Mis
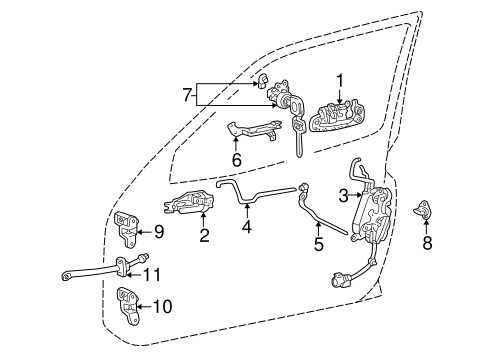
Brake Components Location and Diagram

Understanding the layout of the braking system is crucial for efficient maintenance and repair. This section provides a clear overview of where the key elements of the braking mechanism are positioned, helping to visualize the system’s structure without getting into specific technical definitions. Proper knowledge of these components ensures that the braking function remains reliable.
Main Elements of the Braking System
The essential elements include the hydraulic lines, calipers, brake pads, and rotors. These components work together to convert the force from the pedal into the stopping power needed for safe vehicle operation. The lines distribute pressure, while the calipers and pads interact with the rotors to slow the vehicle down.
Positioning of the Components

The calipers are mounted near the wheels, with the brake pads housed inside them. The rotors are attached directly to the wheel hubs, allowing them to rotate with the wheels. The hydraulic lines connect these parts, ensuring fluid transfers the pressure from the pedal to the calipers. This layout allows for smooth and efficient braking under various conditions.
Cooling System Parts and Layout
The cooling system is essential for maintaining the optimal temperature of the engine during operation. It ensures that the engine doesn’t overheat by circulating coolant through various components. This system is made up of several elements that work together to transfer heat away from the engine and dissipate it efficiently.
Key Components of the System

At the core of this system is the radiator, which plays a crucial role in cooling down the liquid that has absorbed heat from the engine. The water pump helps circulate the coolant, while the thermostat regulates the flow depending on the engine’s temperature. Hoses connect different parts, ensuring smooth circulation.
Flow and Functionality
Coolant travels through a network of hoses, guided by the water pump, and absorbs excess heat from the engine. It is then passed through the radiator, where air flow helps cool it before it’s recirculated. The fan, positioned near the radiator, enhances air flow when needed, particularly during low-speed driving.
Steering Mechanism and Key Elements
The steering mechanism plays a crucial role in guiding a vehicle’s direction, ensuring responsive handling and stability during operation. It consists of various components that work together to translate the driver’s inputs into precise movements of the wheels.
Key elements of this system include the steering wheel, which serves as the primary control interface, allowing the driver to initiate changes in direction. Attached to the steering wheel is the steering column, a vital component that connects the wheel to the steering gear.
Another essential part is the rack and pinion assembly, which converts the rotational motion of the steering wheel into linear movement. This system enhances maneuverability, making it easier to navigate tight corners and maintain control at various speeds. Additionally, the tie rods connect the steering gear to the wheels, ensuring that the directional changes are accurately transmitted to the vehicle’s front end.
Regular inspection and maintenance of these components are vital for optimal performance and safety. Any wear or malfunction in the steering system can lead to compromised handling and increased risk during driving.
Fuel System Components Overview
The fuel system plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and efficiency in a vehicle’s operation. It is responsible for delivering the appropriate amount of fuel to the engine, allowing for effective combustion and energy production. Understanding the key components of this system can provide insights into its functionality and maintenance needs.
Fuel Tank: The fuel tank serves as the storage unit for the fuel, holding it until it is needed by the engine. It is designed to withstand pressure and protect the fuel from contamination.
Fuel Pump: This component is essential for transporting fuel from the tank to the engine. It operates either mechanically or electrically and ensures a consistent flow of fuel under varying conditions.
Fuel Filter: The fuel filter’s primary function is to remove impurities and contaminants from the fuel before it reaches the engine. Regular replacement of this part is important to maintain engine performance.
Fuel Injectors: These devices spray the fuel into the combustion chamber in a fine mist, allowing for better mixing with air and more efficient combustion. Proper functioning of fuel injectors is vital for engine power and efficiency.
Fuel Lines: These hoses transport fuel between the tank, pump, filter, and injectors. They must be durable and resistant to wear and tear to prevent leaks and ensure safety.
Understanding these components is key to recognizing potential issues within the fuel system, enabling timely maintenance and repairs for improved vehicle reliability.
Exhaust System Parts Identification
The exhaust mechanism of a vehicle plays a crucial role in managing emissions and enhancing performance. Understanding the various components of this system is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. Each element serves a specific function, contributing to the overall efficiency of the engine and the reduction of harmful pollutants.
Here are the main components of an exhaust system:
- Exhaust Manifold: This part collects exhaust gases from the engine cylinders and directs them into the exhaust system.
- Catalytic Converter: A vital component that transforms harmful emissions into less harmful substances before they exit the vehicle.
- Resonator: This section helps to minimize noise and optimize sound quality within the exhaust system.
- Muffler: Designed to reduce noise generated by the exhaust gases, ensuring a quieter driving experience.
- Exhaust Pipes: These conduits transport exhaust gases from the manifold through the system and ultimately to the tailpipe.
- Oxygen Sensors: These sensors monitor the level of oxygen in the exhaust gases, assisting in optimizing fuel efficiency and emissions control.
Familiarity with these components will aid in identifying issues and performing necessary repairs or replacements to ensure optimal functioning of the exhaust system.
Electrical Wiring Diagram for 1997 RAV4
This section provides an overview of the electrical system layout for a compact SUV model, highlighting the connections and components essential for proper functionality. Understanding this framework is crucial for troubleshooting and maintaining the vehicle’s electrical systems.
Key Components
- Battery
- Fuse Box
- Wiring Harness
- Starter Motor
- Ignition System
Wiring Overview
The electrical system comprises various circuits, each serving specific functions. Below is a brief description of the main circuits:
- Power Distribution: Distributes electrical energy from the battery to various components.
- Lighting Circuit: Controls headlights, taillights, and interior lights.
- Starting Circuit: Engages the starter motor when the ignition is turned on.
- Accessory Circuit: Powers additional features such as the radio and air conditioning.
Having a clear understanding of the electrical wiring can significantly aid in diagnosing issues and ensuring efficient repairs.
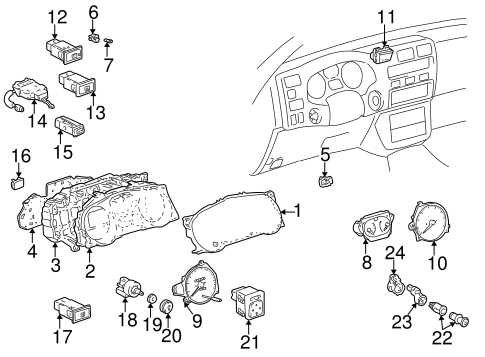
Interior Components and Layout

The interior of a compact SUV is designed to provide a balance of comfort and functionality. This section explores the arrangement of various elements that contribute to an enjoyable driving experience, emphasizing user-friendly design and efficient use of space.
Seating Arrangements

Comfortable seating is essential for both drivers and passengers. The layout typically includes:
- Front bucket seats designed for support and adjustability.
- Rear bench seating that accommodates multiple passengers.
- Flexible seat configurations to maximize cargo space when needed.
Control Interface
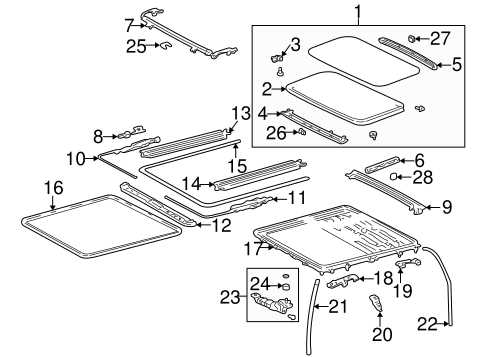
The control interface is integral to the overall driving experience. Key features often include:
- Dashboard with easy-to-read gauges and indicators.
- Central console housing the multimedia system and climate controls.
- Ergonomically placed controls for improved accessibility while driving.
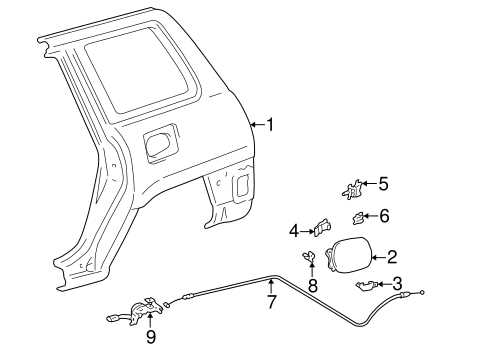
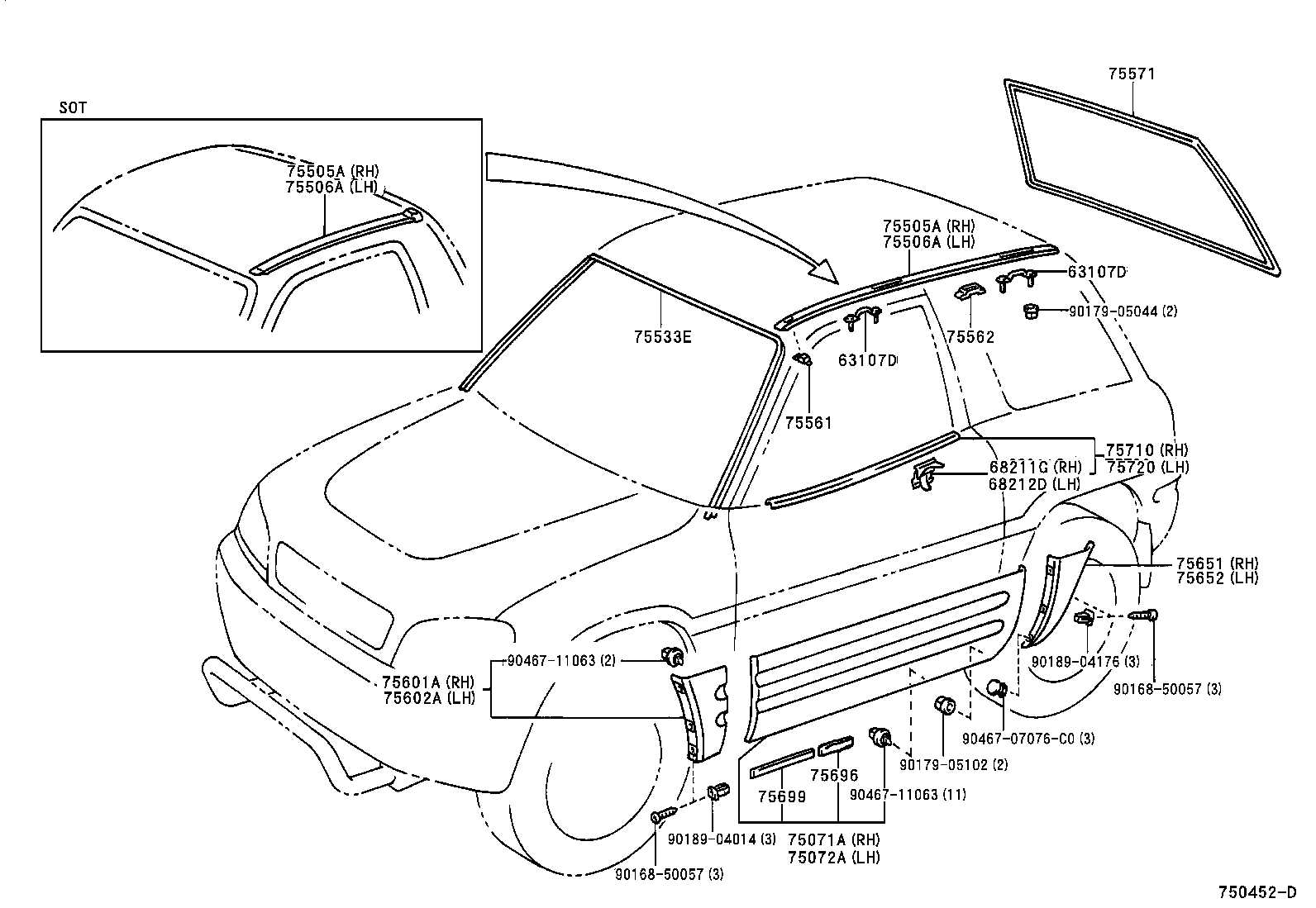
Exterior Body Parts and Assembly
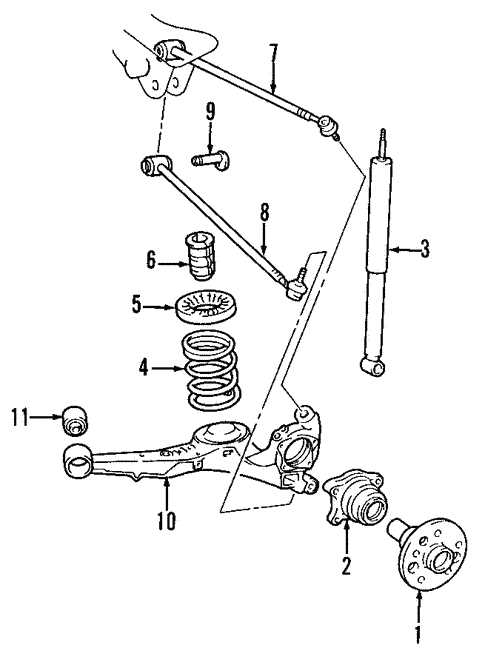
The outer structure of a vehicle is essential for both aesthetics and functionality. This section explores the various components that comprise the vehicle’s exterior, highlighting their roles in providing protection, style, and aerodynamic efficiency. Understanding these elements is crucial for maintenance and repairs, as well as for enhancing the vehicle’s appearance.
Key Components of the Exterior
Several vital elements contribute to the overall design of the vehicle’s outer shell. These include the hood, fenders, doors, and bumpers, each serving a specific purpose. The hood protects the engine while providing access for maintenance. Fenders shield the tires from debris and are integral to the vehicle’s styling. The doors offer entry and exit points, ensuring passenger safety and comfort, while the bumpers absorb impact, reducing damage during collisions.
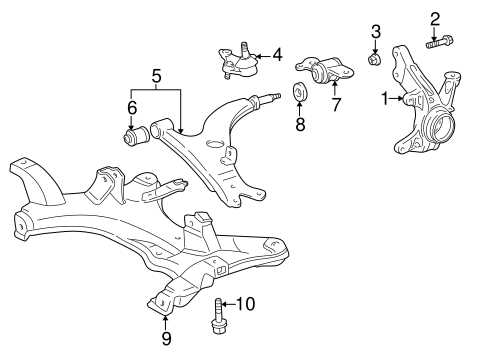
Assembly and Maintenance Considerations
Proper assembly and regular maintenance of the exterior components are vital for the longevity and performance of the vehicle. Ensuring that each part is securely attached and free from rust or damage is crucial for safety. Additionally, regular inspections can prevent costly repairs in the future. Attention to detail during both assembly and maintenance can significantly enhance the vehicle’s lifespan and overall performance.
Air Conditioning System Components
The air conditioning system in a vehicle plays a crucial role in maintaining a comfortable interior climate. It operates by regulating temperature and humidity, utilizing a variety of components that work together seamlessly. Understanding these elements can aid in diagnosing issues and ensuring optimal performance.
Key Elements of the System
Several essential parts contribute to the effective operation of the air conditioning system. Each component has a specific function, making it important to recognize how they interact with one another.
| Component |
Function |
| Compressor |
Pressurizes refrigerant and circulates it through the system. |
| Condenser |
Removes heat from the refrigerant, turning it from gas to liquid. |
| Evaporator |
Absorbs heat from the cabin air, providing cooling. |
| Expansion Valve |
Regulates the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator. |
Maintaining the System
Regular maintenance of the air conditioning system is essential for ensuring its longevity and efficiency. This includes checking refrigerant levels, inspecting components for wear, and cleaning filters to promote proper airflow.