
When it comes to household appliances, maintaining efficiency and ensuring optimal performance often depends on understanding how different elements work together. Every machine consists of various interconnected systems that must operate harmoniously. Knowing the layout and function of these systems is crucial to proper maintenance and troubleshooting.
Each device comes with its unique structure, and recognizing how the core elements are organized can help you address potential issues quickly. Whether you’re performing a routine check or solving a specific problem, familiarizing yourself with the internal framework of the device will save you time and effort in the long run.
Being able to identify specific components and their roles empowers users to make informed decisions, whether it’s replacing a faulty piece or ensuring regular upkeep. This insight into the construction of everyday appliances can extend their life and enhance overall performance.
Kenmore Washer Model 110 Overview
This model is recognized for its efficiency and user-friendly design, providing reliable performance for everyday laundry needs. Its structure allows for smooth handling of various fabric types, making it a popular choice for households looking for dependable washing solutions.
Main Features
- Simple control panel for easy operation
- Multiple wash cycles to accommodate different clothing materials
- Energy-efficient operation for cost savings
Benefits of Use
- Gentle on delicate fabrics, ensuring extended garment life
- Consistent performance for both small and large loads
- Minimal maintenance required for long-lasting durability
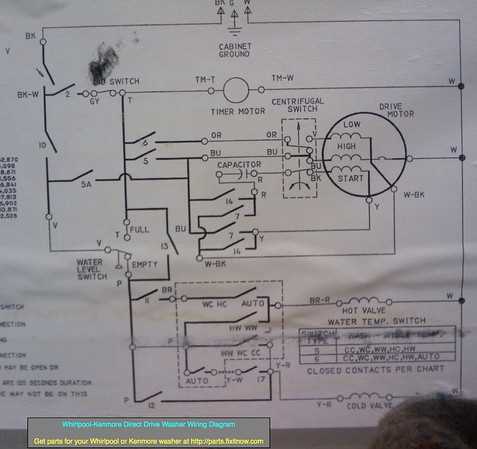
Main Components of Kenmore Washer 110
The overall structure of this appliance is composed of several essential mechanisms working together to ensure efficient operation. Each element plays a critical role in the cleaning process, from controlling water flow to managing the spinning and draining phases.
- Control Panel: The brain of the unit, responsible for managing settings and cycle options.
- Drum: The central compartment where clothes are placed and rotated during different stages.
- Motor: Powers the rotational movement of the drum and the agitator to achieve thorough cleaning.
- Water Inlet Valve: Manages the flow of water into the system, regulating both pressure and temperature.
- Drain Pump: Responsible for removing water from the machine after washing and rinsing cycles.
- Agitator: Located within the drum, this part moves clothes around, improving the wash efficiency by distributing water and detergent evenly.
- Suspension System: Stabilizes the de
Understanding the Washer’s Agitator Mechanism
The central stirring mechanism plays a crucial role in the overall functionality of a laundry appliance. Its primary purpose is to ensure efficient movement of garments during each cycle, facilitating thorough cleaning. This system is designed to move clothing items back and forth, creating the necessary friction for dirt removal. Understanding its structure and function can help in identifying potential issues and maintaining optimal performance.
Main Components of the Agitator Mechanism
- Base structure: This section anchors the mechanism, providing stability and support during operation.
- Rotating fins: These elements are responsible for the movement of water and clothes, ensuring even distribution of detergent.
- Drive shaft: This connects the stirring mechanism to the motor, transferring power for smooth rotation.
Common Issues and Maintenance Tips

- Wear and tear: Over time, the fins or the drive shaft may experience wear, which can affect efficiency.
- Unusual noises: Grinding or sque
Function of the Water Pump in the Washer
The water pump plays a vital role in ensuring the proper flow and drainage of liquid throughout the washing cycle. Its primary task is to circulate water, both when filling and draining, to ensure efficient cleaning of fabrics. This component is essential for maintaining the overall efficiency of the laundry process, helping move the water to and from different sections of the machine.
Water Circulation During the Wash Cycle
During operation, the pump ensures that water is evenly distributed across the fabrics. By maintaining a steady flow, it helps achieve thorough soaking and rinsing, improving the effectiveness of detergents and the removal of dirt.
Draining Water After the Cycle
Once the cleaning is complete, the pump activates to remove the used water from the drum. This process is critical for preparing the machine for the spin cycle and ensuring that no excess moisture remains, preventing damage or mold formation.
How the Motor Powers Kenmore Washers
The electric drive system is central to the functioning of most modern laundry machines. This mechanism converts electrical energy into the mechanical force needed to move the internal components during various cycles. Understanding how the motor operates gives insight into the machine’s efficiency and performance.
Motor Functions in Laundry Machines
The primary task of the drive unit is to rotate the drum, which allows for effective agitation, spinning, and draining. It operates through a combination of pulleys and belts, transferring motion from the power source to the essential parts of the machine. This enables the drum to spin at different speeds, depending on the stage of the wash cycle.
Stages of Operation
- Agitation: The motor alternates between rotating in both directions, causing the drum to shake back and forth.
- Spin: At high speed, the drum rotates rapidly to extract water from clothes.
- Drain: The
Identifying Control Panel Features and Functions
The control panel of a home appliance plays a crucial role in managing its operations and settings. Understanding the various components and their respective functions can greatly enhance user experience and efficiency. This section delves into the key features typically found on the control interface, empowering users to make informed decisions and optimize usage.
Common Components of the Control Interface
- Power Button: Activates or deactivates the appliance.
- Cycle Selector: Allows users to choose from various operational modes based on their needs.
- Indicator Lights: Provide visual feedback regarding the current status and settings.
- Temperature Control: Adjusts the heating level for specific tasks.
- Timer Settings: Enables users to set specific durations for operations.
Understanding Control Features
- Cycle Options: Familiarize yourself with the different cycles available, such as quick wash, delicate, or heavy-duty.
- Customization: Learn how to personalize settings to suit particular requirements for optimal results.
- Monitoring Functions: Utilize indicators to track progress and ensure proper functioning during use.
Recognizing these essential features can significantly improve the effectiveness of using the appliance, ensuring that tasks are completed efficiently and correctly.
Role of the Transmission in Washer Operation
The transmission is a critical component in the functioning of a laundry appliance, serving as the link between the motor and the drum. Its primary function is to convert the rotational motion of the motor into the appropriate speed and torque required for efficient operation. This mechanism ensures that the drum can rotate at various speeds for different cycles, enhancing the overall effectiveness of the cleaning process.
Key responsibilities of the transmission include:
- Speed Regulation: Adjusts the drum’s rotation speed to accommodate different washing cycles, such as delicate or heavy-duty loads.
- Torque Management: Provides the necessary torque to start and stop the drum smoothly, preventing damage to the fabrics.
- Direction Control: Enables the drum to spin in both clockwise and counterclockwise directions, enhancing the agitation and rinsing processes.
- Durability: Designed to withstand significant wear and tear, ensuring long-lasting performance even under heavy usage.
Understanding the role of this crucial component can help users maintain their appliances effectively and troubleshoot issues that may arise during operation.
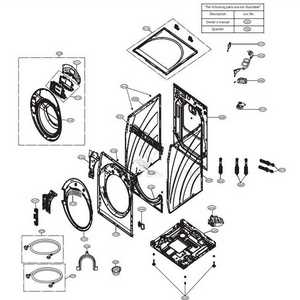
Kenmore 110 Washer Tub Assembly Explained
The tub assembly is a vital component in any laundry appliance, playing a crucial role in the washing process. Understanding its structure and functionality can help users maintain their machines more effectively. This section provides insights into the various elements that make up this assembly, highlighting their importance in ensuring optimal performance.
Components of the Tub Assembly
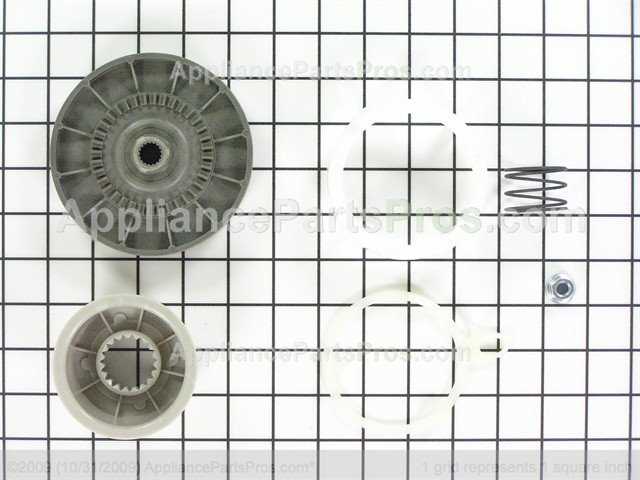
This assembly typically includes several key parts, each serving a specific purpose. The outer shell provides the necessary support and stability, while the inner tub holds the laundry during the wash cycle. Additionally, the drive system facilitates movement, ensuring thorough agitation of the garments. Together, these components work harmoniously to deliver efficient cleaning results.
Common Issues and Maintenance Tips
Over time, wear and tear can lead to issues within the assembly. Common problems may include leaks or inadequate spinning. Regular maintenance, such as checking seals and bearings, can prevent these issues and extend the life of the appliance. It’s essential to address any signs of malfunction promptly to avoid further complications.
Clutch System and Its Importance in Washing Cycles
The clutch mechanism plays a vital role in the operation of laundry machines, facilitating the transition between different phases of the cleaning process. This component ensures that the drum achieves the necessary speed for effective agitation and spin cycles, contributing significantly to overall performance.
Understanding the clutch’s function can help users appreciate its impact on the efficiency of the appliance. Here are key points highlighting its importance:
- Transition Management: The clutch regulates the shift from agitating to spinning, enabling smooth operation.
- Speed Control: It helps maintain optimal speed during various cycles, ensuring thorough cleaning and efficient water extraction.
- Durability: A well-functioning clutch system can extend the lifespan of the machine by reducing strain on other components.
- Noise Reduction: Proper engagement and disengagement minimize vibrations and noise during operation.
Regular maintenance of the clutch assembly is essential to prevent issues that can lead to inefficient washing cycles. Users should be aware of signs of wear or malfunction to ensure timely repairs, ultimately enhancing the longevity and performance of the appliance.
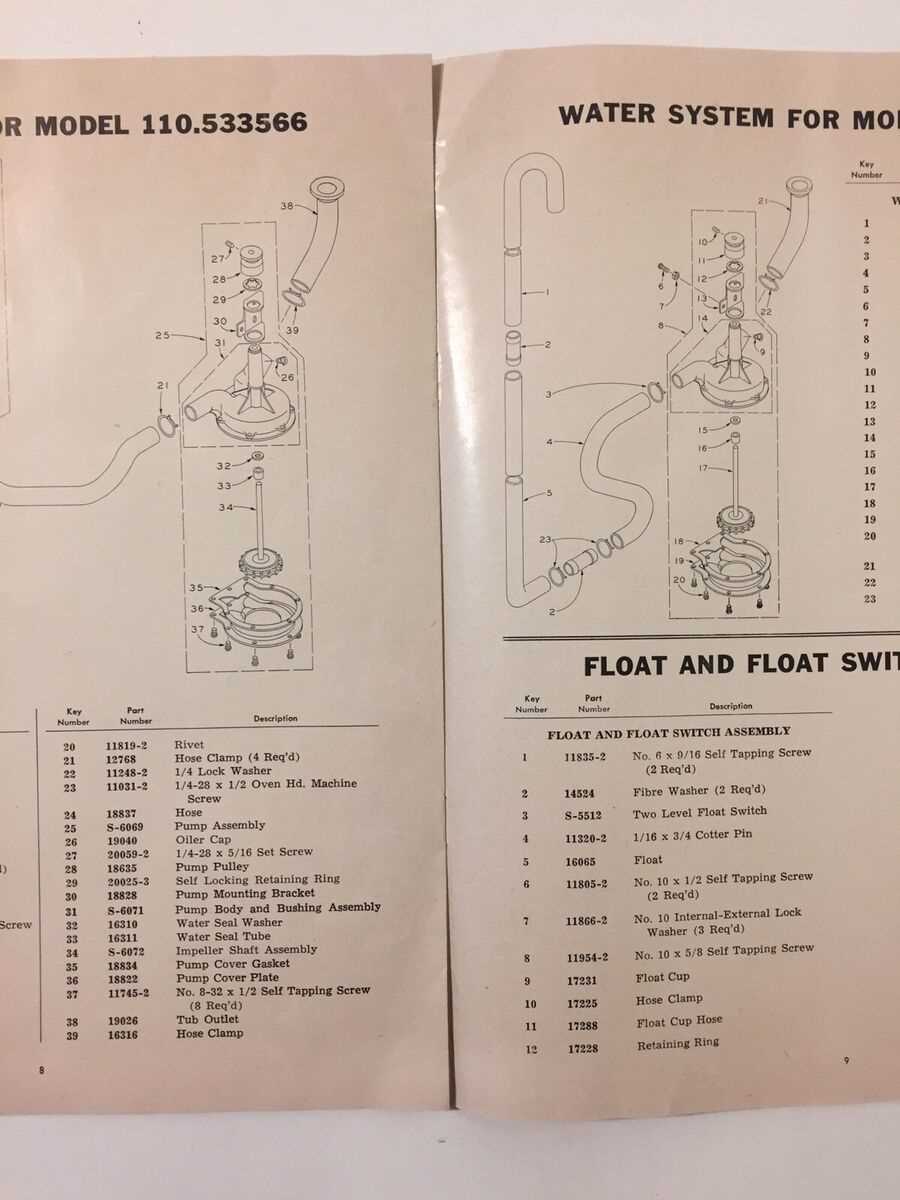
Valve System: Water Inlet and Outlet
The valve system is a crucial component in the operation of any laundry appliance, ensuring the proper flow of water during the wash and rinse cycles. This system controls both the entry of fresh water and the expulsion of used water, playing a vital role in maintaining the efficiency and functionality of the machine.
Water enters through the inlet valves, which open and close based on signals from the control panel. These valves regulate the amount of water that fills the tub, ensuring it reaches the desired level for effective cleaning. On the other hand, the outlet valve allows for the drainage of water once the cycle is complete. This two-way system is essential for the proper functioning of the appliance, as it balances water intake and disposal throughout the entire washing process.
Regular maintenance of the valve system is important to prevent clogs and leaks, which can lead to operational issues. Checking for any signs of wear or damage can help ensure that water flows smoothly, contributing to the overall performance and longevity of the appliance.
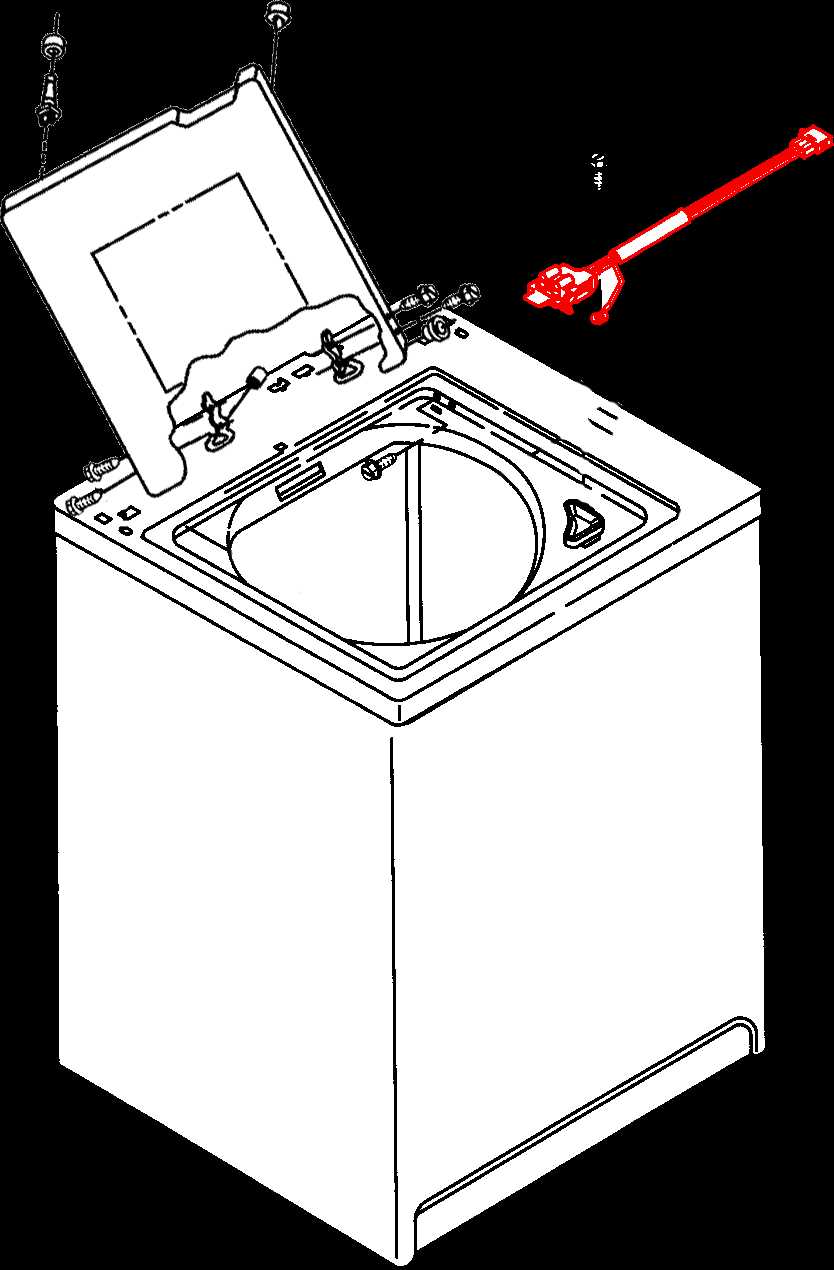
How to Replace Worn Washer Seals
Over time, seals in your appliance may become worn and lose their effectiveness, leading to leaks and decreased performance. Replacing these seals is a straightforward process that can help maintain the efficiency of your device and prevent water damage. This guide will walk you through the steps necessary to replace old seals and ensure a proper fit for optimal functionality.
Step 1: Gather Necessary Tools
Step 2: Disconnect Power and Water Supply
Before performing any maintenance, ensure your appliance is unplugged from the power source, and turn off the water supply. This precaution is essential for your safety and will help prevent any accidental leaks during the replacement.
Step 3: Remove the Old Seals
Locate the worn seals and gently remove them using pliers or your hands. Take care not to damage the surrounding components during this process. If the seals are particularly stubborn, a little twisting may help to loosen them.
Step 4: Install New Seals
Take the new seals and align them properly with the designated grooves. Ensure they fit snugly in place, as this will prevent leaks from occurring after installation. Press firmly to secure them, making sure they are evenly seated all around.
Step 5: Reconnect Everything
After the new seals are in place, reconnect the water supply and plug the appliance back into the power source. Turn on the water supply slowly to check for any leaks and to ensure that the seals are functioning properly.
Conclusion
Replacing worn seals is an essential maintenance task that can prolong the life of your appliance and improve its performance. Regularly inspect seals for signs of wear and replace them as needed to keep your appliance operating at its best.
Troubleshooting Common Kenmore Washer 110 Issues
When dealing with a household laundry appliance, encountering issues can be frustrating. Common challenges can range from mechanical failures to operational inefficiencies. Understanding these problems and their potential solutions can enhance the longevity and performance of your device.
Frequent Problems and Their Solutions
Issue Possible Causes Recommended Solutions No Power Faulty outlet, damaged power cord Check the outlet, replace the power cord Water Leakage Worn hoses, loose connections Inspect hoses, tighten or replace as needed Strange Noises Foreign objects, worn bearings Remove objects, consider bearing replacement Poor Drainage Clogged drain filter, kinked hose Clean the filter, straighten the hose Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance can prevent many issues from arising. Ensure to clean lint traps, check hoses for wear, and periodically inspect all connections. This proactive approach not only saves time but also minimizes the risk of significant repairs.