Understanding the layout and connections of various elements within a widely-used SUV can be essential for maintenance, repair, or customization. Knowing where each element is positioned, and how they interact with others, allows for easier navigation through technical challenges. This guide delves into the intricate details of these placements, offering insights into their relationships.
The focus here is on providing a thorough analysis of how individual assemblies come together to form a cohesive whole. Each system, from the exterior structure to internal mechanisms, is explored to offer a better grasp of their roles and functionalities. These insights aim to support
Comprehensive Overview of 2009 RAV4 Components

This section provides an in-depth look at the various elements that make up this vehicle, emphasizing the key areas of its structure and mechanical design. From the systems that drive it forward to those that ensure a smooth and safe experience, understanding each aspect contributes to a better grasp of its overall performance.
Mechanical and Powertrain Elements
The engine system serves as the heart, connecting to a range of mechanisms that manage acceleration and power distribution. This includes crucial elements like the transmission unit, which ensures seamless shifting and adapts to different driving conditions. Supporting these are the cooling components, ensuring temperature control and maintaining optimal conditions during operation.
- Transmission System: Designed for smooth power
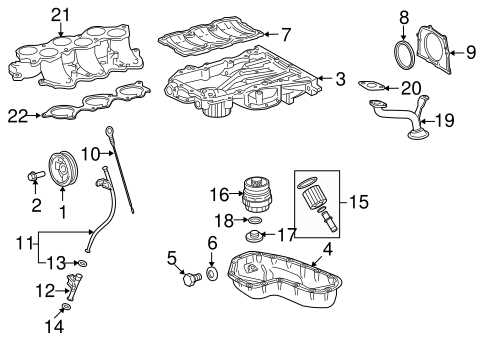
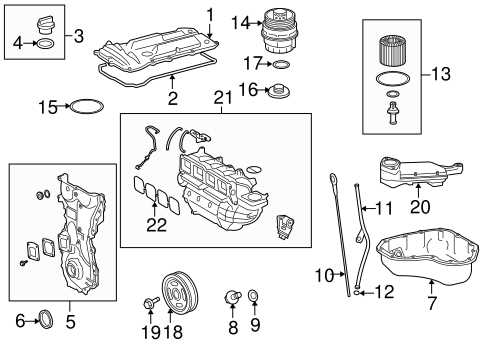
Engine System Layout and Key Elements
The structure of the power unit encompasses various interconnected components that ensure smooth operation and optimal performance. Understanding the arrangement of these elements can help in maintenance, troubleshooting, and efficient repair processes.
- Combustion Chamber: The core of energy conversion, where fuel mixes with air and ignites to create the necessary force for movement.
- Intake and Exhaust Manifolds: These channels guide air into the engine and expel exhaust gases, ensuring a balanced flow and maintaining efficiency.
- Cooling Mechanism: A critical part that prevents overheating, utilizing coolant flow to stabilize the temperature within the unit.
- Fuel Delivery System:
Understanding the Transmission Structure
The mechanism responsible for shifting between different speeds is crucial for efficient movement. It ensures that the vehicle adapts to various driving conditions by controlling power distribution from the engine to the wheels. This structure is a complex assembly of interconnected components that work in harmony to provide smooth acceleration and stability during motion.
Core Components and Their Roles: The system consists of several key parts that interact to change speed and torque. Gears, shafts, and clutches form the core, each playing a vital role in adjusting the output to match driving needs. The gears vary in size and function to modify the power delivered to the wheels, providing either more
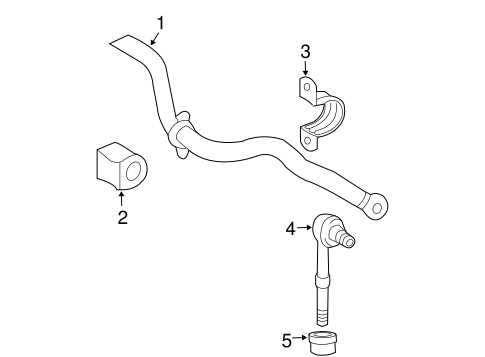
Suspension Design and Main Components
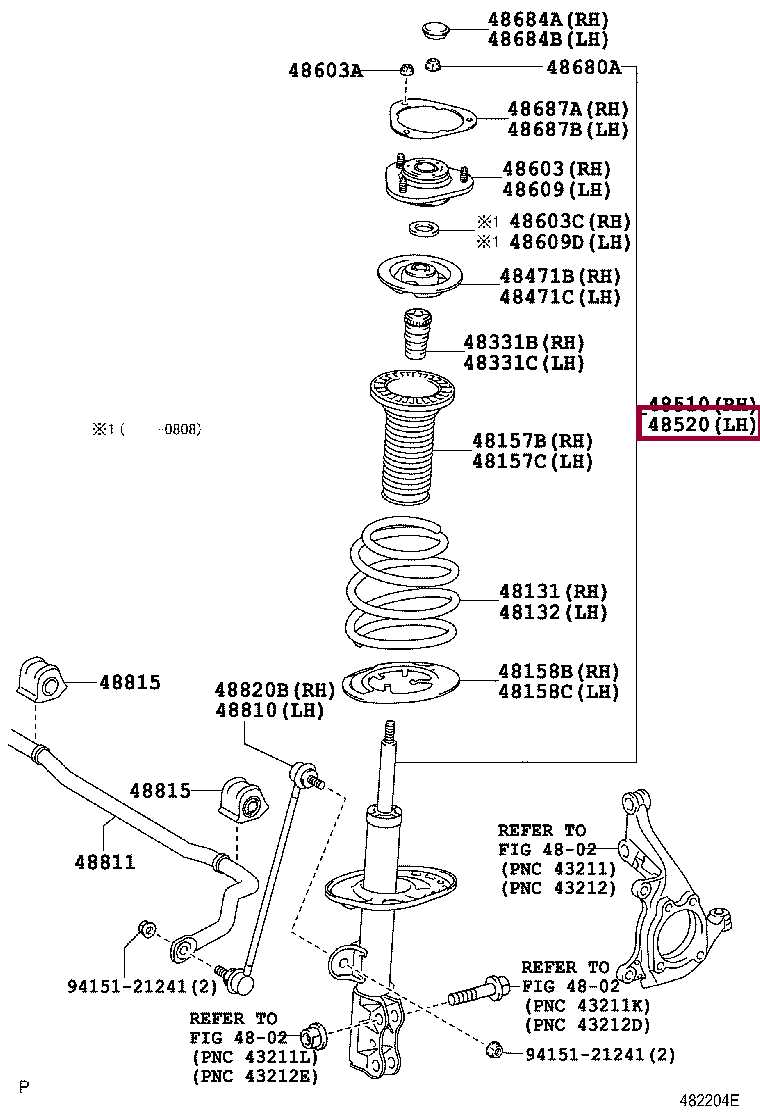
The structure responsible for ensuring a smooth and stable ride involves a complex arrangement of interconnected elements. This system is essential for maintaining road contact, absorbing shocks, and providing control during various driving conditions. Each element within the system works together to manage the vehicle’s dynamics, ensuring stability and comfort.
Shock Absorbers and Struts are crucial in reducing the impact of bumps and uneven surfaces. They help to maintain tire contact with the ground by controlling the movement of the springs, which ensures a balanced driving experience.
Control Arms
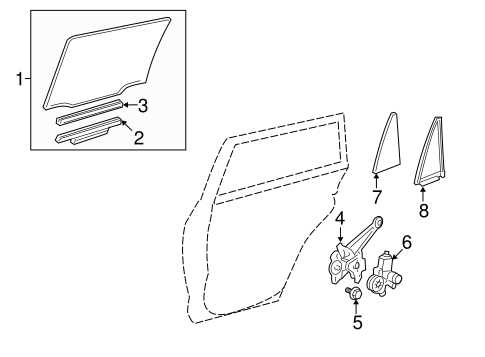
Exploring the Brake Assembly
The brake system is a crucial part of a vehicle, designed to ensure safe and effective stopping power. Understanding the various components that make up this system can help in maintaining and troubleshooting any issues that may arise. Below, we will break down the key elements involved in this assembly, highlighting their roles and interactions.
- Disc and Drum Mechanisms: These are the primary components responsible for generating friction to slow down the vehicle. Discs are common in the front, while drums might be found on the rear wheels, depending on the model.
- Calipers and Wheel Cylinders: These devices apply pressure to the friction surfaces. Calipers are typically used with disc systems,
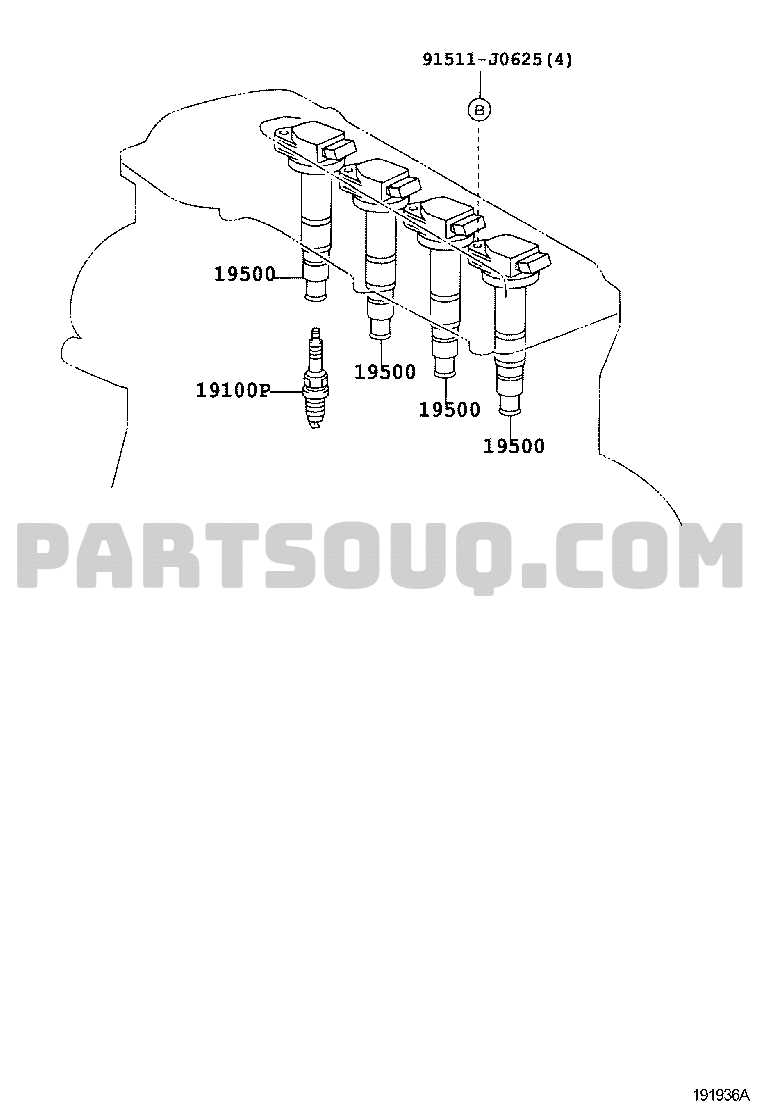
Interior Electrical System Breakdown
The interior electrical network of a vehicle plays a crucial role in ensuring comfort, convenience, and safety. This system encompasses various components that facilitate the functioning of lights, climate control, infotainment, and other essential features within the cabin. Understanding how these elements interconnect provides valuable insights into the overall performance and reliability of the vehicle.
Component Function Dashboard Lights Illuminate gauges and indicators for better visibility during night driving. Power Windows Allow for easy adjustment of window positions with a simple switch. Central Locking System Enables simultaneous locking or unlocking of all doors from the driver’s side. Audio System Provides entertainment and connectivity options for passengers. Climate Control Regulates temperature and airflow for passenger comfort. Interior Lights Enhance visibility inside the cabin and assist entry and exit. Cooling System Parts Overview
The cooling system is a crucial component of any vehicle, ensuring optimal engine performance by regulating temperature. It comprises several key elements that work together to maintain efficient thermal management, preventing overheating and promoting longevity.
Radiator: This essential unit dissipates heat from the coolant fluid, allowing it to cool down before returning to the engine. A properly functioning radiator is vital for maintaining the right operating temperature.
Water Pump: This component circulates coolant throughout the system, ensuring that heat is effectively transferred away from the engine. The water pump’s efficiency directly impacts the overall performance of the cooling mechanism.
Thermostat: Acting as a valve, this device regulates the flow of coolant based on temperature, ensuring that the engine reaches its optimal operating temperature quickly while preventing overheating.
Cooling Fans: These fans help enhance airflow through the radiator, especially when the vehicle is stationary or moving slowly. They activate automatically based on the coolant temperature to maintain proper cooling levels.
Hoses: These flexible conduits transport coolant between various components of the system, playing a critical role in maintaining fluid circulation. The integrity of these hoses is essential to prevent leaks and ensure system efficiency.
Understanding the function of each element in the cooling system is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. Regular checks and timely replacements of these components can significantly enhance engine performance and reliability.
Exhaust Configuration and Parts Layout
The arrangement and components of the exhaust system play a crucial role in optimizing vehicle performance and minimizing emissions. A well-designed exhaust assembly enhances engine efficiency while ensuring that harmful gases are expelled effectively. Understanding the layout of these elements is essential for maintenance and upgrades.
Key Components of the Exhaust System
This system comprises several integral parts that work in harmony to facilitate exhaust flow. The primary components include the manifold, catalytic converter, muffler, and piping. Each element contributes to reducing noise and harmful emissions while improving overall vehicle performance.
Configuration Overview
The configuration typically follows a systematic layout, starting from the engine and extending to the rear of the vehicle. This setup not only aids in efficient gas expulsion but also contributes to sound attenuation. Proper alignment and sealing of these components are vital for optimal functionality.
Component Description Manifold Connects to the engine and collects exhaust gases. Catalytic Converter Reduces harmful emissions through chemical reactions. Muffler Reduces noise produced by the exhaust gases. Piping Directs exhaust flow from the engine to the rear. Body Frame and Structural Details
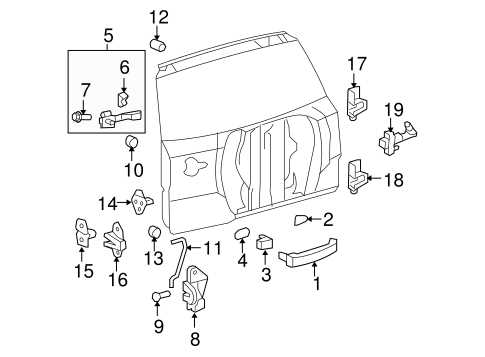
This section provides an overview of the essential components that contribute to the overall framework and rigidity of the vehicle. Understanding these elements is crucial for ensuring optimal safety, performance, and durability over time.
Key Structural Components
- Chassis: The main support structure that houses various parts and systems, providing stability and strength.
- Body Panels: Outer coverings that enhance aesthetic appeal and protect internal components from environmental factors.
- Reinforcement Beams: Additional supports designed to absorb impact and protect occupants during collisions.
- Subframes: Secondary frames that support specific systems such as the engine and suspension, aiding in weight distribution and handling.
Importance of Structural Integrity
Maintaining the integrity of the frame and structural components is vital for vehicle safety and performance. Regular inspections and repairs can help prevent potential issues related to corrosion, wear, and tear.
- Inspect for rust or damage regularly.
- Ensure proper alignment of all structural components.
- Address any signs of deformation immediately.
Fuel Delivery System Analysis
The mechanism responsible for supplying combustible material to the engine plays a crucial role in the overall performance and efficiency of any vehicle. This system encompasses various components that work synergistically to ensure optimal fuel flow, allowing for effective combustion and engine operation.
At the core of this setup is the fuel pump, which is tasked with transporting the liquid fuel from the storage tank to the engine. The pump must maintain a consistent pressure to guarantee that the engine receives the appropriate amount of fuel for its requirements. Following the pump, fuel filters are essential in preventing impurities from reaching the engine, thereby protecting critical components from damage.
The fuel injectors represent another vital element, delivering precise amounts of fuel into the combustion chamber at the right moments. This precision is key to achieving efficient fuel usage and minimizing emissions. Additionally, the fuel rail serves as a conduit, ensuring that the fuel is evenly distributed to all injectors.
Overall, the analysis of the delivery system is integral to understanding how various parts interact to influence fuel efficiency and engine performance. Regular maintenance and inspection of these components can help identify potential issues before they escalate, ensuring a reliable driving experience.
Steering Mechanism and Associated

The steering system is crucial for vehicle handling and maneuverability, enabling precise control over direction and stability. This assembly consists of several components working in unison to ensure smooth operation and responsiveness to driver inputs.
Component Description Steering Wheel The primary interface for the driver to direct the vehicle. Steering Column Connects the steering wheel to the steering mechanism, allowing for rotation and control. Steering Gear Transforms the rotational motion of the steering wheel into lateral movement of the wheels. Linkage Consists of rods and joints that transmit movement from the gear to the wheels. Power Steering Pump Assists in steering by providing hydraulic pressure to reduce effort required by the driver. Steering Rack Converts the rotational motion of the steering gear into linear motion, moving the wheels. Regular maintenance of the steering components is essential for safety and performance. Proper lubrication, alignment, and inspections can prevent wear and enhance the lifespan of the system.