Understanding the intricate layout of essential systems within a modern vehicle can help with maintenance, repairs, and upgrades. Each system, from the engine to the transmission, is meticulously designed to work together efficiently. Whether you are a car enthusiast or a professional mechanic, knowing how different elements are connected is crucial for keeping a vehicle in peak condition.
In this section, we will explore the key aspects of these systems, providing a clear and detailed overview. By identifying how various elements interact, you can better approach any issues that may arise, ensuring that the overall functionality remains intact. This will not only enhance your ability to troubleshoot but also improve the overall understanding of the vehicle’s internal setup.
With this guide, you’ll gain valuable insight into the design and layout of key components, which are critical to the vehicle’s performance and longevity. This knowledge can assist you in making informed decisions about repairs, replacements, and even modifications.
Essential Components of 2013 Hyundai Santa Fe
Understanding the key elements that make up a modern SUV is crucial for maintaining its performance and reliability. Each piece, from the mechanical to the electronic, plays a role in ensuring a smooth ride and safe driving experience. Below is an overview of some of the most vital parts that contribute to the vehicle’s overall function.
- Engine System: The heart of any vehicle, this system ensures power is delivered efficiently. It includes various interconnected components that work together to convert fuel into energy.
- Transmission: This part is responsible for transferring the engine’s power to the wheels. A well-maintained transmission ensures smooth shifting and optimal speed control.
- Suspension and Steering: These elements are crucial for maintaining stability and control on the road. They help absorb shocks and provide accurate handling during turns and uneven surfaces.
- Braking Mechanism: Safety is paramount, and a robust set of brakes ensures the vehicle can come to a stop when necessary. This system includes brake pads, discs,
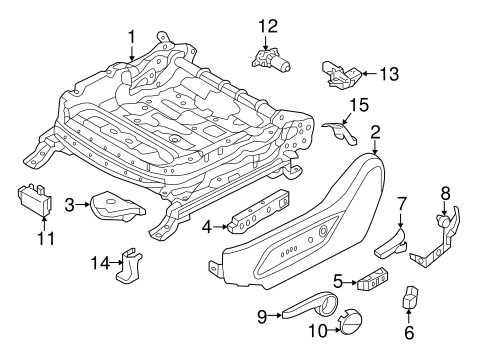
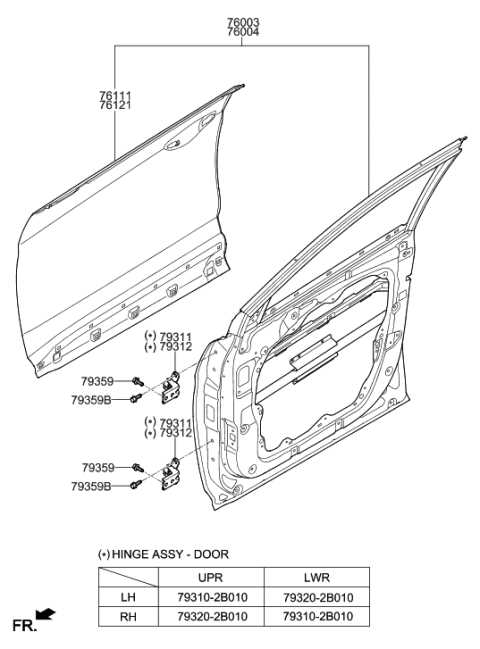
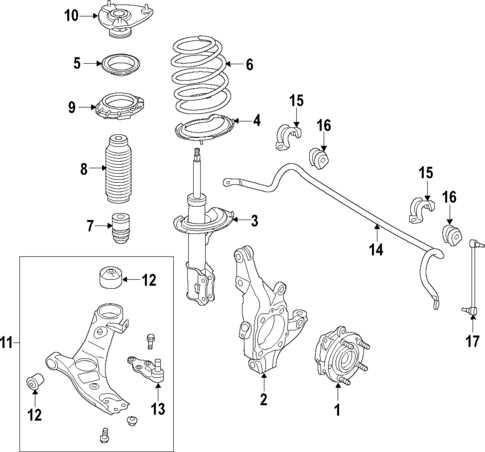
Front Suspension Parts Overview
The front suspension system is a key component that ensures stability and comfort while driving, as it absorbs road impacts and allows for smooth handling. It connects the wheels to the vehicle’s frame, enabling controlled motion and minimizing vibrations. This section provides an outline of the various elements that make up this system, emphasizing their roles in maintaining a balanced and safe ride.
- Control Arms: These components link the wheel assembly to the chassis, allowing up-and-down movement of the wheels. They play a crucial role in steering and alignment.
- Shock Absorbers: Designed to reduce the effect of bumps and uneven surfaces, these parts dampen the shock to provide a smoother ride.
- Springs: These elements support the vehicle’s weight and help in absorbing the energy from road imperfections, maintaining vehicle height and ride comfort.
- Ball Joints: These are pivot points that enable smooth rotation of the wheels while steering, allowing for flexibility and movement in various directions.
- Stabilizer Bar: Also known as the sway bar, this component
Engine Compartment Layout
The layout of the engine compartment is designed to provide easy access to critical components and systems for maintenance and inspection. Each element has its designated space, ensuring efficient cooling, optimal performance, and straightforward servicing when needed.
Main Components
The key elements located within the engine compartment include the power unit, cooling system, air intake system, and electrical connections. These components are arranged to maximize airflow and minimize heat buildup. The placement of reservoirs for essential fluids also allows for easy monitoring and refilling.
Accessibility and Maintenance
Accessibility is a crucial consideration in the design of the engine compartment. Essential maintenance points, such as the oil dipstick, coolant cap, and battery, are positioned within reach, allowing for quick checks and servicing. Additionally, protective covers are used to shield sensitive components, reducing wear and tear while ensuring durability.
Brake System Diagram Breakdown
The brake system plays a crucial role in vehicle safety, ensuring controlled stops and overall handling. By understanding its components and their connections, drivers and technicians can better appreciate how this system works together to provide consistent performance. This breakdown offers an overview of the key elements involved in braking, detailing the flow of power from the pedal to the wheels.
Main Components of the Brake System
The system begins with the brake pedal, where pressure is applied by the driver. This force is transferred through a hydraulic system, typically including a master cylinder, which amplifies the force and sends it to the brake lines. These lines deliver fluid to calipers or drums located at each wheel. In disc brakes, calipers clamp down on rotors to slow the vehicle, while drum systems rely on brake shoes to create friction against the drum.
Supportive Elements and Function
Other critical elements include the brake booster, which helps reduce the effort needed to press the pedal, and anti-lock braking technology, designed to prevent wheel lock-up during sudden stops. Sensors and control modules continuously monitor the system to ensure optimal operation under varying conditions, enhancing safety and response time.
Exhaust System Structure
The exhaust system plays a critical role in directing gases away from the engine, ensuring smooth operation and reducing emissions. Its structure consists of multiple interconnected components, each designed to manage the flow of gases efficiently while minimizing noise and harmful pollutants.
The system begins at the engine’s exhaust manifold, where gases are collected and channeled through pipes. These gases then travel through the catalytic converter, which is responsible for reducing toxic emissions. The system continues through mufflers and resonators that help reduce noise levels before releasing the treated gases safely out through the tailpipe.
Each section of the exhaust system is made to withstand high temperatures and pressures, contributing to overall vehicle performance, fuel efficiency, and environmental protection. Regular inspection and maintenance ensure the system functions effectively, preventing issues like blockages or leaks that could negatively impact the engine’s performance.
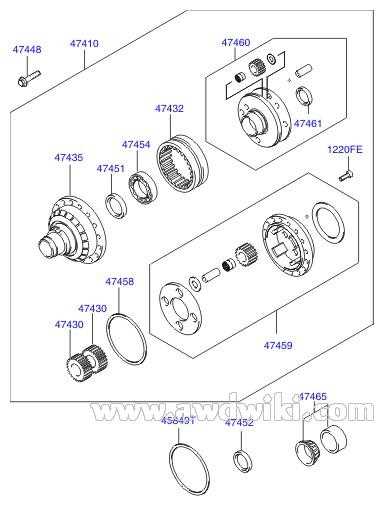
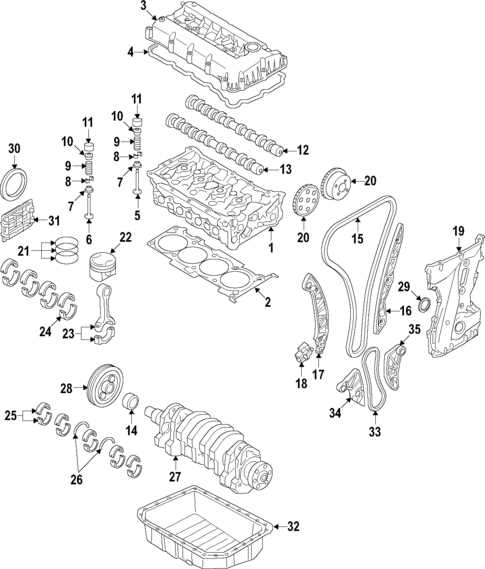
Transmission and Drivetrain Components
The transmission and drivetrain elements are crucial for ensuring smooth operation and efficient power delivery in vehicles. These components work together to manage the transfer of energy from the engine to the wheels, playing a vital role in overall performance and handling.
Key Transmission Elements
The transmission system includes several key components such as the gearbox, torque converter, and shift linkage. The gearbox is responsible for adjusting the engine’s power output to match the vehicle’s speed, while the torque converter facilitates a seamless connection between the engine and transmission, enabling smooth acceleration. Additionally, the shift linkage allows for precise gear changes, enhancing driver control.
Drivetrain Functionality
The drivetrain encompasses elements such as the driveshaft, differential, and axles. The driveshaft transmits power from the transmission to the wheels, while the differential distributes this power to the left and right wheels, ensuring balanced traction. Axles play a pivotal role in supporting the weight of the vehicle and connecting the wheels to the drivetrain, allowing for effective movement and stability on the road.
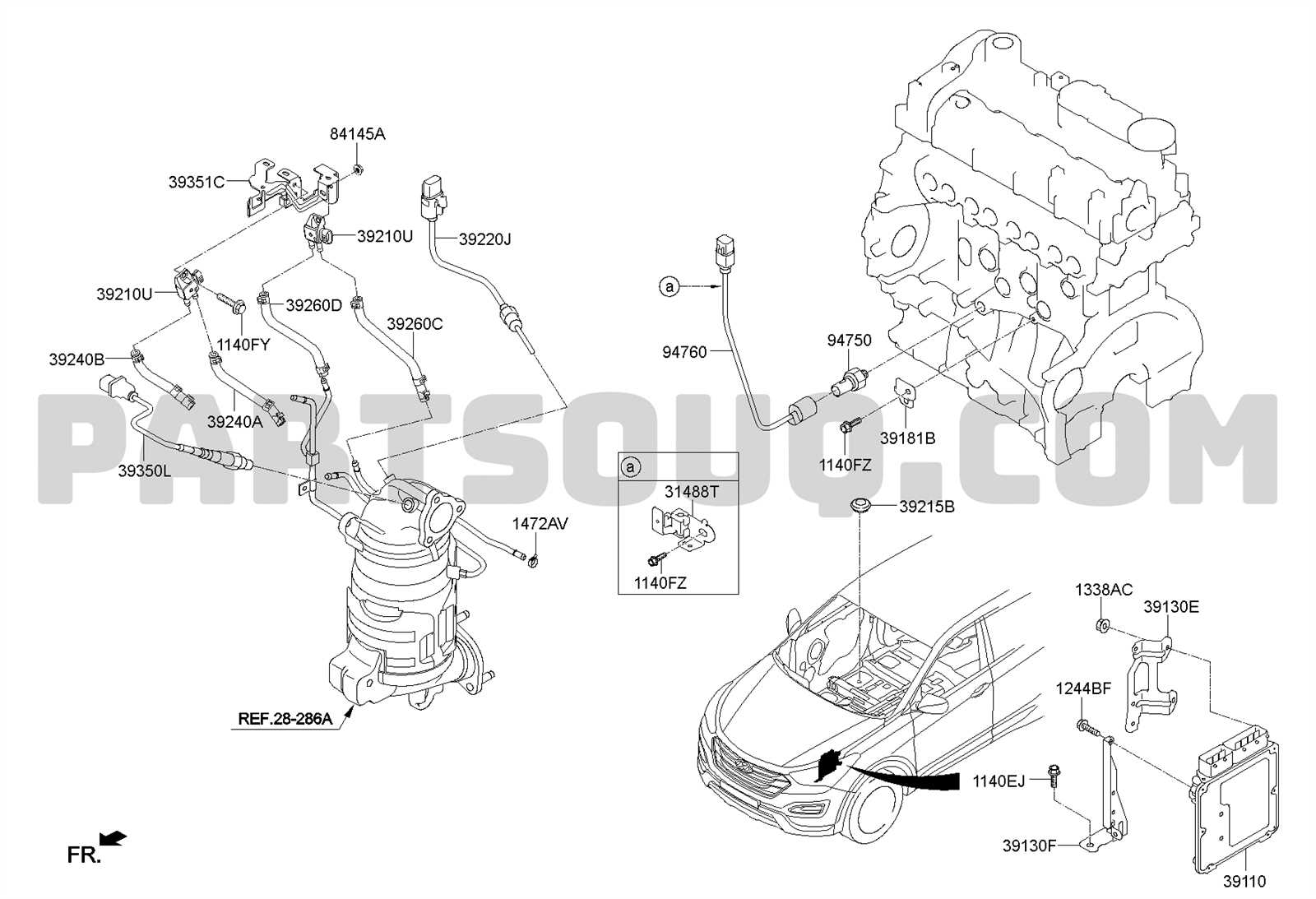
Fuel System Configuration
The configuration of the fuel system plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient operation and performance of the vehicle. This system is responsible for storing, transporting, and delivering fuel to the engine in a manner that optimizes combustion and power generation.
Key components involved in this configuration include:
- Fuel Tank: A reservoir that holds the fuel until it is needed by the engine.
- Fuel Pump: This component transports fuel from the tank to the engine, creating the necessary pressure for proper fuel flow.
- Fuel Filter: A vital element that removes impurities and contaminants from the fuel before it reaches the engine.
- Fuel Injectors: Devices that atomize and deliver the fuel into the combustion chamber at precise intervals.
- Fuel Lines: Hoses that connect the various components of the fuel system, ensuring smooth fuel flow.
Each part of the system must work seamlessly together to enhance performance, fuel efficiency, and reduce emissions. Regular maintenance and inspection of these components are essential for optimal functioning and longevity of the system.
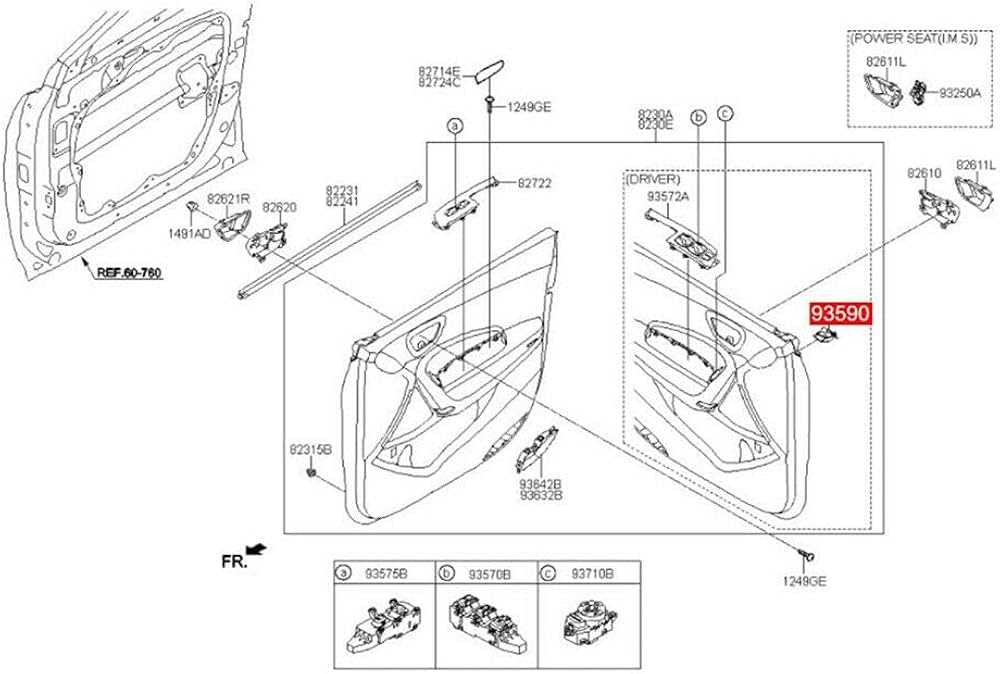
Interior Electrical System Map
The interior electrical framework of a vehicle plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth operation of various components that enhance comfort and convenience. Understanding the layout and functionality of this system is essential for effective troubleshooting and maintenance.
Key Components
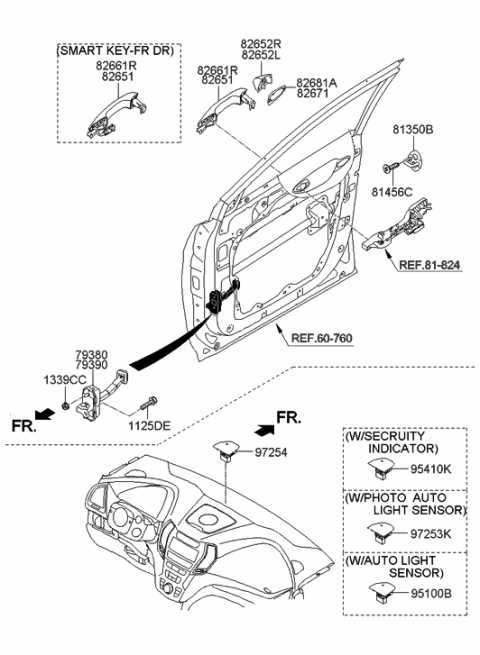
- Power distribution unit
- Fuse box
- Wiring harness
- Lighting circuits
- Infotainment system connections
- Climate control module
Common Issues
Several issues may arise within the electrical network, affecting the performance of various features:
- Blown fuses leading to non-functional devices
- Damaged wiring causing intermittent connectivity
- Malfunctioning sensors impacting system response
- Corroded connectors hindering electrical flow
Proper knowledge of the electrical layout helps in diagnosing these problems efficiently, ensuring optimal performance of the vehicle’s interior functionalities.
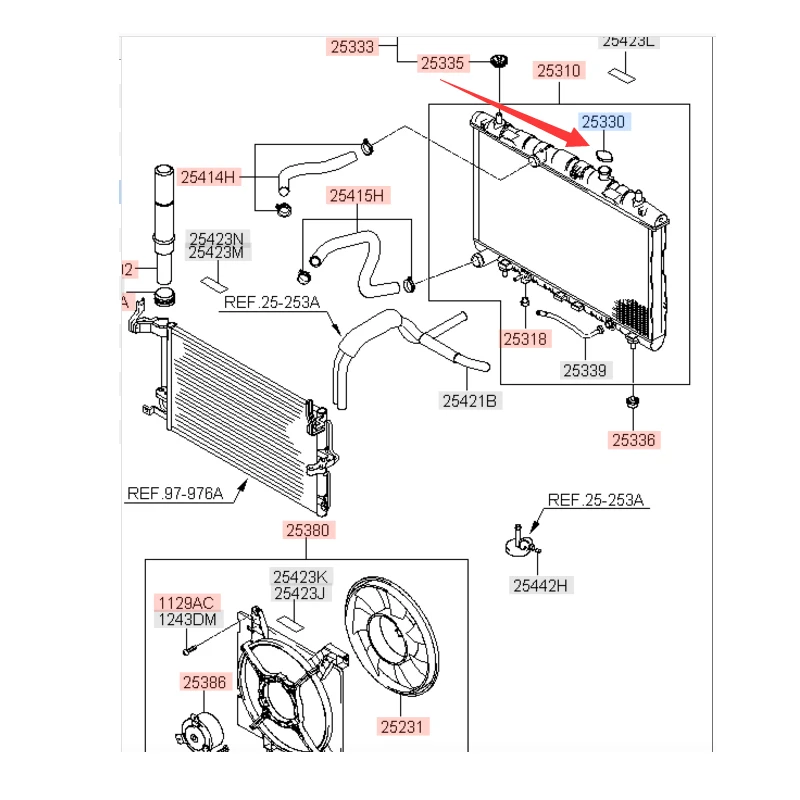
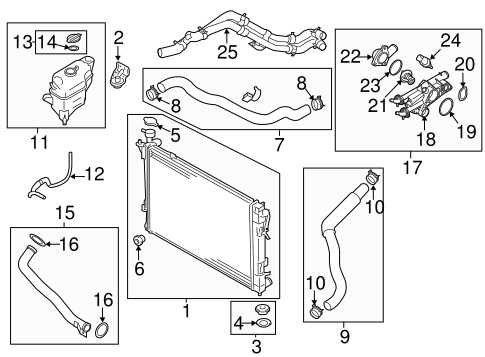
Cooling System Layout
The cooling system is essential for maintaining optimal engine temperature, preventing overheating and ensuring efficient operation. A well-structured layout facilitates effective heat exchange, contributing to the longevity and performance of the vehicle.
Key components of the cooling system include:
- Radiator: Responsible for dissipating heat from the coolant as it circulates through the system.
- Water Pump: Circulates coolant throughout the engine and radiator, ensuring consistent temperature control.
- Thermostat: Regulates coolant flow based on temperature, opening and closing to maintain the ideal operating range.
- Coolant Reservoir: Holds excess coolant and allows for thermal expansion, maintaining appropriate fluid levels.
- Hoses: Connect various components, transporting coolant to and from the engine and radiator.
Understanding the layout of these elements is crucial for troubleshooting and maintenance. Regular inspections can help identify leaks, blockages, or other issues that may affect the system’s efficiency.
Steering System Parts Distribution
The steering system plays a crucial role in vehicle maneuverability, allowing drivers to control direction with precision. Understanding the distribution of its components can aid in effective maintenance and repair, ensuring a safe driving experience. This section explores the various elements that make up the steering mechanism and their respective locations within the assembly.
Key Components
- Steering Wheel: The primary interface for driver input.
- Steering Column: Connects the steering wheel to the mechanism, transmitting movement.
- Rack and Pinion: Converts rotational motion into linear motion for wheel movement.
- Steering Gear: Facilitates the adjustment of steering angle.
- Power Steering Pump: Provides hydraulic assistance to reduce steering effort.
Component Arrangement
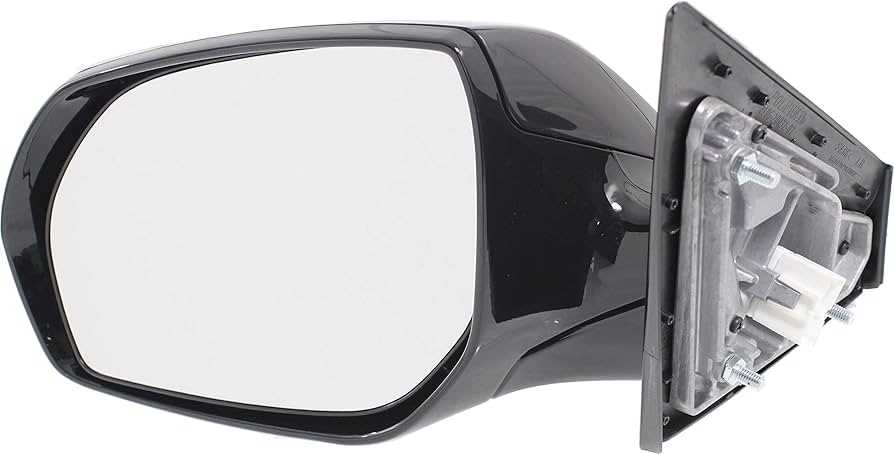

- The steering wheel is positioned at the driver’s end.
- The steering column runs vertically down to the steering gear.
- The rack and pinion assembly is located beneath the vehicle’s front end.
- The power steering pump is often mounted on the engine for easy access to fluid.
By familiarizing oneself with the layout and function of these components, vehicle owners and technicians can ensure optimal performance and address any issues that may arise within the steering system.
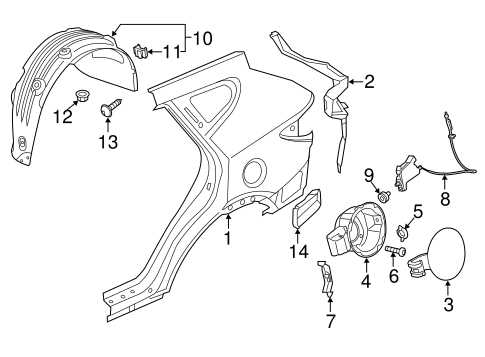
Rear Suspension Elements
The rear suspension system plays a crucial role in ensuring a smooth ride and maintaining vehicle stability. It consists of several components that work together to absorb shocks and support the weight of the vehicle. Understanding these elements is essential for proper maintenance and performance enhancement.
Shock absorbers are vital components that dampen the impact of road irregularities, helping to maintain tire contact with the surface. They prevent excessive bouncing and improve ride comfort. Another significant element is the spring assembly, which supports the vehicle’s weight and absorbs energy from bumps. This assembly is often made up of coil springs or leaf springs, depending on the vehicle’s design.
Control arms also play a critical role in the rear suspension setup. These components connect the suspension system to the vehicle’s chassis, allowing for controlled movement and alignment. Additionally, stabilizer bars enhance stability during cornering, reducing body roll and improving handling characteristics.
Regular inspection and maintenance of these rear suspension elements are essential for vehicle safety and performance. Proper functioning ensures that the vehicle handles well, providing a comfortable driving experience.
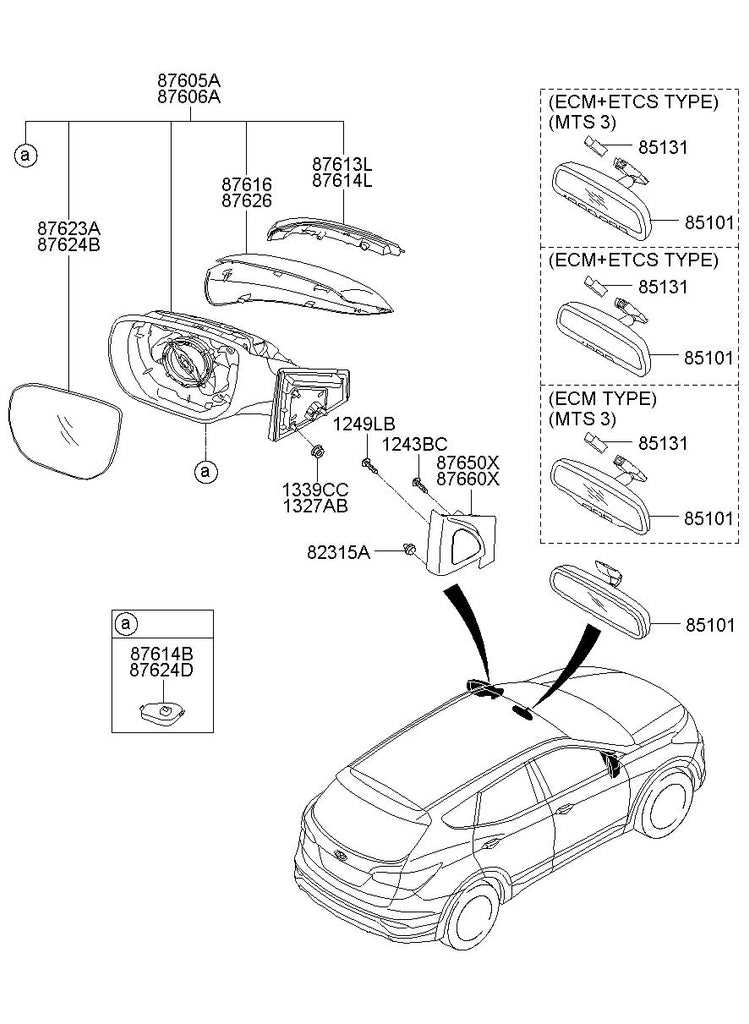
Safety Systems and Sensors Placement
In modern vehicles, the strategic positioning of safety mechanisms and detection devices is crucial for ensuring optimal protection and functionality. These elements work synergistically to enhance the driving experience and provide essential feedback to the driver, allowing for timely interventions in critical situations.
Collision avoidance sensors are typically located in the front and rear bumpers, enabling them to detect obstacles and potential hazards in the vehicle’s path. This placement maximizes their effectiveness in identifying threats from various angles, enhancing overall awareness.
Airbag sensors are often embedded in multiple locations throughout the cabin, including the dashboard and side panels. This arrangement ensures that they can accurately assess impact forces and deploy the appropriate airbags in the event of a collision, offering vital protection to occupants.
Additionally, lane departure warning systems utilize cameras strategically positioned near the windshield to monitor road markings. This setup allows for continuous observation of the vehicle’s lane positioning, providing alerts when unintentional lane changes occur.
Overall, the thoughtful arrangement of safety systems and sensors is integral to modern vehicle design, contributing to enhanced safety features and improved driver confidence on the road.