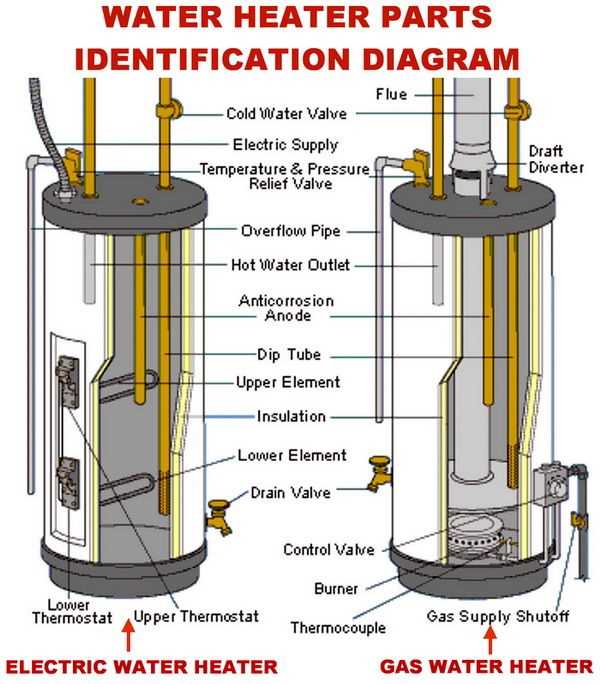
In any system designed to provide warmth, a variety of essential elements work together to ensure optimal functionality. Each component plays a crucial role, contributing to the overall efficiency and performance of the unit. By examining these elements, one can gain a deeper appreciation for how they interact to deliver a reliable source of heat.
Familiarity with the various mechanisms within such systems can lead to more informed decisions regarding maintenance, repairs, and upgrades. Understanding these integral components not only enhances one’s knowledge but also empowers individuals to troubleshoot issues effectively when they arise. This exploration serves as a foundation for both novice users and seasoned professionals alike.
As we delve into the specifics of each element, it becomes clear how vital their individual and collective functions are in achieving desired outcomes. Analyzing these aspects provides valuable insights into the technology behind thermal systems and underscores the importance of each piece within the larger framework.
This section delves into the fundamental elements and functionalities of heating systems used for residential or commercial applications. Understanding the various components involved is crucial for proper maintenance and troubleshooting, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of the system.
Key Components Overview
The main constituents of a heating system play significant roles in the overall efficiency and safety of the unit. Each element contributes uniquely, from energy supply to temperature regulation, creating a seamless process for hot fluid production.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Thermostat | Controls the desired temperature and activates the heating mechanism. |
| Heating Element | Generates heat to warm the fluid. |
| Insulation | Minimizes heat loss, maintaining efficiency. |
| Pressure Relief Valve | Prevents excessive pressure buildup, ensuring safety. |
Importance of Understanding Each Element
Familiarity with each part not only aids in effective maintenance practices but also enhances troubleshooting skills. Knowledge of how these components interact and function can lead to quicker resolutions of any issues that may arise, thus improving the overall reliability of the heating system.
Main Components of a Water Heater
Understanding the essential elements that contribute to the functionality of a thermal storage unit is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. These fundamental components work in unison to ensure efficient operation, offering both comfort and convenience in daily life.
Key Elements
- Tank: The primary container where the liquid is stored and heated.
- Heating Element: The mechanism responsible for raising the temperature of the fluid.
- Thermostat: A device that regulates the temperature, ensuring it remains within the desired range.
- Inlet and Outlet Pipes: Pathways that facilitate the flow of liquid into and out of the storage unit.
- Pressure Relief Valve: A safety feature that prevents excessive pressure buildup within the system.
Additional Features
- Insulation: Material surrounding the tank to minimize heat loss and improve efficiency.
- Anode Rod: A protective component that helps prevent corrosion inside the tank.
- Drain Valve: A valve located at the bottom for easy maintenance and flushing of sediment.
Heating Mechanisms Explained
The methods by which heat is generated and distributed within a system are crucial for achieving efficient temperature control. Understanding these mechanisms helps in optimizing performance and ensuring longevity in operation. Various technologies serve to convert energy into warmth, each with its own principles and applications.
Types of Heating Mechanisms
- Electric Resistance: Utilizes electrical currents passing through resistive materials to produce heat. Commonly found in household appliances, this method is known for its simplicity and effectiveness.
- Gas Combustion: Involves the burning of natural gas or propane to generate thermal energy. This method is prevalent in many industrial settings and offers rapid heating capabilities.
- Heat Pumps: These systems extract heat from external sources and transfer it indoors. They are known for their energy efficiency, as they move heat rather than generate it through combustion.
Key Components in Heating Systems
- Thermostat: A control device that regulates temperature by switching the heating mechanism on or off based on the desired settings.
- Heat Exchanger: Facilitates the transfer of thermal energy from one medium to another, enhancing the efficiency of the heating process.
- Insulation: Critical for minimizing heat loss, ensuring that the generated warmth is retained within the intended area.
Importance of Insulation in Design
Effective thermal management is crucial in the construction of any system that relies on maintaining specific temperatures. Proper insulation serves as a barrier, minimizing energy loss and enhancing efficiency, ultimately leading to significant operational savings and environmental benefits.
Key Benefits of Proper Insulation
- Energy Efficiency: Reduces energy consumption by preventing heat transfer.
- Cost Savings: Lowers utility bills by maintaining desired temperatures with less energy.
- Enhanced Performance: Ensures optimal functioning of equipment by stabilizing temperature fluctuations.
- Environmental Impact: Contributes to sustainability efforts by decreasing overall energy use.
Materials Commonly Used for Insulation
- Fiberglass
- Foam Board
- Mineral Wool
- Reflective Barriers
Investing in high-quality insulation materials not only improves system efficiency but also extends the lifespan of components by protecting them from extreme temperature variations. This underscores the importance of integrating effective insulation strategies in design considerations.
Common Types of Water Heaters
There are various methods to provide heated liquid for domestic and industrial use. Each approach has its own set of features, benefits, and efficiencies, making them suitable for different applications and user preferences.
Storage Units
These units store a significant amount of heated liquid, allowing for immediate access when needed. They typically come in various sizes to accommodate different household demands.
Instantaneous Units
Unlike storage options, these systems heat liquid on demand, providing a continuous supply without the need for a storage tank. This can lead to energy savings and space efficiency.
| Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Storage Units | Immediate supply, easy installation | Limited supply, energy loss during standby |
| Instantaneous Units | Energy efficient, compact design | Higher initial cost, potential flow rate limitations |
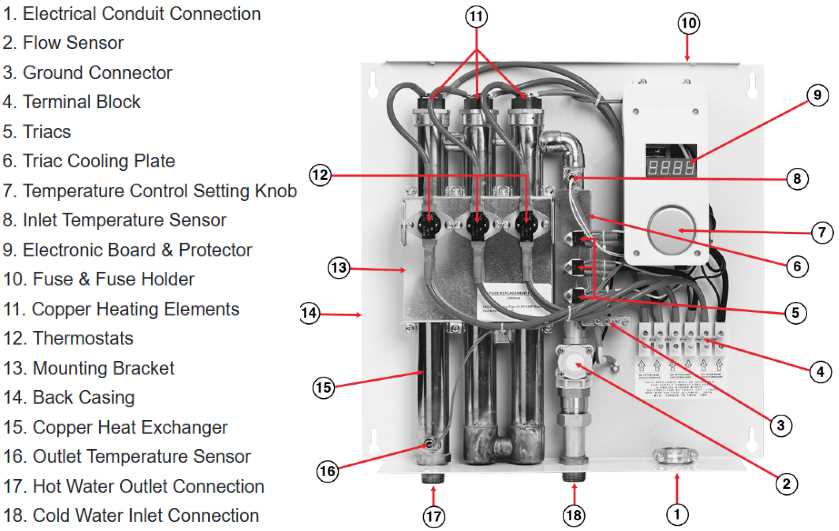
Identifying Electrical Parts and Functions
This section focuses on recognizing various electrical components and their roles in heating systems. Understanding these elements is crucial for troubleshooting and maintaining efficient operation. Each component contributes to the overall functionality, ensuring that the system operates safely and effectively.
Key Electrical Components
Several essential components work together to facilitate heating processes. The thermostat regulates the temperature, providing control over the heating cycle. The relay serves as a switch that controls the flow of electricity, enabling or disabling the heating mechanism as needed. Additionally, the circuit breaker is a safety device designed to interrupt the electrical flow in case of an overload, preventing potential hazards.
Understanding Their Functions
Each electrical component plays a specific role in the system’s operation. The thermostat senses the current temperature and communicates with the control unit, ensuring optimal heating. The relay activates the heating element based on the signals received, while the circuit breaker safeguards the system by cutting off power when irregularities are detected. Familiarity with these functions enhances the ability to diagnose issues and perform effective maintenance.
Understanding the Plumbing Layout

This section aims to clarify the arrangement of components that facilitate the flow of liquids within a specific system. A well-organized configuration ensures efficient operation and helps prevent issues such as leaks or blockages. By grasping the fundamental principles of the setup, individuals can better appreciate how each element contributes to the overall functionality.
Key Components of the System
Several crucial elements play a role in maintaining an effective configuration. These include the main supply lines, valves, and connections that guide the flow. Each segment is designed to perform a specific function, such as controlling the temperature or regulating pressure. Understanding these components enhances the ability to troubleshoot any challenges that may arise.
Flow Direction and Pressure Management
The direction of flow is a vital aspect of this arrangement, influencing how efficiently liquids move through the system. Additionally, effective pressure management is essential to avoid potential failures. Utilizing appropriate fittings and maintaining correct alignments can significantly improve performance and longevity.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
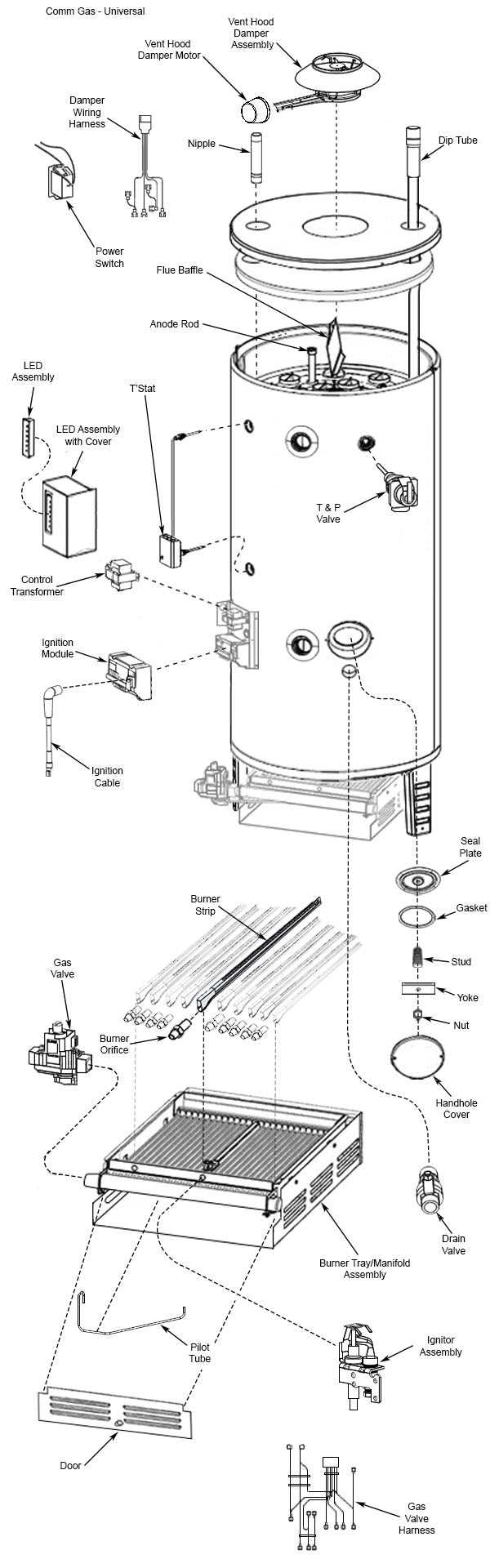
Ensuring the extended lifespan of your appliance requires regular care and attention. By adopting specific practices, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of breakdowns and enhance efficiency. This section highlights essential maintenance strategies that contribute to the durability of your system.
Routine Inspections
Regular checks are crucial for identifying potential issues before they escalate. Schedule periodic evaluations to assess functionality and detect wear. Focus on key components that play a vital role in overall performance.
Water Quality Management
The quality of the liquid used can impact the health of your system. Monitor levels of minerals and impurities that may lead to scaling or corrosion. Implementing filtration systems can be an effective way to maintain optimal conditions.
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Inspect connections and fittings | Every 6 months | Prevents leaks and ensures proper operation |
| Flush the system | Annually | Removes sediment build-up |
| Check the temperature setting | Every 3 months | Enhances energy efficiency |
| Test safety features | Every 6 months | Ensures safe operation |
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Identifying and resolving common problems with heating systems can greatly enhance their efficiency and longevity. By understanding typical symptoms and employing effective strategies, users can address malfunctions promptly and effectively.
Identifying Symptoms
Before proceeding with repairs, it’s essential to recognize the signs indicating an underlying issue. Here are some frequent indicators to watch for:
- No hot liquid flow
- Unusual noises during operation
- Fluctuations in temperature
- Leaking or damp areas around the unit
- Strange odors emanating from the system
Common Solutions
Once symptoms are identified, various approaches can be utilized to rectify the problems:
- Check the power supply and ensure proper connections.
- Inspect for clogs or blockages in the circulation pathways.
- Examine pressure settings and adjust if necessary.
- Replace any damaged components or seals.
- Regularly clean and maintain to prevent future issues.
By following these guidelines, users can effectively manage and troubleshoot their heating systems, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Safety Features in Water Heaters
Ensuring secure operation is paramount in any heating system. Various mechanisms and components are integrated to protect users from potential hazards. These features not only enhance performance but also provide peace of mind, making the system safer for daily use.
Key Safety Mechanisms
- Thermal Cutoff: This mechanism automatically shuts off the system when it reaches a predetermined temperature, preventing overheating.
- Pressure Relief Valve: This valve releases excess pressure, reducing the risk of explosions or ruptures.
- Flame Sensor: This device detects the presence of flames and shuts down the unit if the flame goes out, preventing gas accumulation.
Regular Maintenance Importance
To ensure these safety features function correctly, regular inspections and maintenance are essential. Neglecting routine checks can lead to malfunctions, increasing the risk of accidents. Homeowners should:
- Schedule annual inspections with qualified technicians.
- Flush the system periodically to remove sediment buildup.
- Check and test safety features regularly to ensure reliability.
Replacement Parts and Upgrades
Ensuring the longevity and efficiency of your system involves considering the various components that may require attention or enhancement over time. This section focuses on essential elements that can either be substituted or upgraded to maintain optimal performance. By identifying the right alternatives, you can achieve improved functionality and potentially enhance energy efficiency.
Essential Components for Substitution
When it comes to keeping your system running smoothly, certain elements may wear out or become less effective with time. Common substitutes include thermostats, valves, and insulation materials. Upgrading to high-efficiency models of these components can lead to better temperature regulation and lower energy consumption.
Enhancements for Improved Performance
In addition to replacements, there are several enhancements worth considering. For instance, integrating advanced control systems can provide greater precision and adaptability to varying demands. Additionally, implementing better insulation can significantly reduce heat loss, further optimizing overall efficiency and effectiveness.
Understanding the Energy Efficiency Ratings
Energy efficiency is a critical aspect of modern appliances, significantly impacting both environmental sustainability and household expenses. Recognizing how different devices achieve their efficiency ratings can help consumers make informed choices, leading to reduced energy consumption and cost savings over time. This section delves into the various ratings and what they mean for overall performance.
Key Efficiency Standards
Several standardized measures exist to assess the energy efficiency of appliances. These ratings are designed to provide consumers with a clear understanding of how much energy an appliance consumes relative to its output. Familiarity with these standards is essential for evaluating options effectively.
| Rating | Description | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| ENERGY STAR | Indicates superior energy efficiency compared to federal standards. | Helps save money on energy bills and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. |
| EF Rating | Measures the efficiency of a device based on energy input versus hot water output. | A higher EF value indicates better efficiency and lower operating costs. |
| U.S. DOE | Government-established guidelines for minimum efficiency requirements. | Ensures appliances meet a baseline level of efficiency. |
Choosing the Right Option
When selecting an appliance, consider its efficiency rating alongside other features. Higher ratings often correlate with more advanced technology and features, which can enhance user experience. By prioritizing energy-efficient models, consumers can enjoy long-term savings and contribute to a more sustainable future.