
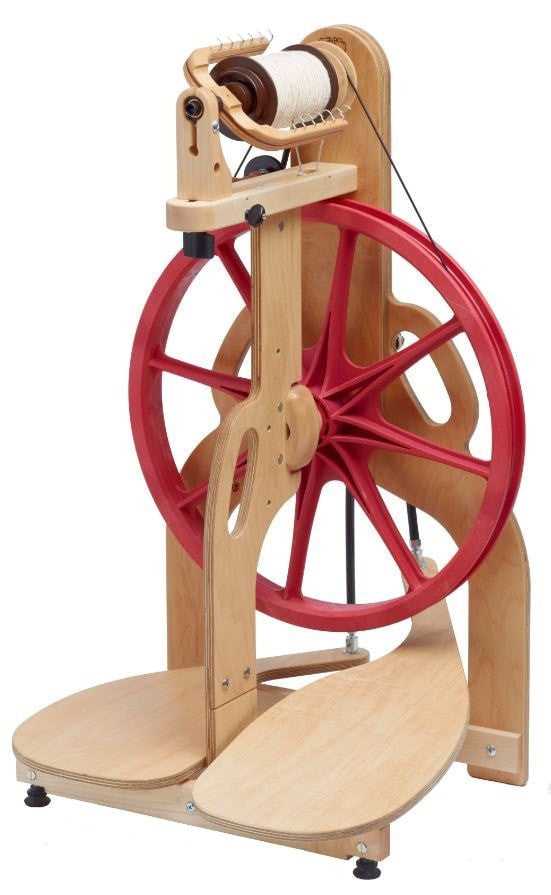
The intricate design of a textile tool plays a crucial role in the creation of yarn, allowing artisans to transform fibers into beautiful threads. Each element within this mechanism contributes to its overall functionality, enhancing the user’s experience and efficiency.
By examining the various components, one can appreciate the craftsmanship and engineering that goes into these devices. From the main structure to the minor accessories, each piece has a specific purpose, working harmoniously to achieve the ultimate goal of producing high-quality strands.
In this section, we will explore these essential elements in detail, shedding light on their arrangement and significance. Understanding these components not only enriches the knowledge of crafters but also deepens the appreciation for the art of textile creation.
Understanding Spinning Wheel Components
Grasping the intricacies of the essential elements involved in fiber processing enhances both the experience and the outcome of crafting. Each component plays a crucial role in transforming raw materials into finished threads, making familiarity with their functions invaluable for enthusiasts and artisans alike.
Key Elements Overview
In this section, we will explore the fundamental constituents that contribute to the overall functionality of the crafting device. Understanding these components allows users to optimize their techniques and troubleshoot issues effectively.
Component Functionality
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Drive Mechanism | Transfers motion to enable fiber twisting. |
| Distaff | Holds and feeds raw fibers into the crafting area. |
| Bobbin | Collects the finished thread for easy storage. |
| Flyer | Twists and guides the fiber as it is drawn out. |
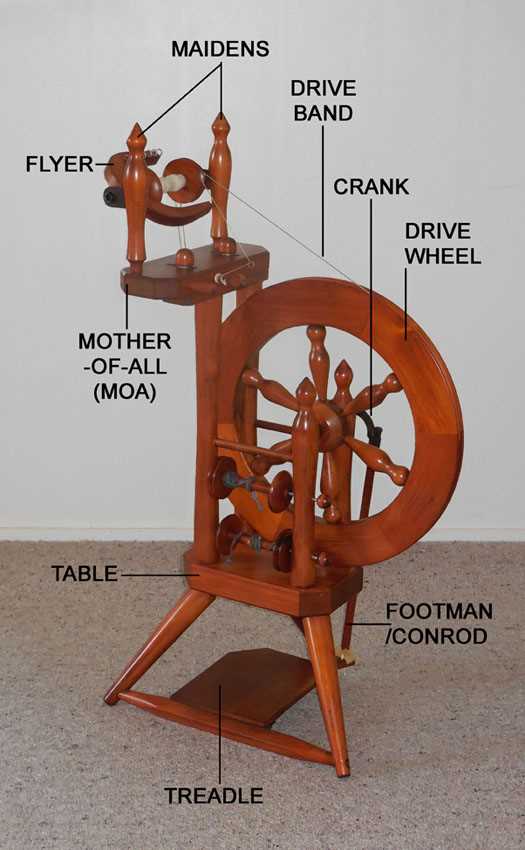
Basic Structure of Spinning Wheels
The framework of traditional textile tools encompasses various essential components that work in harmony to transform fibers into yarn. Understanding these elements is crucial for both enthusiasts and craftsmen, as it enhances the knowledge of functionality and design.
Core Components
- Frame: The foundational structure that supports the entire assembly, providing stability and balance.
- Drive Mechanism: This element facilitates the rotation necessary for twisting fibers, often powered by a foot pedal or hand crank.
- Bobbin: A spool where the finished thread is wound, essential for storage and further processing.
- Orifice: An opening that allows fibers to enter the spinning area, ensuring smooth operation.
Supportive Elements
- Tensioning Device: Maintains the proper tightness of the fiber as it is drawn out, crucial for consistency.
- Flyer: A rotating component that guides the yarn onto the bobbin while providing twist to the fibers.
- Legs: Provide support and stability to the entire mechanism, ensuring it remains grounded during use.
Each of these elements contributes to the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the tool, allowing for a seamless and productive spinning experience.
Types of Spinning Wheels Explained
In the realm of textile creation, various mechanisms play pivotal roles in transforming fibers into yarn. Each design serves unique purposes, catering to different crafting techniques and user preferences. Understanding the distinctions among these tools can greatly enhance the crafting experience, allowing artisans to choose the most suitable option for their projects.
Traditional Models
Classic mechanisms are often characterized by their historical significance and time-tested designs. These models typically feature a simple yet effective structure, allowing users to engage in the process with ease. They are favored for their reliability and the nostalgic charm they bring to the art of fiber manipulation.
Modern Innovations
Contemporary designs incorporate advanced features aimed at improving efficiency and comfort. These creations often include adjustable components and ergonomic enhancements, making the crafting experience more enjoyable. With their versatility and user-friendly attributes, modern options appeal to a broader audience, encouraging more individuals to explore the world of fiber artistry.
Main Parts of a Spinning Wheel
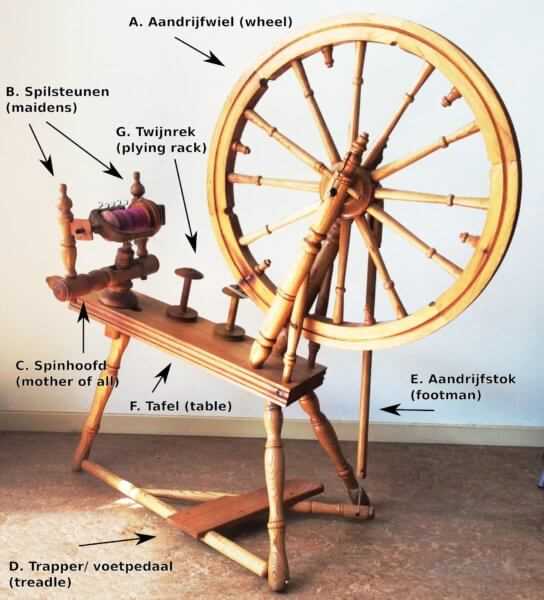
Understanding the essential components of this ancient craft tool enhances both its functionality and the art of fiber manipulation. Each element plays a crucial role in transforming raw materials into fine threads, showcasing a blend of engineering and creativity.
The drive mechanism, often the core of operation, facilitates the rotation necessary for fiber processing. The tensioning system allows for precise control over the material’s tightness, impacting the final product’s texture. Additionally, the spindle, where the actual twisting occurs, is vital for creating the desired yarn thickness. Lastly, the orifice serves as the entry point for fibers, guiding them seamlessly into the spinning process.
Function of the Drive Wheel
The drive wheel plays a crucial role in the operation of fiber processing machines, providing the necessary force to facilitate movement. Its design and functionality are essential for ensuring smooth and efficient processing of materials, enabling artisans to create fine threads from raw fibers.
Mechanics of Movement
This component transfers energy from the machine’s motor to the various elements involved in the transformation of fibers. By rotating, it generates the momentum required for the entire mechanism, allowing for consistent tension and speed throughout the process.
Impact on Quality
The effectiveness of the drive wheel directly influences the final quality of the produced threads. A well-functioning drive wheel ensures uniformity and reduces the likelihood of defects, ultimately enhancing the overall craftsmanship.
| Feature | Importance |
|---|---|
| Rotation Speed | Affects processing efficiency |
| Material | Determines durability and performance |
| Tension Control | Ensures consistency in output |
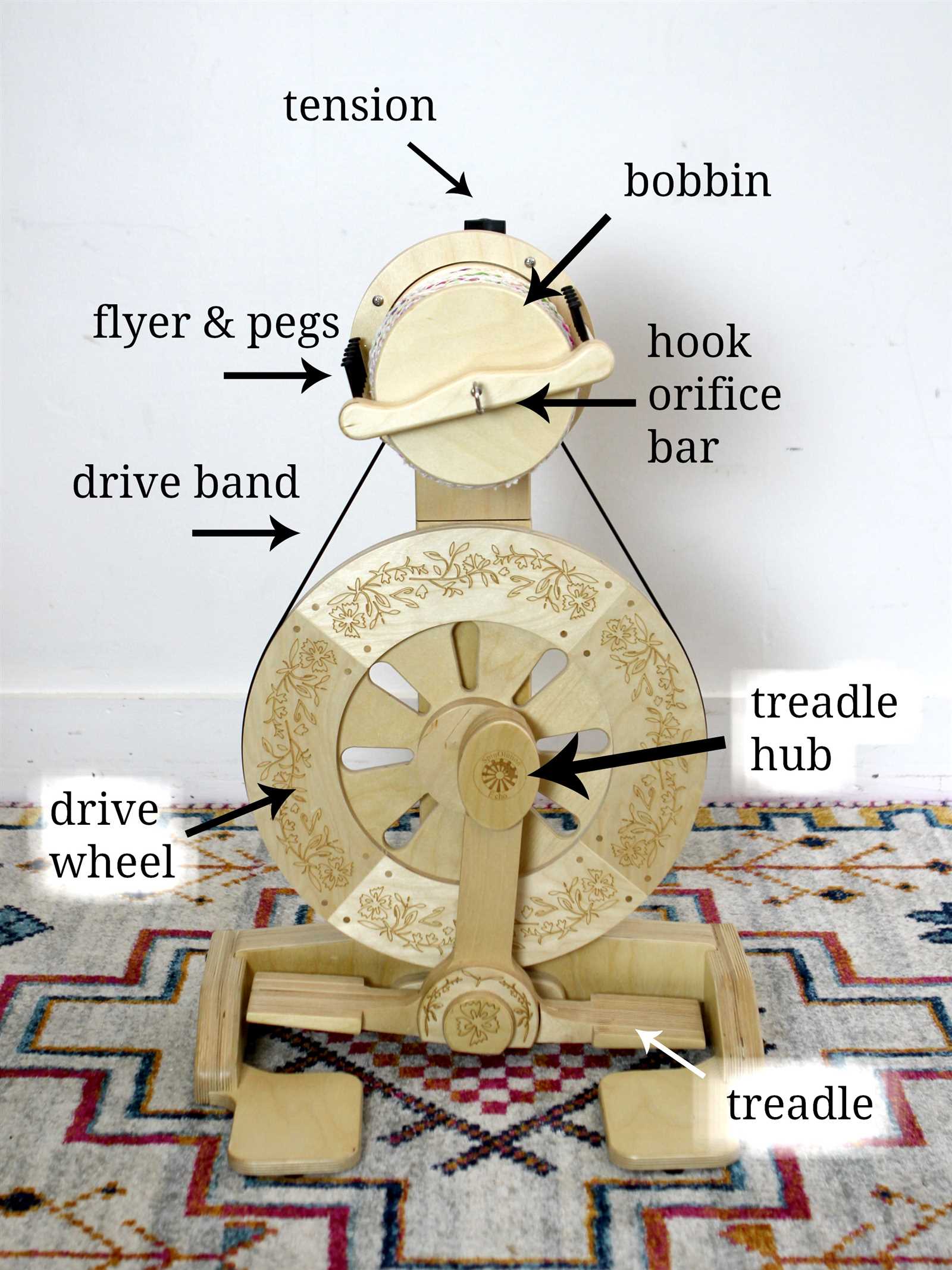
Role of the Bobbin in Spinning
The bobbin serves as a crucial component in the yarn-making process, enabling the efficient collection and storage of fibers as they transform from loose strands into tightly wound threads. This essential element is integral to ensuring a smooth flow of material during creation, contributing significantly to the overall functionality of the equipment.
Functionality: The primary role of the bobbin is to hold the newly formed thread, allowing for continuous production without interruption. It provides a dedicated space for the accumulation of yarn, ensuring that the process remains organized and efficient.
Design: Typically cylindrical, the bobbin is designed to facilitate easy handling and quick replacement. Its shape allows for optimal tension management, which is vital in achieving a uniform thickness in the final product.
Impact on Quality: A well-functioning bobbin directly influences the quality of the yarn produced. If the thread is not wound evenly, it can lead to inconsistencies, affecting the texture and strength of the final textile.
In summary, the bobbin plays an indispensable role in the transformation of fibers into yarn, ensuring efficiency, quality, and ease of use throughout the production process.
The Importance of the Treadle

The treadle plays a crucial role in the functionality and efficiency of fiber crafting equipment. Its design allows for seamless operation, facilitating the transformation of raw materials into finished threads.
- Provides a rhythmic motion that enhances user control.
- Supports even tension, crucial for consistent output.
- Enables hands-free operation, allowing multitasking.
Understanding the significance of this component can greatly improve the crafting experience.
How the Flyer Works
The flyer is a crucial component in the process of transforming fibers into thread. It plays an essential role in the drafting and twisting of the material, ensuring a consistent and smooth output. By understanding its mechanics, one can appreciate how this element contributes to the overall functionality of the apparatus.
Mechanism of Action
The flyer operates by creating a controlled environment where fibers are drawn and twisted together. As the fibers pass through, they are stretched and aligned, allowing for optimal blending and strength. The rotation of the flyer introduces a twist, which binds the fibers together, resulting in a cohesive strand ready for further processing.
Importance of Tension

Maintaining the correct tension is vital for achieving the desired thickness and strength of the thread. The flyer aids in regulating this tension, ensuring that the fibers are neither too loose nor overly tight. This balance is critical for producing high-quality yarn that meets the specific needs of various projects.
Understanding the Tension Mechanism
The mechanism responsible for maintaining appropriate pressure in fiber processing is crucial for achieving optimal results. This system regulates the tightness or looseness of the material, influencing both the flow and quality of the final product. A precise balance ensures that the fibers are adequately managed during the transformation process.
Components of this mechanism typically include a spring or a lever that adjusts tension dynamically. Proper calibration is essential; too much tension can lead to breakage, while too little can cause uneven processing. Understanding how these elements interact allows for greater control over the crafting procedure.
Additionally, maintenance of the tension mechanism is vital for longevity and efficiency. Regular checks can prevent wear and tear, ensuring consistent performance. By delving into the intricacies of this system, users can achieve the ultimate mastery over their crafting techniques.
Components of the Orifice Hook

The orifice hook serves as a crucial element in fiber processing, influencing both functionality and efficiency. Understanding its components allows for enhanced performance and optimal outcomes in textile production.
- Base: The foundational structure that supports the entire assembly.
- Hook: The curved part designed to hold the fiber securely during operation.
- Guide: A component that directs the fiber flow, ensuring consistency in production.
- Adjustment Mechanism: Allows for fine-tuning the hook’s position to accommodate different fiber types.
- Fasteners: Secure the components together, maintaining stability during use.
Each of these elements plays a vital role in achieving the ultimate effectiveness of the orifice hook, contributing to a smoother process in fiber management.
Using the Whorl Effectively

Harnessing the potential of this crucial component can greatly enhance the overall crafting experience. Mastering its role not only improves efficiency but also influences the quality of the final product. Understanding the relationship between tension and rotation allows for better control and customization of the output.
To optimize performance, one must consider the weight and shape of the device. Different configurations yield distinct results, making it essential to experiment with various options. This hands-on approach enables artisans to find their preferred setup, ultimately leading to a more satisfying and productive process.
Regular maintenance also plays a vital role in ensuring consistent outcomes. Keeping the component clean and free from debris allows for smoother operation, while periodic checks can prevent unexpected issues. By taking these steps, crafters can maximize their results and enjoy a seamless experience.
Exploring the Spindle’s Function
The component in focus plays a pivotal role in the art of transforming fibers into yarn. This intricate mechanism is essential for creating the continuous strands that are fundamental to textile production. Understanding its operation reveals the craftsmanship involved in fiber manipulation.
Mechanics of Fiber Transformation

At the core of this process lies the ability to draw and twist fibers together. As the mechanism rotates, it generates tension that allows individual strands to intertwine seamlessly. This action not only enhances the strength of the resulting thread but also dictates the texture and thickness, enabling artisans to achieve a variety of outcomes.
Importance of Maintenance
To ensure optimal functionality, regular upkeep of this device is crucial. Lubrication and alignment adjustments prevent wear and tear, allowing for consistent performance over time. A well-maintained mechanism not only improves efficiency but also enhances the overall quality of the final product.
Maintenance Tips for Wheel Parts
Regular upkeep is essential to ensure the longevity and efficiency of your equipment. By following a few simple practices, you can significantly enhance performance and minimize the risk of malfunctions. Proper care not only extends the lifespan of components but also contributes to smoother operation during use.
Start by frequently inspecting all elements for signs of wear or damage. Look for cracks, rust, or any irregularities that could affect functionality. Keeping the surface clean and free of debris will also prevent unnecessary friction and deterioration.
Lubrication is crucial; ensure that moving components are adequately oiled to reduce friction and wear. Use appropriate lubricants recommended for specific materials to avoid any adverse reactions. Regularly check the tension and alignment of various elements to maintain optimal performance.
Finally, store your equipment in a dry, sheltered environment to prevent exposure to moisture and harsh conditions. Proper storage practices will protect your gear from environmental factors that can lead to corrosion and other forms of damage.