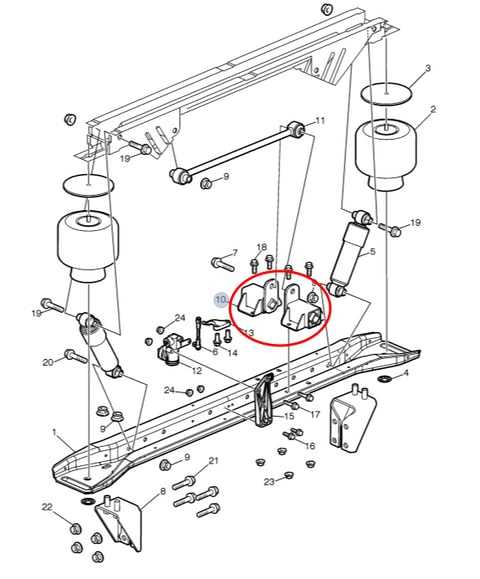
Reduce body roll during cornering, improving handling.
Cabin Comfort and Control Module Breakdown
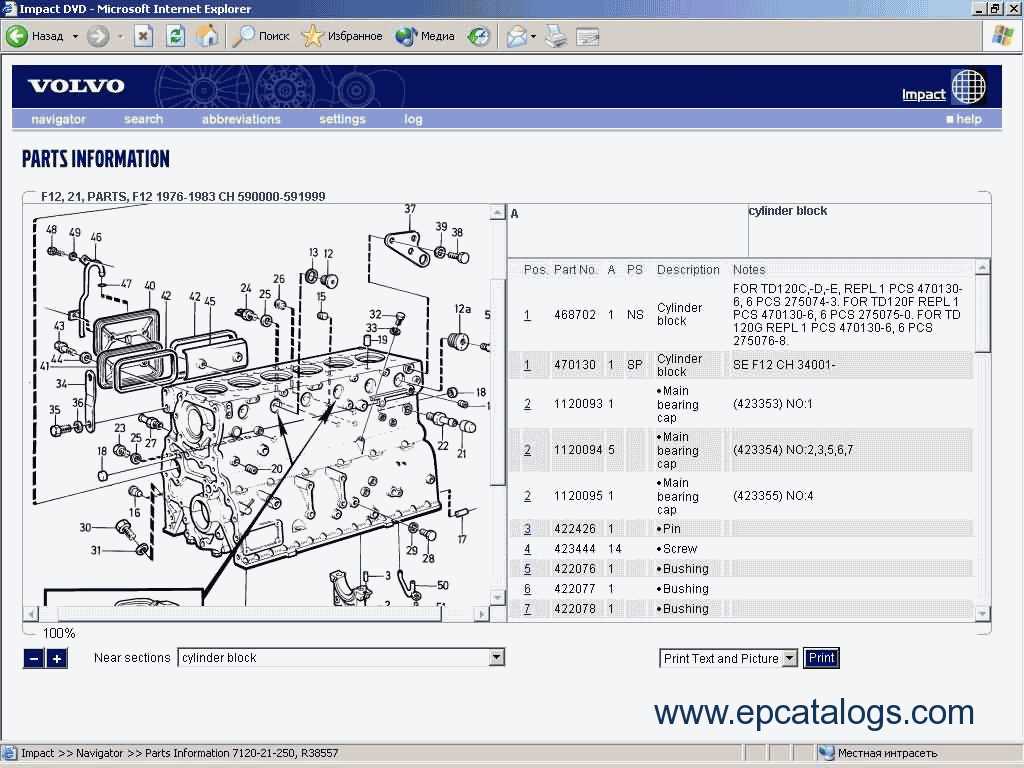
The comfort and control system inside modern vehicles is designed to enhance the driver’s experience by offering intuitive management of various in-cabin features. This section explores the functionality and configuration of modules responsible for regulating essential comfort mechanisms. Understanding these components helps in troubleshooting and optimizing performance for smoother, more efficient operation.
Core Functions and Features: The central module integrates multiple systems, controlling aspects such as climate regulation, seat adjustments, and interior lighting. These features are interconnected to provide seamless coordination, ensuring that the environment inside the cabin is consistently pleasant and user-friendly.
Component Connectivity and Diagnostics: Each unit within the control module communicates with other internal systems, using advanced protocols to manage inputs from various sensors. This coordination allows for real-time adjustments, improving both comfort and safety. Diagnosing issues often involves checking the connections between the control module and these subsystems.
Detailed View of Transmission Mechanisms
The transmission system plays a vital role in the functionality of heavy machinery, ensuring the effective transfer of power from the engine to the wheels. Understanding the intricacies of these mechanisms is essential for optimizing performance and enhancing reliability.
Key Components of Transmission Systems
- Gearbox: This assembly is responsible for adjusting the torque and speed of the output, allowing for smooth operation under various conditions.
- Clutch: This element engages and disengages the engine from the transmission, enabling gear shifts without damaging the system.
- Driveshaft: This component transmits power from the transmission to the drive wheels, ensuring efficient movement.
- Transmission Fluid: Essential for lubrication and cooling, this fluid maintains optimal operating conditions within the system.
Functionality and Operation
- The engine generates power, which is transmitted to the gearbox.
- The clutch engages, allowing the driver to select the appropriate gear.
- Power flows through the driveshaft to the wheels, propelling the vehicle forward.
- Transmission fluid circulates, lubricating components and preventing overheating.
Understanding these elements and their interactions is crucial for diagnosing issues and ensuring the efficient operation of any heavy-duty vehicle. Regular maintenance and checks of the transmission system can significantly extend its lifespan and performance.
Brake System Components in Large Trucks
The braking system in heavy vehicles plays a crucial role in ensuring safety and control. It is essential for effective deceleration and stopping, particularly under demanding conditions. Understanding the key elements of this system can aid in maintenance and troubleshooting, ultimately enhancing the vehicle’s reliability on the road.
Here are the primary components of the braking system:
- Brake Pads: These friction materials are essential for creating the necessary force to slow down or stop the vehicle.
- Brake Rotors: These discs work in conjunction with the pads to convert kinetic energy into thermal energy through friction.
- Calipers: These hydraulic devices clamp the pads against the rotors, enabling effective braking action.
- Brake Lines: These conduits carry brake fluid from the master cylinder to the calipers, allowing for the transmission of hydraulic pressure.
- Master Cylinder: This component generates hydraulic pressure within the braking system when the brake pedal is pressed.
- Brake Fluid: This hydraulic fluid is critical for transferring force within the system and ensuring efficient operation.
Regular inspection and maintenance of these components are vital for optimal performance. Neglecting any part can lead to significant safety hazards and operational issues.
In conclusion, familiarity with the braking system’s components and their functions can significantly enhance the performance and safety of heavy-duty vehicles, contributing to more efficient and secure operations on the road.
Cooling System Parts and Diagrams

The efficiency of any vehicle’s thermal management is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Understanding the components involved in regulating temperature can help in maintenance and troubleshooting. This section delves into the essential elements that constitute a typical thermal regulation system, highlighting their functions and interconnections.
Radiator: This vital component dissipates heat from the coolant, allowing it to return to a lower temperature before re-entering the engine. Its efficiency is key to preventing overheating.
Water Pump: The water pump circulates coolant throughout the system, ensuring that all components receive the necessary thermal management. A malfunctioning pump can lead to insufficient coolant flow and overheating issues.
Thermostat: This device regulates coolant flow based on the engine’s temperature. It opens and closes to maintain optimal operating temperatures, playing a critical role in the overall efficiency of the system.
Coolant Hoses: These flexible tubes transport coolant between the various components, ensuring that heated fluid is efficiently carried away and cooler fluid is supplied. Their integrity is vital for maintaining system pressure and preventing leaks.
Expansion Tank: This reservoir accommodates changes in coolant volume due to temperature fluctuations. It plays a crucial role in maintaining system pressure and ensuring proper coolant levels.
Familiarizing oneself with these components can aid in identifying issues and ensuring the reliability of the thermal management system. Regular inspections and understanding of each part’s role will contribute significantly to the overall health of the vehicle.
Lighting Systems and Electrical Circuitry Overview
The effective operation of illumination mechanisms and electrical frameworks is crucial for optimal functionality in various vehicles. These systems encompass a range of components that work together to ensure visibility and safety, especially in low-light conditions. Understanding the layout and interconnections of these elements is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting.
Components of Illumination Mechanisms
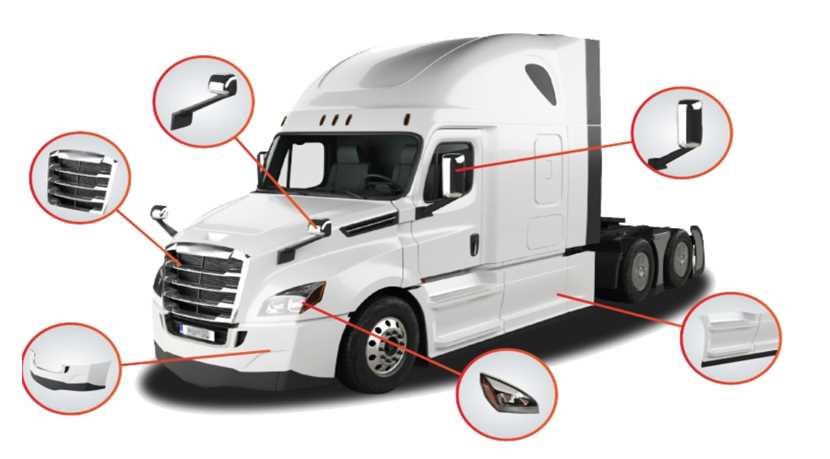
Illumination systems consist of several key elements, including lamps, switches, and wiring harnesses. Each component plays a vital role in the overall effectiveness of the lighting system. Proper alignment and maintenance of these components can significantly enhance the performance and longevity of the lighting systems.
Electrical Framework and Connectivity
The electrical circuitry serves as the backbone for all electronic functions within the vehicle. It comprises various circuits that supply power to different systems, ensuring that all components operate harmoniously. Understanding the intricacies of this circuitry allows for more effective troubleshooting and repairs, facilitating a smoother operational experience.
Fuel Delivery and Injection Parts Breakdown
This section explores the critical components involved in the delivery and injection of fuel within combustion systems. Understanding these elements is essential for ensuring optimal performance and efficiency of the engine. Each component plays a vital role in the precise control and timing of fuel supply, contributing to the overall operation of the system.
Key Components
- Fuel Pump: Responsible for moving fuel from the tank to the injection system, maintaining the necessary pressure for optimal flow.
- Fuel Filter: Ensures that contaminants are removed from the fuel before it reaches the injection system, protecting sensitive components.
- Fuel Injectors: Atomize the fuel for efficient combustion, delivering it directly into the combustion chamber at precise intervals.
- Pressure Regulator: Maintains the correct fuel pressure within the system, adjusting flow based on demand and engine conditions.
- Fuel Rail: Distributes fuel to each injector, ensuring consistent delivery and pressure across all cylinders.
Functionality Overview
Each component works in concert to create a reliable fuel delivery system. The fuel pump draws liquid from the reservoir, sending it through the filter to remove any impurities. Clean fuel then travels to the injectors via the rail, where it is atomized and injected into the engine. The pressure regulator ensures that fuel is delivered at the right pressure, adjusting as needed to meet the demands of the engine under varying conditions.
- Maintenance of this system is crucial for preventing issues such as misfires, reduced power output, and increased emissions.
- Regular checks on filters and injectors can significantly enhance the longevity and performance of the engine.
Air Intake and Exhaust System Elements
The efficiency of any internal combustion engine heavily relies on the intricate components that facilitate the intake of air and the expulsion of exhaust gases. These systems play a vital role in optimizing engine performance, enhancing fuel combustion, and minimizing emissions. Understanding the various elements involved can significantly improve maintenance and troubleshooting efforts.
Air Intake Components: The primary function of the air intake assembly is to channel clean air into the engine. This involves several crucial elements, such as the air filter, which prevents debris from entering the engine and ensures optimal airflow. Additionally, the intake manifold distributes the incoming air evenly across the engine cylinders, enhancing combustion efficiency.
Exhaust System Features: Conversely, the exhaust system is responsible for directing spent gases away from the engine. Key components include the exhaust manifold, which collects gases from the cylinders and directs them into the exhaust pipe. A well-designed catalytic converter is essential for reducing harmful emissions, while the muffler minimizes noise produced during gas expulsion, contributing to a smoother operation.
Hydraulic Systems for Steering and Lifting
Hydraulic mechanisms play a crucial role in modern machinery, enabling efficient movement and control. These systems utilize fluid dynamics to transmit power, offering enhanced performance in steering and lifting applications. By harnessing the properties of hydraulic fluid, these systems ensure precise handling and reliable lifting capabilities in various operational environments.
The fundamental components of hydraulic systems typically include pumps, cylinders, valves, and fluid reservoirs. Each element contributes to the overall functionality, working in unison to achieve desired movements. Understanding the interplay between these components is essential for effective maintenance and operation.
| Component |
Description |
Function |
| Pump |
Device that generates hydraulic pressure |
Transports hydraulic fluid to other system components |
| Cylinder |
Tube that houses the piston |
Converts hydraulic pressure into linear motion |
| Valve |
Control device for fluid flow |
Regulates the direction and pressure of fluid |
| Reservoir |
Storage tank for hydraulic fluid |
Holds excess fluid and allows for cooling |
Proper maintenance of hydraulic systems is vital to ensure longevity and optimal performance. Regular checks for leaks, fluid levels, and component wear can prevent unexpected failures. Implementing a routine inspection schedule contributes to the reliability and safety of operations.
|