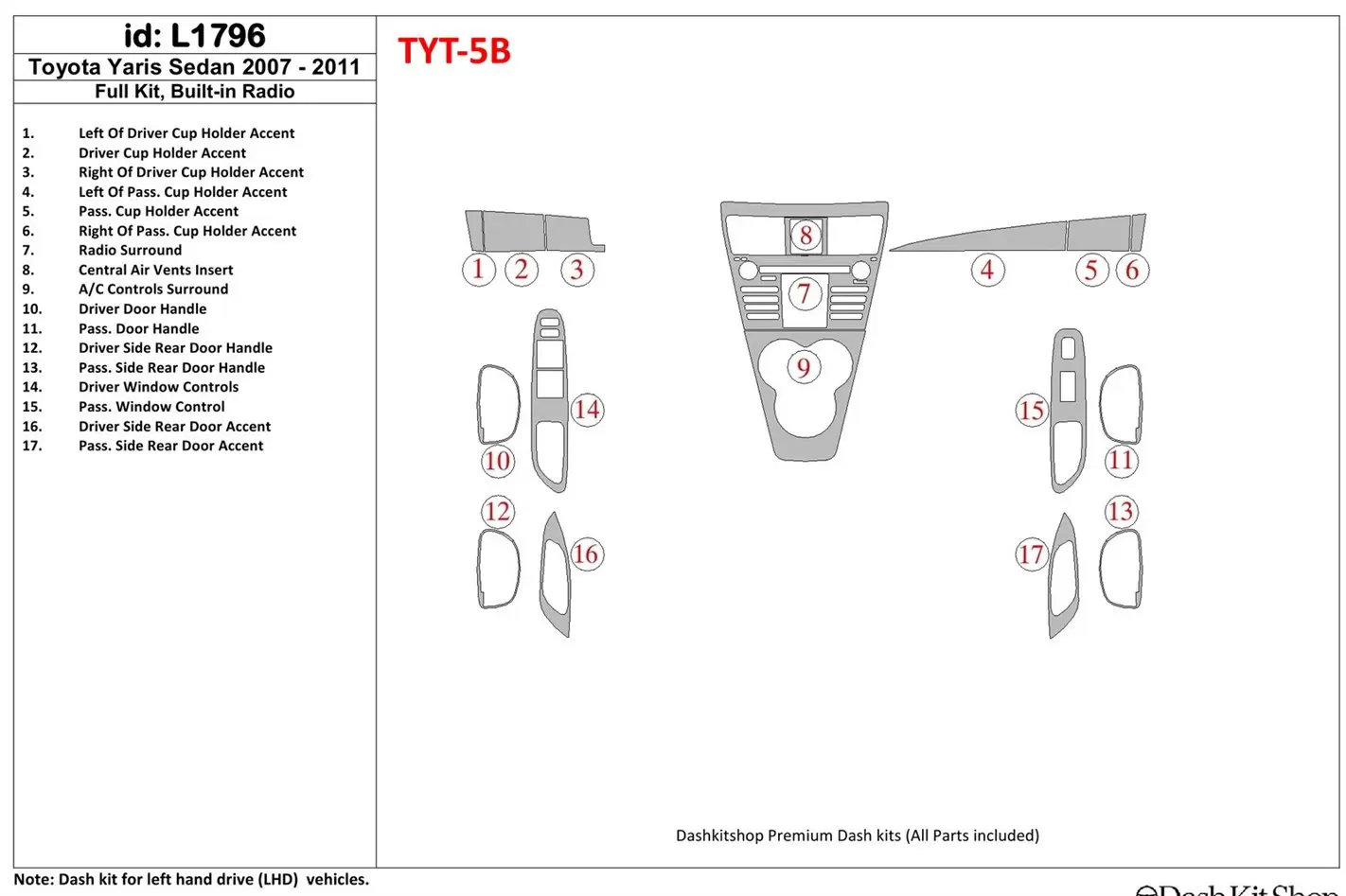
In this section, we will explore the essential elements and structural features that make up the vehicle’s exterior framework. Understanding these interconnected elements is crucial for ensuring both functionality and aesthetic appeal, as well as for maintaining and repairing the external system effectively.
The focus will be on the detailed description of external assemblies, panels, and connections. These components are designed to protect the core mechanical systems and contribute to the vehicle’s aerodynamic efficiency, while also playing a significant role in the overall safety and durability of the car.
By examining the structure in detail, you’ll gain insight into how different sections come together, ensuring a cohesive and well-functioning whole. This will also help identify specific areas that may need attention over time, whether for maintenance or upgrades.
Exterior Design Overview of the 2007 Yaris
The compact vehicle showcases a streamlined silhouette, designed to blend functionality with aesthetics. Its contours highlight an efficient use of space, while maintaining a modern and dynamic appearance. This model is built with urban driving in mind, offering both practicality and visual appeal for city dwellers.
Sleek lines emphasize the aerodynamics, contributing to improved performance on the road. The front section is characterized by a well-proportioned grille and headlights, which flow seamlessly into the overall design. The rear section, with its balanced shape, provides a clean and cohesive look, enhancing the vehicle’s overall aesthetic.
Attention to detail is evident in the carefully crafted exterior, from the bold accents to the smooth curves. This design is not just about looks–it’s built to maximize efficiency and offer a confident presence on the road, merging style with everyday practicality.
Essential Body Panels and Features
Understanding the key external components of a vehicle is important for both aesthetics and functionality. These panels and features play a critical role in providing structural integrity, protecting internal systems, and enhancing the overall look of the car.
- Front Section Elements: Includes components that form the visible front portion, offering both style and impact resistance.
- Side Sections: Panels on each side that not only contribute to the streamlined design but also provide protection from external impacts.
- Rear Structure: These elements define the back end, housing important safety features and storage access points.
- Protective Features: Reinforcements designed to absorb shock, minimize damage, and ensure the safety of passengers and cargo.
Each of these components works together to create a durable and visually appealing exterior, ensuring the vehicle remains reliable and attractive.
Front Bumper Assembly and Components
The front bumper plays a crucial role in both the aesthetics and safety of a vehicle. It not only enhances the overall appearance but also serves to absorb impact during collisions. This section provides an overview of the various elements that come together to form the complete front bumper assembly.
Main Structural Elements
The bumper is typically made of a sturdy material designed to withstand minor impacts. Its core structure often includes reinforcements and brackets that help secure the assembly to the car frame. These components work together to provide stability and protect critical areas of the vehicle’s front.
Additional Components
In addition to the main structure, the assembly includes smaller elements such as clips, covers, and fasteners. These parts ensure that everything stays in place and contributes to a seamless appearance. Some assemblies may also feature slots for additional accessories like fog lights or sensors for enhanced functionality.
Parts Breakdown for Impact Protection
When it comes to ensuring safety during a collision, specific components are designed to absorb and redistribute force. These elements work together to minimize damage and protect passengers, reducing the potential for injury.
- Reinforcement beams: These are integral structures within the vehicle that provide additional strength to the frame, helping to withstand side and frontal impacts.
- Crumple zones: Specially engineered sections that deform upon impact, absorbing energy to prevent it from transferring to the cabin.
- Bumper assemblies: Designed to take the brunt of lower-speed collisions, these assemblies cushion the initial shock and reduce damage to critical areas.
- Airbag systems: Though not part of the external structure, airbags play a crucial role in protecting passengers from direct impact.
By working in unison, these components offer comprehensive protection, allowing the vehicle to manage energy efficiently during a collision.
Understanding the Hood Structure and Materials
The front cover plays a crucial role in both protecting the engine compartment and contributing to the vehicle’s overall aerodynamic efficiency. It is designed to withstand various external elements while maintaining a balance between strength and weight. This section explores how the front panel is constructed and the materials commonly used for its production, emphasizing durability, safety, and performance.
Key Components of the Cover Design
The front panel consists of an outer shell and an inner support structure. The outer layer is primarily responsible for the vehicle’s sleek appearance, while the inner framework provides structural integrity. These two layers work in tandem to absorb impact forces, enhancing safety in the event of a collision.
Materials Commonly Used in Construction
Modern panels are often made from lightweight metals, such as aluminum or steel alloys, chosen for their durability and resistance to corrosion. In some cases, composite materials like carbon fiber or reinforced plastics are also utilized to further reduce weight without compromising on strength.
Key Aspects of Durability and Functionality
Understanding the essential characteristics that contribute to the longevity and performance of vehicle components is crucial for any car owner. This section delves into the vital elements that enhance both resilience and operational efficiency of various automotive components.
- Material Quality: The choice of materials directly impacts the lifespan of components. High-grade metals and polymers are typically preferred for their strength and resistance to wear.
- Design Engineering: Thoughtful design enhances the integration of parts, ensuring they work harmoniously together. This synergy is essential for optimal functionality.
- Maintenance Considerations: Regular upkeep is vital for maintaining performance. Proper servicing can significantly extend the life of vehicle elements.
- Environmental Resistance: Components should be designed to withstand various environmental factors, including moisture, heat, and corrosive substances, to prevent premature failure.
Overall, the combination of high-quality materials, innovative design, and proactive maintenance plays a significant role in ensuring that automotive components deliver reliable performance over time.
Fender Analysis for the 2007 Yaris
The fender plays a crucial role in the overall structure of a vehicle, contributing not only to aesthetic appeal but also to functional integrity. This section explores the significance of this component, examining its design, materials, and impact on performance.
Design Considerations
The shape and curvature of the fender are engineered to enhance aerodynamics and protect vital systems. Its contours must seamlessly align with adjacent sections, ensuring a cohesive appearance while minimizing air resistance. Attention to detail in design aids in optimizing vehicle dynamics.
Material Composition
Fenders are commonly constructed from a variety of materials, each offering unique benefits. Lightweight composites, metals, and plastics are frequently utilized, striking a balance between durability and weight. Understanding the material properties is essential for assessing repairability and longevity.
Impact on Performance
The fender’s design directly influences both safety and handling. In the event of an impact, it absorbs energy, reducing damage to internal components. Additionally, its integration with the suspension system plays a vital role in managing road contact, thereby affecting driving stability and comfort.
In conclusion, a comprehensive analysis of the fender reveals its multifaceted importance in vehicle design and functionality. By understanding its role, owners and enthusiasts can better appreciate the engineering that goes into maintaining optimal performance.
Materials and Positioning of Side Panels
The side panels of a vehicle play a crucial role in both aesthetic appeal and structural integrity. They are designed to provide support and protection while enhancing the overall look of the automobile. Understanding the materials used and their positioning is essential for ensuring durability and functionality.
Common Materials Used
- Steel: Often utilized for its strength and resilience, offering excellent protection against impacts.
- Aluminum: Lighter than steel, this material contributes to improved fuel efficiency while maintaining sufficient rigidity.
- Plastic: Frequently used in modern designs, plastics are lightweight and can be molded into various shapes, allowing for more complex designs.
Positioning Considerations

Proper positioning of the side panels is vital for both safety and aesthetics. Factors influencing their placement include:
- Alignment with Frame: Ensuring panels are correctly aligned with the vehicle’s frame enhances structural stability.
- Sealing and Weatherproofing: Accurate positioning helps in creating effective seals, preventing water and debris intrusion.
- Impact Zones: Strategically placing panels in high-impact areas enhances the vehicle’s safety profile.
Detailed View of the Rear Bumper
The rear protective structure of a vehicle plays a crucial role in both aesthetics and functionality. It not only enhances the overall design but also safeguards the rear section from potential impacts. Understanding its components and design features can aid in maintenance and repairs.
Components Overview
This protective element consists of several key components, including the main casing, reinforcement elements, and mounting brackets. Each component is designed to absorb shock and provide durability. The outer shell is typically made from resilient materials, ensuring long-lasting protection against wear and tear.
Installation and Maintenance
Proper installation is vital for optimal performance. It is essential to ensure that all fittings are secure and aligned accurately. Regular inspections can help identify any signs of damage or wear, allowing for timely repairs. Keeping this part in good condition not only preserves the vehicle’s appearance but also contributes to overall safety.
Crash Resistance and Key Elements
The structural integrity and safety features of a vehicle are crucial for ensuring protection during collisions. Various components work together to absorb impact forces and maintain occupant safety. Understanding these elements can enhance awareness of a vehicle’s resilience in the event of an accident.
- Frame Design: The framework plays a pivotal role in distributing impact forces, minimizing deformation during a crash.
- Crush Zones: These areas are strategically engineered to deform in a controlled manner, absorbing energy and reducing the force transmitted to occupants.
- Safety Cell: A reinforced compartment that surrounds passengers, designed to preserve integrity and protect occupants from external forces.
- Airbags: Deployed in various scenarios, these devices cushion occupants during collisions, significantly reducing the risk of injury.
- Seatbelt Systems: Advanced restraining systems ensure that occupants remain securely in place, minimizing movement during sudden stops or impacts.
Overall, a vehicle’s safety architecture integrates these features, significantly enhancing crash resistance and occupant protection. Understanding these elements helps drivers make informed choices regarding vehicle safety and design.
Doors and Related Mechanisms Breakdown
This section provides an in-depth overview of the various components associated with vehicle entryways and their functional elements. Understanding these elements is essential for maintaining optimal performance and ensuring security.
Key Components of Entryways
- Outer panels
- Inner panels
- Window assemblies
- Locks and latches
- Seals and weatherstrips
Functionality and Importance
The mechanisms that facilitate the opening and closing of entryways play a crucial role in user experience and vehicle safety. Proper operation of these components ensures secure access while protecting against environmental factors.
Regular inspection of these mechanisms is advised to prevent malfunctions and prolong their lifespan. Neglecting maintenance can lead to issues such as improper sealing or difficulty in accessing the vehicle.
Locks, Handles, and Internal Structures
This section delves into the essential components that ensure functionality and security within a vehicle’s entry and closure systems. These elements play a crucial role in the overall usability and safety of the automobile, contributing to both convenience and protection.
Key Components
- Locks: Mechanisms that provide security, preventing unauthorized access and ensuring that doors remain closed during operation.
- Handles: Interfaces that allow occupants to easily open and close doors, often designed for ergonomic efficiency.
- Internal Structures: Frameworks that support locking mechanisms and handles, ensuring durability and reliability under various conditions.
Functionality and Design
The integration of these components reflects a balance between aesthetics and practical function. Locks must be robust yet unobtrusive, while handles need to be accessible without compromising the vehicle’s design integrity. The internal structures must withstand daily use while maintaining the vehicle’s structural integrity.
- Regular maintenance is essential for optimal performance of locking systems.
- Handle ergonomics significantly influence user experience.
- Innovations in materials enhance the durability of internal frameworks.
Roof Design and Components
The structure atop a compact vehicle plays a vital role in both aesthetics and functionality. It is designed to ensure stability while contributing to the overall appearance. The materials and components used in its construction are engineered to withstand various environmental factors, enhancing durability and safety.
Within this framework, several essential elements work in unison to provide support and protection. These components include reinforcements, drainage systems, and insulation, all of which are crucial for maintaining comfort and preventing water ingress. Understanding the interplay of these features can aid in appreciating the design intricacies involved.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Roof Panel | Main structural element that defines the roof’s shape. |
| Reinforcement Beams | Support structures that enhance rigidity and safety. |
| Weather Stripping | Seals that prevent water and air leaks. |
| Drainage Channels | Paths that direct water away from the interior. |
| Insulation Material | Reduces noise and temperature fluctuations. |