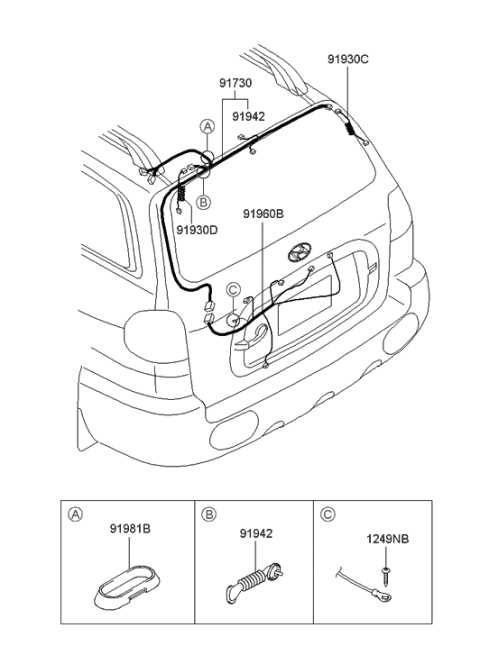
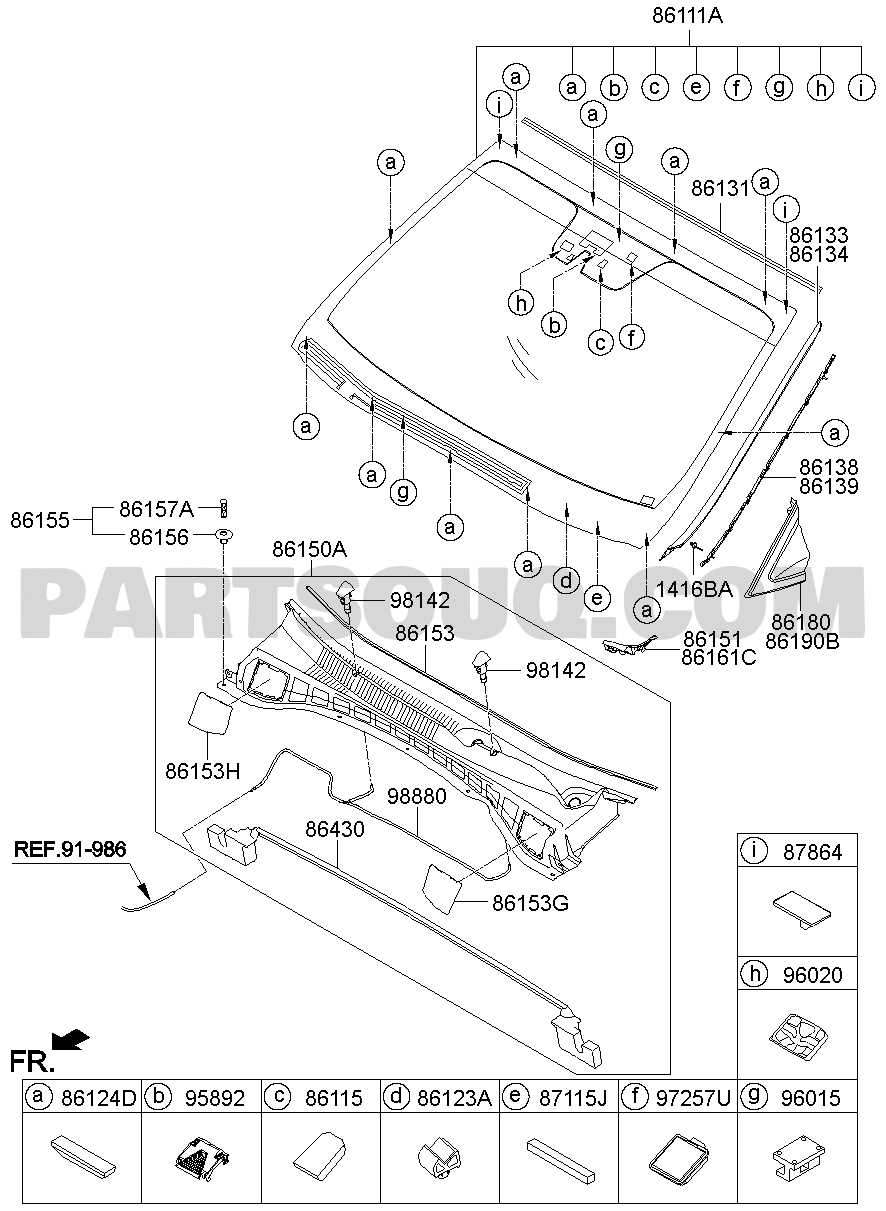
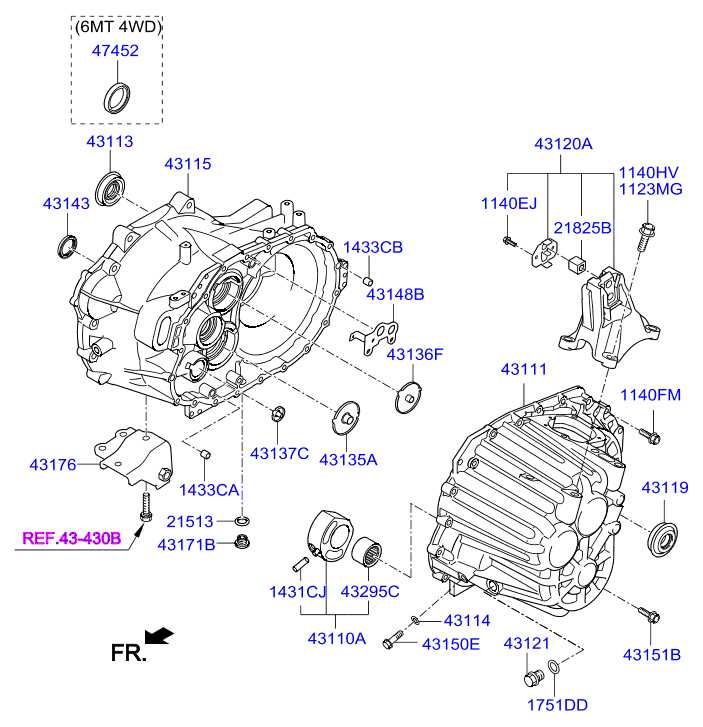
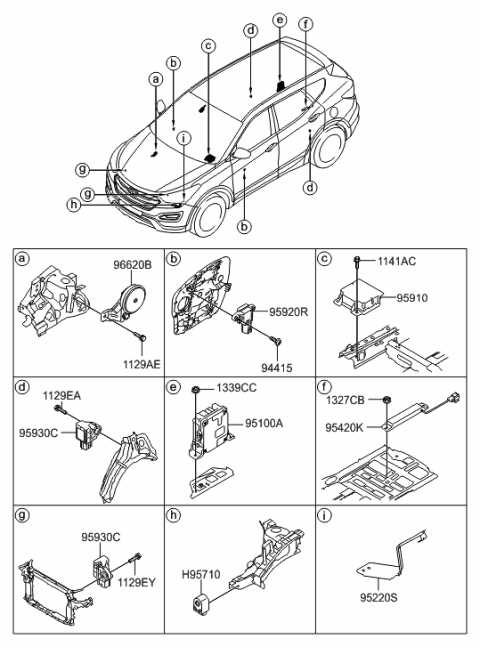
Calipers: Located around the wheels, calipers are designed to squeeze the brake pads against the rotors to
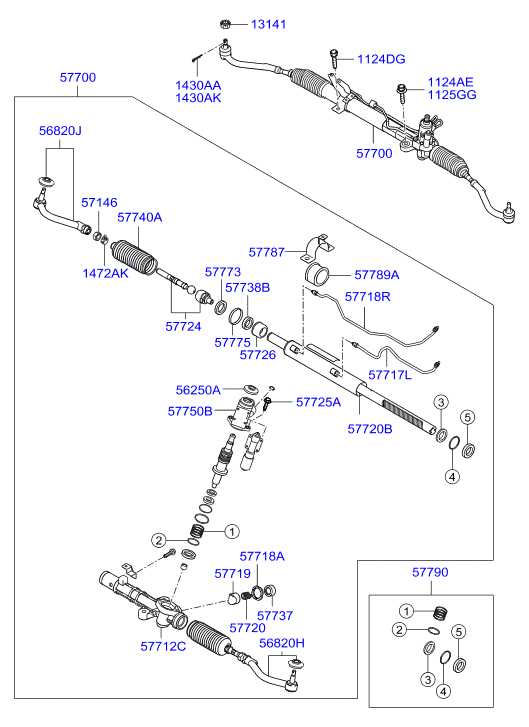
Steering Mechanism Breakdown and Functions
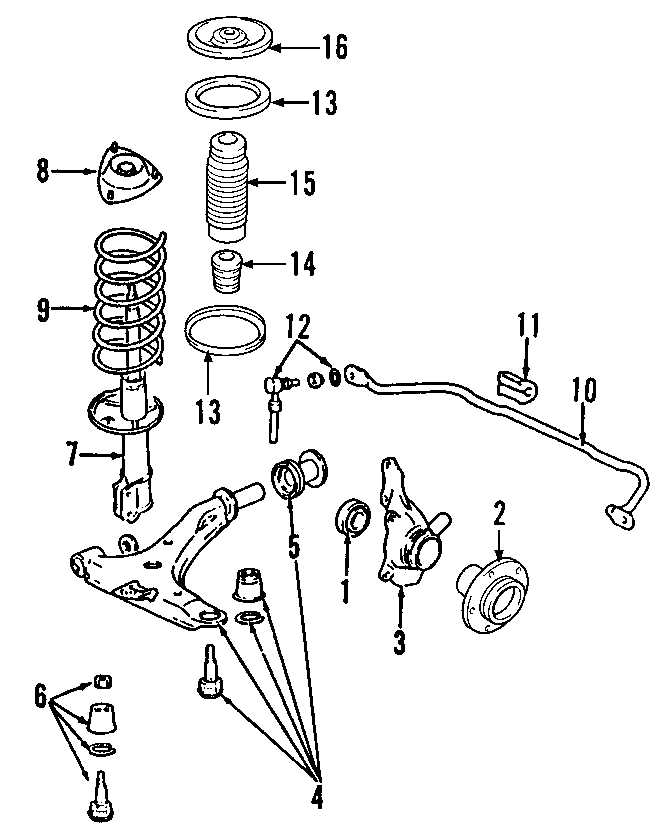
The steering system is a crucial component of any vehicle, ensuring the driver can control direction with precision and ease. It consists of various elements that work together to translate the driver’s input into smooth movement. Understanding the functions of each part within this system can enhance overall vehicle handling and performance.
Key Components of the Steering System
The steering system typically includes several vital components, such as the steering wheel, column, gear, and linkage. The steering wheel allows the driver to input direction, which is transmitted through the steering column. This input is then converted by the gear mechanism, which can either be rack-and-pinion or recirculating ball type, allowing for efficient directional changes. The linkage connects the gear to the wheels, translating rotational motion into linear movement, enabling the vehicle to navigate turns.
Functions of the Steering Mechanism
Each component of the steering system plays a specific role. The steering wheel is designed for ease of use, providing a comfortable grip and responsive feedback. The steering column serves as a conduit for the driver’s commands, while the gear mechanism ensures that the input is effectively transformed into movement. The linkage is essential for maintaining stability and control during steering, allowing the vehicle to respond accurately to the driver’s intentions, even at high speeds or during sharp turns.
Fuel System and Related Elements
The fuel delivery mechanism in modern vehicles plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal engine performance. This system is designed to supply the necessary fuel for combustion while maintaining efficiency and emissions standards. Understanding the various components involved can help in diagnosing issues and performing maintenance effectively.
Key components of the fuel delivery mechanism include:
- Fuel Tank: The reservoir that stores fuel before it is pumped to the engine.
- Fuel Pump: Responsible for transporting fuel from the tank to the engine under pressure.
- Fuel Filter: Ensures that any impurities in the fuel are removed before it reaches the engine.
- Fuel Injector: Delivers the precise amount of fuel into the combustion chamber at the right moment.
- Fuel Lines: The piping that connects the various components, allowing for the flow of fuel.
- Pressure Regulator: Maintains the appropriate pressure within the fuel system, ensuring consistent fuel delivery.
Each of these elements works together harmoniously, contributing to the overall efficiency and reliability of the vehicle’s powertrain. Regular inspection and maintenance of the fuel system are essential to prevent performance issues and ensure a smooth driving experience.
Exhaust System Layout and Design
The exhaust framework in a vehicle is crucial for directing gases produced during combustion away from the engine and minimizing noise. Its design plays a vital role in both performance and emissions, ensuring that the vehicle operates efficiently while meeting environmental standards.
Key Components of the Exhaust Framework
- Exhaust Manifold: Collects exhaust gases from the engine cylinders and directs them into the exhaust system.
- Catalytic Converter: Reduces harmful emissions by converting them into less harmful substances.
- Muffler: Attenuates noise produced by the exhaust gases while maintaining the necessary back pressure for optimal engine performance.
- Exhaust Pipes: Carry exhaust gases from the engine to the rear of the vehicle, ensuring efficient flow and minimal obstruction.
- Resonator: Fine-tunes the sound of the exhaust, providing a more desirable acoustic experience.
Design Considerations
- Material Selection: Durable materials like stainless steel or aluminized steel are commonly used for longevity and corrosion resistance.
- Pipe Sizing: Proper diameter is essential for maintaining optimal flow and performance; larger diameters may enhance performance but could lead to a decrease in back pressure.
- Routing: The path of the exhaust system should minimize bends and turns to enhance gas flow and reduce back pressure.
- Thermal Management: Insulation may be applied to certain components to prevent heat-related damage and improve efficiency.
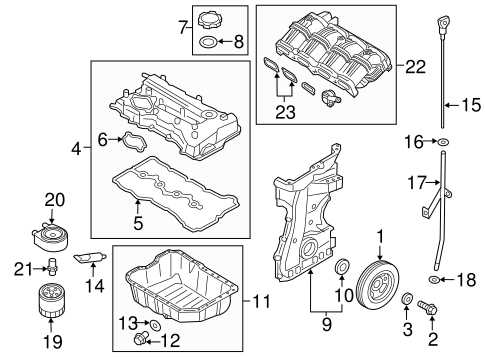
Cooling System Parts Overview
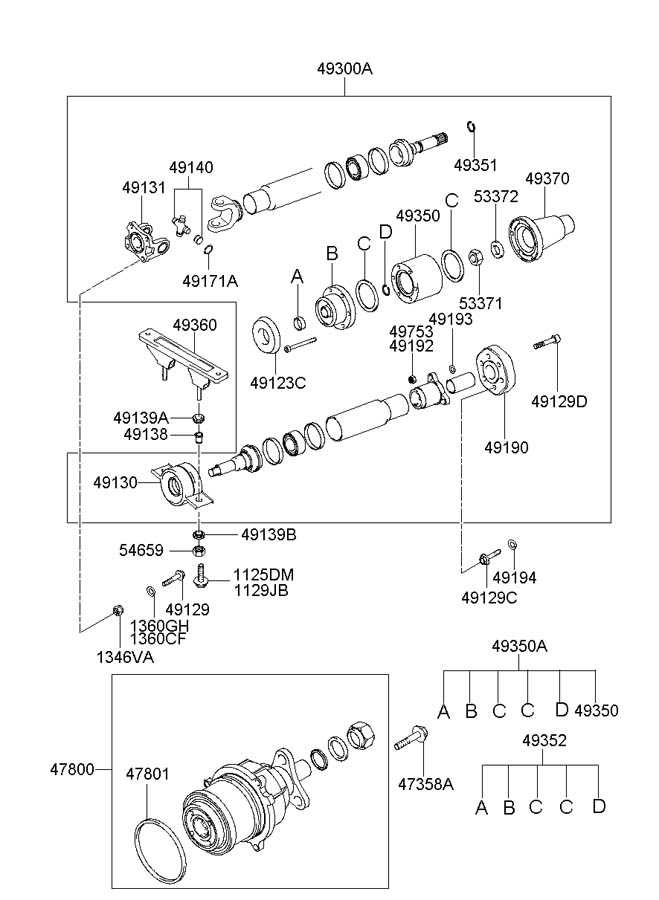
The cooling mechanism of a vehicle is crucial for maintaining optimal engine temperatures and preventing overheating. This system encompasses various components that work together to regulate the temperature effectively, ensuring smooth operation and longevity of the engine.
At the heart of the cooling mechanism is the radiator, which dissipates heat absorbed from the engine coolant. The water pump circulates this coolant through the engine, enabling efficient heat exchange. Additionally, the thermostat plays a vital role by controlling the flow of coolant based on the engine’s temperature, ensuring that it remains within a designated range.
Moreover, hoses connect these essential components, allowing coolant to flow seamlessly throughout the system. Regular maintenance and inspection of these elements are imperative to prevent failures and ensure that the cooling mechanism operates effectively, thus safeguarding the engine from potential damage.
Electrical Wiring Diagram Explained
Understanding the layout and connections of an electrical system is crucial for effective troubleshooting and maintenance. This visual representation serves as a roadmap, detailing how various components interconnect, ensuring optimal functionality.
Electrical schematics provide insights into the arrangement of wires, terminals, and devices. Key features often include:
- Symbols: Unique representations for different components, allowing for quick identification.
- Connections: Lines indicating how elements are linked, crucial for understanding circuit flow.
- Annotations: Descriptive notes that clarify the purpose and specifications of components.
By interpreting these schematics, technicians can diagnose issues more efficiently. Here are some essential elements to consider:
- Power Sources: Identify where the electrical supply originates.
- Load Components: Recognize devices that consume power, such as lights and motors.
- Ground Connections: Understand the grounding paths for safety and stability.
Ultimately, a comprehensive understanding of wiring layouts enhances repair capabilities and ensures reliable performance of the electrical system.
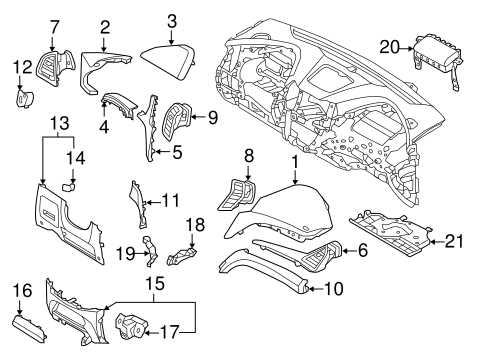
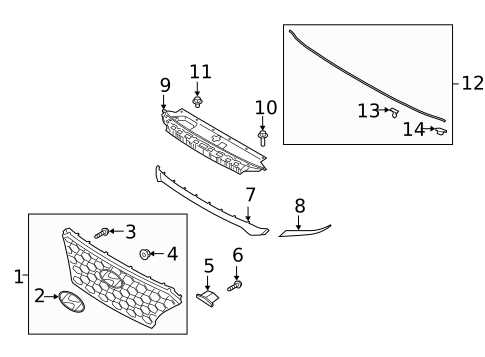
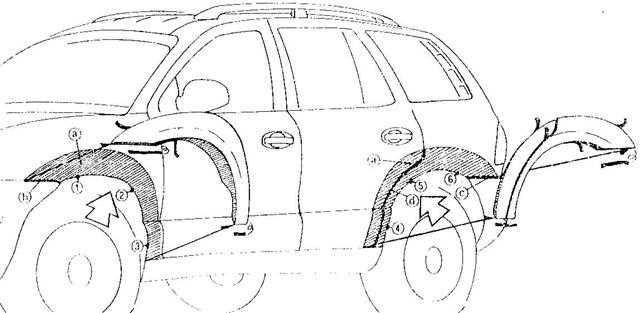
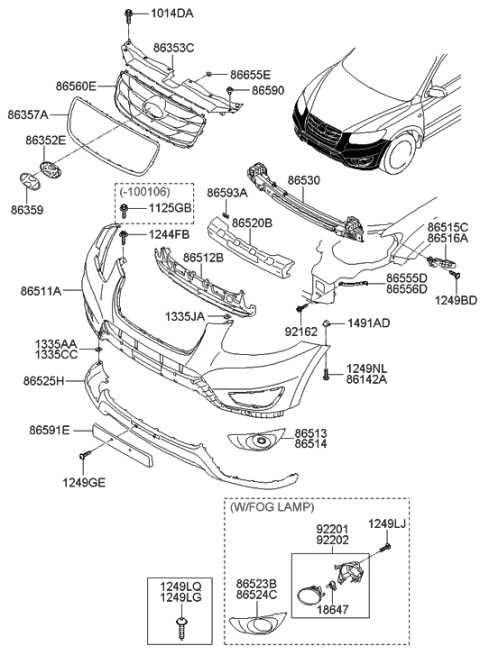
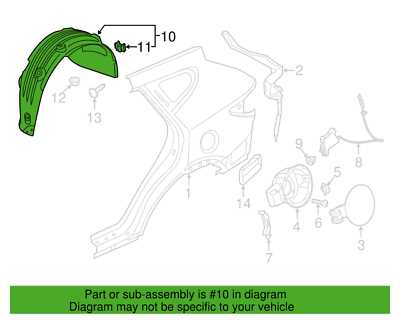
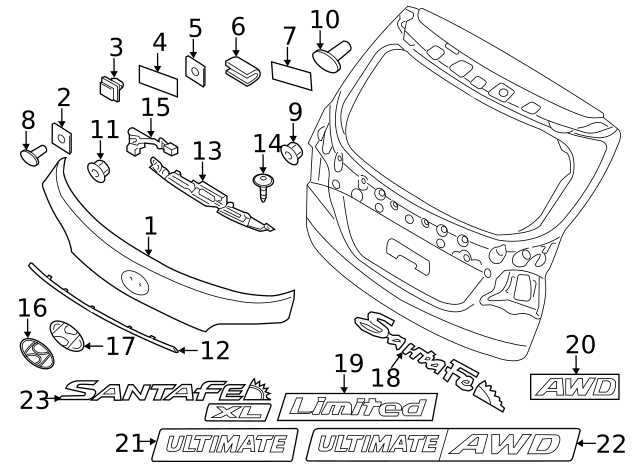
Body Frame and Exterior Panel Components
The structural integrity and aesthetic appeal of a vehicle largely depend on its frame and outer panels. These elements work in unison to provide support, safety, and visual character to the automobile. Understanding the various components that constitute the body frame and exterior panels can enhance maintenance and repair efforts, ensuring longevity and optimal performance.
Key components of the body frame and outer panels include:
- Chassis: The main supporting structure that houses the drivetrain and suspension.
- Fenders: Panels located over the wheels that protect against debris and enhance aerodynamics.
- Doors: Access points that facilitate entry and exit while also contributing to the vehicle’s security.
- Hood: The cover that protects the engine and provides access for maintenance.
- Roof: The uppermost part that offers shelter to occupants and can influence the overall styling.
- Bumpers: Components designed to absorb impact and protect the vehicle’s structure during minor collisions.
- Quarter Panels: Panels located at the rear sides of the vehicle, providing structural support and aesthetic continuity.
Each of these elements is crafted from durable materials to withstand the rigors of daily use. Regular inspections and maintenance of the body frame and exterior components are essential for ensuring the vehicle remains in optimal condition. Addressing any signs of wear or damage promptly can prevent more significant issues down the road.