Exploring the internal structure of mechanical systems in agricultural equipment can be highly beneficial for maintenance and repairs. A detailed schematic helps in visualizing the arrangement and function of various elements, offering a clear path to troubleshooting and part identification. This overview simplifies the process, making it more accessible even for those with limited technical experience.
By breaking down complex assemblies into smaller segments, it becomes easier to pinpoint the location of specific items and understand their interactions. Such insights are crucial for ensuring efficient operation, as well as extending the lifespan of the machinery through proper upkeep. This guide aims to provide a clear understanding of how these systems work together.
Ford NAA Tractor Overview
This model, introduced in the early 1950s, marked a significant step forward in agricultural machinery. It was designed to meet the evolving needs of farmers by offering more advanced features and a stronger build, ideal for a wide range of fieldwork tasks. With its innovative engineering, this machine quickly became popular for its reliability and efficiency.
One of the standout characteristics of this agricultural tool is its enhanced engine power, which allowed for better performance in tougher conditions. Additionally, the hydraulics system was an upgrade from previous models, offering smoother operation and more control during various activities.
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Engine Type | 4-cylinder gasoline |
| Horsepower | 32 hp |
| Hydraulic System | Live hydraulics |
| Transmission | 4-speed manual |
Main Components of the Ford NAA Tractor
The machine in question is composed of several key systems that ensure its smooth operation. These components work together, allowing the equipment to perform a variety of tasks efficiently in agricultural settings. Understanding the basic structure and functions of each part is essential for maintaining the machinery in good working condition.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Engine | Provides the necessary power for all mechanical functions, converting fuel into energy. |
| Transmission | Allows the operator to control speed and direction by transmitting power from the motor to the wheels. |
| Hydraulic System | Facilitates the lifting and lowering of attachments, such as plows or loaders. |
| Steering Mechanism | Enables smooth maneuvering of the equipment, providing precision control in various conditions. |
| Braking System | Ensures the equipment can be safely stopped when necessary, controlling its movement during operation. |
Engine Parts Diagram for Ford NAA

The structure of the power unit is a complex system, consisting of multiple key components that work together to ensure smooth operation. Understanding how these elements are interconnected helps in maintaining and servicing the machinery efficiently. This section will provide an overview of essential components, highlighting their roles within the engine assembly.
- Cylinder Block: The foundation that houses essential moving parts, providing structural integrity to the entire assembly.
- Pistons: These parts convert the energy from combustion into mechanical power, driving the machinery.
- Crankshaft: A crucial rotating element that translates the linear movement of pistons into rotational energy.
- Valves: Responsible for controlling the flow of air and fuel into the engine while allowing exhaust gases to exit.
- Camshaft: This component synchronizes the opening and closing of valves, ensuring precise timing during the operation.
- Oil Pump: Essential for lubricating all moving parts, reducing friction, and ensuring a longer lifespan of the engine.
- Flywheel: Helps in stabilizing the speed of the engine by storing rotational energy.
Each of these components plays a critical role in ensuring that the engine operates efficiently. Proper maintenance of these elements is vital for preventing malfunctions and extending the life of the machinery.
Key Engine Components Breakdown
Understanding the main elements that form the heart of an engine is crucial for anyone looking to maintain or repair it. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring the machine operates smoothly and efficiently. In this section, we will provide an overview of the core systems that contribute to its performance, without diving into overly technical terms.
Cylinder and Piston System
The cylinder and piston assembly is where the combustion process takes place, converting fuel into mechanical power. The piston moves within the cylinder, compressing the fuel-air mixture and allowing ignition to occur, which in turn drives the machinery.
Crankshaft and Camshaft Interaction
The crankshaft transforms the vertical motion of the pistons into rotational energy, while the camshaft controls the opening and closing of the valves, ensuring precise timing for fuel intake and exhaust release. These two components work in harmony to regulate engine cycles and maintain efficient operation.
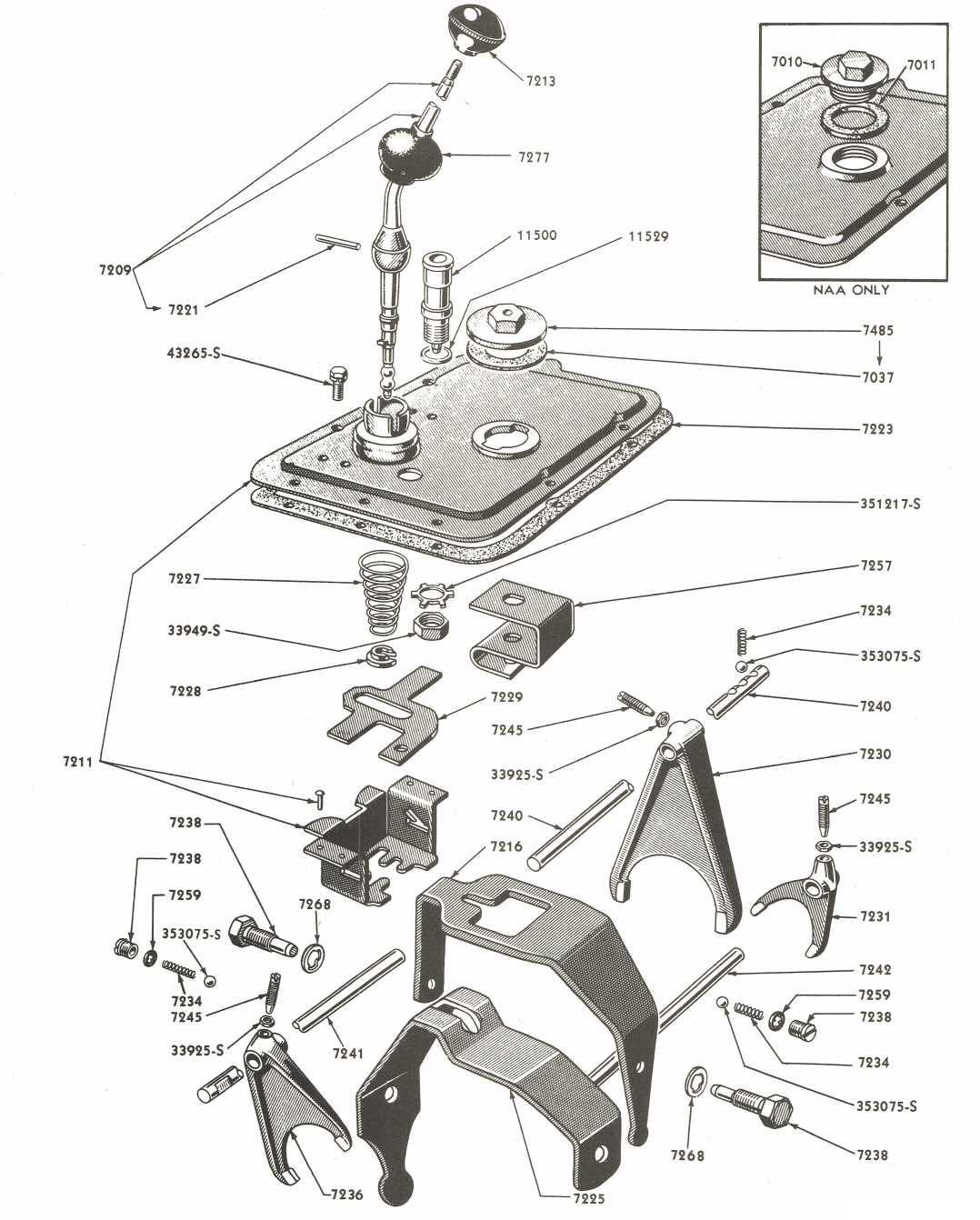
Transmission System Overview for Ford NAA

The transmission mechanism is a crucial component that manages the transfer of power from the engine to the wheels, enabling smooth movement and control of the machinery. Understanding its structure and functions allows for efficient operation and troubleshooting when needed.
The system consists of multiple elements that work together in harmony to ensure the machine can change gears, manage speed, and handle various loads during operation. Below is a breakdown of the main components:
- Clutch: Engages and disengages the power flow between the engine and transmission, allowing for gear shifting without damaging the machine.
- Gearbox: Houses the gears that alter the speed and torque, providing the necessary range for different operational conditions.
- Drive Shaft: Transfers the rotational power from the gearbox to the differential.
- Differential: Balances the power distribution between the wheels, especially when turning or working on uneven terrain.
Each component plays a vital role in ensuring the overall efficiency of the machine’s operation, making regular inspection and maintenance essential for long-term reliability.
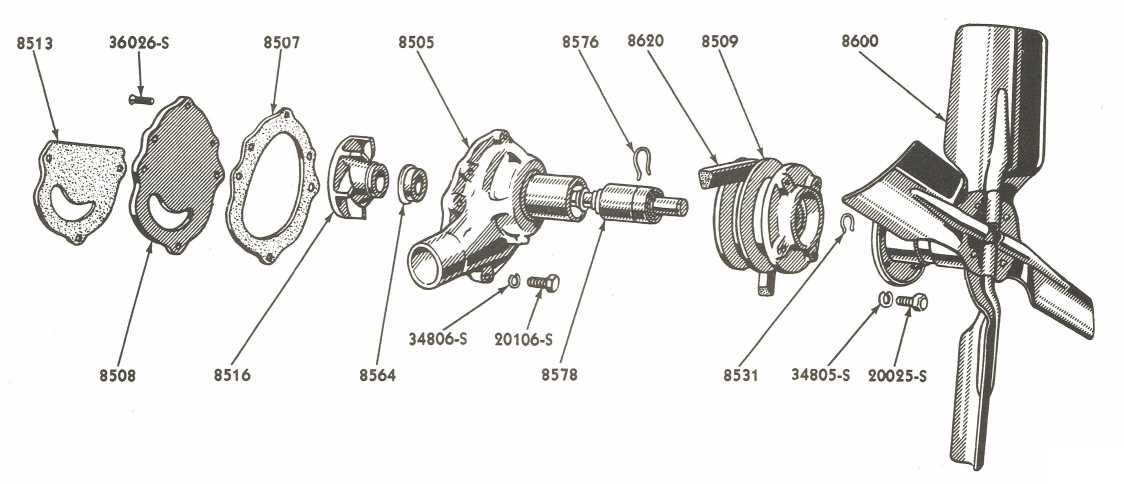
Ford NAA Transmission Parts Layout
This section provides an overview of the configuration and arrangement of key components within the transmission system of a specific agricultural vehicle. Understanding the layout is essential for effective maintenance and repair, ensuring optimal performance during operation.
Component Overview
The transmission system consists of various elements that work together to facilitate the transfer of power from the engine to the wheels. Major components include gears, shafts, and synchronizers, each playing a vital role in the overall functionality.
Layout Significance
A clear understanding of the configuration allows technicians to identify potential issues quickly and perform necessary adjustments or replacements. This knowledge is crucial for prolonging the lifespan of the system and enhancing the machine’s efficiency in the field.
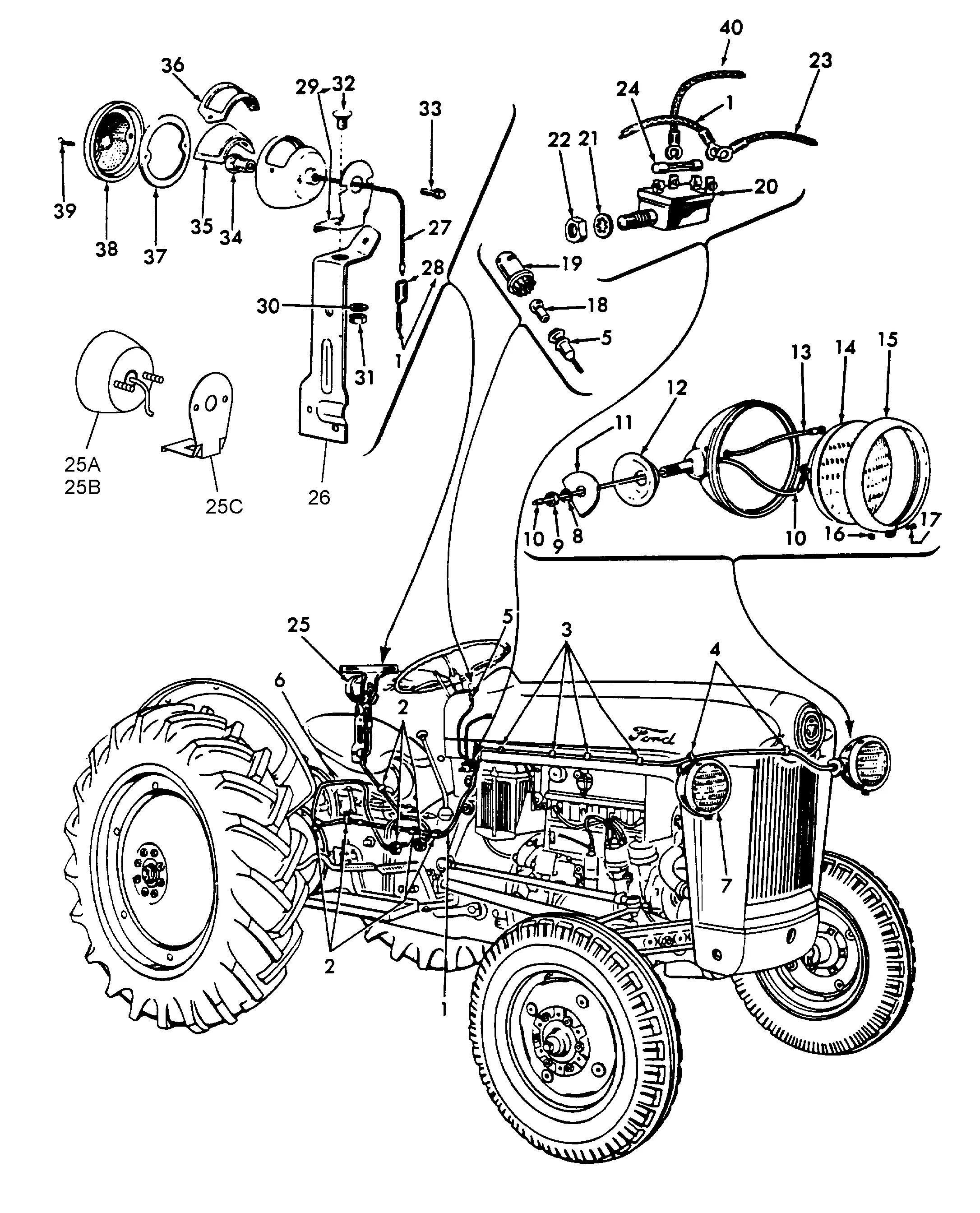
Ford NAA Tractor Electrical System
The electrical setup of classic machinery plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient operation and reliability. Understanding the components and their functions is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key Components
- Battery: Provides the necessary power to start the engine and run electrical systems.
- Starter Motor: Engages the engine to initiate the combustion process.
- Alternator: Generates electricity to recharge the battery and power the electrical systems while the engine is running.
- Wiring Harness: Connects all electrical components, ensuring proper signal and power distribution.
- Ignition System: Responsible for creating the spark needed to ignite the fuel-air mixture in the combustion chamber.
Maintenance Tips
- Regularly check battery connections for corrosion and tightness.
- Inspect wiring for signs of wear, fraying, or damage.
- Ensure all electrical connections are clean and secure.
- Test the alternator’s output to confirm it is functioning correctly.
- Replace any faulty components promptly to avoid system failure.
Understanding the Wiring and Circuits
Comprehending the electrical systems and connections is essential for effective machinery maintenance and troubleshooting. A clear grasp of how components interact through wiring allows for efficient diagnostics and repairs. This section aims to elucidate the basics of electrical circuitry, ensuring a thorough understanding of its functioning.
Key Components of Electrical Systems
Electrical systems consist of various elements that work together to power the machine efficiently. The primary components include batteries, switches, fuses, and connectors. Each of these plays a crucial role in the overall operation and safety of the system.
Common Circuit Configurations

Circuit configurations can vary widely depending on the specific application. However, most circuits can be classified into two main types: series and parallel. Understanding the differences between these configurations is vital for troubleshooting and repair.
| Type | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Series | Components connected in a single path. | Simplicity and fewer connections. | Failure of one component affects the entire circuit. |
| Parallel | Components connected across multiple paths. | Failure of one component does not disrupt the circuit. | More complex wiring and increased potential for issues. |
Hydraulic System Diagram for Ford NAA
The hydraulic mechanism plays a vital role in the functionality of agricultural machinery, facilitating smooth operation and enhanced performance. Understanding its layout and components is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
This section outlines the key elements involved in the hydraulic system, providing clarity on their arrangement and function.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Pump | Generates hydraulic pressure by converting mechanical energy. |
| Reservoir | Stores hydraulic fluid, ensuring an adequate supply for the system. |
| Actuator | Converts hydraulic energy back into mechanical energy to perform work. |
| Control Valve | Regulates the flow and direction of hydraulic fluid within the system. |
| Hoses and Lines | Facilitate the movement of hydraulic fluid between components. |
Main Hydraulic Components and Functions
The hydraulic system of agricultural machinery plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient operation and performance. Understanding the essential components and their specific functions is vital for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. Each element contributes to the overall functionality, facilitating the movement and control of various implements and attachments.
Key Elements of the Hydraulic System
Central to the hydraulic setup are components such as pumps, cylinders, and valves. The pump generates hydraulic pressure, which is essential for transferring fluid throughout the system. Cylinders convert this hydraulic energy into mechanical motion, allowing for precise control of attachments. Valves regulate the flow and direction of hydraulic fluid, ensuring that the system operates smoothly and efficiently.
Importance of Proper Maintenance
Regular maintenance of hydraulic components is critical to prevent wear and tear, which can lead to system failures. Routine checks on fluid levels, leaks, and the condition of hoses and fittings help maintain optimal performance. By ensuring that these components function correctly, operators can enhance the durability and reliability of their machinery.
Steering Mechanism Parts for Ford NAA

The steering system in agricultural machinery plays a vital role in ensuring accurate navigation and maneuverability. Understanding the components involved in this mechanism is essential for proper maintenance and repair, allowing operators to effectively control their vehicles in various terrains.
Key Components of the Steering System
The steering assembly consists of several crucial elements that work together to provide smooth handling. Each component contributes to the overall functionality and reliability of the system.
| Component Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Steering Wheel | The primary control interface that allows the operator to direct the vehicle. |
| Steering Column | The vertical shaft connecting the steering wheel to the gear mechanism. |
| Gear Box | Translates the motion from the steering wheel into directional movement. |
| Pitman Arm | Links the gear box to the steering linkage, enabling movement transfer. |
| Drag Link | Connects the pitman arm to the steering knuckles, facilitating wheel movement. |
| Steering Knuckles | Pivot points that allow the wheels to turn in response to steering input. |
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Regular inspection and maintenance of the steering mechanism are crucial for optimal performance and safety. Identifying wear or damage in any of the components can prevent larger issues and enhance the lifespan of the machinery.
Key Elements of the Steering System
The steering mechanism plays a crucial role in guiding and controlling the movement of the vehicle. Its design ensures stability and responsiveness, allowing the operator to navigate effectively in various conditions. Understanding the core components is essential for maintaining optimal performance and safety.
Components Overview
At the heart of the steering system lies the steering wheel, which connects to a series of linkages and gears. This arrangement translates the driver’s input into directional movement. Essential elements include the steering column, which supports the wheel, and the gear assembly, which adjusts the angle of the wheels based on the driver’s actions.
Functionality and Maintenance

Regular inspection and maintenance of the steering components are vital for ensuring smooth operation. Lubrication of the joints and checking for wear can prevent mechanical failures. Properly functioning elements contribute to enhanced maneuverability, providing a safe and efficient driving experience.
Braking System Parts for Ford NAA Tractor
The braking mechanism of a certain agricultural vehicle plays a crucial role in ensuring safety and efficiency during operation. Understanding the components that make up this system can help operators maintain and troubleshoot effectively. Each element contributes to the overall functionality, providing reliable stopping power when needed.
Main Components of the Braking Mechanism
This assembly typically includes items such as brake shoes, cylinders, and levers. The brake shoes apply friction against a drum or disc to slow down or halt movement. Hydraulic cylinders facilitate the transmission of force, while levers assist in engaging the system smoothly.