When it comes to maintaining or upgrading your vehicle, having a clear overview of its mechanical structure is essential. Knowing the specific elements and how they interact can help ensure smoother repairs and a deeper understanding of the overall functionality. A visual breakdown of the components offers an accessible way to identify, locate, and assess the condition of various elements.
By exploring the layout of essential assemblies, you gain valuable insight into how different systems are interconnected. This knowledge can save both time and effort when troubleshooting issues or when planning modifications. Having a clear view of these systems can also aid in choosing the right solutions for keeping your vehicle running optimally.
Overview of the Suzuki Sidekick Components
The vehicle’s structure consists of various essential systems working in unison to ensure optimal performance and safety. Each system plays a unique role, from power generation to maintaining control on the road, contributing to the overall functionality. Understanding these individual components is crucial for effective maintenance and repairs.
Engine and Transmission System
The heart of the vehicle lies in its engine and transmission system. These elements are responsible for producing the necessary power and efficiently transferring it to the wheels. The engine generates the force needed for movement, while the transmission controls the distribution of power depending on driving conditions.
Suspension and Steering Mechanism
The suspension and steering mechanism ensure that the vehicle remains stable and manageable, regardless of terrain. The suspension system absorbs shocks from uneven surfaces, providing comfort during the ride, while the steering mechanism allows precise control, making navigation smooth and responsive.
Suspension System and Key Parts
The suspension mechanism in any vehicle is crucial for ensuring a smooth and stable ride. It is responsible for maintaining contact between the tires and the road, absorbing shocks from uneven surfaces, and enhancing overall vehicle control. This system is composed of multiple components that work together to improve handling, comfort, and safety.
- Shock Absorbers: These are vital for controlling the impact of road irregularities, ensuring the vehicle remains stable and comfortable during motion.
- Control Arms: Essential links between the frame and the wheels, these parts allow the wheels to move up and down while maintaining proper alignment.
- Springs: Whether coil or leaf, springs are critical for supporting the weight of the vehicle and absorbing shocks from the road surface.
- Stabilizer
Engine Bay Layout and Components
The engine bay is a critical section of any vehicle, housing essential mechanical and electrical components that power and support the vehicle’s operation. A clear understanding of this layout helps in identifying the location and function of various systems and components, enabling easier maintenance and troubleshooting.
Main Systems and Their Locations
- Engine Block: The central part of the engine bay, serving as the powerhouse where fuel combustion occurs.
- Transmission: Typically located beneath or adjacent to the engine, this component transfers power to the wheels.
- Cooling System: The radiator and cooling fan, often placed near the front of the bay, regulate engine temperature.
- Air Intake System: Positioned on the side of the bay, the air filter and intake manifold ensure a smooth air supply for combustion.
Additional Key Components
- Battery: Commonly located near the engine bay’s edge, providing power to the electrical system.
- Fuel Tank: The reservoir that stores the fuel before it is sent to the engine.
- Fuel Pump: A device that moves fuel from the tank to the engine, usually located inside the fuel tank.
- Fuel Filter: A component that removes impurities and debris from the fuel before it reaches the engine.
- Fuel Injectors: Nozzles that spray a precise amount of fuel into the engine’s intake manifold or combustion chamber.
- Fuel Lines: Hoses that transport fuel from the tank to the engine and back, designed to withstand high pressure.
- Fenders: Essential for protecting the wheels and reducing splashback.
- Hoods: Serve as a cover for the engine compartment, impacting aerodynamics.
- Doors: Provide access to the cabin while ensuring passenger safety.
- Bumpers: Act as shock absorbers, minimizing damage during low-speed collisions.
- Grilles: Allow airflow to the engine while enhancing the vehicle’s front design.
- Tailgates: Facilitate access to the rear storage area, offering convenience.
Transmission and Gearbox Assembly
The transmission and gearbox unit is essential for transferring engine power to the wheels, ensuring smooth operation and control over different driving conditions. This section outlines the key components involved in the assembly, including the mechanisms that enable gear shifting and power distribution. Understanding the structure and functionality of this system is critical for maintaining optimal vehicle performance.
Main Components
The transmission system includes various components that work together to ensure efficient torque conversion and power delivery. These include the clutch, gear sets, synchronizers, and bearings, all playing a vital role in controlling speed and torque transmission.
Gear Shifting Mechanism
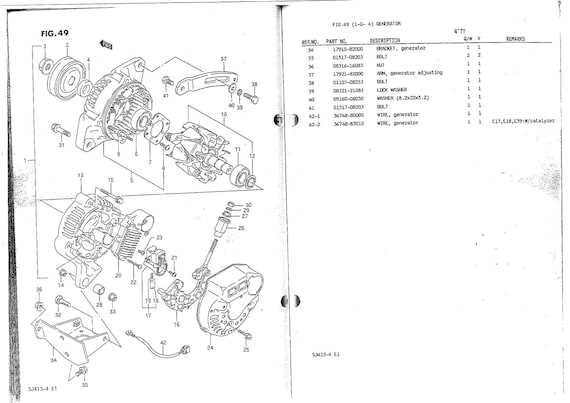
The gear shifting mechanism involves several intricate parts responsible for enabling smooth transitions between different gear ratios. This mechanism relies on a network of selectors, shafts, and linkages to engage and disengage gears effectively.
Component Exhaust System Configuration
The exhaust system plays a crucial role in vehicle performance and environmental impact. Its primary function is to guide combustion gases safely out of the engine while minimizing noise and harmful emissions. Proper design ensures efficiency and compliance with emission standards, while maintaining optimal power output.
Components such as the manifold, catalytic converter, and muffler are key elements that work together to manage exhaust flow. The system’s configuration affects backpressure, which directly influences engine performance. A well-maintained exhaust system helps reduce fuel consumption and improves overall driving experience
Brake Mechanism Structure
The braking system plays a crucial role in ensuring vehicle safety and performance. This mechanism is designed to effectively slow down or halt the motion of the vehicle, relying on various components that work together seamlessly. Understanding the structure of this system is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting.
Components Overview
The brake mechanism consists of several key elements, including the brake pads, rotors, and calipers. The brake pads create friction against the rotors, generating the necessary force to decelerate the vehicle. The calipers house the pads and are responsible for applying pressure, while the rotors provide a surface for the pads to grip.
Working Principle
When the driver engages the brake pedal, hydraulic pressure is created within the system. This pressure activates the calipers, which then push the brake pads against the rotating rotors. The friction produced during this contact generates the stopping power needed to slow down the vehicle. Regular inspection and maintenance of these components are vital to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Electrical Wiring and Fuse Placement
This section provides a comprehensive overview of the electrical connections and fuse locations within the vehicle’s system. Proper understanding of these components is essential for maintaining the functionality and safety of the electrical systems.
Wiring Connections
The wiring harness in a vehicle serves as the nervous system, transmitting power and signals to various electrical components. Ensuring these connections are secure and free from corrosion is vital for optimal performance. Regular inspections can prevent electrical failures and ensure longevity.
Fuse Locations
Fuses are critical for protecting the electrical circuits from overloads. Knowing their locations allows for quick replacements when necessary. Each fuse corresponds to a specific circuit, and understanding their layout aids in troubleshooting electrical issues effectively.
Fuse Number Function Location 1 Headlights Under dashboard 2 Power windows Engine compartment 3 Radio Under steering wheel 4 Air conditioning Fuse box Cooling System and Radiator Diagram
The cooling system is essential for maintaining optimal operating temperatures in an engine. It ensures that the engine does not overheat while functioning, thus preventing potential damage and ensuring longevity. Understanding the components involved is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
At the heart of this system is the radiator, which dissipates heat absorbed from the engine coolant. As the coolant circulates through the engine, it collects heat and then travels to the radiator. Here, the heat is released into the atmosphere, allowing the coolant to return to the engine at a lower temperature.
Key components of the cooling system include the water pump, which circulates the coolant, the thermostat, which regulates coolant flow based on temperature, and various hoses that connect these parts. Each of these elements plays a vital role in ensuring efficient heat management within the engine.
Proper understanding of this system aids in diagnosing issues such as overheating or coolant leaks. Regular inspection and maintenance can help prevent breakdowns and extend the lifespan of the vehicle.
Steering Assembly and Linkage Setup
The steering assembly plays a crucial role in the overall functionality of a vehicle’s directional system. Proper installation and adjustment of the linkage components are essential for optimal performance and control. This section will explore the fundamental aspects of setting up the steering mechanism, ensuring that all elements work in harmony.
To begin, it is important to identify the key components of the steering assembly, including the steering wheel, column, rack and pinion, and linkage rods. Each part must be securely fastened and aligned correctly to facilitate smooth steering. Pay close attention to the torque specifications provided by the manufacturer to avoid any potential issues.
Next, focus on the linkage setup, which connects the steering column to the wheels. The angles and lengths of the rods must be adjusted to maintain accurate alignment. Proper adjustments will enhance the responsiveness of the steering and prevent uneven tire wear.
After assembling the components, conduct a thorough inspection to ensure that all connections are tight and free from wear. Test the steering system by turning the wheel and observing the response of the wheels. Any unusual noises or resistance may indicate a misalignment or a need for further adjustment. Regular maintenance and inspections will contribute to the longevity and reliability of the steering assembly.
Fuel Delivery System Overview
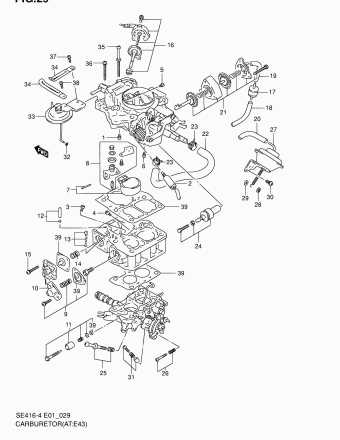
The fuel delivery system plays a crucial role in ensuring the efficient operation of an internal combustion engine. This system is responsible for transporting fuel from the tank to the engine, where it is mixed with air and combusted to generate power. Understanding the components and functioning of this system is essential for proper maintenance and troubleshooting.
Each part of the fuel delivery system works together to ensure that the engine receives a consistent supply of fuel. Regular inspections and maintenance of these components can prevent fuel delivery issues and enhance engine performance.
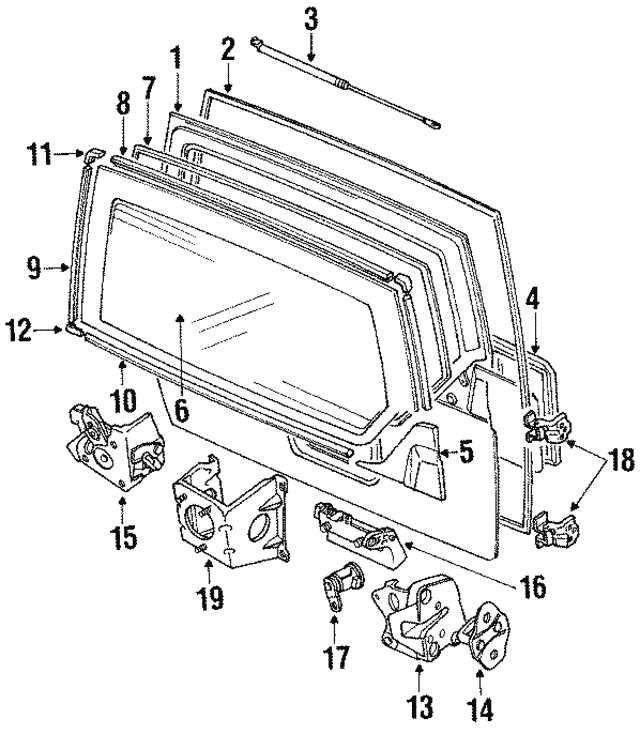
Body Panels and Exterior Components
The exterior elements of a vehicle play a crucial role in its overall appearance, functionality, and structural integrity. These components not only contribute to the aesthetics but also provide protection against environmental factors and impacts.
Key exterior elements include:
Understanding the various components is essential for maintenance and repair, ensuring longevity and performance. When considering modifications or replacements, it’s important to source high-quality materials that match the vehicle’s specifications.
Interior Dashboard and Console Parts
The dashboard and console area of a vehicle play a crucial role in providing a functional and aesthetically pleasing environment for the driver and passengers. This section covers the various components that contribute to the overall operation and comfort of the interior space.
Key Components
In this area, several essential elements work together to enhance the driving experience. Each component serves a specific purpose, from housing controls to displaying vital information about the vehicle’s status.
Common Elements Overview
Component Description Instrument Cluster Displays speed, fuel level, and other critical data. Center Console Houses the gear shifter, audio controls, and storage compartments. Dashboard Trim Provides a decorative finish and protects underlying components. Air Vents Distributes climate-controlled air throughout the cabin. Infotainment System Integrates navigation, audio, and connectivity features. Axle and Drivetrain Layout
This section provides an overview of the configuration of the axle and drivetrain system, which plays a crucial role in transferring power from the engine to the wheels. Understanding this layout is essential for diagnosing performance issues and ensuring optimal functionality.
Components of the Drivetrain
The drivetrain consists of several key elements that work together to deliver power efficiently. These components include the transmission, driveshafts, differentials, and axles. Each part has its specific function, contributing to the overall performance of the vehicle.
Axle Configuration
The axle configuration is designed to support the weight of the vehicle while facilitating smooth motion. Different configurations can affect handling and stability, making it important to understand their arrangement and operation.
Component Function Transmission Transmits power from the engine to the driveshaft. Driveshaft Transfers torque from the transmission to the differential. Differential Allows wheels to rotate at different speeds while providing power. Axles Support the weight of the vehicle and transmit power to the wheels.