
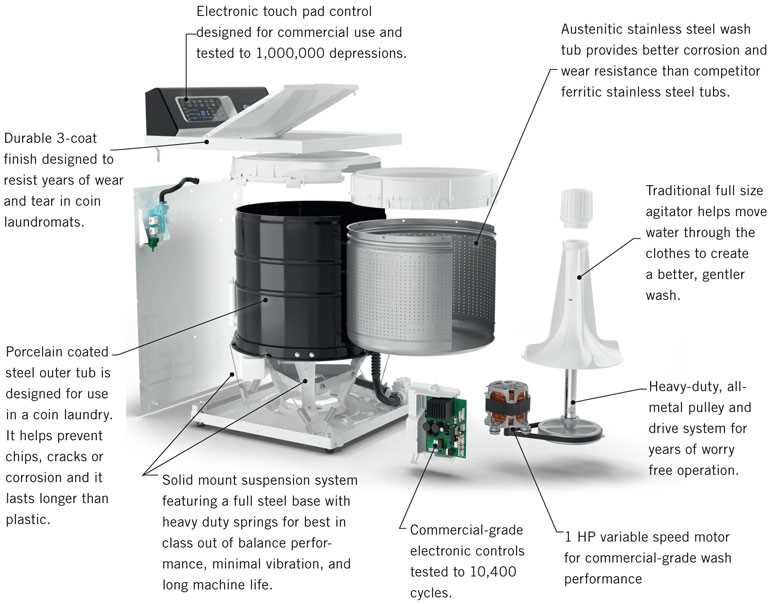
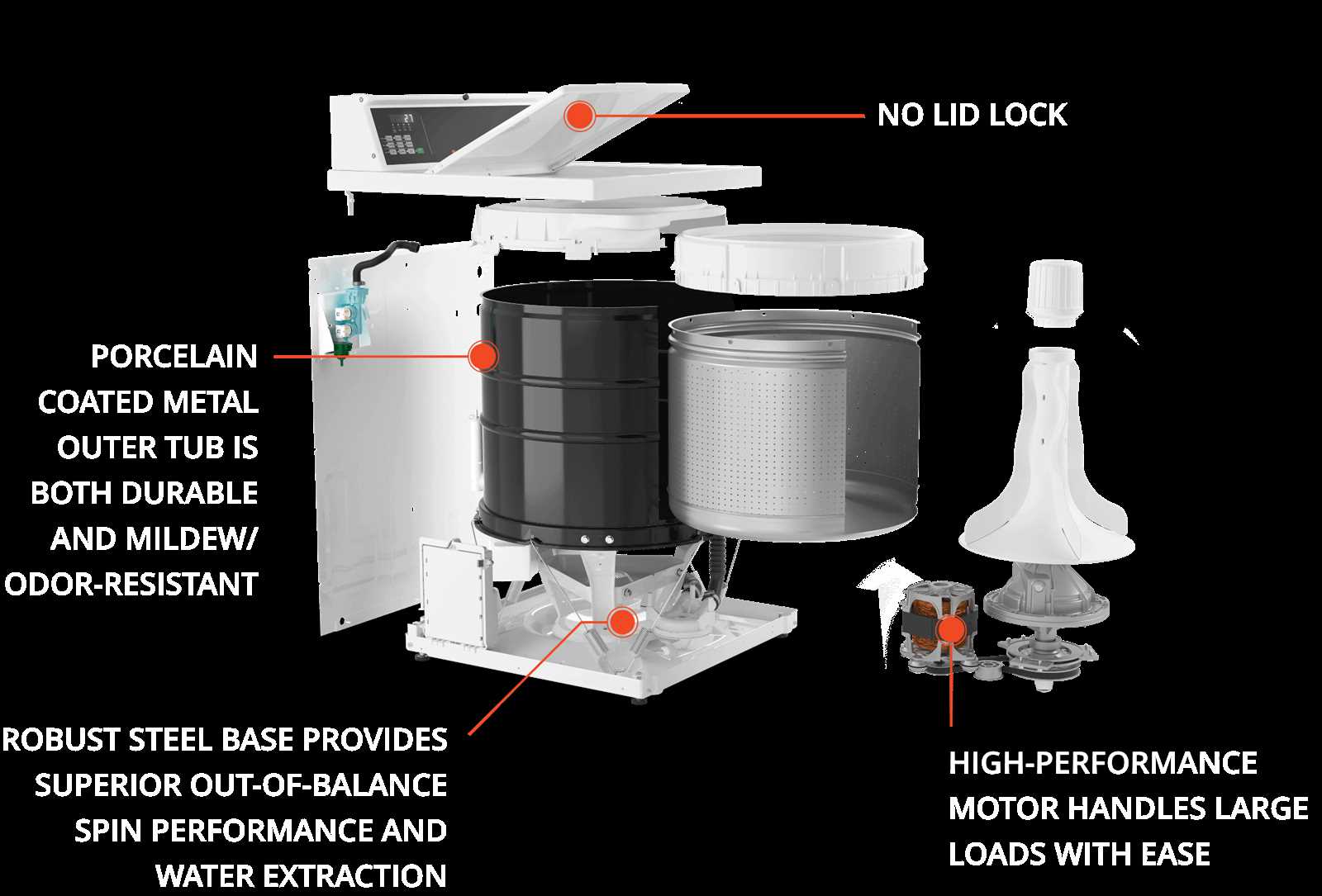
The internal structure of household devices often consists of interconnected elements, each playing a distinct role. Knowing how these components align and function together provides valuable insights for maintenance and troubleshooting. A deeper understanding of such configurations can make replacing individual units much more efficient.
Exploring the arrangement of these elements helps identify key functional zones. Whether dealing with control modules, fluid pathways, or rotational systems, each part contributes to the overall performance. Proper alignment ensures smooth operation, reducing downtime and enhancing durability over time.
This section focuses on the organization of essential modules within a particular household device. Highlighting the correct connections and their relationships aids in identifying potential issues before they escalate. With this knowledge, users can approach repairs with greater confidence and precision.
Understanding Internal Components Layout
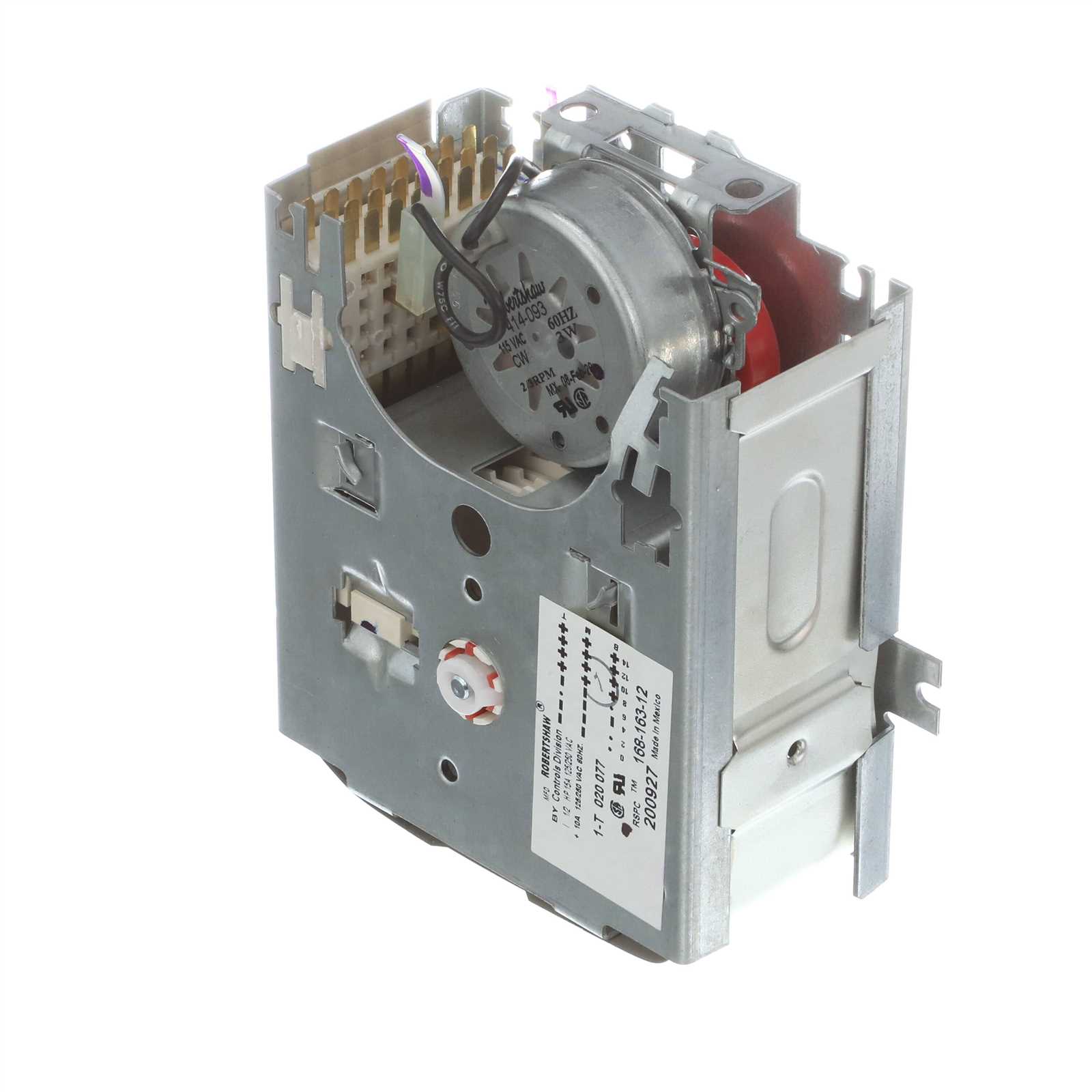

Exploring the arrangement of internal elements reveals the thoughtful design behind modern appliances. Each part has a distinct function, and their placement ensures optimal operation, making repairs and maintenance more manageable. A structured overview helps identify how these components work together harmoniously within a confined space.
Key Functional Areas
The interior can be divided into distinct sections, each responsible for specific tasks. Some areas manage the water flow, while others regulate electrical operations or control cycles. Identifying these zones allows for more precise troubleshooting and helps locate potential issues faster.
Connection and Integration of Elements

Efficient appliances rely heavily on how individual parts connect and interact. Tubes, wiring harnesses, and control boards link essential sections, ensuring synchronized performance. Understanding the layout and these interconnections provides valuable insight into maintaining the appliance and prolonging its lifespan.
Control System Overview
The control system serves as the central hub that governs all operational processes, ensuring smooth coordination between mechanical and electronic components. It manages inputs from sensors and user commands to optimize performance throughout each cycle.
Key Components: This framework consists of interconnected modules such as controllers, actuators, and monitoring devices. Each element plays a crucial role in maintaining the desired operations by interpreting signals and triggering appropriate responses.
How It Works: Commands initiated by the user interface are processed and translated into specific actions, which the mechanical components execute. The control system ensures consistency, adapting to varying conditions to enhance efficiency and minimize disruptions.
Breakdown of Drum Assembly
The drum assembly plays a pivotal role in ensuring smooth rotation and even distribution of contents. This section explores the components involved in the drum structure, highlighting their interactions and importance in maintaining operational efficiency.
Main Structural Components
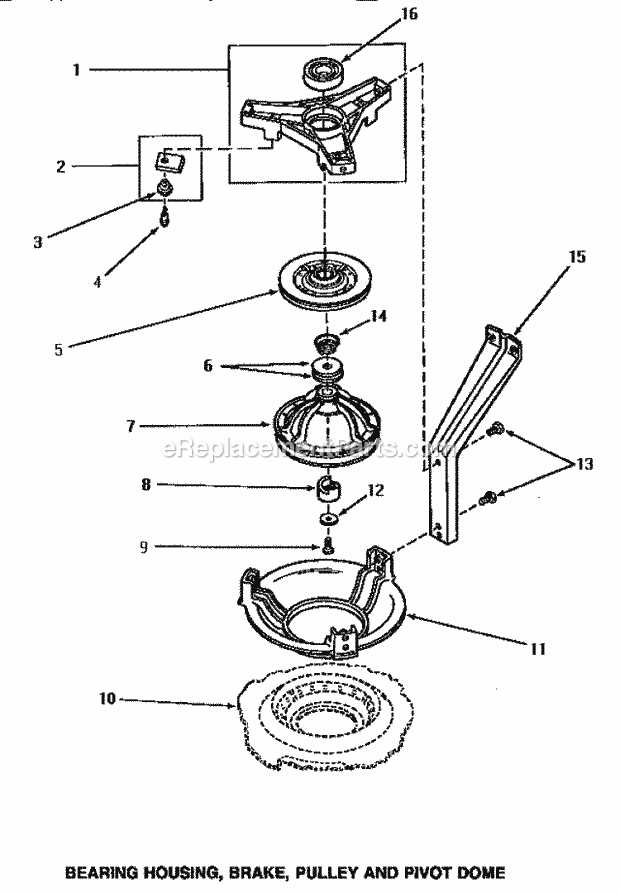
- Outer Shell: Encases the internal elements and provides a stable frame for rotations.
- Inner Drum: Perforated cylinder that holds the load while allowing fluid to pass through during cycles.
- Suspension System: Absorbs vibrations and keeps the drum balanced during high-speed operation.
- Drive Pulley: Connects to the motor via a belt, ensuring controlled movement of the drum.
Critical Supporting Elements
- Bearings: Enable smooth rotation and reduce friction between the drum and surrounding components.
- Seals: Prevent water leakage from the drum assembly, ensuring long-term durability.
- Exploring the Water Inlet Mechanism
The process of guiding water into the device involves a set of precisely arranged components that regulate flow, pressure, and direction. This mechanism ensures efficient water management, promoting consistent operation and avoiding potential issues related to overflows or insufficient supply.
Key Components of the Inlet System
At the heart of the mechanism lies a set of valves that control when water enters. These valves respond to electrical signals, opening or closing as needed. Additionally, filters are installed to block impurities, maintaining smooth operation and protecting downstream elements from damage.
How the Flow Regulation Works
The mechanism also includes sensors that monitor water levels and adjust intake accordingly. If external conditions cause fluctuations in pressure, the system compensates to maintain optimal balance. This ensures that each cycle operates within expected parameters, regardless of environmental changes or variations in water supply.
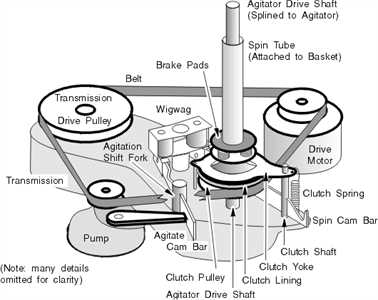
Role of the Agitator in Cleaning
The central stirring element plays a crucial part in ensuring fabrics are effectively refreshed. By generating consistent motion and water flow, it promotes the interaction between water, detergent, and clothing, enhancing the breakdown of dirt and stains. This mechanism ensures that materials receive thorough treatment across multiple cycles.
How Movement Affects Fabric Care
Through rotational or pulsating actions, the agitator evenly distributes detergent, preventing residues from settling on garments. Its rhythmic motion also prevents clothing from tangling, maintaining the quality of fibers over time. The regulated turbulence contributes to efficient rinsing, ensuring that every corner of the load is reached.
Balancing Efficiency and Fabric Protection
Modern designs ensure that the agitator’s force is balanced with the need to protect delicate items. Adjustable settings offer flexibility, allowing users to match agitation levels to the type of load, whether handling soft linens or more durable textiles. This combination of power and care makes the system both effective and versatile in different scenarios.
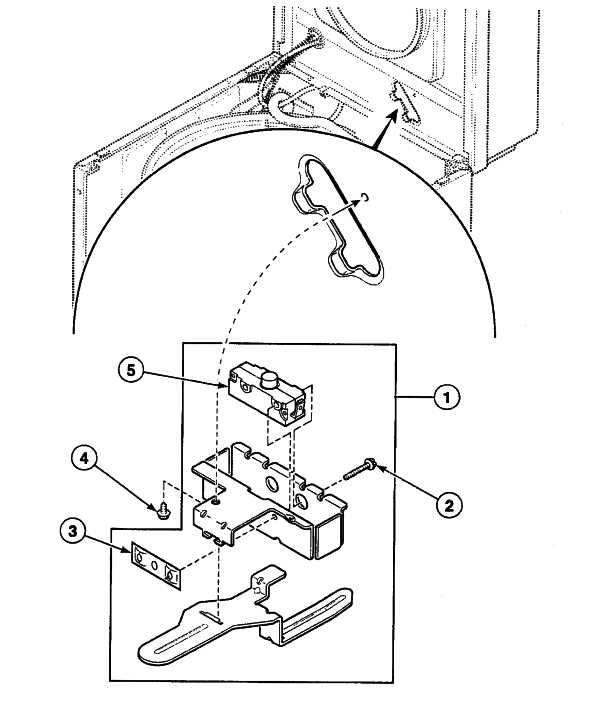
Electrical Wiring and Connectivity Map

This section provides an overview of the essential connections and electrical configurations required for optimal functionality. Understanding the layout of electrical pathways is crucial for effective troubleshooting and maintenance. A clear representation of the wiring can aid in identifying potential issues and ensuring all components work harmoniously.
Key Components and Their Connections
In order to ensure seamless operation, it is vital to understand the primary elements and their interconnections. Below is a table summarizing the key components and their respective roles in the overall electrical framework.
Component Description Power Supply Provides the necessary voltage for operation. Control Unit Manages the operational settings and sequences. Heating Element Heats the water to the desired temperature. Motor Drives the rotation of the internal components. Drain Pump Removes excess water from the unit. Wiring Layout and Best Practices
To facilitate efficient functionality, following a structured wiring layout is recommended. Proper insulation and secure connections minimize the risk of electrical failures. It is advisable to periodically inspect the wiring for wear and tear, ensuring long-term reliability.
Drainage Setup and Pump Configuration
Proper configuration of the drainage system and pump mechanism is essential for optimal performance. A well-designed setup ensures efficient water removal and prevents issues such as leaks or blockages, which can lead to prolonged cycle times and increased wear on components.
When establishing the drainage system, it is crucial to consider the positioning of the outlet hose. It should be installed at a suitable height to facilitate gravity drainage, while also being free from kinks or sharp bends that could obstruct flow. Additionally, the pump must be calibrated correctly to match the capacity of the appliance, allowing it to handle the expected water volume without straining.
Furthermore, regular maintenance of the pump and drainage components is vital. This includes checking for clogs in the hoses and inspecting the pump for signs of wear or malfunction. By maintaining these elements, users can significantly enhance the longevity and efficiency of the entire system.
Temperature Regulation and Heating Elements
The effective management of warmth within a laundry appliance is crucial for optimal functionality and garment care. This aspect plays a significant role in ensuring fabrics are treated with the appropriate temperature, allowing for efficient cleaning and maintenance. Understanding the components responsible for regulating and producing heat is essential for troubleshooting and performance enhancement.
Several key elements contribute to the temperature control system:
- Thermostat: This device monitors and regulates the internal temperature, ensuring it remains within designated limits for various cycles.
- Heating Element: Responsible for generating heat, this component activates when higher temperatures are needed, effectively raising the water temperature to the required level.
- Temperature Sensors: These sensors provide real-time data on the water’s temperature, enabling the control system to make necessary adjustments promptly.
- Control Board: The central unit that interprets information from the sensors and commands the heating element and thermostat to operate as needed.
In summary, understanding the interplay between these components is vital for ensuring effective temperature management, which directly impacts cleaning efficiency and fabric longevity.
Maintenance Tips for Seals and Gaskets
Ensuring the longevity and effectiveness of vital components in your appliance requires proper care and attention. Regular maintenance of flexible barriers and closures is essential to prevent leaks and maintain optimal performance. Here are some best practices to enhance the lifespan of these crucial elements.
Begin by routinely inspecting the condition of the seals and gaskets. Look for signs of wear, such as cracks, splits, or hardening, which can compromise their ability to function properly. Clean the surfaces where these components are installed to remove any debris or residue that may cause damage or hinder proper sealing.
Tip Description Regular Inspection Check seals and gaskets for wear and tear, ensuring they are intact and functioning correctly. Proper Cleaning Gently clean surfaces to eliminate dirt and residue that could impair the seal’s effectiveness. Lubrication Apply a suitable lubricant to enhance flexibility and prevent deterioration of the materials. Replacement Replace worn or damaged components promptly to avoid potential leaks and inefficiencies. By following these maintenance strategies, you can ensure that your appliance operates efficiently, reducing the risk of costly repairs and extending its lifespan.
Identifying Issues with the Motor Unit
Understanding the functionality of the propulsion component is essential for maintaining optimal performance. This section delves into common complications that may arise within this critical assembly, providing insights into diagnostics and solutions.
One prevalent issue is insufficient rotation, which can be attributed to several factors. Electrical malfunctions, such as faulty connections or damaged wiring, may disrupt the power supply. Additionally, mechanical problems, like worn bearings or obstructions, can hinder movement and lead to operational inefficiencies.
Another concern involves unusual noises emanating from the unit during operation. Grinding or squeaking sounds often indicate internal friction or misalignment, necessitating prompt inspection. Addressing these symptoms early can prevent further damage and ensure longevity.
Lastly, overheating is a critical warning sign that should not be overlooked. Excessive heat can result from overloading or inadequate ventilation, posing risks to both the unit and the entire system. Regular checks and maintenance are vital to mitigate these risks and maintain efficiency.
Connections for Detergent Dispensers

The integration of liquid cleaning agents into the washing process is crucial for optimal performance. Understanding the linkages involved in these systems ensures effective functionality and proper maintenance. Various components work together to facilitate the delivery of detergents at the appropriate stages of the cleaning cycle, enhancing overall efficiency.
Key Components of the Delivery System
Within this framework, several essential elements play a role in transporting cleaning solutions. These include tubing, valves, and dispensing mechanisms that ensure accurate distribution. Each component must be carefully designed to withstand chemical exposure and pressure fluctuations, allowing for reliable operation over time.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular inspection of the connections is necessary to prevent clogs and leaks. Proper care involves checking for wear on hoses and ensuring that valves open and close correctly. Addressing issues early can significantly extend the lifespan of the entire dispensing assembly, ensuring a consistently effective cleaning experience.
Common Replacement Parts and Their Placement
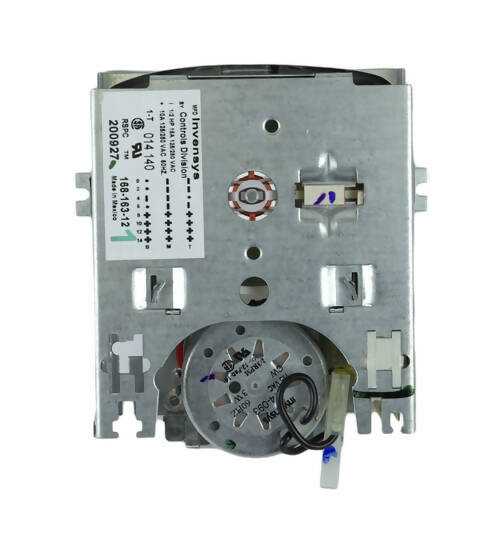

This section provides an overview of frequently needed components for laundry appliances and their respective locations. Understanding these essential elements can facilitate maintenance and enhance the longevity of the appliance.
Below are some of the commonly replaced components, along with their typical placements:
- Door Seal: Typically located around the entryway, this component prevents leaks and maintains a tight closure during operation.
- Drum Bearings: Found at the rear and sides of the drum, these ensure smooth rotation and minimize noise during cycles.
- Water Inlet Valve: Usually situated at the back, this valve controls the flow of water into the drum, responding to the appliance’s demands.
- Drain Pump: Positioned at the bottom, this component removes excess water after washing and spinning cycles.
- Drive Belt: Located around the motor and drum assembly, this part connects both and facilitates the drum’s movement.
- Control Board: Often found behind the front panel, this electronic unit regulates all operations and settings.
Knowing the location and function of these elements is crucial for effective troubleshooting and timely replacements.