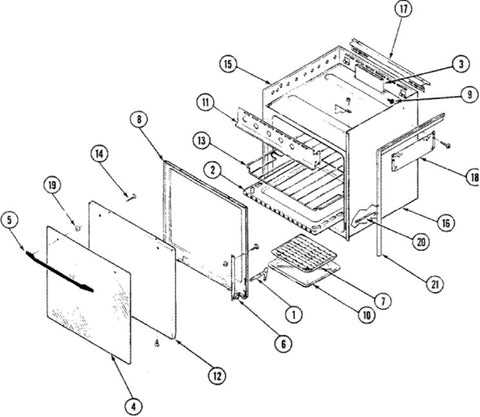
The cooling system relies heavily on two key components that work together to maintain an ideal temperature within the unit. These elements manage the transfer and removal of thermal energy, ensuring the internal environment remains cool while excess heat is efficiently expelled.
- Condenser: This part plays a crucial role in dissipating heat. As the system circulates fluid, it absorbs warmth from inside and releases it outside. The process is driven by the condenser’s ability to change the state of the fluid, turning it from a gas back into a liquid as it cools.
- Evaporator: This element focuses on absorbing warmth from the interior. As the fluid enters the evaporator, it transforms into a gas, drawing heat away from the interior space. This phase change is essential for reducing the internal temperature and keeping the environment cool.
Together, these components create a balanced cycle, with one drawing out heat while the other expels it. Their coordinated operation ensures consistent cooling performance, contributing significantly to the overall efficiency of the
Assessing the Drainage System Design

The efficiency of a cooling unit’s moisture management plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal performance. A well-thought-out water removal mechanism helps prevent issues like excess condensation and water pooling, which can lead to operational inefficiencies. Understanding how this mechanism is structured allows for better troubleshooting and maintenance practices.
Key Components of the Water Flow Mechanism: The setup typically includes a channel to direct excess moisture, a collection basin, and a pathway for safe disposal. These elements work together to ensure that liquid build-up is minimized, maintaining a stable environment within the cooling area.
Common Issues in the Moisture Evacuation System: Over time, clogs and blockages can form, often due to dirt or residue buildup. This can disrupt the normal flow, leading to overflows and potential damage to the unit. Regular inspection and cleaning of these pathways help ensure long-term functionality and prevent unnecessary wear.
By thoroughly understanding this aspect of the design, users can more effectively address any disruptions and extend the overall lifespan of their cooling device. This insight is essential for both routine maintenance and addressing any unexpected concerns that might arise.
Maintenance of Internal Insulation Layers
Proper upkeep of the inner thermal barriers is crucial for efficient cooling and long-term performance. These layers help maintain a consistent environment by reducing thermal exchange, ensuring that internal conditions remain stable over time. Regular care of these materials can enhance overall energy efficiency and longevity.
Key Signs of Wear and Tear
- Condensation Build-Up: Moisture on internal surfaces may indicate compromised insulation, leading to inefficient cooling.
- Temperature Fluctuations: Noticeable changes in internal conditions can suggest that the thermal barriers are not functioning properly.
- Visible Cracks or Gaps: Physical damage to the lining can significantly reduce its insulating capabilities.
Steps for Proper Care

- Regular Inspection: Periodically check the inner surfaces for any signs of damage or moisture build-up.
- Seal Replacement: Replace damaged or worn seals to prevent air leakage, which can stress the cooling system.
- Clean and Dry: Ensure that the inner surfaces are kept clean and dry to prevent mold or mildew, which can damage insulation over time.
Consistent attention to these aspects will help preserve the