The internal structure of modern vehicles is a complex combination of various systems working in harmony. Identifying and understanding the individual elements within these systems can be crucial for maintaining optimal performance. Knowing the exact configuration of key assemblies allows for more efficient repairs and upgrades, ensuring a smoother and safer driving experience.
Whether it’s the powertrain, electrical connections, or safety features, each section of the vehicle serves a distinct role. Gaining insight into the arrangement of these components can help technicians and enthusiasts alike in diagnosing issues and performing necessary adjustments. This guide will provide a comprehensive look into how these different modules fit together.
By exploring the connections and layout of critical assemblies, we can better understand the engin
Understanding the Structure of Key Components
The layout and organization of essential elements in a vehicle are designed with precision to ensure functionality and performance. By examining how these crucial systems interact, it is possible to gain deeper insight into the overall design and operational efficiency.
Engine and Transmission System
The power unit and the gearbox are the heart of any automobile. These mechanisms are closely interconnected, allowing smooth power transfer and optimal control. A well-designed integration ensures efficient energy use, enhancing both performance and reliability. Understanding the structure of these components reveals how they contribute to driving dynamics.
Suspension and Steering Assembly
The suspension and control systems are critical for maintaining stability and providing a comfortable ride. Each element within these assemblies is engineered to absorb shocks and enable responsive handling. These components work in harmony to maintain balance, ensuring both comfort and safety during operation.
Analyzing the Layout of the Suspension System
The suspension system in any vehicle plays a pivotal role in ensuring a smooth and stable ride. It is designed to absorb shocks from uneven surfaces, providing both comfort and control for the driver and passengers. Understanding the arrangement of its various components is crucial for anyone looking to maintain or repair these essential mechanisms. By exploring the design and structure, we can see how each element contributes to the overall performance and safety of the vehicle.
Core Components of the System
At the heart of this configuration are several key elements that work in unison to stabilize the vehicle. These include shock absorbers, springs, and control arms. Each part has a distinct function, with springs acting to support the weight, while shock absorbers dampen any movement caused by road irregularities. The control arms ensure proper alignment, maintaining balance as the vehicle moves.
Exploring the Electrical Wiring Framework
The electrical system of any modern vehicle is a complex network responsible for powering various components, ensuring seamless communication between essential systems. This framework connects key electronic elements, providing the necessary energy for both basic functions and advanced technologies. Understanding this network is critical for troubleshooting issues and maintaining efficiency.
Key components of the system include the power supply lines, which route electricity to different sections, and the communication pathways, which allow signals to travel between sensors and control modules. These intricate connections form the foundation of a vehicle’s overall functionality.
Maintaining this network ensures the safety and reliability of the system. Recognizing the different routes and connections involved is vital for any maintenance work or upgrades, helping avoid disruptions to the overall performance of the electronic systems.
Guide to the Engine and Transmission Arrangement
Understanding how key components of the vehicle’s powertrain work together is essential for efficient maintenance and repair. The layout of these elements is designed to optimize performance, ensuring smooth operation and longevity. This section focuses on the structure and interaction between the central power unit and the gear system, emphasizing the flow of power and the way these components are positioned in relation to each other.
- The power unit is positioned to balance weight distribution, improving both stability and handling.
- The transmission system is mounted in a way that enhances efficient power transfer to the wheels, supporting various driving conditions.
- Certain areas within the assembly are strategically placed to facilitate cooling, preventing overheating during intense use.
- Connections between the power source and the gearbox are designed for minimal energy loss, contributing to overall fuel efficiency.
- Additional components, such as the exhaust and intake systems, are arranged to complement the overall
Brake System Breakdown and Component Mapping
Understanding the intricate structure of the braking system is essential for maintaining safety and optimal performance. This section explores the key elements that work together to control and regulate braking forces, ensuring smooth operation during a variety of driving conditions.
Core Mechanisms and Their Functions
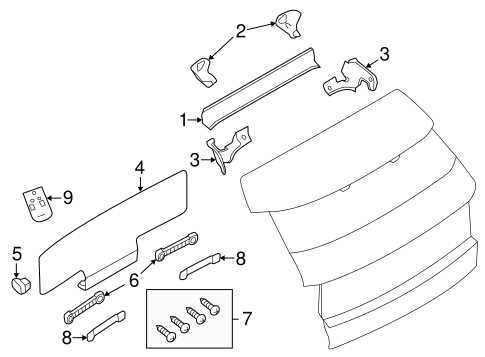
The system is built around several core components, each responsible for a specific function. The primary mechanism includes the pedal, which initiates the process when pressure is applied. This triggers a hydraulic response, activating the master cylinder that distributes force evenly across the wheels. Other critical parts include calipers, rotors, and fluid lines, all working in sync to ensure consistent stopping power.
Mapping the Connections
All components are interconnected to provide efficient performance. The hydraulic lines link the foot pedal to the rest of the system, while sensors monitor pressure
Cooling System Overview and Part Identification
The cooling mechanism in vehicles plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal operating temperatures, preventing overheating and ensuring efficient performance. This system comprises several components that work in unison to regulate heat and maintain engine functionality.
Key elements of this mechanism include the radiator, responsible for dissipating heat from the coolant; the water pump, which circulates the coolant throughout the system; and the thermostat, regulating the flow based on temperature changes. Additional components such as the coolant reservoir and various hoses facilitate the movement of the coolant, ensuring that every part operates seamlessly.
Understanding these components and their functions is essential for diagnosing potential issues and maintaining overall system efficiency. Proper identification of each element aids in effective troubleshooting and repair processes, ultimately contributing to the longevity of the engine.
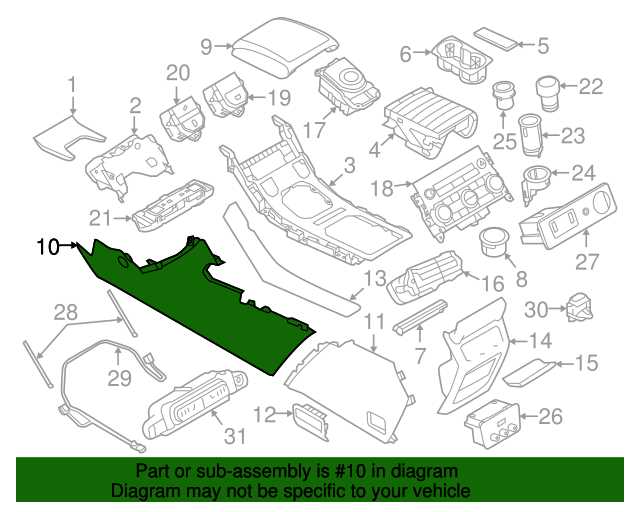
Examining the Interior Layout and Accessories
The configuration of the cabin in a contemporary vehicle plays a crucial role in enhancing both functionality and aesthetics. A well-thought-out arrangement not only provides comfort for occupants but also ensures that essential controls and features are intuitively accessible. This section delves into the specific components and enhancements that contribute to a luxurious and user-friendly interior experience.
Within the cockpit, the placement of instruments, infotainment systems, and storage options reflects a commitment to ergonomic design. Attention to detail is evident in the choice of materials, from soft-touch surfaces to premium finishes, creating an inviting atmosphere. Additionally, accessories such as ambient lighting, adjustable seating, and integrated technology further elevate the overall driving experience.
Moreover, the incorporation of practical features, like versatile storage compartments and easy-to-reach controls, caters to the needs of both drivers and passengers. The careful organization of these elements not only optimizes space but also enhances usability, making each journey enjoyable and convenient.
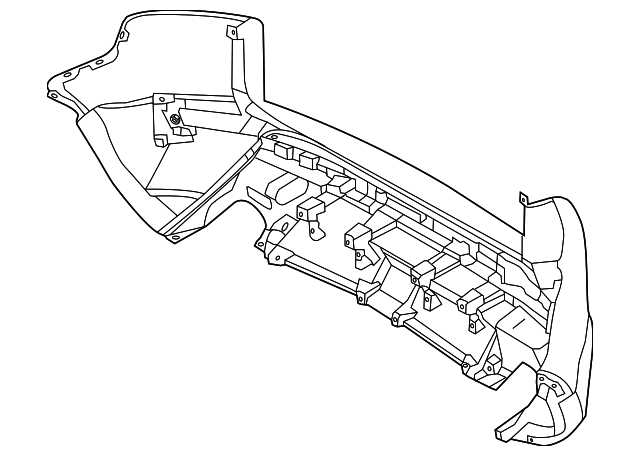
Body Panels and Exterior Part Placement
The arrangement and composition of external components significantly influence the aesthetics and functionality of a vehicle. Understanding the layout of these elements is crucial for maintenance and repairs, as well as for enhancing overall performance. This section delves into the various sections that comprise the outer shell and their respective placements.
Types of Body Components
The outer structure is primarily made up of several distinct components, each serving a specific purpose. Fenders, doors, and hoods are essential parts that contribute to both protection and visual appeal. Additionally, grilles and bumpers play vital roles in airflow management and impact resistance. The precise alignment of these components ensures not only a seamless look but also optimal performance.
Placement Considerations
Proper placement of these external elements is vital for aerodynamics and safety. Each part must be carefully fitted to reduce drag and improve fuel efficiency. Furthermore, correct positioning can enhance the structural integrity of the vehicle, allowing it to withstand various forces during operation. Regular inspections and adjustments may be necessary to maintain the ideal configuration of these outer elements.
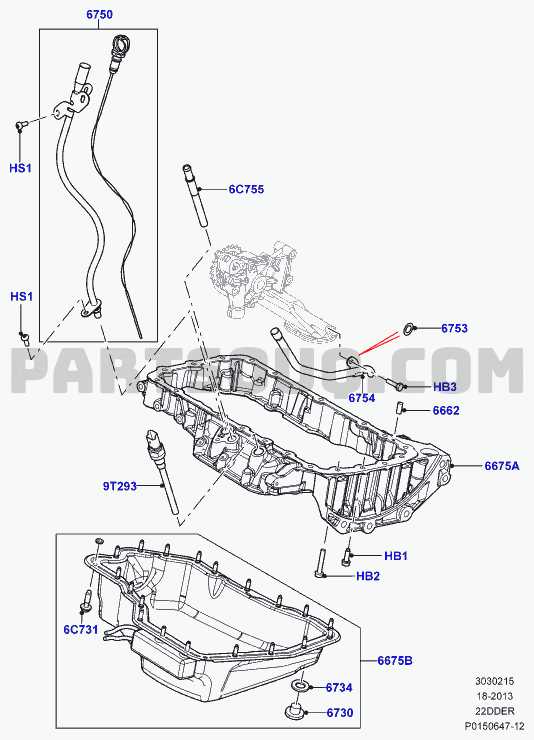
Fuel System Layout and Key Components
The fuel delivery system is a crucial aspect of any automotive design, responsible for supplying the engine with the necessary fuel for optimal performance. Understanding its configuration and essential elements is vital for diagnosing issues and ensuring efficient operation.
This system typically consists of several key components, including the fuel tank, fuel pump, fuel filter, fuel injectors, and various lines and connectors. Each element plays a specific role in the process of storing, transporting, and delivering fuel to the engine, ensuring that it operates smoothly and efficiently.
The fuel tank serves as the reservoir, holding the gasoline or diesel until needed. The fuel pump, usually located within the tank, draws fuel and sends it through the fuel lines to the engine. A fuel filter is positioned along the pathway to remove impurities, safeguarding the injectors and other components from damage. Finally, the injectors atomize the fuel, delivering it directly into the combustion chamber for efficient mixing with air.
Exhaust System Configuration Overview
The configuration of the exhaust system is crucial for optimizing performance and efficiency in any vehicle. This intricate arrangement plays a significant role in managing emissions and enhancing engine output. Understanding its components and layout can provide insights into how to maintain and improve functionality.
Key Components
The exhaust system consists of several essential elements that work together to direct exhaust gases away from the engine. Each part is designed to perform a specific function, ensuring the overall system operates effectively.
Component Function Exhaust Manifold Collects gases from the engine’s cylinders and directs them into the exhaust system. Catalytic Converter Reduces harmful emissions by converting them into less harmful substances. Resonator Modifies sound waves to enhance the exhaust note and reduce noise levels. Muffler Further reduces noise produced by the engine’s exhaust gases before they exit the tailpipe. Exhaust Pipe Channels exhaust gases from the engine to the rear of the vehicle, expelling them into the atmosphere. System Layout
The arrangement of the exhaust system can vary based on design and performance requirements. An efficient layout minimizes back pressure and allows for optimal gas flow, which is essential for enhancing power and fuel economy.
Steering Mechanism Layout and Parts Location
This section provides a comprehensive overview of the steering assembly’s configuration and the positioning of its components within the vehicle. Understanding this layout is crucial for maintenance and troubleshooting, ensuring optimal performance and safety during operation.
The steering mechanism consists of several key components that work in harmony to provide precise handling and control. Below is a list of the main elements involved:
- Steering Wheel: The primary control interface for the driver, allowing for directional changes.
- Steering Column: Connects the steering wheel to the rest of the system, transmitting the driver’s inputs.
- Steering Gearbox: Converts the rotational motion of the steering wheel into linear motion, assisting in wheel movement.
- Linkage Assembly: Comprises rods and joints that connect the gearbox to the wheels, facilitating their turning.
- Power Assist System: Enhances steering ease, providing support for turning and maneuvering.
Each component has a specific location within the assembly, and their arrangement plays a vital role in ensuring effective operation:
- The steering wheel is mounted atop the column, accessible to the driver.
- The column runs down through the dashboard, housing the necessary electrical connections.
- Attached to the lower end of the column is the steering gearbox, typically located near the vehicle’s firewall.
- The linkage assembly extends from the gearbox to each front wheel, ensuring synchronized movement.
- The power assist system is integrated into the column or gearbox, depending on the design.
By familiarizing oneself with the layout and locations of these components, vehicle owners and technicians can more effectively address any issues related to steering control.